Lesson 2: Cell Membrane characteristics and Biogenesis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Cell Membrane
-thin continuous shee that spreads over entire cell surface
-formed by lipid, proteins and carbohydrates
Functions cell membrane
Barrier: seperates compartments
Communication: substance and information exchange
Lipids
Cell membranes main compartment (50% of the mass)
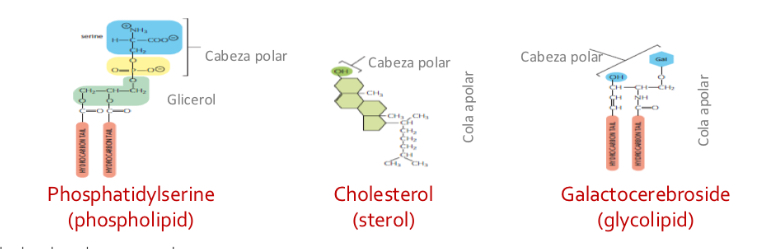
Types of membrane lipids
Phospholipids: most abundant and form the bilayer. A polar head group towards the surface and two hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails.
Cholestrol: small polar group
Glycolipids: contain oligosaccharrides and are located on Luther side of cell membrane
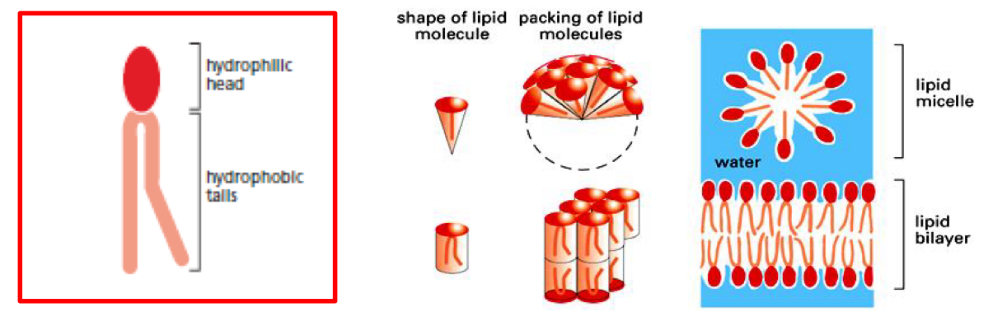
Lipid structure
Hydrophilic head (polar)
Hydrophobic tail: (nonpolar)
Lipids in contact with water
Bilateral: Polar Head on outside and nonpolar on the inside
Micelles
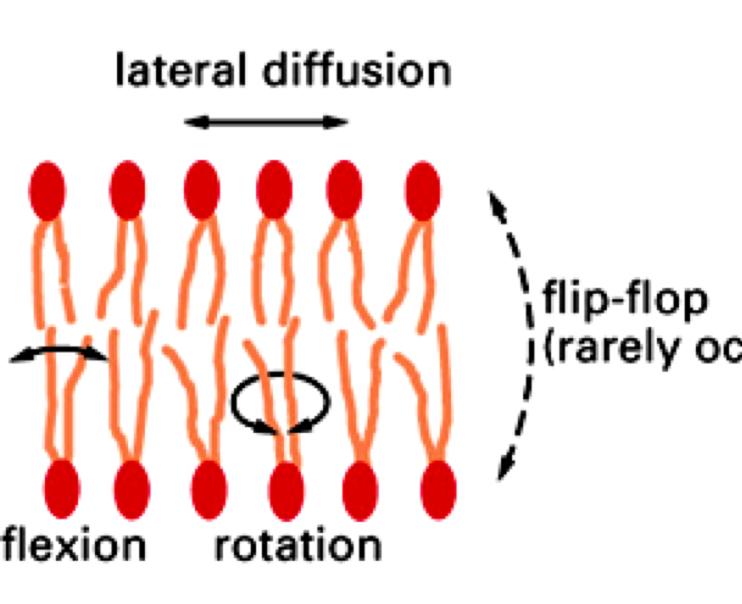
Types of movement
Cell membranes are highly dynamic systems
-Lateral diffusion: exchange of place sidewards
-Rotation: turn of lipid like globus
-Flexion: movement of tails
-Flip-flop: change of bilayer site
Proteins
-Involved in Structure, Recognition (receptors), adhesion (connection), transport or cell metabolism (enzymes)
-Around 40-50% of cells membrane mass
-More lipid molecules than protein molecules
Classification: Degree of association with membrane
Peripheral: inside or outside the bilayer and easily separated from membrane -Cytosolic or extracellular
Intergal: Strongly attached to the cell membrane -cytosolic, extracellular and transmembrane
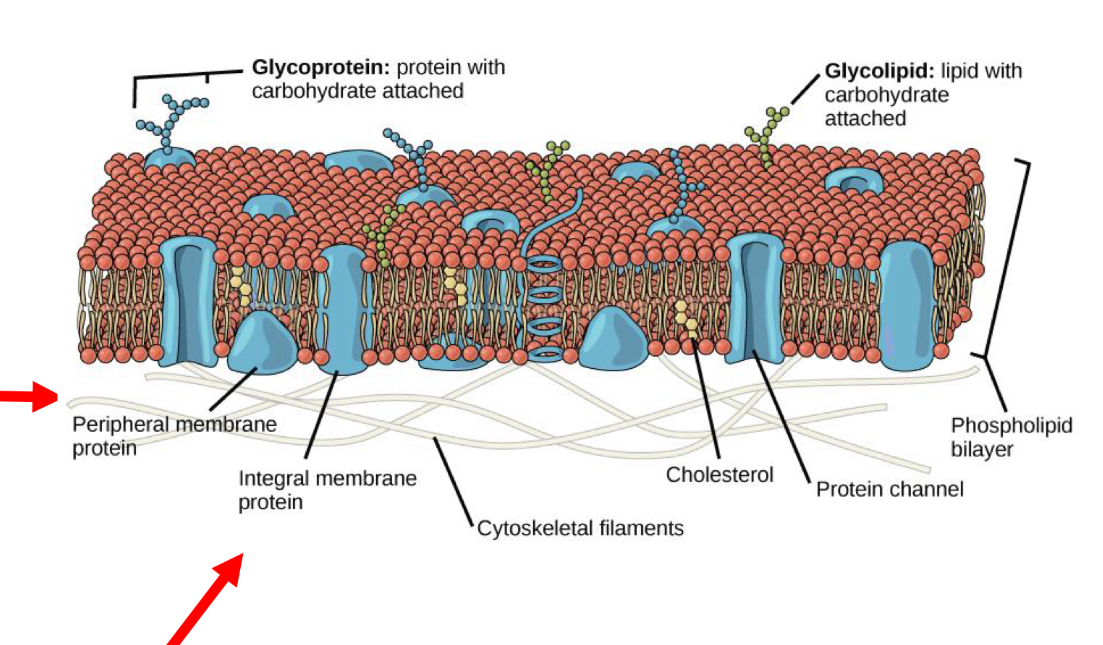
Classification: According to their Location in the cell membrane
Transmembrane proteins: Cross entire bilayer and out of both side of bilayer
-Amphiphatic molecules: aminoacids pass are apolar
-can be bound to fatty acids
Cytosolic proteins: completely in cytosol
-Bound to monolayer by: helix, one or more fatty acids, other proteins
Extracellular proteins: located outside of cell membrane

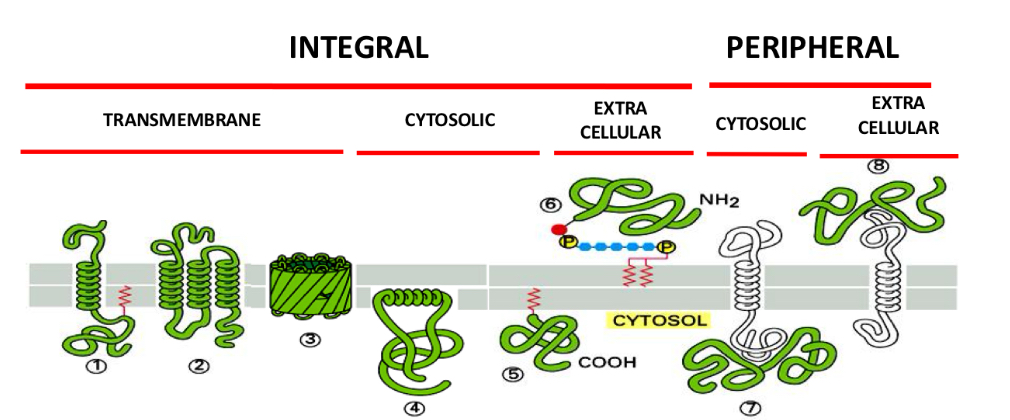
Relation transmembrane proteins and integral proteins
Every transmembrane proteins are integral proteins, but not all integral protein is a transmembrane protein.
Transmembrane proteins
-Always have the same orientation, depending their function (eg. Surface receptors)
-Most highly glycosylated in the outer layer of the cell membrane
-Rotation and lateral movement
Carbohydrates
-Only found on outer surface of bilayer
-Associated with lipids or proteins (glycolipids and glycoproteins)
-Glycocalyx loose layer of oligosaccharide and polysaccharide on outer surface of plasma membrane
-Layer with secreted proteins outside glycocalx → extracellular matrix
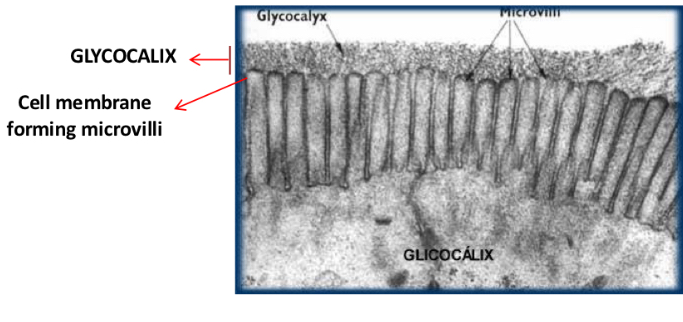
Functions of the Glycocalyx
-Protection of cell surface
-viscosity
-Cell recognition: Immunity and cell identification, receptor, cell growth and division, fertilization (sperm recognise and bind to eggs)
Self sealing
Closing edges by itself
-small tear in bilayer: lipids rearrange and close
-larger tear in bilayer: repaired by fusion of vesicles
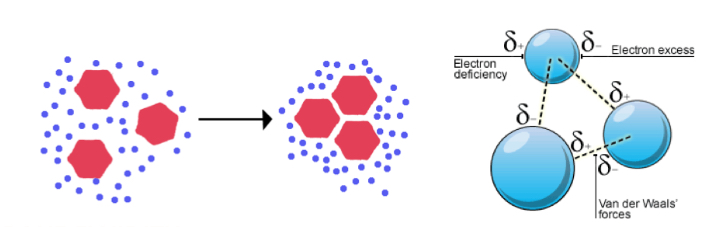
Fluidity
Lipid molecules are able to diffuse freely
Weak interactions: Van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions
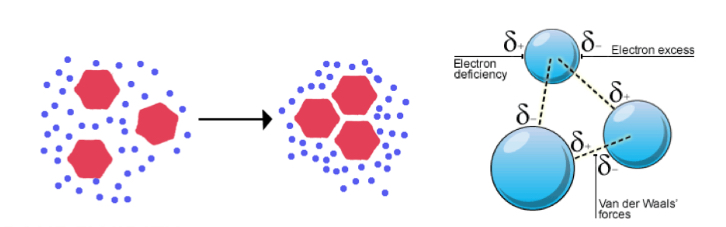
Factors influencing membrane fluidity
-Temperature: increases fluidity
-Molecular composition of lipids: Bilayers are more fluid of the hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids are short or double bonded
-Presence of cholesterol
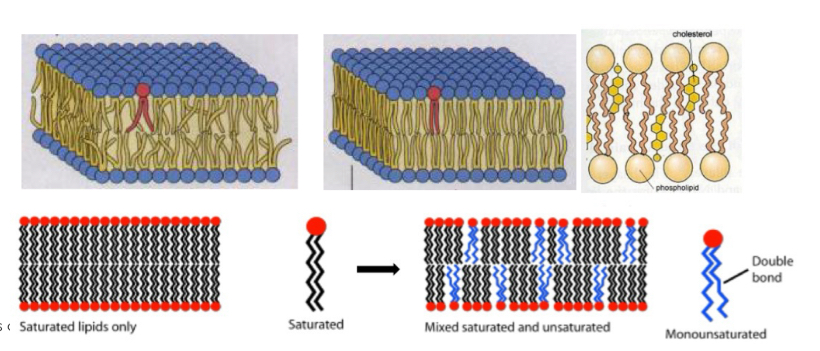
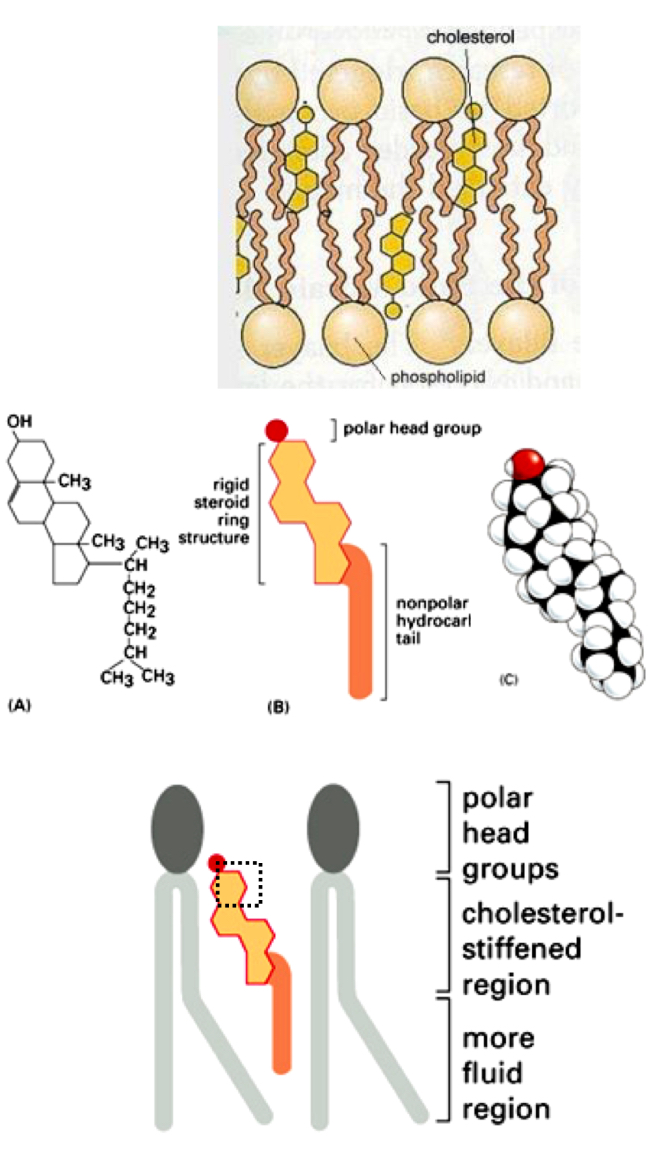
Cholesterol effects and structure
-decreases fluidity and flexibility
-avoids crystallisation of tails at low temperature
-mechanical stability
-polar head group, rigid steroid in central area, nonpolar tail
Asymmetry
-asymmetric distribution of components in each monolayer
-proteins and lipids different in each side
-Carbohydrates only on external surface, forming glycoprotein and glyoclipids
-functionally important, each monolayer performs different functions
Permeability of plasma membrane
- Small polar and nonpolar molecules and water can cross the cell membrane.
- Larger polar molecules and ions are not able to cross the bilayer.
BIOGENESIS
The cell membrane renews constantly
Origin of its components
• The lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol)are synthesized by enzymes of the smooth ER membrane (SER).
• The proteins are synthesized at the ribosomes in the rough ER (RER).
• The oligosaccharides that will bind the lipids and proteins and produced in the ER.
the terminal glycosylation of lipids and proteins is performed in the Golgi, forming glycolipids and glycoproteins.
Transport
Packaged in vesicles and delivered to cell membrane
Transport
-Nutrients in, waste products out
• According the flow-direction of the transport and the type of substance that is going to cross the membrane:
- Ingestion: molecules needed for the cell metabolism enter into the cytoplasm.
- Excretion: waste products are secreted out of the cell.
- Secretion: when the secreted product is not waste but molecules synthesized for being exported out of the cell.
-Water and small non-polar molecules diffuse rapidly across
Types of Transport depending on energy requirements
Passive Transport:
• It does not require energy; it is driven by a concentration or voltage gradient.
Types:
- Simple (simple diffusion)
- Facilitated
Active Transport:
Against a concentration or chemical gradient; it always requires energy.
• Types:
- Primary active transport
- Secondary active transport
- Transport of macromolecules
Passive Transport: Simple diffusion
Molecules that can diffuse spontaneously
-Gases (CO2, O2)
-Small hydrophobic molecules
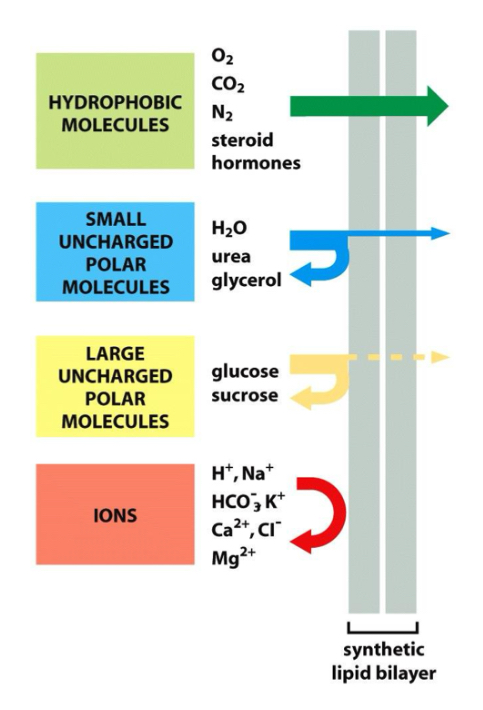
Passive Transport: Faciliated diffusion
Carried out by membrane proteins
-Hydrophilic molecules: Amino acids, nucleotides
-Charged molecules: ions
Channel proteins: Channel proteins, Carriers (change conformation and binding molecules cross membrane)
Primary active transport
• Uses energy in the form of ATP
against electrochemical gradient
• e.g. Na+ - K+ pump
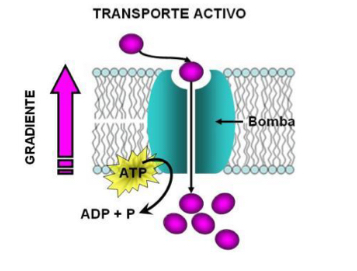
Secondary active transport
• It uses the energy stored in the electrochemical gradient of an ion to transport another solute.
• ATP synthesis
Macromolecules transport
Transport of macromolecules
- Requires energy (active transport).
- Through the deformations in the membrane and the formation of vesicles.
- Necessary to transport large molecules
- Types:
▪ Exocytosis
▪ Endocytosis
▪ Transcytosis
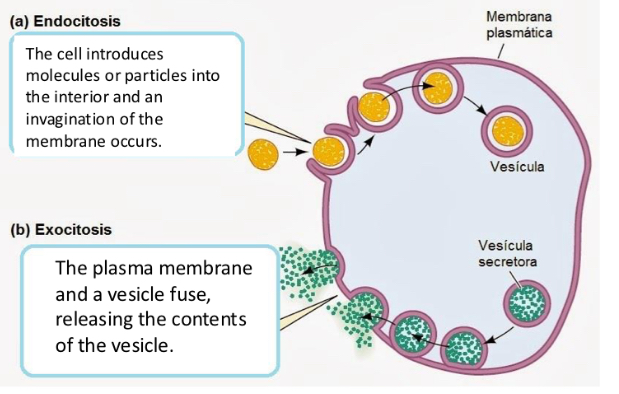
Exocytosis
-Secretion or excretion through the flow of vesicles that leave the Golgi complex and move towards the cell membrane
-Secretion of products to the extracellular matrix and also renewal of the cell membrane
Constitutive Exocytosis
• In all eukaryotic cells.
• there is a continuous flow of vesicles leaving the Golgi Complex and moving towards the cell membrane, where they fuse with the lipid bilayer.
▪ Function: Renewal of the cell membrane and secretion of proteins.
Secreted proteins:
-Incorporate to the extracellular layer of the cell membrane.
▪Form part of the extracellular matrix.
▪Diffuse through the extracellular fluid and serve as nutrients or
signalling molecules to adjacent cells.
Induced
• Found in cells specialized in secretory processes that produce large amounts of a secretory product that is stored in secretory vesicles.
- These vesicles are formed in the Golgi apparatus and accumulate
near the cell membrane.
- In response to an external stimulus, the vesicles fuse with the cell
membrane and discharge their content into the extracellular matrix.
Endocytosis and types
▪ Ingestion of substances by vesicles formed within the cell membrane.
▪ Types:
• Phagocytosis
• Pinocytosis
• Receptor-mediated endocytosis

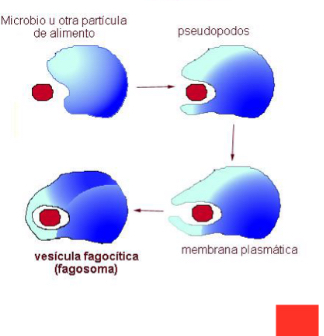
Phagocytosis
-Ingestion of large solid particles
-after endocytosis, there is a phagocytic vacuole or phagosome in the
cytoplasm.
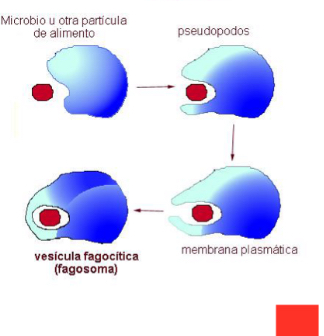
Functions Phagocytosis
• Function:
• In unicellular organisms it is a form of feeding.
• In multicellular organisms it can have a defensive role.
Specialized cells: Phagocytes
- The ingested membrane must be renewed by exocytosis.
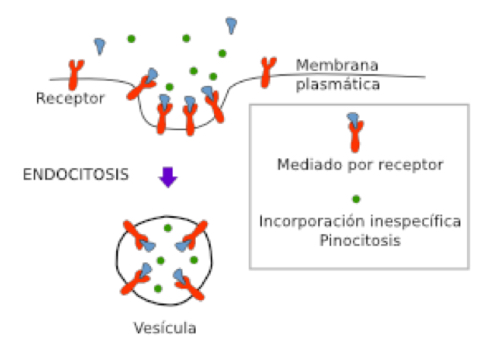
Pinocytosis
• Ingestion of substances dissolved in the form of small liquid drops that will cross the cell membrane when there is an infolding of the membrane.
• Small pinocytic vesicles are formed.
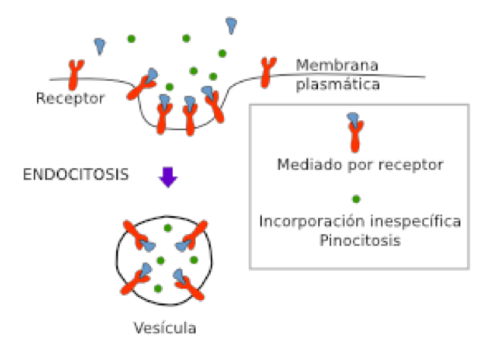
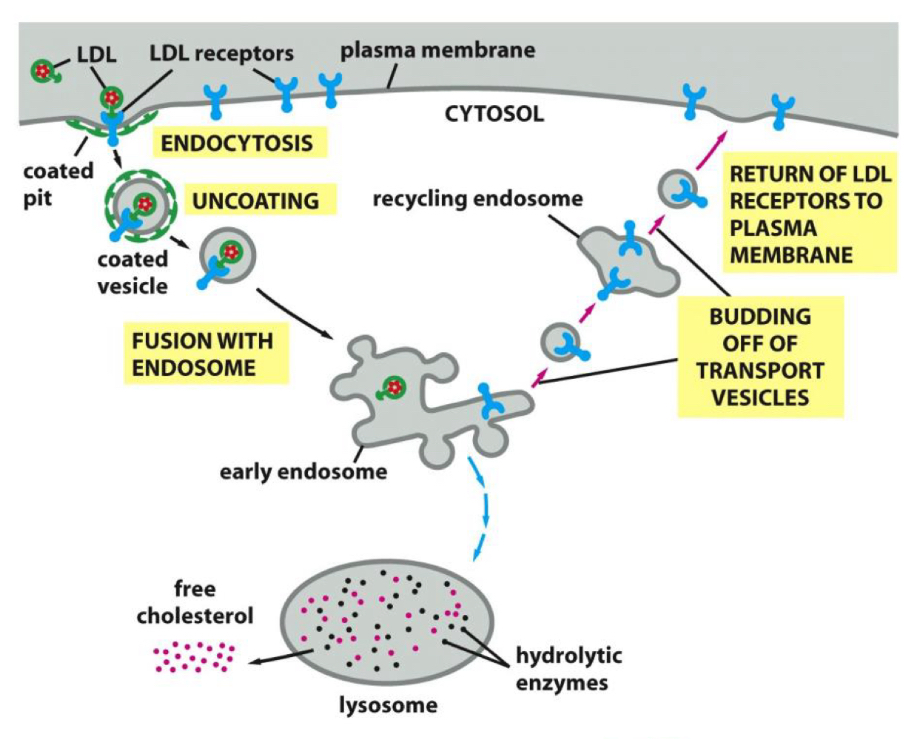
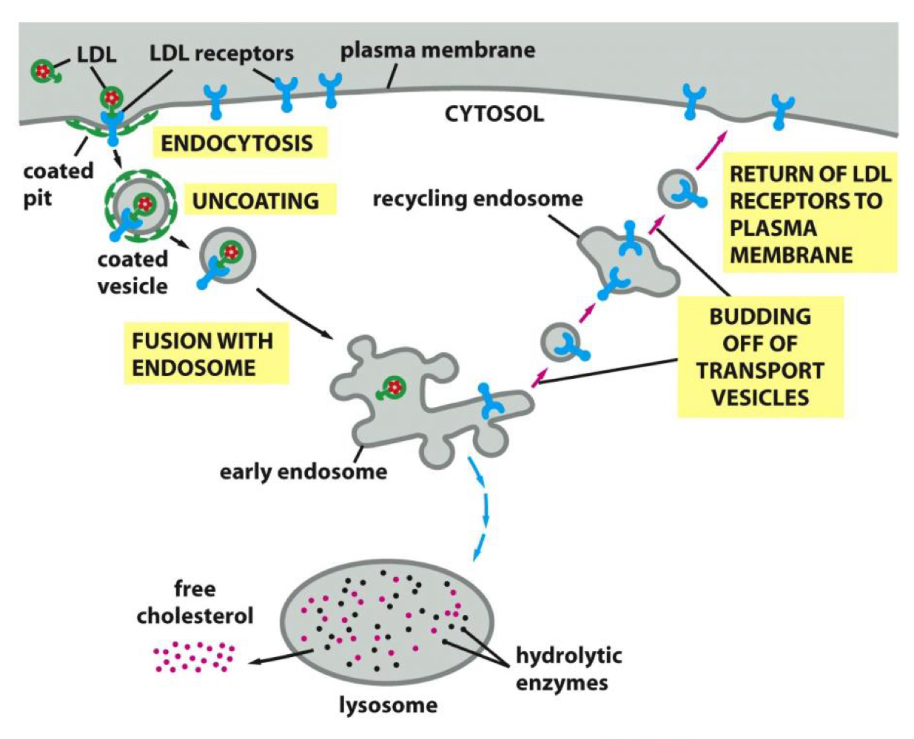
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
• These vesicles are coated with clathrin, a coat protein found on
the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
• Types:
• Constitutive
• Regulated (receptor-mediated)

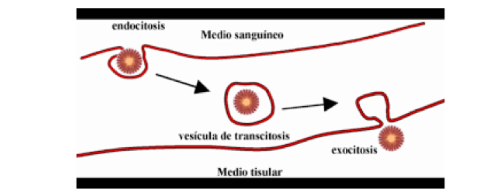
Transcytosis
• Transcellular transport.
• Combination of endocytosis and exocytosis.
• Receptors from the surface of certain polarized cells can transfer specific macromolecules from one extracellular space to another, through vesicle formation.
• Example: epithelial cells