Lecture 31 & 32: Trematodes
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What two trematodes are contracted by ingestion of metacercaria encysted on vegetation?
fasciola hepatica (liver fluke), paramphistomum sp.
What two trematodes are contracted by ingestion of metacercaria encysted in fish, crawdad, crabs, etc.?
nanophytes salmincola, paragonimus kellicotti
What two trematodes are contracted by ingestion of metacercaria encysted in insects/invertebrates?
dicrocoelium dendriticum, platynosum fastosum
What treamatode is contracted by skin penetration by swimming cercariae?
heterobilharzia americana (canine blood fluke)
What is the adult worm morphology of liver and lung flukes?
dorsoventrally flattened
bilaterally symmetrical
monoecious and hermaphroditic
What does the lifecycle of liver and lung flukes involve?
2 intermediated hosts that are mostly aquatic
What must the first intermediate host of liver and lung flukes always be?
snail
True or false: trematodes are parasitic in all systems of vertebrate DHs.
true
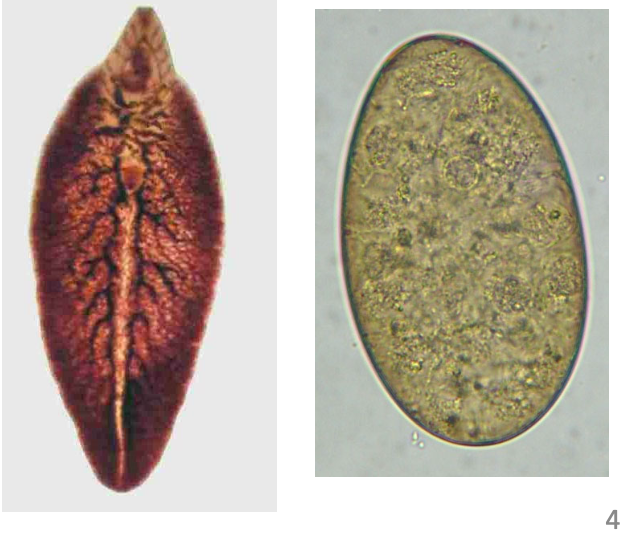
Liver/lung fluke
What stage of trematode life cycle is transferred from the first IH to the second?
cercariae
What stage of trematode life cycle is transferred to the DH?
metacercariae
Who is the DH of paragonimus kellicoti?
dogs, cats, people
What is the common name of paragonimus kellicoti?
lung fluke
How is paragonimus kellicoti contracted?
ingestion of uncooked or poorly cooked crayfish
What are the clinical signs of a paragonimus kellicoti infection?
dyspnea, hemoptysis (bloody septum), pneumothorax
How are paragonimus kellicoti infections diagnosed?
fecal exam
What trematode species is this?
paragonimus kellicoti
Where do the adult paragonimus kellicoti worms live and reproduce?
lungs
What is the disease in a paragonimus kellicoti infection associated with?
inflammatory response to excretory/secretory (cysteine proteases) products of adult worms
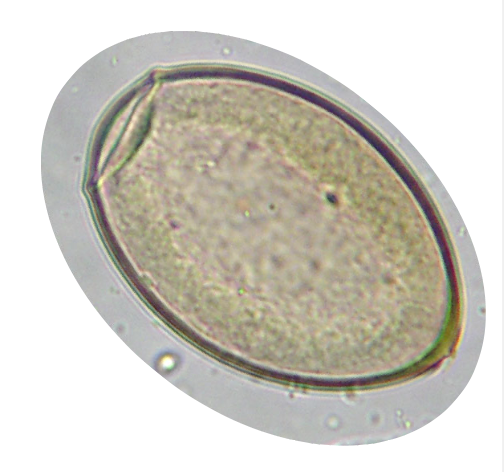
What trematode is commonly called the canine blood fluke?
hetrobilharzia americana
What species is hetrobilharzia Americana typically associated with?
raccoons
Where two paired adult hetrobilharzia Americana worms live?
mesenteric vessels → granulomatous transport through the tissues to GI
How many IH hosts does hetrobilharzia Americana have?
one
How is hetrobilharzia americana transferred?
infection by skin penetration
What is the causative agent of zoonotic “swimmer’s itch”?
hetrobilharzia americana
What are clinical signs of hetrobilharzia Americana infections?
weight loss, dysrexia, elevated liver enzymes, vomiting, diarrhea, polyuria, polydipsia
Describe the life cycle of hetrobilharzia Americana?
Eggs in host feces
In water, miracidium hatches from egg
Miracidium infects IH snail
Cercariae released into water by snail
Cercariae penetrate skin of DH
Paired adult worms live in blood vessels
Hetrobilharzia americana
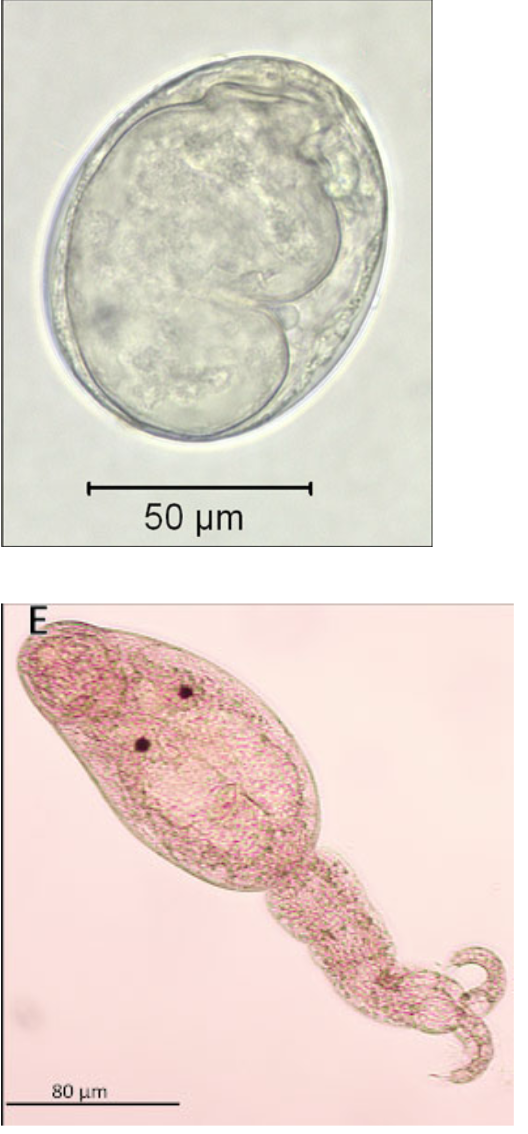
What trematode species is commonly called salmon poisoning fluke?
nanophyetus salmicola
nanophyetus salmicola
Who are the DHs of nanophyetus salmicola?
dogs, cats, fish eating mammals
Who are the IHs of nanophyetus salmicola?
snail, salmonid fish
How are nanophyetus salmicola flukes acquired?
by ingestion of metacercaria in kidneys, muscles, and fins of raw salmonid fish
Nanophyetus salmicola are vectors for __________.
salmon poisoning by Neorickettsia helminthoeca
What are the clinical signs of salmon poisoning?
hemorrhagic enteritis, lymphadenopathy, clinically indistinguishable from canine parvovirus
What trematode species is commonly called liver poisoning fluke?
platynosomum fastosum
Who is the DH of platynosomum fastosum and where does it reside?
felines, bile ducts
Who are the IHs of platynosomum fastosum?
pulmonate snail, pill bugs, lizards may by paratenic host
How are platynosomum fastosum infections acquired?
ingestion of metacercaria → migrate up bile ducts
What are the clinical signs of platynosomum fastosum infections?
vomiting, diarrhea, icterus
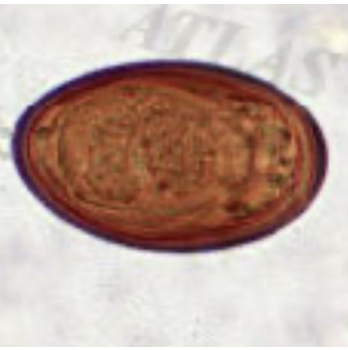
platynosomum fastosum
What trematode species is commonly called raccoon pancreatic fluke?
eurytrema procyonis
How are the DHs of eurytrema procyonis?
felines, red and grey fox, raccoons
Who are the IHs of eurytrema procyonis?
terrestrial snail, arthropods
How are eurytrema procyonis infections contracted and where do they end up?
ingestion of metacercaria → pancreatic ducts with periductal fibrosis
What are the clinical signs of eurytrema procyonis?
weight loss, vomiting, pancreatitis
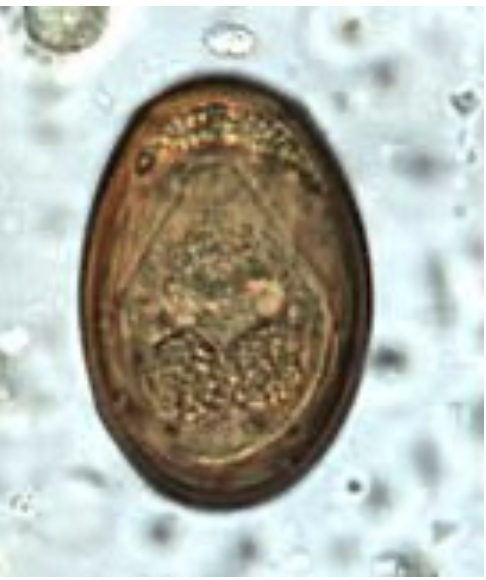
Eurytrema procyonis
Who are the IHs and DHs of alaria sp.?
IH:
Snail (1)
Tadpole (2)
Snake (alt 2)
DH:
cat
dog
The ____ stage of alaria sp. is capable of being passed from host to host and via lactogenic transmission.
larval
What are the adverse effects of alaria sp. associated with?
aberrant migration of mesocercaria
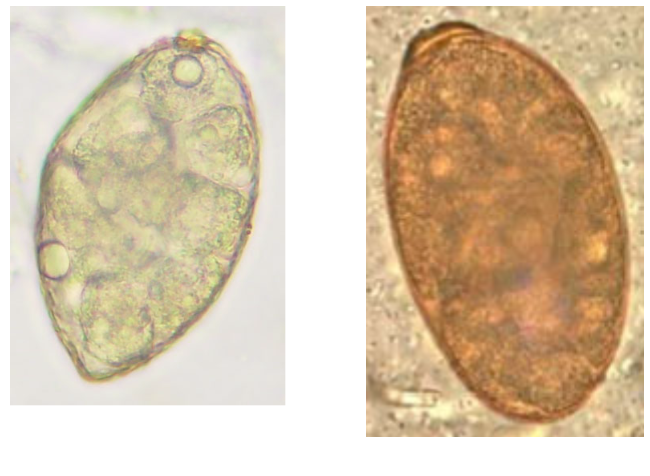
What trematode species is commonly called the liver fluke?
fasiciola hepatica
Who are the DHs of fasciola hepatica?
cattle, sheep, and goats
How are fasciola hepatica infections acquired?
ingestion of metacercaria encysted on vegetation
What are the clinical signs of a fasciola hepatica infection?
liver disease, anemia, hypoproteinemia, bottle jaw, loss of condition
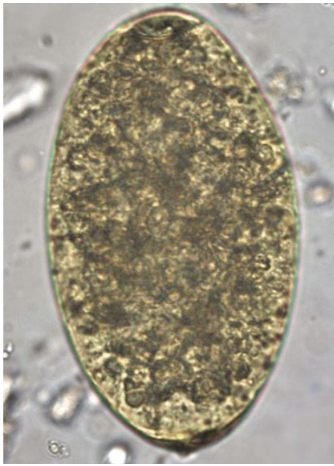
Fasciola hepatica
What is the distribution of fascioliasis based on?
presence/absence of infected hosts
presence of suitable snail IH
suitable soil substrate promotes moisture retention (snail habitat)
slope, drainage, water runoff
natural and artificial ponds for watering herd
What are the two therapeutic options for treating fascioliasis?
clorsulon and albendazole
How does clorsulon treat fascioliasis?
binds to serum proteins and ingested by the fluke
inhibits enzymes important in glycolytic energy process
not able to extract energy from glucose, disruption of cellular energy production
How does albendazole treat fascioliasis?
binds to beta-tubulin, interferes with development and energy uptake
Why are herd level outbreaks of fascioliasis often associated with drought conditions?
shrinking water line exposes green vegetation
What trematode species is commonly called deer liver fluke?
fascioloides magna
What trematode species is commonly called the rumen fluke?
paramphistomum sp.
Where are adult paramphistomum sp. formed?
stomach (abomasum)
What stage of paramphistomum sp. are pathogenic and where are they found?
immature stages in duodenum and ileum
What are the clinical signs of parmphistomum sp. infections?
necrosis, hemorrhagic inflammatory disease, hypoproteinaemia, diarrhea, dehydration
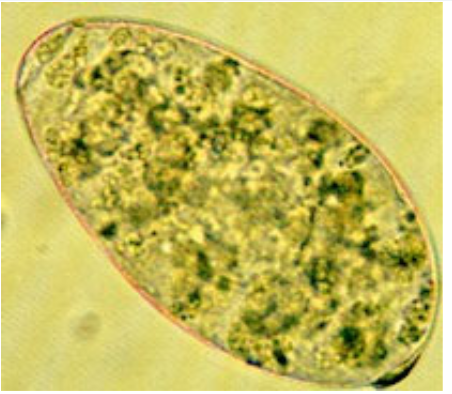
paramphistomum sp.
True or false: established flukecidal drugs are the preferred tx of paramphistomum sp.
false
What trematode species is commonly called lancet liver fluke?
dicroelium dendriticum
Who are the DHs of dicrocoelium dendriticum?
cattle, sheep, goats, pig, wild ungulates, rodents, rabbits
Who are the IHs of dicrocoelkum dendriticum?
terrestrial snail, ants
What is the dicrocoelium dendriticum life cycle through the snail?
miracida hatch from egg when ingested by snail, asexual replication in snail, emerge in slime ball
What is the dicrocoelium dendriticum life cycle through the ant?
ingested by ant, infect brain, remain attached to vegetation