Intelligence
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Alfred Binet - 1905
Worked with Theodore Simon to develop tests of intelligence
Believed in “higher” mental processes → memory, problem solving, language, judgements
Developed tests to examine these skills
Believed in the idea of mental age
Brought to North America by Louis Terman
Became more politicized, more innate based thinking of intelligence
Intelligence Testing: Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test
Mean score of 100 if you are acting at your mental/chrono age
Originally used intelligence quotient (mental age/chronological age x 100)
Scores now given based on deviation– where a child scores relative to the average at their age
Mental age isn’t applicable once you get to adults, thus why we rely on deviations
Initially provided 1 general score, now also provides sub scores
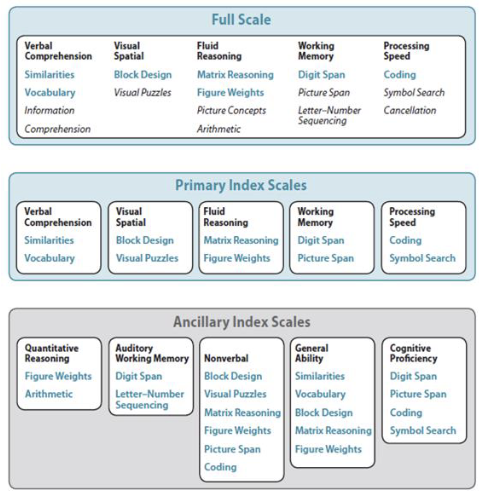
Intelligence Testing: Wechsler Intelligent Scale for Children (WISC)
Criticized that Stanford Binet test was biased towards kids vocabulary and language abilities, over-relied on vocabover-relied
Provides general score plus 5 composite scores
Ages 6-16
There is also wechsler preschool and primary scale of intelligence (WPPSI)
2.5-6 years old
Involves alot pattern detecting, not relying on verbal abilities, less language based
Most common tests to use on children
Reliability (Intelligence testing)
Refers to consistency
Split-half reliability
Measuring if first half and second half of test show the same scores
Test-retest reliability
Is the test/score consistent if you are given it multiple times
People who do better earlier in life on IQ tests, do better later in life on IQ tests
Validity (intelligence testing)
Are these tests an accurate valid measure of what we think intelligence is?
Content & Construct Validity
Does content of questions relate to what we think intelligence is? (specific questions)
Is this test a good measurement of the construct of intelligence? (overall construction of test)
Predictive validity
Do tests predict real world performance?
High Iq tests are highly correlated with training success in military, job performance of high complexity jobs
Lack of Bias (intelligence testing)
Should be equivalently accurate at measuring intelligence across all backgrounds
Content-validity bias
Is the content equally relevant to all participants to measure IQ?
Predictive-validity bias
Are these equally predictive of IQ across all groups?
Psychometric Approach
Intelligence operationalized as –> IQ Tests
These tests measure what they test
Not an agreed upon conception of what intelligence is**
Defining Intelligence: General Intelligence (g)
General intelligence as multiple abilities/processes
“People who are good at math are also good at science and English and other subjects”
General Intelligence is comprised of:
Crystallized Intelligence:
Factual knowledge
Knowing who George Washington is, hamburgers are hot…etc
Crystallized knowledge grows with age
Fluid Intelligence
Ability to solve new problems, think on the spot
Fluid intelligence declines with age
This theory suggests that people who have higher levels of crystallized intelligence, should have high levels of fluid intelligence
Also talks about sub abilities/sub component scores: visual perception, audio perception
But all of these sub abilities correlate back into overall general intelligence
Defining Intelligence: Multiple types of intelligence
Sternberg’s Theory of Successful Intelligence
Analytical Intelligence
Problem solving ability
What IQ tests usually test for
Creative Intelligence
Can you come up with new solutions?
Practical Intelligence
Street smarts
Can you adapt on the spot if entering a new neighbourhood, city?
Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences
8 or more different types of intelligence
Musical, bodily-kinaesthetic, interpersonal, verbal-linguistic, logical-mathematical, naturalistic, intrapersonal, visual-spatial
Has been influential in educational settings
No best one theory that is agreed upon
IQ Scores: Individual Differences
Genetics
Fraternal vs Identical Twins: MZ twins more similar in IQ as they get older, whereas DZ twins IQ become more dissimilar with age
Choices they make to match their genetic tendencies… active effects
IQ and Genetically, Environmentally related or both: The more similar genes are, the more similar IQ scores are
Gene-environment correlations
Passive effects: Parents create an environment that also fits the genetic tendencies of child
E.g parents who like reading alot have books in their house, thus kids can read more and learn more reading skills/vocab
Evocative effects: child has genetic tendency to evoke an environment that fits their genetic tendency
e.g. Child talks alot and talks at grocery store and more ppl will talk back to them, thus increasing there communication skills
Active effects: Childs genetic tendency leads them to actively select things int their environment that fits their genes
e.g. Kids stronger in math asking for harder math assignments
IQ Scores: Individual Differences (Environment)
Schooling
Being in school is associated with higher IQ scores
Family/home environement
Parents who are more involved/talked more to their kids = higher IQ scores
SES
Higher SES = higher IQ
Time Period
IQ continues to rise over the years/decades
IQ Testing Today
Administered and scored by trained professionals
Very strict guidelines
Most tests are continuously re-normed
For the population being tested (ie, a culturally diverse Canadian-based sample)
To re-determine what an IQ of 100 means (vs 70 vs 130 vs…)
In some regions/schools, used to quality for…
Learning disability diagnosis and access to supports
Access to special education classes
Access to giftedness programs and supports
Sometimes used in court cases, policy
Example: death penalty in US
IQ scores are correlated with many other variables
Job performance
Attitudues
Health
Mortality
& others
Can IQ be used as a tool for research and policy decisions?
Yes
E.g. IQ & Lead
Old belief: only large amounts of lead exposure are toxic
Research –> even small amounts of lead is associated with a drop in IQ
Led to policies banning in gasoline!
What other changes/differences in IQ can/have be used to study the impacts of?
Poverty
Exposure to violence
Pollution
Breaks from school
Etc
Is it certain that IQ tests only measure intelligence?
IQ tests may not actually measure “intelligence”
Test performance is sensitive to motivation ($$ incentive), to coaching
Suggests your score may not be innately influenced but more so by motivation?
Bias in testing
Cultural differences, certain tests white people get more correct because it’s more common in their culture (e.g. a regatta)
Problem of IQ Testing
we tend to interpret IQ scores as evidence of a person’s underlying mental ability...
not as evidence of their cultural knowledge, motivation, coaching, stress that day, hunger, etc
History of IQ testing and Eugenics
History of IQ tests being used and
developed for eugenics
”The science of improving stock” (Galton) → the idea that heritable human characteristics should be controlled, through breeding, to improve the human species
IQ tests used to sort
Created racial hierarchies in armies … extended into society
IQ tests used for policies on forced sterilization, restrictions on marriage, etc
E.g. Leilani Muir… didn’t know she was forcibly sterilized because of her IQ
Interpreting group differences in IQ scores (Dangerous use continued)
Gender → spatial abilities
Women perform worse than men
This gender difference only shows up ages 6-7, prior there is no difference
Race
White individuals score higher than Black individuals (10pt difference)
Have been interpreted in terms of “genetic advantage” for higher-scoring groups
Not accurate science!!!
Race is socially (not genetically) constructed
Why racial group differences in IQ tests?
Social class differences?
Culturally biased tests?
Stereotype threat?
Stereotype Threat Gist
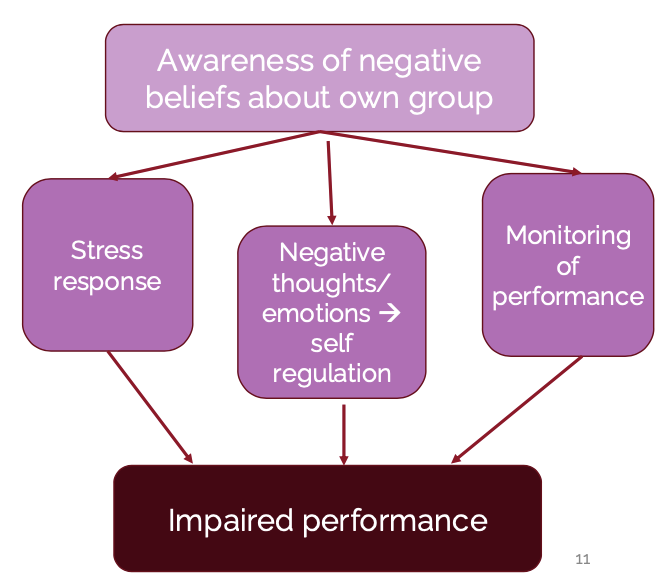
We belong to social groups associated with stereotypes related to intelligence.
Our awareness of these stereotypes can impact our thoughts and performance
A psychological burden caused by the concern that one’s performance
or behavior might confirm a negative stereotype about one’s group.
Mechanisms of Stereotype Threat
Know all steps/factors that lead to impaired performance
Ambady et al Stereotype Threat Study
Studied asian American girls and math performance
Conflicting stereotypes +/-
Condition 1: girls are primed with their Asian identity
Condition 2: girls are primed with gender identity
Results:
Priming asian identity = better math scores
Priming girl (gender) identity = worse math scores
Except perform better in upper elementary
Details of Picho & Schmader Stereotype Threat Study
When do Gender Stereotypes Impair Math
Performance? A Study of Stereotype Threat among Ugandan Adolescence
Extending research on stereotype treat beyond WEIRD populations
Examine how expectations of others holding gender stereotypes and own endorsement of gender stereotypes contribute to stereotype threat
(Uganda typically relies less on gender stereotypes)
Picho & Schmader Ugandan Girls Math Study Conditions

Picho & Schamder Ugandan Girls mAth Scores Study Results
Stereotype threat present only when participants expected that the test-giver held gendered expectations
Same pattern for both girls and boys
Perhaps differences in how stereotype threat impacts us across age/culture are due to when and whether we become aware of stereotypes...
People are acting according to what they believe the test-takers gendered beliefs are
Intelligence Mindsets
Predicts response to challenges, failure
Associated with academic outcomes
Growth mindset taught through intervention → linked with better
academic performance
Fixed Mindset (Entity Theory)
Intelligence and talent are fixed at birth
Growth Mindset (Incremental Theory)
Intelligence and talent can go up or down
Controversy becuase not all studies find that growth mindset is linked with better performance…
Are there differences in who growth mindsets might be beneficial for?
Intelligence & IQ testing: How might we improve IQ test?
Improvements in the test structure/design?
Efforts to counteract stereotype threat
Dynamic assessment –> goal is to examine learning potential, test how much a child can learn with assistance
Shift how we think about IQ?
How IQ scores are interpreted
Sun et al Article DETAILS
Are there cultural differences in mindsets and in the association between mindsets and better academic performance?
In China, the belief of intelligence as due to “innate” ability?
Compared to US, Chinese youth more likely to link learning/achievement to “purposes of life”, working hard, vs determined by intelligence?
Sun et al RESULTS
Are there cultural differences in mindsets and in the association between mindsets and better academic performance?
Growth mindset more common in US
Fixed mindset more common in China
In china, mindset about intelligence has no relationship with academic performance
In USA, mindset is associated with performance
growth mindset associated with better performance
Intelligence Mindsets across cultures
Differences across cultures
More impact for low-achieving students
When teachers and peers are also supportive of growth mindset beliefs
When contexts allow for growth!
Standard Deviation
A score of 100 means you match the average of your age group
1 SD above means 115
1 SD below means 85
68% of individuals are within 1 SD from the mean
How can we tell if an IQ test is a good measurement of intelligence
Reliable, Valid, and lack of bias