Lecture 6: Memory Applications in Psychology: Key Concepts and Errors
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What facilitates learning for retrieval?
Learning for retrieval is facilitated by organizing and understanding the meaning of information.
How are acquisition, retrieval, and storage connected?
Acquisition, retrieval, and storage are interconnected processes that influence how well information is recalled.
What does the success of memory retrieval depend on?
The success of memory retrieval depends on what is already known (memory network) and what happens during learning (e.g., maintenance/elaborative rehearsal).
How can memory be conceptualized?
Memory can be thought of as a vast network of ideas, where ideas are nodes connected by associative links.
What is spreading activation in memory networks?
Spreading activation refers to the process where activation travels within a network from one node to another, increasing a node's activation level when neighboring nodes activate.
What is the role of summation in memory activation?
Summation allows subthreshold activations to accumulate, causing a node to fire if the response threshold is reached, which in turn activates neighboring nodes.
What explains the effectiveness of retrieval cues?
The memory network model explains why hints work, as they activate related nodes and facilitate recall.
What is semantic priming?
Semantic priming is the activation of an idea that spreads to related ideas, demonstrated in lexical-decision tasks.
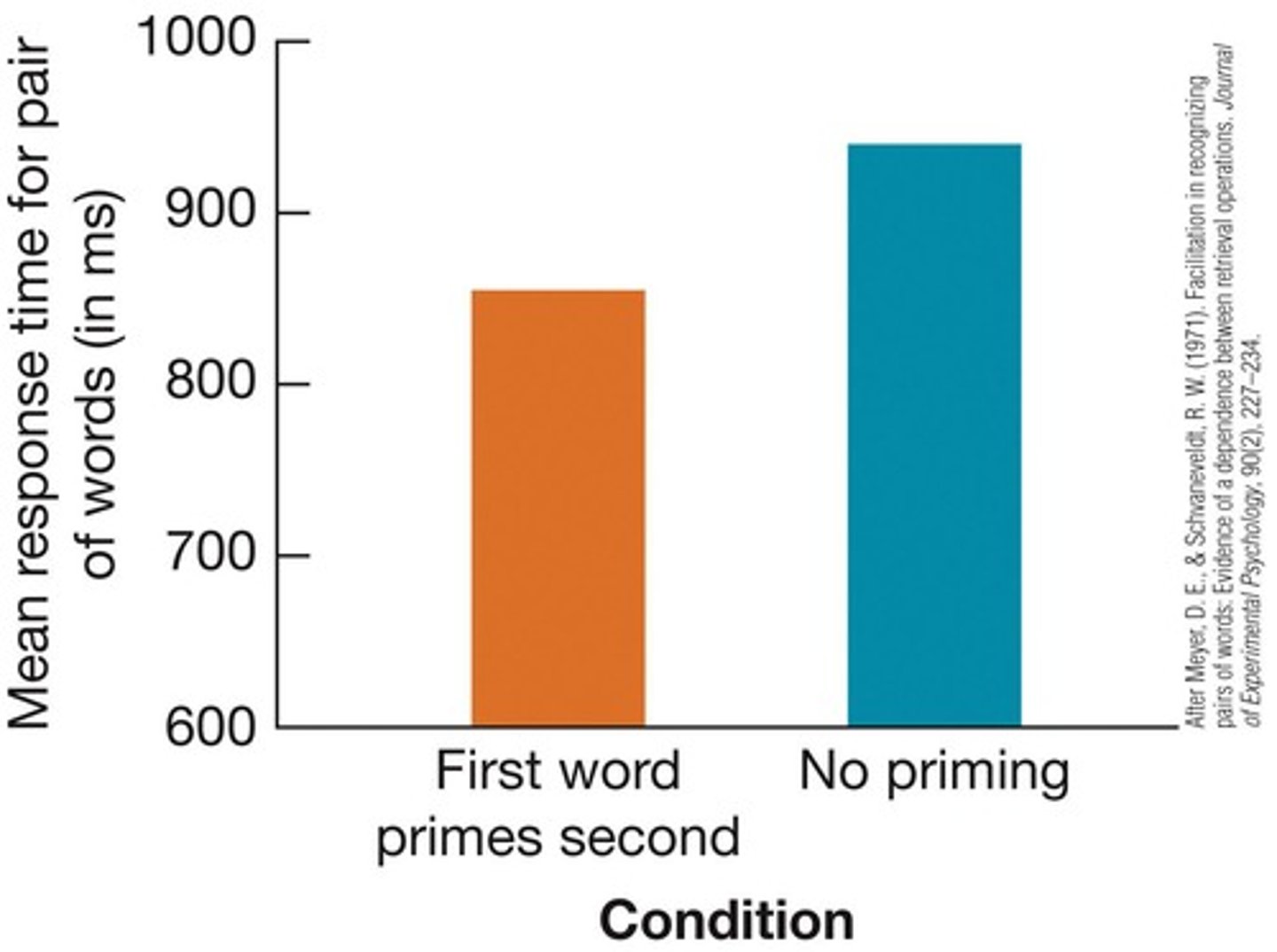
What are retrieval paths in memory?
Retrieval paths are connections that link new material with existing memory, aiding in the retrieval of information.
How does attention to meaning enhance retrieval?
Attention to meaning involves considering relationships between words, which can enhance retrieval by creating more connections.
What is context-dependent learning?
Context-dependent learning refers to the phenomenon where the state of the learner during acquisition affects memory retrieval.
What did Smith et al. (1978) demonstrate about context-dependent learning?
Smith et al. found that participants were not affected by a room change during testing if they thought about the original room context before the test.
What is context reinstatement?
Context reinstatement involves re-creating the context of the learning episode, including thoughts and feelings, to aid retrieval.
What is encoding specificity?
Encoding specificity is the principle that materials are better recognized if they are presented in or cued by a similar context to the one in which they were learned.
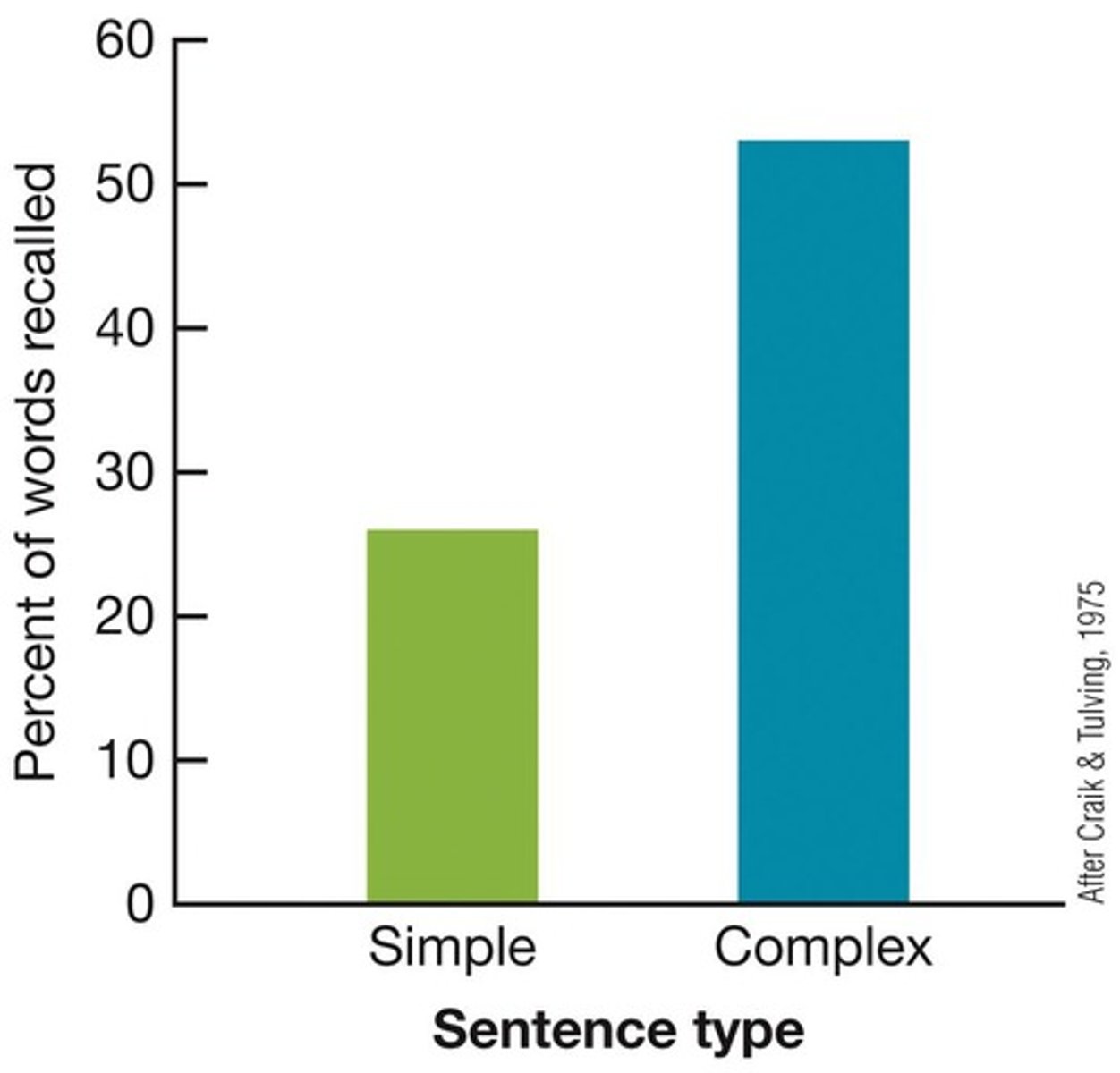
How do elaborate sentences affect memory?
Elaborate sentences lead to richer retrieval paths, resulting in better recall compared to simple sentences.
What are mnemonic strategies?
Mnemonic strategies improve memory by organizing information and imposing structure, such as through first-letter mnemonics.
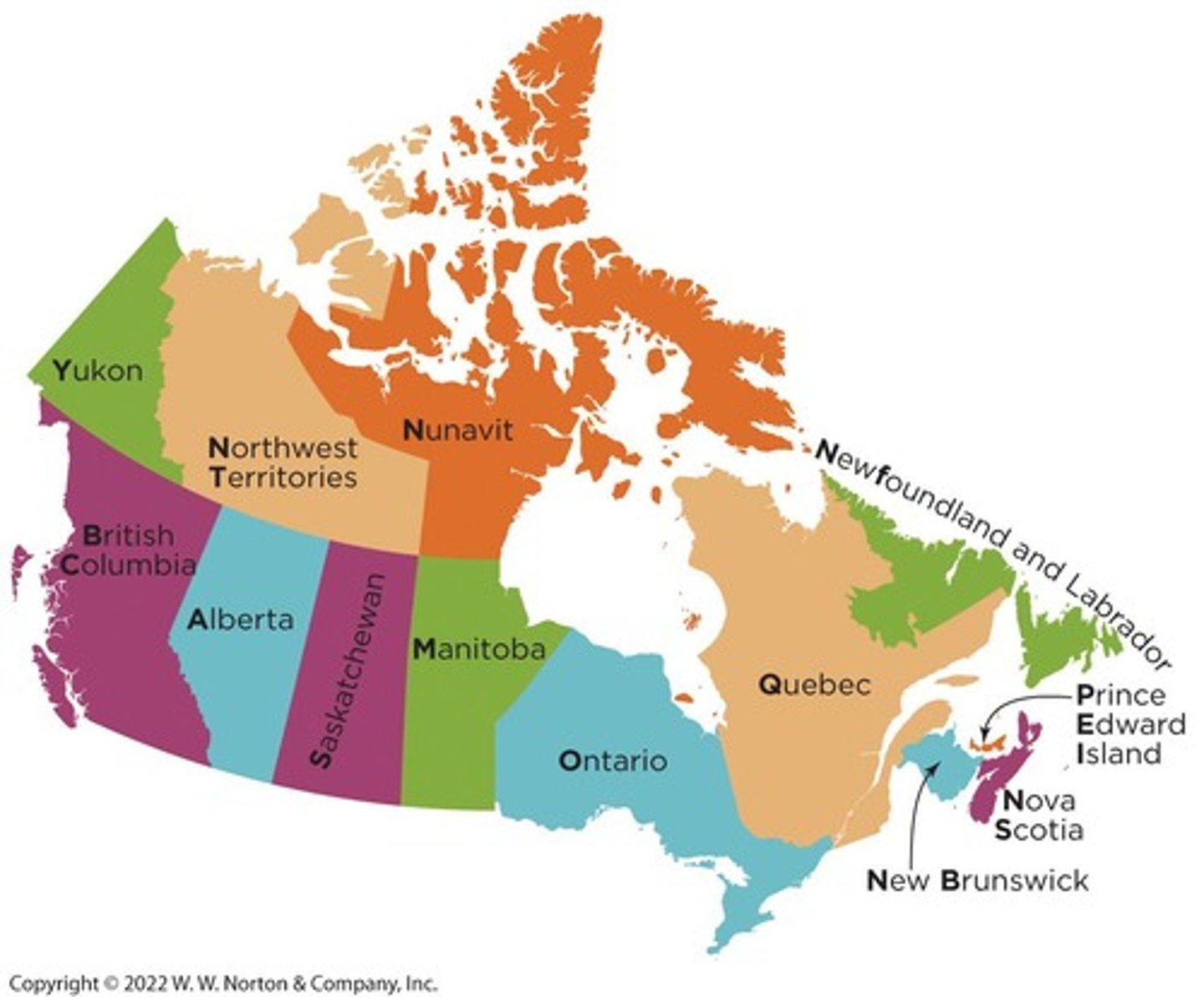
What is the significance of the phrase 'Breakfast Cooks Always Sell More Omelets'?
This phrase is a mnemonic device that helps remember the three northern territories of Canada.
Why is maintenance rehearsal important?
Maintenance rehearsal helps retain information in memory by repeatedly focusing on it without adding meaning.
What is elaborative rehearsal?
Elaborative rehearsal involves connecting new information to existing knowledge, enhancing understanding and recall.
What is the impact of studying for different types of tests?
The way of studying should be suited to the type of retrieval required, such as using sample exam questions for practice.
How do connections between new knowledge aid retrieval?
Connections between new knowledge create multiple retrieval paths, making it easier to access information.
What is a mnemonic device?
A technique used to aid memory, often through patterns or associations.
What is the peg-word system in mnemonics?
A mnemonic strategy where items to be remembered are associated with a pre-established list of words or images, such as 'one is a bun, two is a shoe'.
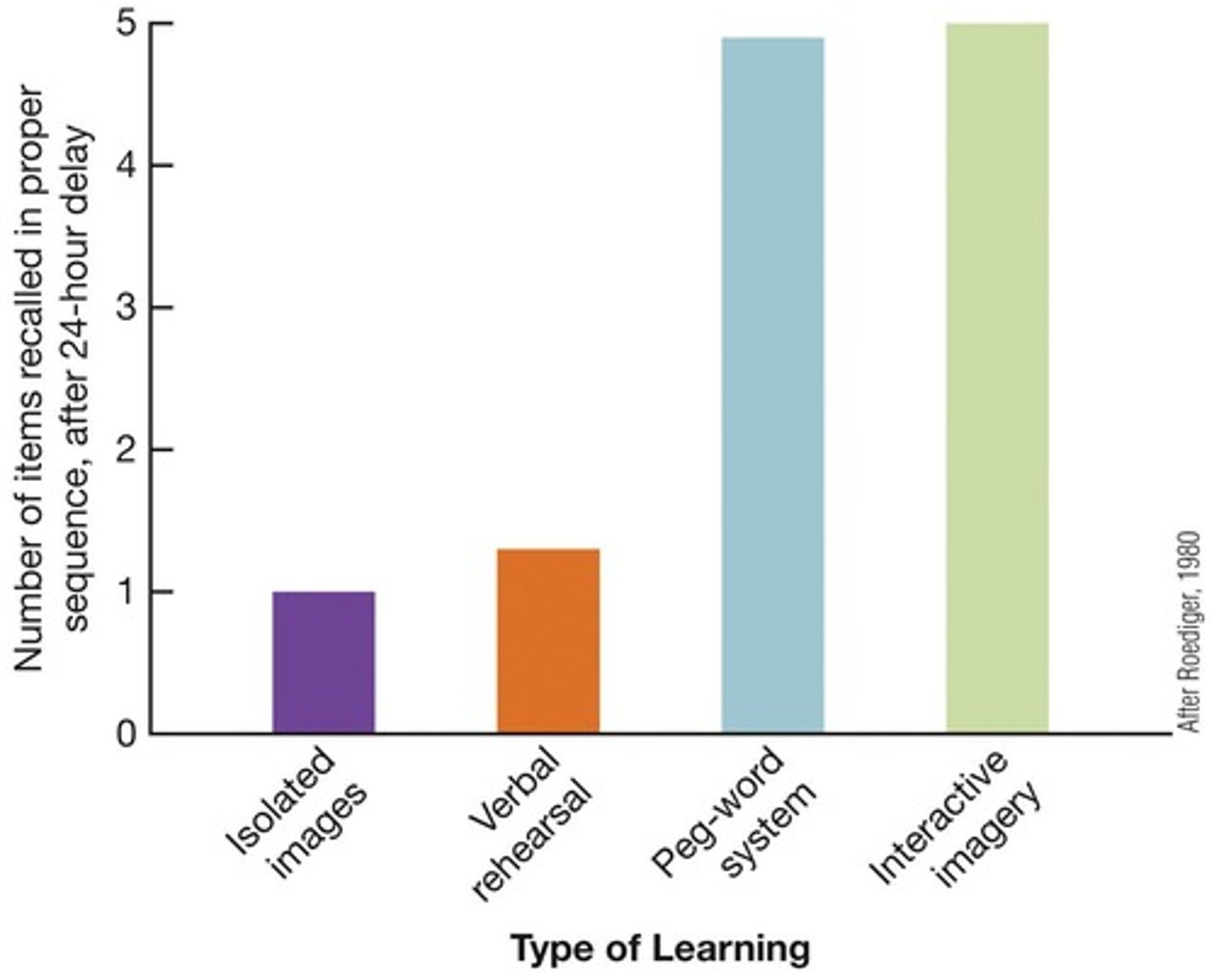
How can mental imagery assist in memory?
It aids in forming associations between items and their mnemonic pegs.
What is the first step in the procedure for understanding and memorizing information?
Arrange items into different groups.
Why is it better to do fewer things at once when memorizing?
Doing too many things can lead to complications and mistakes.
What are some common memory errors?
Low-confidence recall, drawing a blank, incorrect recall, and false memories.
What was the outcome of the 1992 cargo plane crash study regarding memory?
55% of participants falsely reported seeing the crash on TV, despite no footage existing.
What does the DRM paradigm demonstrate about memory errors?
Participants often recall a theme word that was not presented, indicating that memory can be influenced by expectations.
What is a schema in the context of memory?
Knowledge about what is typical in a situation, event, or location that helps in remembering and reconstructing memories.
How can shared connections in memory lead to errors?
They can make similar memories less distinguishable, leading to confusion and incorrect recall.
What is the significance of schematic knowledge in memory retrieval?
It helps regularize memory and fill in gaps during recall.
What is the relationship between memory errors and expectations?
Memory recall can be driven by expectations rather than actual events, leading to inaccuracies.
What is the importance of learning for retrieval?
It emphasizes the need to organize and structure information for effective recall.
What can happen when trying to retrieve a memory?
One may experience low-confidence recall, drawing a blank, or incorrect details.
What is autobiographical memory?
Memory of personal experiences and events from one's own life.
What is the cost of memory errors?
Memory errors can lead to significant misunderstandings and misremembering of events.
What is the role of connections in memory?
Connections can serve as retrieval paths but can also lead to errors if memories are too similar.
What is the impact of expectations on memory recall?
Expectations can cause individuals to remember details that were not actually present.
What is the procedure for organizing materials for memorization?
Arrange materials into groups, place them appropriately, and repeat the process as needed.
How does the process of memory retrieval relate to everyday life?
It is a common task that involves organizing and recalling information regularly.
What should one avoid when memorizing information?
Avoid overloading oneself with too much information at once.
What is the significance of arranging items into groups during learning?
It helps in structuring information for better understanding and recall.
What classic demonstration illustrated the effects of schemata on memory?
Frederick Bartlett's study in 1932, where British participants remembered a Native American story by recalling the gist but altering details to fit their background knowledge.
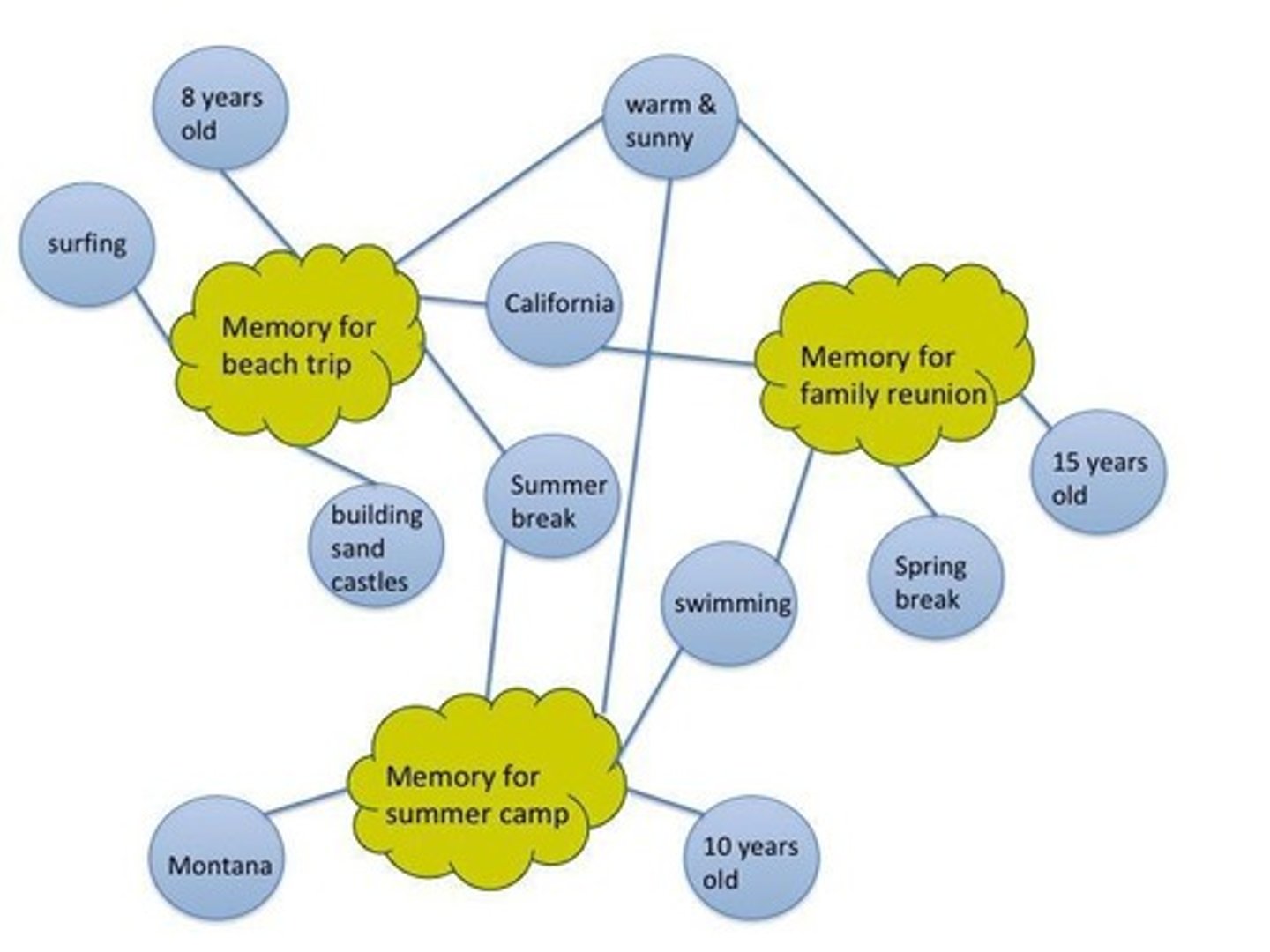
How do people use their schema when recalling memories?
They reconstruct what must have happened or been true at the time based on their existing knowledge.
What is one advantage of connecting new information to prior knowledge?
It cements the new material in memory more securely, making it less likely to decay.
What is a negative consequence of memory connections?
They can undermine the accuracy of memories.
What percentage of false convictions overturned in recent years were contributed to by eyewitness errors?
At least 75%.
What was the main finding of Loftus and Palmer's 1974 study on planting false memories?
Participants incorporated misleading suggestions about a car accident into their memories.

What are the steps in the misinformation effect?
1. Experience an event. 2. Be exposed to misleading suggestions about the event. 3. Delay. 4. Memory test.
What factors make it easier to plant false memories?
It is easier to plant plausible memories than implausible ones and to add to a memory than to replace one.
How can visual imagery affect false memories?
Imagery can increase confidence in a false memory by helping individuals visualize the event.
What did Shaw and Porter (2015) demonstrate about false memories?
They showed that participants could be persuaded to believe they committed a crime that never happened, and they remembered this imaginary event years later.
What is the relationship between memory confidence and accuracy?
People tend to trust memories expressed with confidence, but confidence can be influenced by factors beyond the memory itself.
What is the decay theory of forgetting?
It suggests that memories fade or erode over time.
What is the best predictor of retention interval?
The time between initial learning and retrieval.
What is one way to avoid memory errors?
Recollection is often detailed, long-lasting, and correct; however, there is no foolproof method to know when a mistake has been made.
What role do schemata play in memory errors?
Schemata can lead to merging of related memories, which may cause inaccuracies.
What is one of the objectives of Elizabeth Loftus's TED talk?
Discussing memory errors and the implications of false memories.
Why might memory errors be considered a small price to pay?
They may be a necessary trade-off for the efficiency of memory retrieval.
What is one challenge in determining which memories to trust?
There are no widespread, reliable indicators of memory accuracy.
What is the significance of eyewitness testimony in legal contexts?
Eyewitness testimony can lead to wrongful convictions, highlighting the unreliability of memory.
What are some techniques that can lead to false confessions?
Repetition, social pressure, and guided imagery can persuade individuals to confess to crimes they did not commit.
What is a common misconception about memory accuracy?
That confidence in a memory is a reliable indicator of its accuracy.
What is the best predictor of memory retention?
The retention interval, which is the time between initial learning and retrieval.
What does decay theory of forgetting suggest?
Memories fade or erode over time.
What is interference theory in the context of forgetting?
Newer learning may disrupt older memories.
What is retrieval failure?
Memories may be intact but inaccessible due to changes in context or perspective.
What phenomenon can occur during retrieval failure?
The tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon.
How can the Cognitive Interview procedure assist in memory retrieval?
It helps retrieval without increasing false memory, emphasizing context reinstatement and diverse retrieval cues.
What is the testing effect?
Repeated retrieval and testing can prevent forgetting, and formal testing is not required to experience these effects.
What is a potential downside of hypnosis regarding memory?
Hypnosis can make individuals more open to misinformation and prone to errors.
What is autobiographical memory?
Memory of episodes and events in one's own life.
How do memories about ourselves tend to be constructed?
They are a mix of genuine recall and schema-based reconstruction, often biased towards consistency and positive traits.
Why does emotion enhance memory?
Emotion helps with memory consolidation and increases activity in the amygdala, which enhances hippocampal activity.
What are flashbulb memories?
Memories of extraordinary clarity for highly emotional events, retained over many years with high confidence.
What was observed in the study of flashbulb memories after the September 11 attacks?
37% of participants gave a substantially different account one year later, despite high confidence.
What can lead to inaccuracies in flashbulb memories?
Discussion with others can alter memories through rehearsal and co-witness contamination.
How does physiological arousal affect traumatic memories?
It increases consolidation but can also lead to the loss or effortful recall of some traumatic memories.
What is the effect of stress on memory?
Stress enhances memory for materials directly relevant to the source of stress but undermines memory for details.
What is repression in the context of memory?
The idea that traumatic memories can be 'lost' and later 'recovered', though many may actually be false memories.
How does the establishment of memories affect their fading over time?
How quickly memories fade may depend on how well established they were initially.
What is a unique aspect of autobiographical memory?
The role of emotion in shaping autobiographical memory is somewhat unique compared to general memory principles.
What are some factors that can lead to fragmented memories?
Head injuries, sleep deprivation, drugs or alcohol, and stress.
What is the significance of schema in memory?
Memories are formed and reconstructed via schemata, which can lead to intrusion errors and susceptibility to misinformation.
What is the relationship between emotional events and attention?
Emotional events narrow attention and shift focus to emotion-relevant goals.
What is the tendency to mull over emotional events equivalent to?
It is equivalent to repeated rehearsal.