Junior Promotion Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) Study Materials
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Treatments that cause ___________, due to penetration to the gingival pockets require ____________
Bacteremia
Antibiotic Premed
List 6 procedures requiring premed
1. Probing
2. Any scaling
3. Coronal polishing
4. PDL or intraosseous injections
5. Orthodontic BAND placements
6. Endo/periodontal surgery.
Premed is NOT required for 4 procedures
1. Supragingival procedures
2. Oral hygiene procedures which pt will perform at home
3. Dental bracket placement
4. Anesthetic blocks.
AHA premed guidelines for which compromised patients?
1. Prosthetic cardiac valves
2. Prosthetic material used in cardiac valve repair
3. Previous IE
4. Unrepaired cyanotic congenital heart defect or repaired CHD with residual effects
5. Cardiac transplant with valve regurgitation (due to structurally abnormal valve)
(ALL other CHD does not need premed)
Total Joint Replacement: MED CONSULT ONLY for high risk pts with 8 comorbidities including
1. Same joint replaced more than once OR hx of previous joint infection
2. Rheumatoid arthritis/Systemic lupus
3. Hemophilia
4. Insulin-dependent diabetics
5. Drug-induced immunosuppression
6. Malnourishment
7. HIV
8. Malignancy/Chemo.
Drug, dosages for cardiac premed, NO allergy to penicillin:
Amoxicillin or Cephalexin 2000 mg
Drug, dosages for cardiac premed, pt ALLERGIC to penicillin:
Doxycycline 100 mg
Timing of premed:___ to ___ minutes before procedure, ____ is IDEAL
Up to ___ hours after procedure—in emergency only
30-60 minutes
60
2 hrs
INR is used to monitor all patients on __________ Treatable range = ______
Coumadin (Warfarin)
2 to 3 (<3.5)
What does the A1c measure?
Whats the normal and treatable range?
measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months.
Normal: 6 Treatable Range: <8.5
What does the blood glucose measure?
Treatable range/Controlled range?
the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood at a single point in time.
Treatable Range for FBG: 70 - 130
Postprandial (2 hrs after a meal): 180
3 consecutive readings of >200 = med consult required
rapid onset of severe emergency
Hypoglycemia
gradual deterioration, eventually emergent
Hyperglycemia
Treatment for Hypoglycemia: Conscious
oral glucose: juice, frosting, soda
Treatment for Hypoglycemia: Unconscious
injectable glucose or glucagon
Syncope is the most common adverse reaction in dental office, associated with administration of
local anesthetic
Symptoms of Syncope
Pallor, sweating, loss of consciousness. Tx: Supine position, 02 administration
Hyperventilation
Signs/Symptoms
Tx?
anxiety increases
pulse/respiration increases
palpitation
tightness in chest/suffocating
dizziness
lightheadedness
paresthesia (numbness or cold) perioral and extremities
Upright position, reassure pt, paced breathing (4-6/minute)
AAP: Health
CAL, ppds, BOP?
no CAL or radiographic bone loss
ppds: <3mm
may have slight localized (<10% of teeth) BOP
AAP: Healthy but Reduced Periodontium
CAL, BOP, PPDs?
CAL present
NO BOP
PPDs: <4 mm
AAP: Stage I Perio (early/slight perio)
Bone loss, CAL, PPDs, BOP?
<15% Rad bone loss
1-2 mm CAL
4 mm PPDs
BOP present
AAP: Stage II Perio (mod perio)
Bone loss, CAL, PPDs, BOP?
15-33% rad bone loss
3-4 mm CAL
5 mm PPDs
BOP present
AAP: Stage III Perio (advanced-severe perio)
Bone loss (horizontal + verticle), CAL, PPDs, BOP
>33% horizontal bone loss
>3 mm verticle bone loss
>5 mm CAL
6 mm PPDs
BOP present
AAP: Stage IV Perio (severe-complex perio)
Furcation, Mobility, Defects, Remaining teeth?
Class 2-3 furcations
Class 2-3 mobility
Severe ridge defects
<20 remaining teeth
Complex rehabilitation needed
_________ presents in pts with normal clinical attachment level
Height of alveolar crest lies ______-______ mm apical to level of CEJ
Biologic space
1-1.5 mm
Post crest level should parallel line btwn distal CEJ of one tooth and mesial CEJ of adjacent tooth
Well-mineralized alveolar crest
Classifications of periodontitis in regard to bone loss
Slight, Moderate, Severe
Slight: <15% bone loss
Mod: 15-33% bone loss
Severe: >33% bone loss
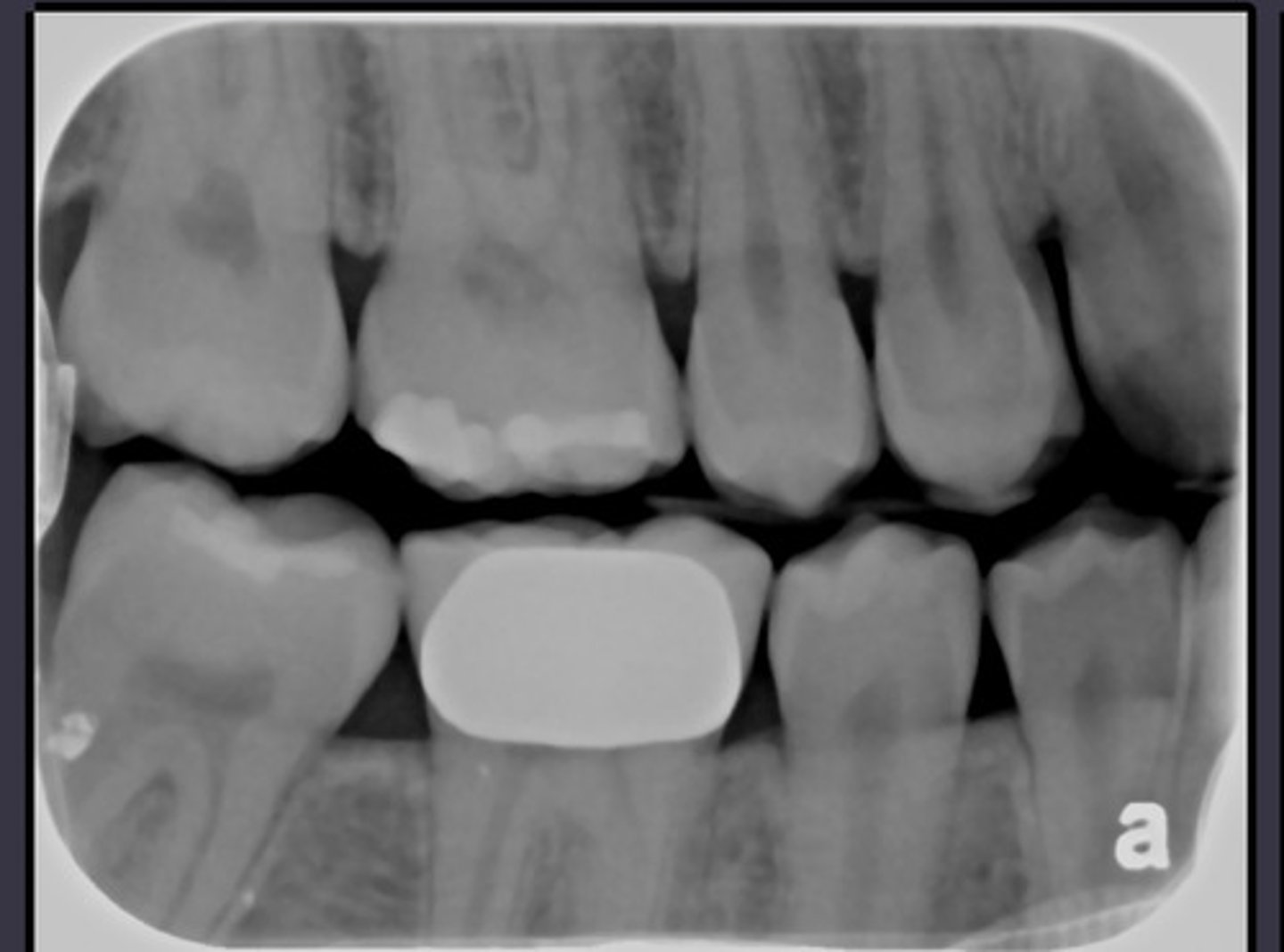
What is this?
Health or gingivitis
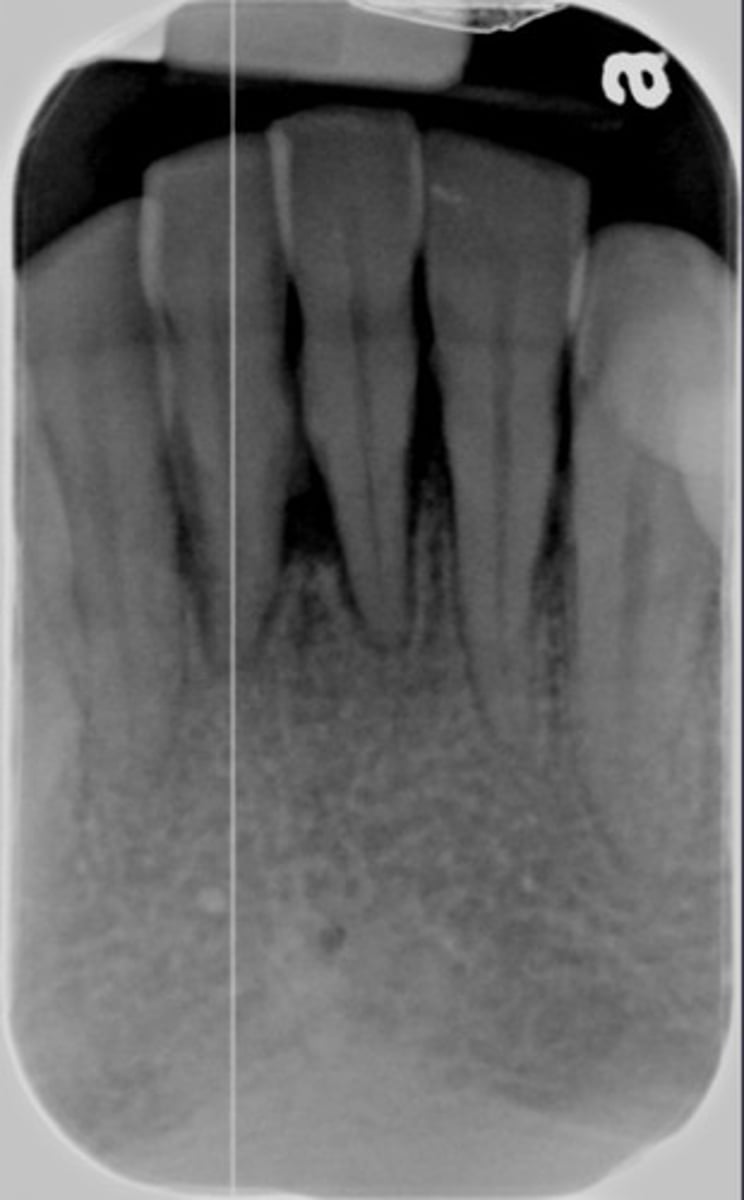
whats this
Stage 1 perio
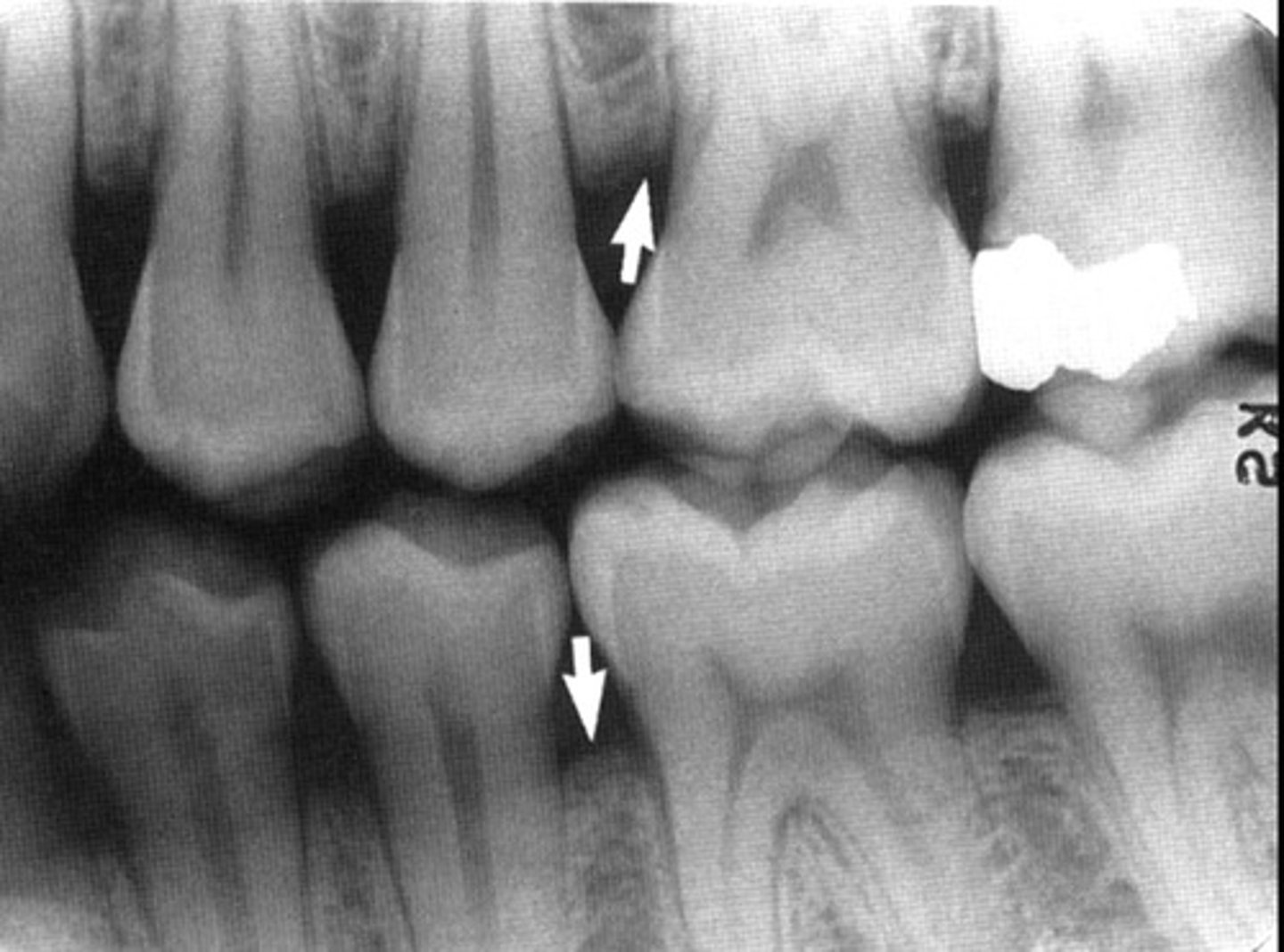
Whats this
Stage IV Perio
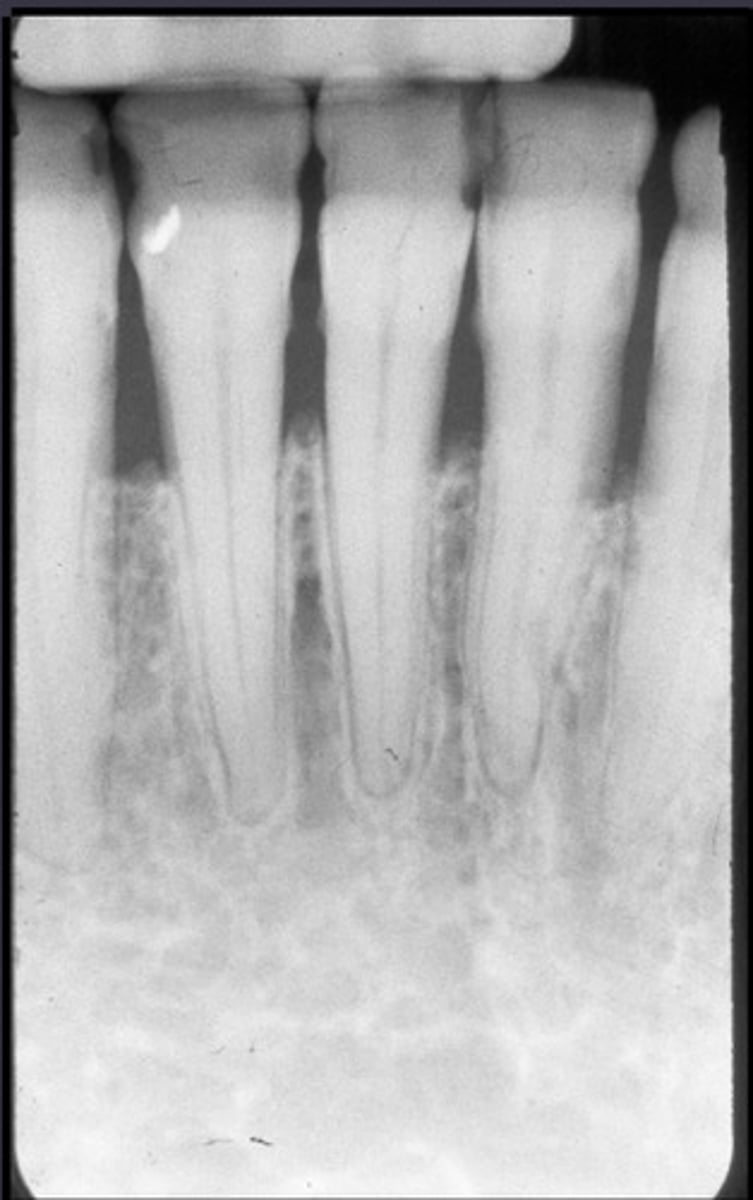
Whats this
Stage II/III Perio
4 Steps in formulating a TX plan
1. Assessment
2. Diagnosis + Plan for hygiene procedure
3. Implement Hygiene tx
4. Post-treatment evaluation
What evaluation is rare? But will occur 1-2 weeks following SRP?
Tissue Check (evaluates tissue healing in acute conditions
When is does the perio re-eval occur after SRP?
4-6 wks re-eval of active Tx (full data and perio consult)
Either recall (every ____ mo) or Referral if_____ or Additional_____
3 months (perio maintenance)
Perio, restorative, oral surgery, endo (dentist can't provide this tx)
Active tx (re-RP)
A patient has 6mm PPD, but 3mm coronal (gingival margin) to the CEJ, how many mm is CAL?
3 mm CAL
A patient has 6 mm from CEJ to the base of the pocket, how many mm is CAL?
6 mm CAL
A patient has 6mm PPD and 3 mm recession, how many mm is CAL?
9 mm CAL
MOst common referrals?
Grad perio
Dental student for POE
Restorative TX
Root planing by quad or sextant
quad: when 4 or more teeth in a quad need RP
sextant: 1-3 teeth in sextant need root planing
Pateints with current perio disease have recalls ___ mos to start. WHY? What 3 goals?
3 months
12 weeks allows for the recolonization of perio pockets
1. Maintain health/prevent disease
2. Maintain control of disease
3. NO BLEEDING
Perio consult is needed for?
Perio disease diagnosis
Tx plan approval for RP
Diagnosis for additional perio tx (surgery) at re-eval
Grade A
bone loss/CAL
Biofilm?
Smoking/Diabetes?
No bone loss/CAL over 5 yrs
Heavy Biofilm, low destruction
Non-smoker
No diabetes
Grade B
Bone loss/CAL
Biofilm?
How many cigarettes/A1c?
<2 mm bone loss/CAL over 5 yrs
Destructive biofilm
<10 cigarettes/day
A1c <7% in diabetics
Grade C
Bone loss/CAL
Biofilm?
How many cigarettes/A1c?
> 2mm bone loss/CAL over 5 yrs
Excessive destructive biofilm
Rapid progression
>10 cigarettes/day
A1c >7% in diabetics
ASA 1
<120/80 - 139/89
ASA II
140/90 - 150/99
Stress reduction
ASA III
160/100 - 170/109
Stress reduction med consult advised
(MI/CVA > 6 mo ago)
ASA IV
>180/110
MED CONSULT NEEDED
(MI/CVA < 6 mo ago)
10 Absolute contraindications to VASO
1. BP > 180/110
2. Severe hypertension
3. Uncontrolled CHF
4. Unstable angina
5. Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
6. Uncontrolled diabetes
7. Recent heart attack/stroke/coronary bypass surgeru <60 mo
8. Sulfite allergy
9. Drug abuse
10. Glaucoma
Whats the cardiac dose of epinephrine?
2 carts (0.04 mg)
14 VASO with caution using cardiac dose
1. Hypertension
2. Stable angina
3. Heart attack/stroke >6 mo
4. Heart transplant patients
5. Arrhythmias (especially if taking beta blockers 'olol' or digoxin)
6. CHF
8. Hyperthyroid
9. Chronic Hep C
10. Pt taking antidiabetics
11. Pregnant (best during 2nd tri)
12. Sickle cell anemia
13. Tricyclic antidepressants
5 Absolute contraindications to nitrous
1. Communication difficulties
2. Inability to use nasal mask
3. Middle ear infection, sinusitis, recent inner ear surgery (due to gas expansion)
4. Latex allergy
5. Cocaine/meth within 24 hrs
Relative contraindications to nitrous
1. Drug or alcohol abuse
2. Previous negative experience
3. Pregnancy
4. COPD/emphysema (avoid with severe)
5. Psychiatric disorders
6. Asthma (okay unless attack occurs)
7. Sickle cell disease
A blood platelet count below_____ requires med consult
50,000
If your patient has HIV what two tests do you ask for?
CD4 (<200 is low) or ANC (<1500 is low)