Pelvis, Hip, Femur
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What SID is used for femur, hip, and pelvis images?
40”
What are breathing instructions for femur, hip, and pelvis images?
suspend breathing
What is Aurora’s pelvis routine?
AP
Explain patient and CR position for AP pelvis
Patient
supine (or upright)
true AP (no rotation)
invert feet 15-20o
CR
centered midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis (2 inches below ASIS or 2 inches above symphysis)
top of IR 1-1½ inches above crest
centered at MSP
perpendicular tube angle
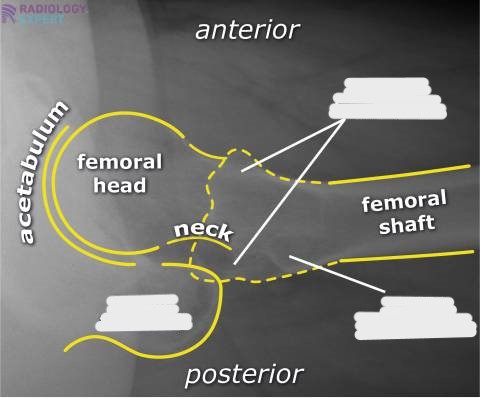
Why do we invert the feet for most AP images?
overcomes the anteversion of the femoral necks
places necks parallel to IR
unsuperimposes greater trochanter and femoral neck
should not see lesser trochanter
What is demonstrated on an AP pelvis image (film eval)?
greater trochanters in profile
head, neck, trochanters, and upper 1/3 of femur
lesser trochanter not seen
marker at bottom of image (either R or L)
no rotation
What are 3 things you can look at on the pelvis to check for rotation?
obturator foramen are equal
iliac wings are equal
symphysis pubis is in line with sacrum
What are some other names for a lateral pelvis image?
bilateral frog, modified cleaves
Explain patient and CR position for lateral pelvis/bilateral frog (not in Aurora’s routine)
patient
supine
flex knees and hips 90o and abduct thighs 40-45o to put femoral neck parallel to IR
brace soles of feet against each other
can use a support under the knees
can use a sandbag across ankle
CR
perpendicular 1 inch superior to symphysis pubis (or 3 inches distal to ASIS)
aligned to MSP
What is demonstrated on a lateral pelvis image (film eval)?
no rotation
axiolateral view of both femoral heads, necks, and trochanteric areas
marker (R or L)
What is Aurora’s hip routine?
AP and lateral
Explain patient and CR position for AP hip
patient
supine
true AP (no rotation)
invert foot 15-20o
CR
perpendicular to femoral neck
top of IR at ASIS
10×12 LW
What are two ways you can locate the femoral neck?
draw a line from ASIS to symphysis, go 2½ inches perpendicularly distal from the middle of that line
1-2 inches medial to ASIS and 3-4 inches distal
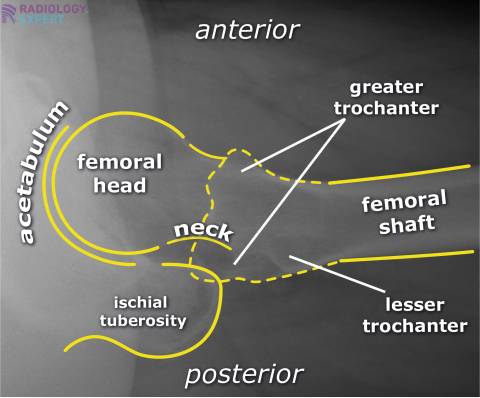
What is demonstrated on an AP hip image (film eval)?
AP projection of head, neck, trochanters, and upper 1/3 of femoral shaft
include pubic symphysis
don’t need to include crest
entire orthopedic appliances must be demonstrated
marker lateral and on bottom of image
What are some other names for a lateral hip image?
modified cleaves unilateral
unilateral frog leg
Explain patient and CR position for lateral hip
patient
supine (true AP)
flex knee and hip 90o and abduct thigh 40-45o
CR
perpendicular to femoral neck
3-4 inches distal to ASIS
If a patient can’t abduct their thigh for a lateral hip, what can you do?
frog-leg patient rotation method (roll patient toward affected side)
What is demonstrated on a lateral hip image (film eval)?
axiolateral view of femoral head, neck, and trochanteric areas
lesser trochanter in profile medially
don’t need to include symphysis
What is Aurora’s femur routine?
AP (proximal and distal) and lateral (proximal and distal)
Explain patient and CR position for AP proximal femur
patient
supine
rotate leg in 15-20o
CR
top of IR at ASIS
align long axis of CR to long axis of leg
10×12 or 14×17 LW
What is demonstrated on an AP proximal femur image (film eval)?
include entire proximal femur (through the joint)
try to include soft tissue if patient body habitus allows
marker lateral
Explain patient and CR position for AP distal femur
patient
supine
rotate leg in 5o to get patella parallel
CR
bottom of IR 2 inches below knee joint
align long axis of CR to long axis of leg
What is demonstrated on an AP distal femur image (film eval)?
overlap between proximal and distal
entire distal femur (through the joint)
marker lateral
Explain patient and CR position for lateral proximal femur
patient
turn onto affected side
proximal femur in contact with table
unaffected leg behind patient
10-15o posterior pelvic rotation
flex knee 45o
patella perpendicular to IR
CR
perpendicular with top of IR at ASIS
align long axis of leg to IR
What is demonstrated on a lateral proximal femur image (film eval)?
marker lateral
include entire proximal femur (through the joint)
Explain patient and CR position for lateral distal femur
patient
turn onto affected side
true lateral
pelvis lateral and patella perpendicular to IR
CR
IR 2 inches below knee joint
align long axis of leg to IR
What is demonstrated on a lateral distal femur image (film eval)?
lateral view of ¾ of femur and knee joint
mark anterior
knee joint may not be open (due to beam divergence)
What is the sign that usually indicates a broken/displaced hip?
affected leg will be externally rotated
What do you need to do for an AP image if there is a suspected fracture?
take the image with the patient as presented (don’t rotate the leg)
What are other names for the trauma lateral hip?
shoot thru lateral, cross table lateral, Danelius Miller, modified axiolateral
Explain the patient and CR/IR positioning for the Danelius Miller method (trauma hip)
patient
supine
elevate pelvis if necessary
raise unaffected leg so thigh is perpendicular to table
invert affected foot if possible
CR/IR
IR placed vertically with top of IR just above crest
angle lower border of IR to place perpendicular to femoral neck
use grid (make sure you are using CW grid or put lead strips horizontal)
angle CR to be perpendicular to IR and femoral neck
What is demonstrated on a lateral trauma hip image (film eval)?
axiolateral view of head and neck
“true lateral” hip
acetabulum visible
lesser trochanter should be pointing down
What do you have to do extra if a patient has a prosthetic?
include the entire prosthetic
What is a trauma lateral femur routine?
proximal (Danelius Miller) and distal (shoot thru)
What techniques are used for a pelvis?
80 kVp @ 20 mAs
What should the EI # be for pelvis and hip images?
EI: 200-600
S: 200-600
What techniques are used for a hip?
80 kVp @ 12 mAs
What techniques are used for a femur?
proximal: 80 kVp @ 12 mAs
distal: 80 kVp @ 6 mAs
What should the EI # be for femur images?
EI: 200-600
S: 150-400
When is the Clements Nakayama image done?
when patient has bilateral hip fractures
bilateral hip arthroplasty
pt unable to raise unaffected leg
Explain patient, IR, and CR positioning for the Clements Nakayama image
patient
supine
affected side near the edge of the table
IR
grid lines parallel to long axis of femoral neck
tilt top back 15 degrees
upper border at iliac crest
CR
directed 15o posteriorly
perpendicular to femoral neck and IR
What is demonstrated on a Clements Nakayama image (film eval)?
lateral hip
visualized acetabulum, head, neck, and trochanters of femur
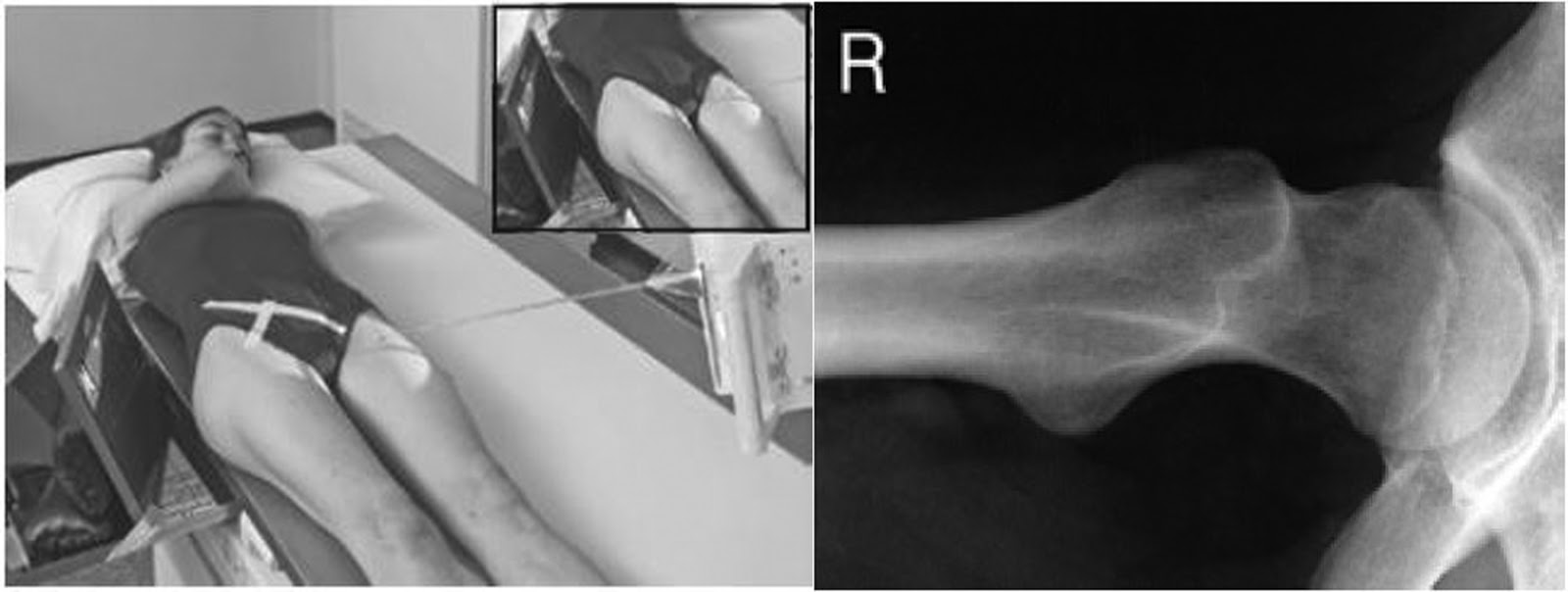
What method is shown in the image?
Clements Nakayama
What is another name for the AP axial outlet projection?
Taylor method
Explain patient and CR positioning for the pelvic outlet image
patient
supine, true AP
CR
1-2 inches distal to upper border of symphysis
male
20-35o cephalic angle
female
30-45o cephalic angle
What is demonstrated on a pelvic outlet image (film eval)?
AP projection of pubic and ischial bones, pubic symphysis, obturator foramen
assess for vertical fractures and displacements
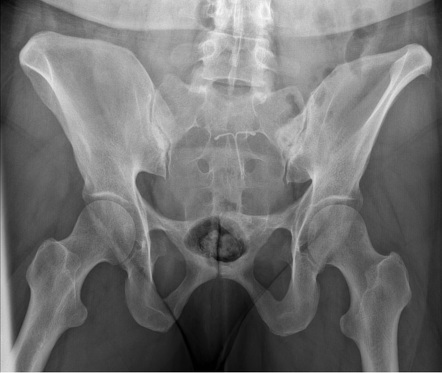
What type of image is this?
pelvic outlet
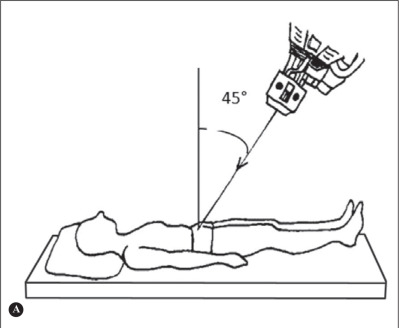
What type of image will this result in?
pelvic outlet
What is another name for the AP axial inlet projection?
Bridgeman method
Explain patient and CR positioning for the pelvic inlet image
patient
supine, true AP
CR
at level of ASIS
40o caudal angle
What is demonstrated on a pelvic inlet image (film eval)?
axial projection of pubic and ischial bones and symphysis pubis
pelvic ring
asses pelvic trauma (anterior and posterior displacement)
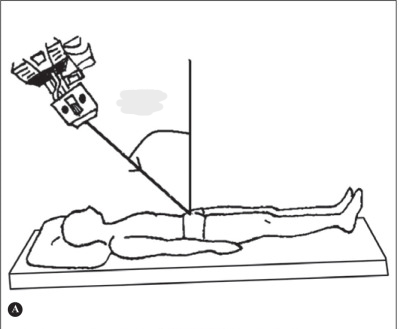
What type of image will this result in?
pelvic inlet
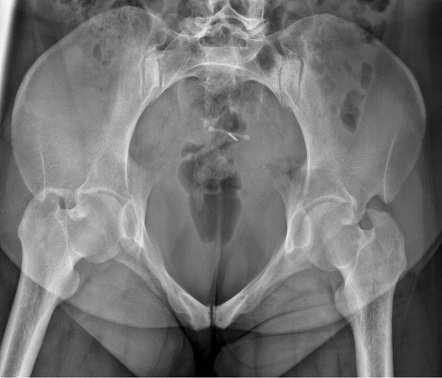
What type of image is this?
pelvic inlet
What do the Judet views demonstrate?
acetabular fractures
anterior and posterior acetabular rims
Explain the Judet view for the posterior acetabular rim
patient
45o oblique (RPO or LPO)
affected side up
CR
perpendicular
2 inches distal to ASIS of affected side
What is demonstrated on a Judet (posterior acetabular rim) image (film eval)?
affected side up (posterior rim of affected acetabulum)
anterior iliopubic column
obturator foramen
iliopubic line
Explain the Judet view for the anterior acetabular rim
patient
45o oblique (RPO or LPO)
affected side down
CR
perpendicular
2 inches distal and 2 inches medial to ASIS of affected side
What is demonstrated on a Judet (anterior acetabular rim) image (film eval)?
affected side down (anterior rim of affected acetabulum)
posterior ilioischial column
iliac wing
ilioischial line
In the Judet views, which side will have an open obturatur foramen?
Which side will have a wide iliac wing?
foramen: side up
wing: side down