Molec Cell Ch 5 - Genome Orgnaization
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Humans have a total of __ chromosomes, organized as __ pairs.
46, 23.
This represents about 2 meters of DNA.
Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear and contain thousands of genes.
True
______ can be used to observe chromosomal abnormalities in individuals.
Karyotypes
________ associate chromosomal aberrations with phenotypic anomalies
Cytogeneticists
Most eukaryotic genes contain introns.
true
Closely related species can have different chromosomal numbers.
True
important regions of eukaryotic chromosomes:
Centromere, telomere, replication origins.
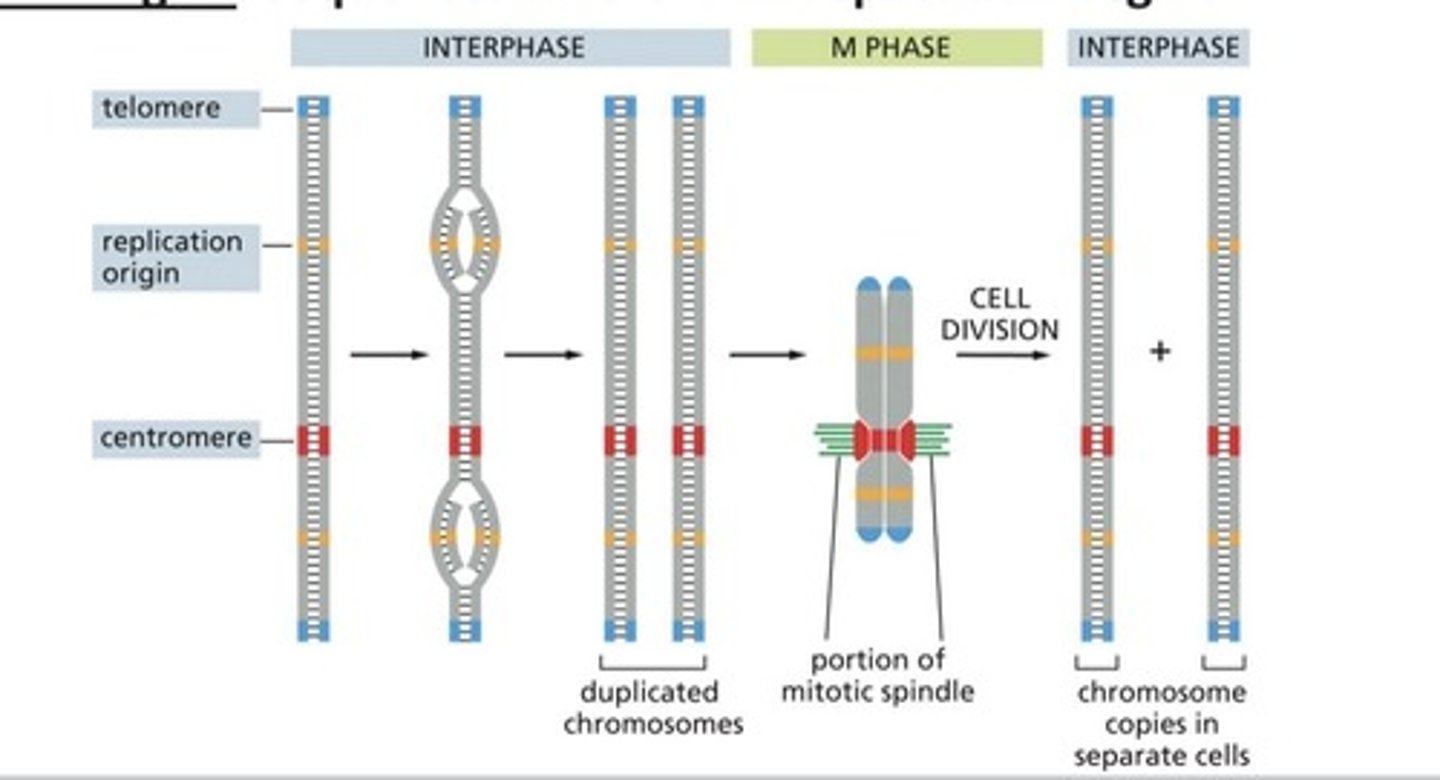
_______ is the point of junction between sister chromosomes.
Centromere
_________ are the stable ends of linear chromosomes.
Telomeres
________ are sequences where DNA replication begins.
Replication origins
Mitotic chromosomes are extremely condensed (and duplicated)
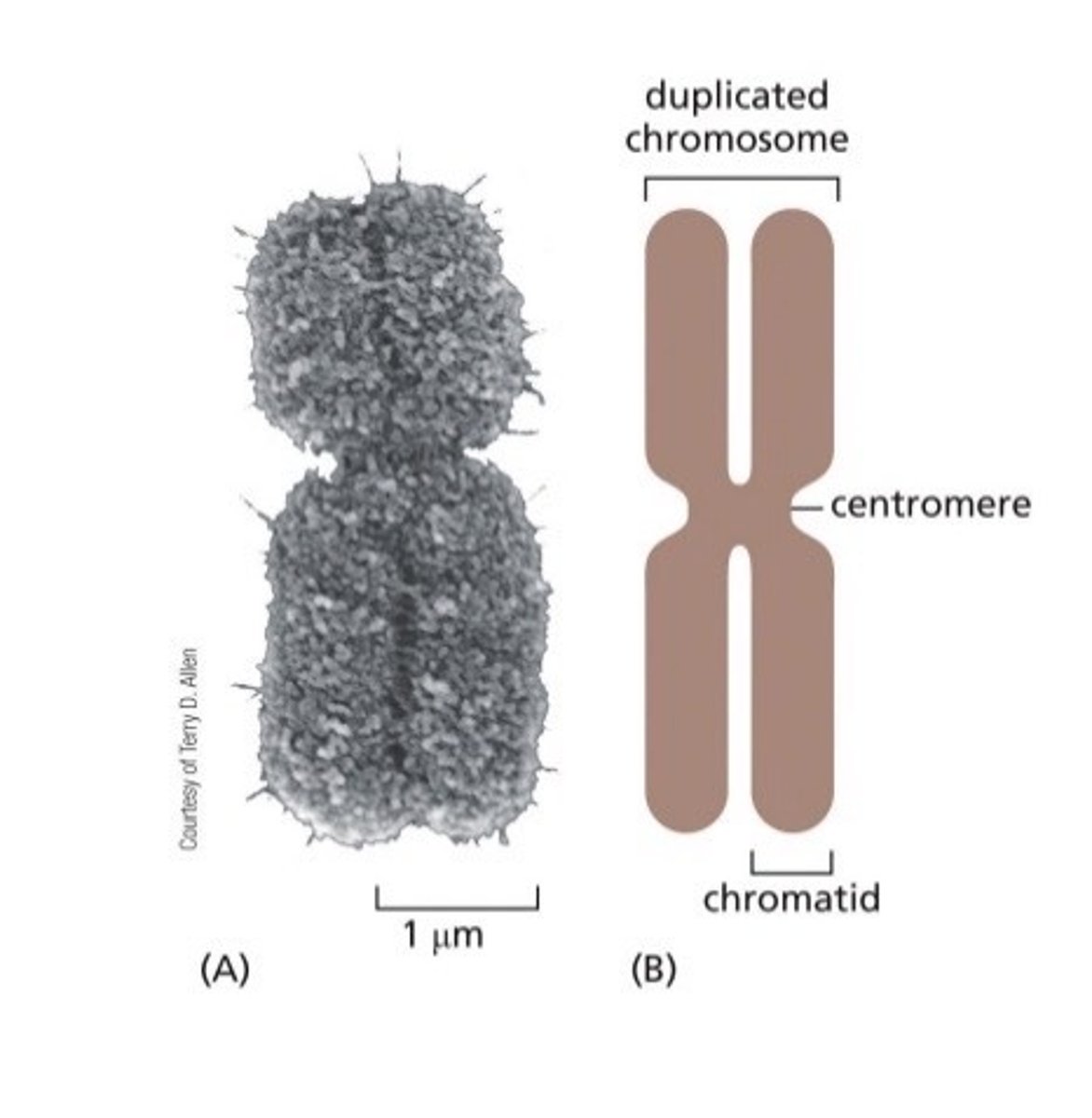
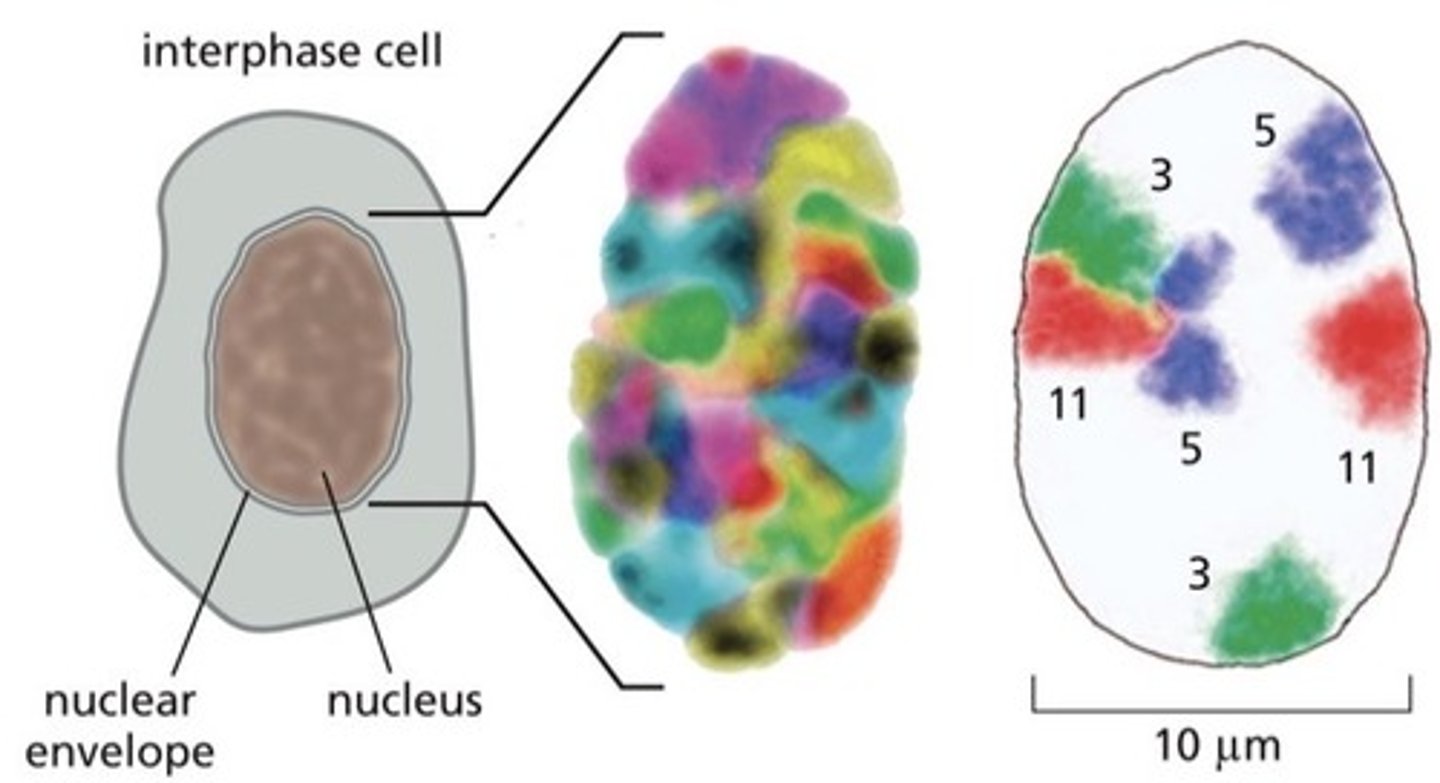
Interphase chromosomes are less condensed (and unduplicated). They maintain their own location within the nucleus.
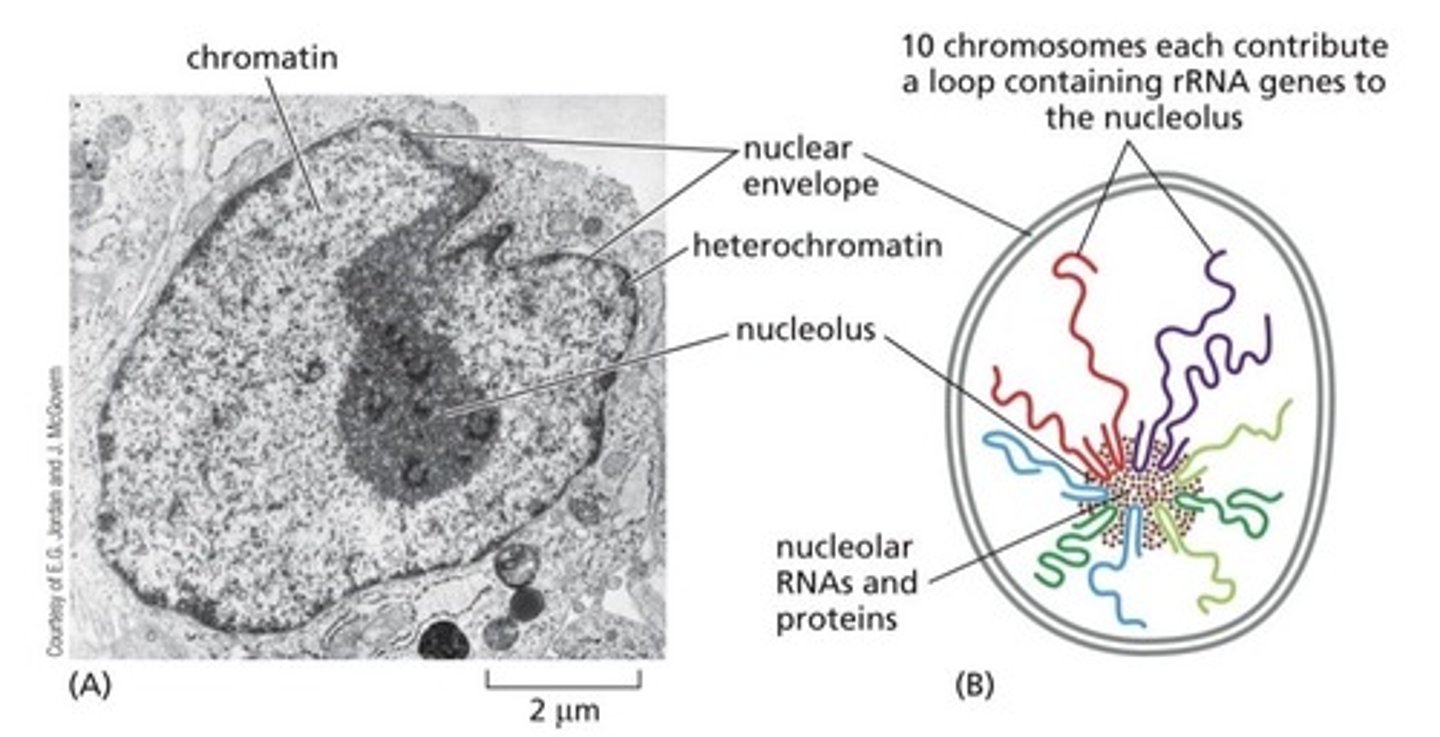
The nucleus is the site where rRNA genes (rDNA) are being transcribed into rRNA. rRNA is located on 10 chromosomes.
_________ are the basic units of eukaryotic chromosome structure.
Histones
An ______ of histones organizes to produce a _______, around which 147bp of DNA wraps
Octomer; nucleosome
Linker histone _____ binds DNA that is exiting the nucleosome and allows tighter packing.
H1
Nucleosome are organized into loops by ________.
SMC complexes.
Loops are associated with gene regulation and sequence specific ________.
Clamp proteins
Clamp proteins are associated with certain cell types/developmental stages.
True
Mitotic chromosomes undergoes about 10-fold more condensation.
True
Cohesins are replaced with different SMC ring proteins-___________
Condensin I and Condensin II
There are levels of DNA compaction.
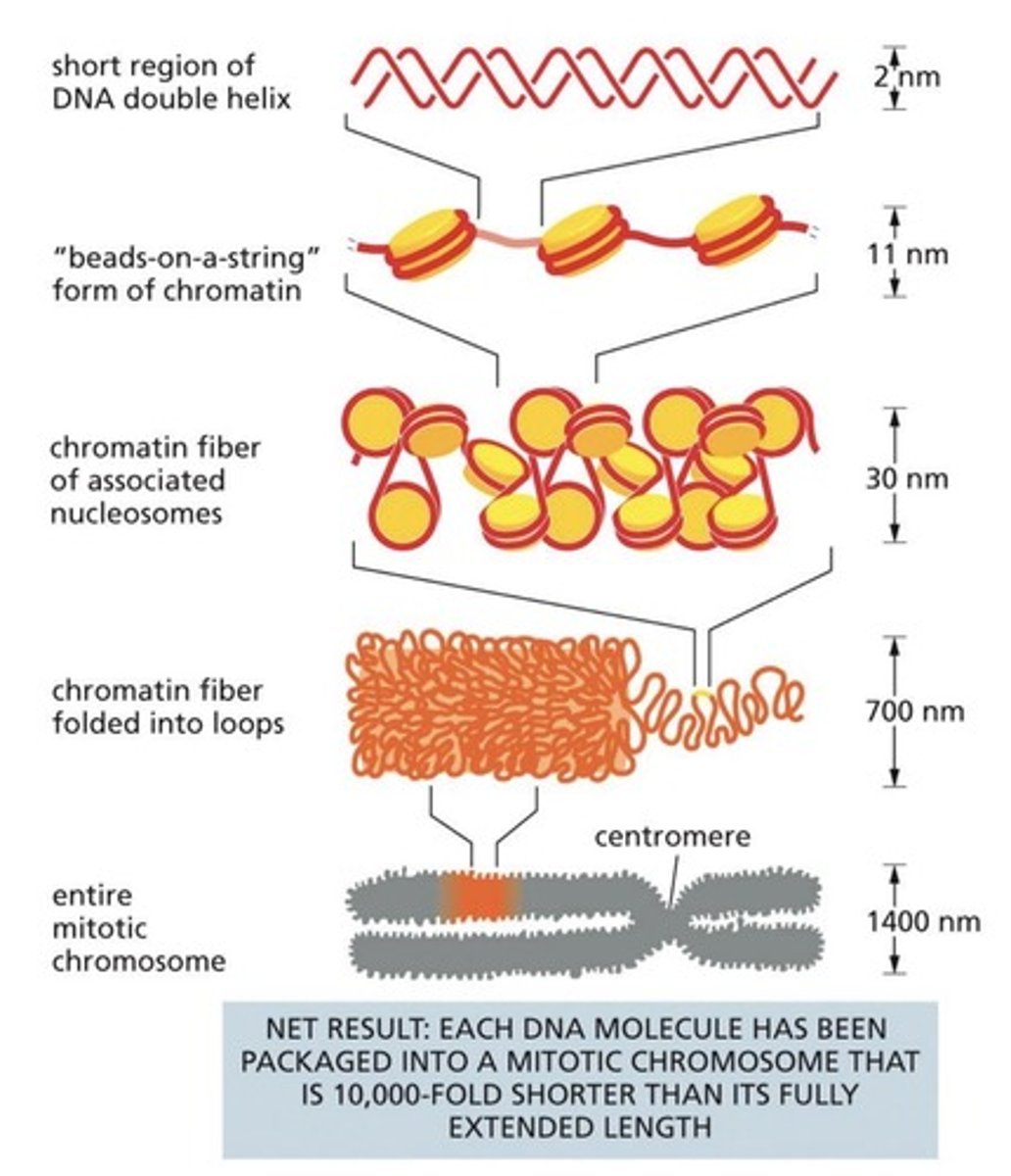
What is the function of each chromosomal structural element?
Centromere, Telomere, and Ori:
Access to different regions of DNA is dynamic and must be regulated. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes use ATP to move histones.
True
_____ can be modified. The H3-N-terminal domain is most documented.
Histones
Histones organization produces regions of _________ and regions of _________ along chromosomes.
heterochromatin ; euchromatin
________ is always heterochromatic, centromeres and telomeres.
Constitutive heterochromatin
__________ is related to the differentiation state of the cell-varies by chromosome, cell types, developmental state.
Facultative heterochromatin
________ is actively being transcribed.
Active euchromatin
________ is available for transcription.
Quiescent euchromatin
_________ modifications are recognized by heterochromatin specific proteins. _________ proteins and associated ________ proteins put the mark on adjacent histones.
Histone ; reader ; writer
____________ ___________ results in gene silencing of a whole chromosome through heterochromatin formation.
X-chromosome inactivation (its random nature produces the calico cat fur pattern).
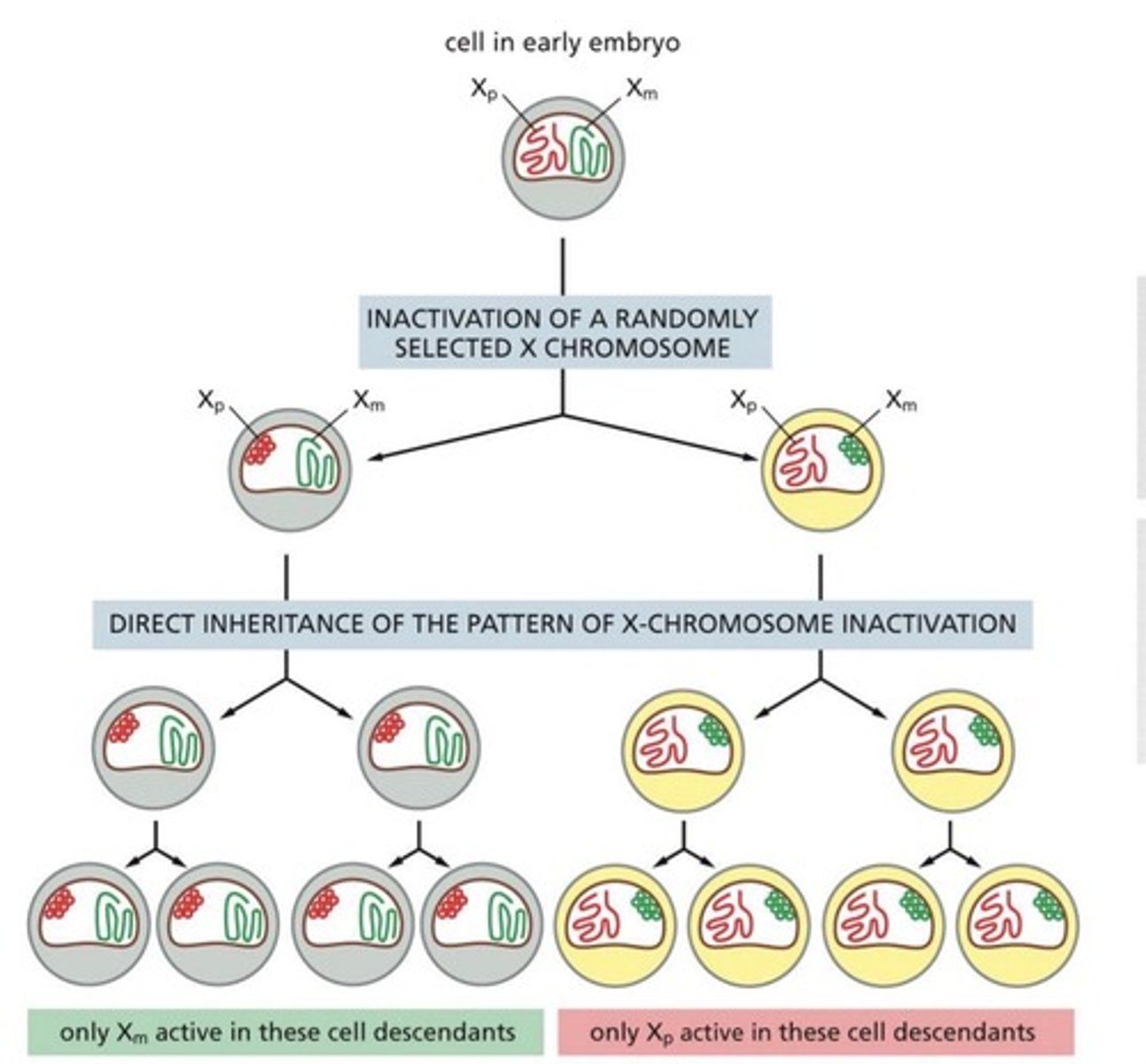
Histone modifications are passed down during DNA replication and about 1/2 of the old, marked histones will be distributed to each daughter strand.
True (example of epigenetic inheritance)
How does the composition of a nucleosome correlate with its function?
What mechanisms are used to remodel chromatin structure?
What is the effect of chromatin remodeling on the function of the cell?
How are genes organized on chromosomes?