Diffusion/Osmosis, Diffusion and Osmosis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Diffusion
What is the movement of molecules from an area high concentration to an area of low concentration?
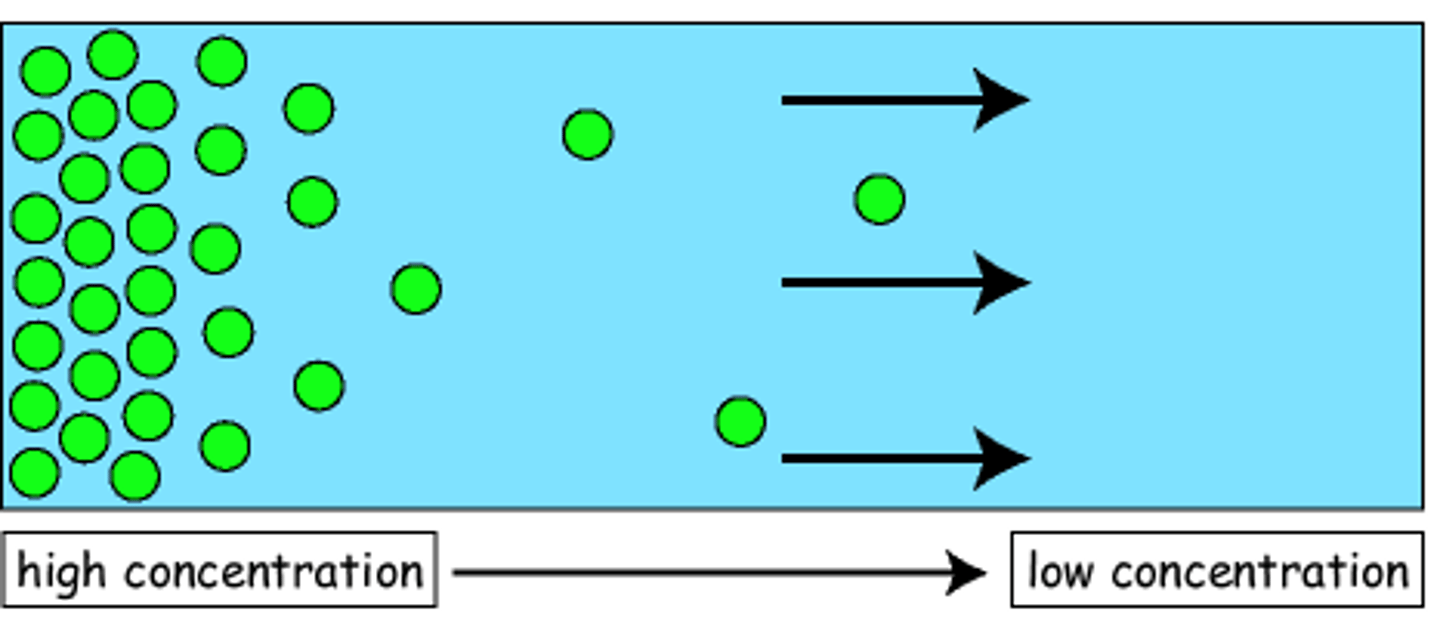
Concentration gradient and temperature
What are two factors that influence the rate of diffusion?
Faster
A steeper concentration gradient causes diffusion to move faster or slower?
Slow down
What will happen to the rate of diffusion if the temperature is decreased?
Speed up
What will happen to the rate of diffusion if the temperature is increased?
Osmosis
What is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane?
Isotonic
The cell in the picture is sitting in what type of tonic solution?
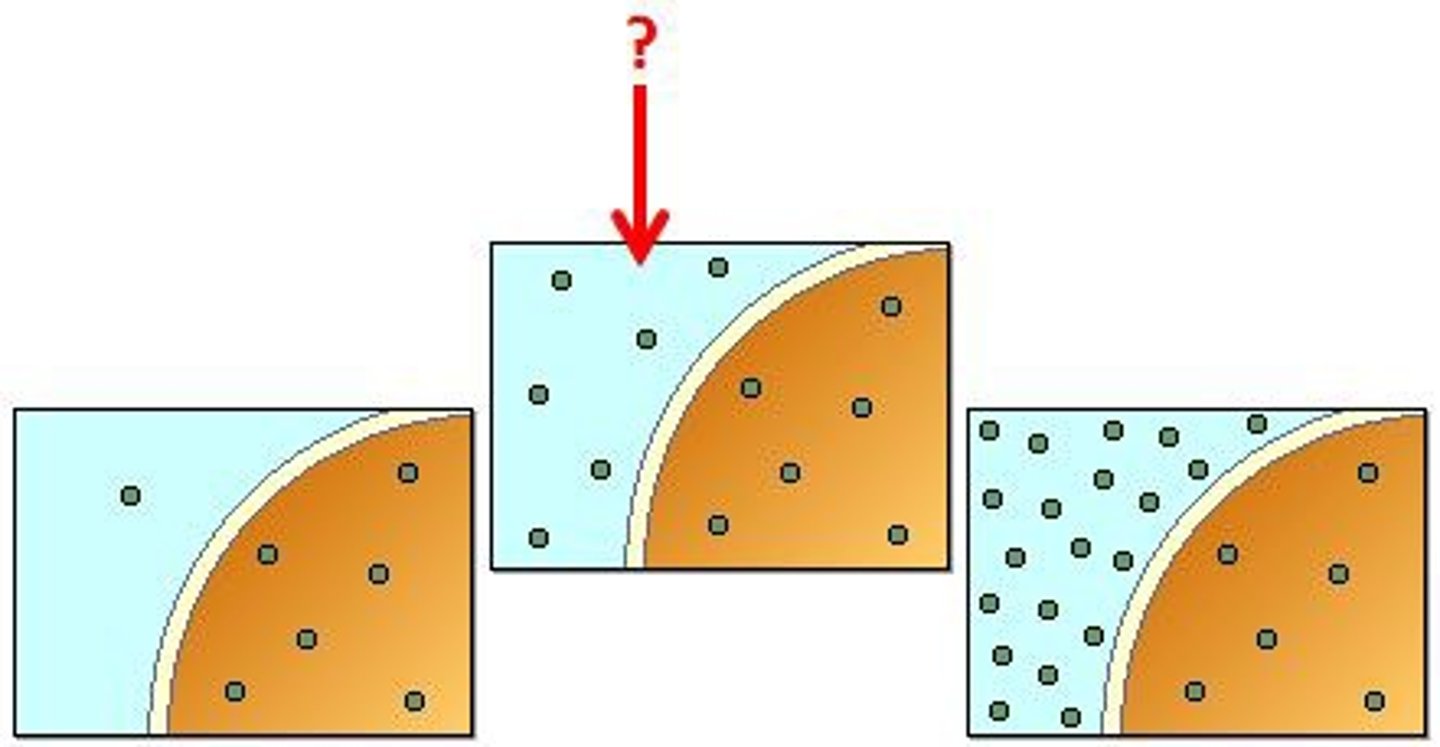
Remain the same. This is the ideal environment.
What will happen to a red blood cell placed in an isotonic solution?
hypotonic
The cell in the picture is sitting in what type of tonic solution?
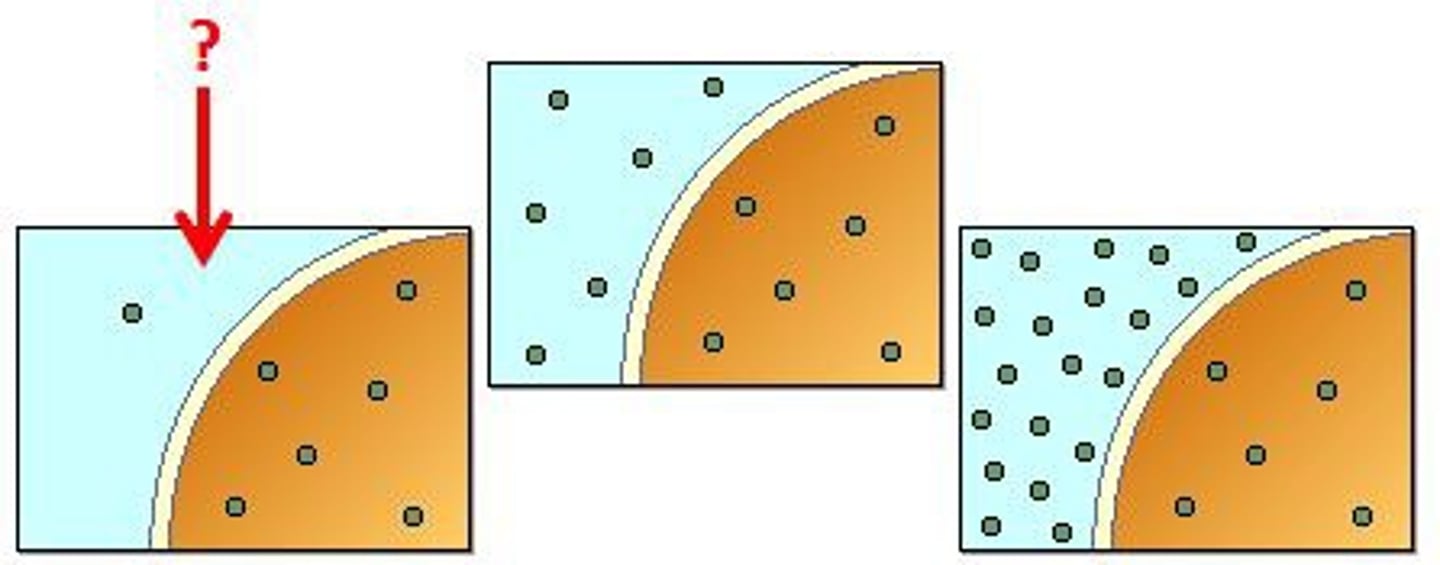
swell and possibly lyse (pop)
What will happen to a red blood cell placed in a hypotonic solution?
Hypertonic
The cell in the picture is sitting in what type of tonic solution?
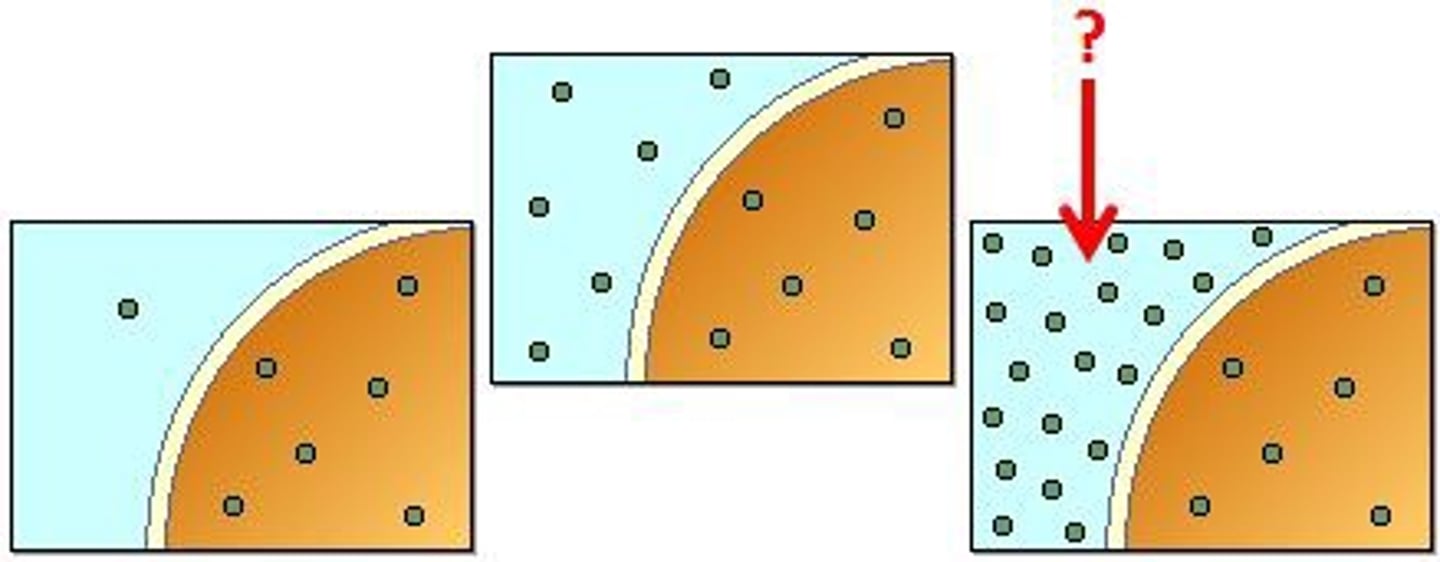
No, it continues to go back and forth at equal rates.
Once equilibrium is reached in diffusion and osmosis does movement stop?
Back and forth in equal amounts
Which way will the water move?

Isotonic solution
The cell is sitting in an ________________ solution.

Selective Permeability
Plasma membrane allows certain molecules cross it depending on size and polarity; small nonpolar molecules pass through easily
Passive Transport (Diffusion)
Requires no energy to move molecules down their concentration gradient(from high to low concentration)
Active Transport
Requires energy and carrier proteins to move molecules down or against their concentration gradient
Solvent
Dissolving agent
Solute
Substance dissolved in solvent
Osmosis
Diffusion of water
Hypotonic Solution
Low solute concentration; cells burst.
Hypertonic Solution
High solute concentration, cells shrivel up (hyper- think high energy)
Isotonic Solution
Concentration of the solutes on both sides of the membrane are equal; at osmotic equillibrium
Temperature and Diffusion
The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion
Osmotic equilibrium
Osmotic equilibrium is the term used to indicate that the concentration of a solute in water is the same on both sides of a semi-permeable membrane.