Geography paper 1 2 3
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is quantitative data and examples
Data that contains numbers
Eg beach profile pebble size and shape
What’s qualitative and examples
data that consists of opinions
Example field sketch and environmental quality survey
What’s random sampling
Pick sample at random
What’s systematic sampling
Choosing the sample systematically for example every 3rd person that walks by
What is stratified sampling
Choosing sample based on knowledge
A place has been regenerated
What coastal fieldwork did you conduct
Field sketch of beach
Sediment size and shape
Beach profile
What urban fieldwork did we conduct
Field sketch of the high street
Pedestrian count
Environmental quality survey
Land use
How did you present your pedestrian count data
a tally chart
What was the name of the scale used fto determine sediment shape
Powers index of roundness
Powers scale
What’s the best way to present environmental quality survey and why
Use a radar graph
Plot multiple category’s on the graph at once
However it can be hard to read one complete once placing 2 or more sites
Name some topics that could come up in section c of paper 3 geography
Uk population challenges
Uk energy landscape climate challenges development challenges and coastal challenges
How do you compare pedestrian count
Use a bar chat or a pictogram
However it’s difficult to determine reasons for pattern
non renewable
Energy sources that can only be used once
Renewable resource
Energy that come from sources that can be replenished
Not run out
Fossil fuel
Fuels that been formed from dead organisms
necessities
Resources needed to survive
Abiotic
Physical non living environment
Biotic
Living organism
Natural resource
Any features of environment that can be used for human needs
Name 3 main resources
Food energy Water
Factors that affect distribution of reasources
Climate
Volcanic eruption
Plate tectonics
Solar power
Advantages and disadvantages of coal
A-mining it is cheap. easy to create into energy.
D-creating mines destroyed wildlife. Dangerous and cause death. Burning it releases co2 into atmosphere
Advantages and disadvantages of wind farms
A-avoid harmful gas emissions some tourist attractions
D-high construction cost noise affects locals and wildlife
How is water exploited and what are the impacts
Exploited- extraction of minerals
Impacts - toxins enter water decrease biodiversity
How is food exploited and what are the impacts
Exploited -Overfishing Land overgrazed
Impact - decrease fertility of soil decrease biodiversity
How is energy exploited and what are the impacts
Exploited - extraction of fossil fuels
Impact- reduction in air quality reserves of oil and gas decrease massively
Energy mix
Range of different primary energy sources used to meet a energy needs of a population
Explain one reason why some countries have low percentages of their population living in urban areas
Low development many people in primary industry’s such as farming
Assess the importance of historical and economic factors in the development of countries (8)
Historical- civil war corrupt government colonisation (hati and french empire)
Economic- trade block trade surplus and deficit natural reasources
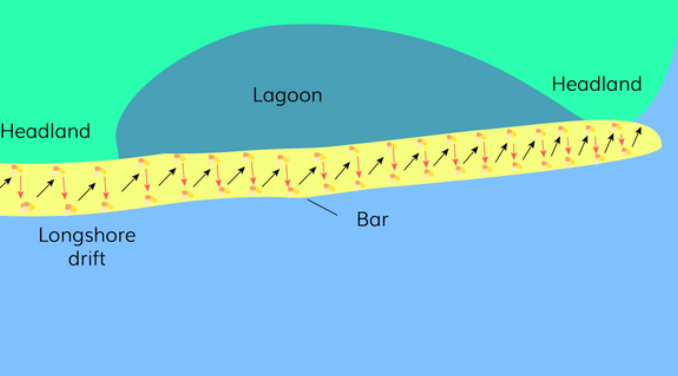
Name this land form
A spit
slumping
A large area of soil moves down a slope due to being saturated
Explain one way seasonal changes in uks weather affects coastal erosion
Storms have more power in winter increasing rate of erosion
discordant coastline
alternating hard and soft rock
Forms headland
mass movement
Movement of material due to gravity
Name one coastal landform created by deposition
Spit
Explain one way rock type leads to formation of headland
Hard rock type will erode more slowly than soft rock
What is fracking
Drilling deep into the ground for shale rock
Advantages of fracking
Cleanest fossil fuel
Simple to extract
Increase number of energy mix
Disadvantages of fracking
Expensive
Causes Earth quakes
Releases co2 contributing to climate change
Water contamination
Why is there a increased demand for energy
Population growth
Increased wealth
Technological advancements
Explain one reason why temperature varies seasonally in the uk (3)
Axil tilt means less sunlight received in winter meaning it’s colder
Name natural causes of climate change
Sunspots milankovitch cycle volcanic eruptions and asteroid impacts
How does ice cores support past climate change
Co2 levels tell how us much co2 was in the atmosphere
How does dendrochronology support past climate change
Thick ring - climate was warm and wet
Thin ring - cold and dry climate
How do historical records support past climate change
Thames frozen- paintings
Journals from Romans
How does pollen records support past climate change
More pollen trapped in layer - warm and wet climate
Less pollen trapped - cold and dry climate
Why do trfs have a high biodiversity
There’s a high solar radiation and rain all year round so plants can grow creating habitat for animals
How are oceans affected by climate change
Temperature increased - species endangered - ice sheets melt - sea levels rise then causes regular flooding
How is food impacted by climate change
Growing food becomes more difficult causing famine
How is health impacted my climate change
Burning energy - releases smog causing increase risk on lung disease and cancer
More frequent heatwaves
Impacts on typhoon Haiyan
Primary impacts -Houses destroyed water sources polluted
Secondary impacts - homelessness increased diseases lack of food
Immediate responses of typhoon haiyan and advantages and disadvantages of them
Government issued warning a- people could prepare d-stadium flooded where people evacuated to
Power restored and 1 million food packs a-connect with country’s d- hard to distribute food
Long term responses of typhoon haiyan and advantages and disadvantages of them
Build back better (government plan) A-protect damaged houses rebuilt to prevent damage D- very expensive not all rebuilt
Storm surge warning system A-evacuate earlier and quicker D- not everyone has access to technology expensive
Environmental impact of hurricane sandy
1.5 million litres of oil spilt damaging wildlife
Storm surge lead sea water into fresh water habits
Social impacts of hurricane sandy
117 people killed
650 000 homes destroyed or damaged
Economic impacts of hurricane sandy
Damage to NYC was 19 billion
Insurance claims to New Jersey was 3.3 billion
Impacts of rapid urbanisation in Mexico City
Social - aquifers are running dry increase suffering from respiratory disease class disvide and tension
Environmental -biodiversity decreases as city expands. 13000 tonnes of rubbish each day
Economic -over half jobs informal economy -government misses out on tax
Straigies to manage rapid urbanisation
Top down — metro bus system and public bikes reduce traffic reduces air pollution and travel time
Bottom up — rainwater harvest increased diseases lack sanitation collect rainwater reduce spread of disease
Gentrification
An area is redeveloped attracting wealth to the area often displacing poorer people
Multiplier effect
Investment———)provides jobs and income ——) government will get more tax money Government spends on services such as education and healthcare
How is igneous rock formed
Formed when lava or magma cools
Example of igneous rock
Granite
How is sedimentary rock formed
Sediment falls to sea floor deep layers form rocks through heat and pressure
Example of sedimentary rock
Chalk
How is metamorphic rock formed
2 or more rocks are chemically changed through heat and pressure
Example of metamorphic rock
Marble
What’s a concordat coastline