unit 8 bio - transport in plants
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the function of xylem?
The transport of water and mineral ions and support
What is the function of phloem?
The transport of sucrose and amino acids
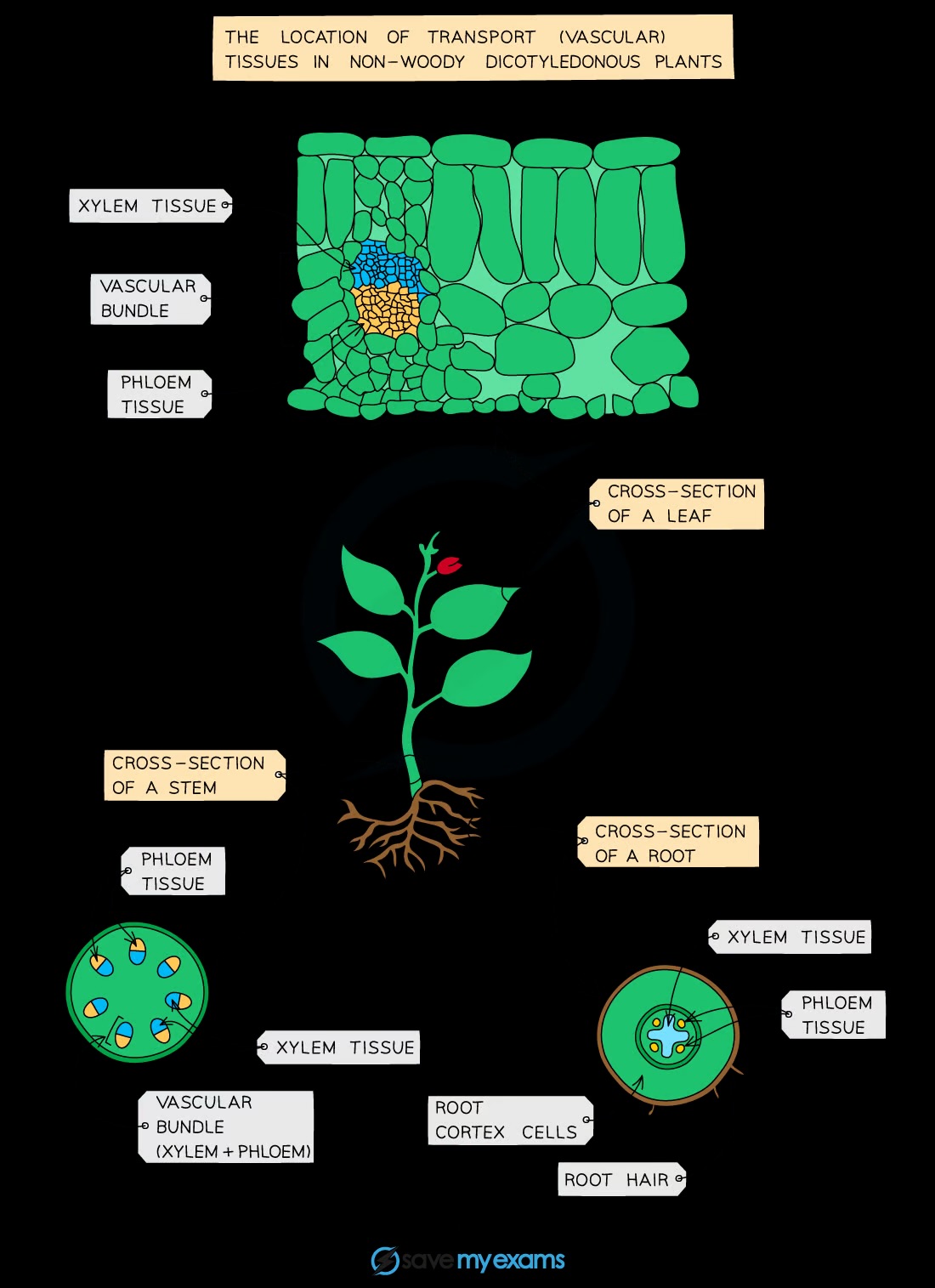
Where are xylem and phloem found in non-woody dicotyledonous plants?
Xylem and phloem are found in the roots, stems, and leaves
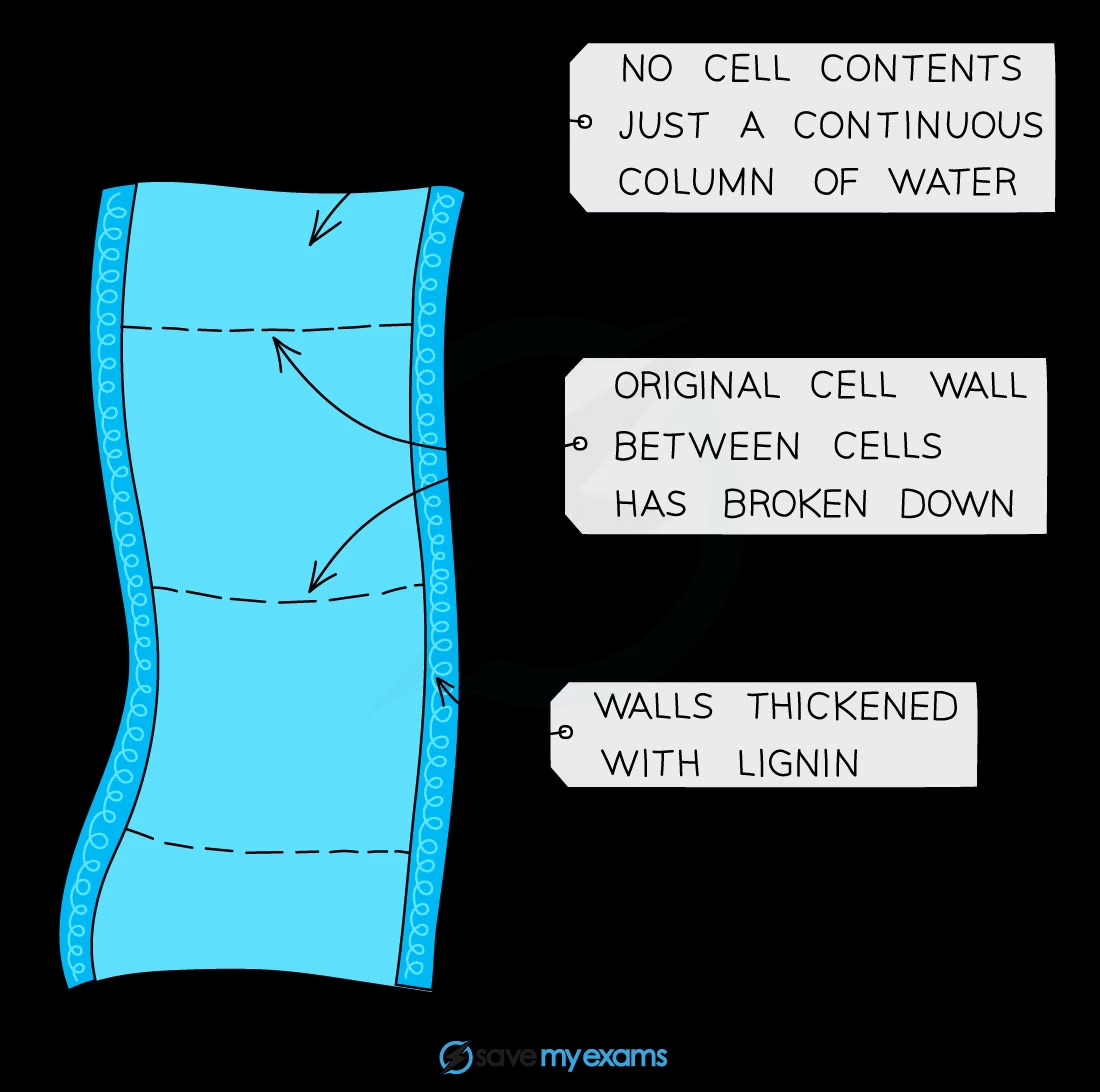
What is the structure of xylem vessels?
Thick walls with lignin, no cell contents, and cells joined end to end with no cross walls to form a continuous tube
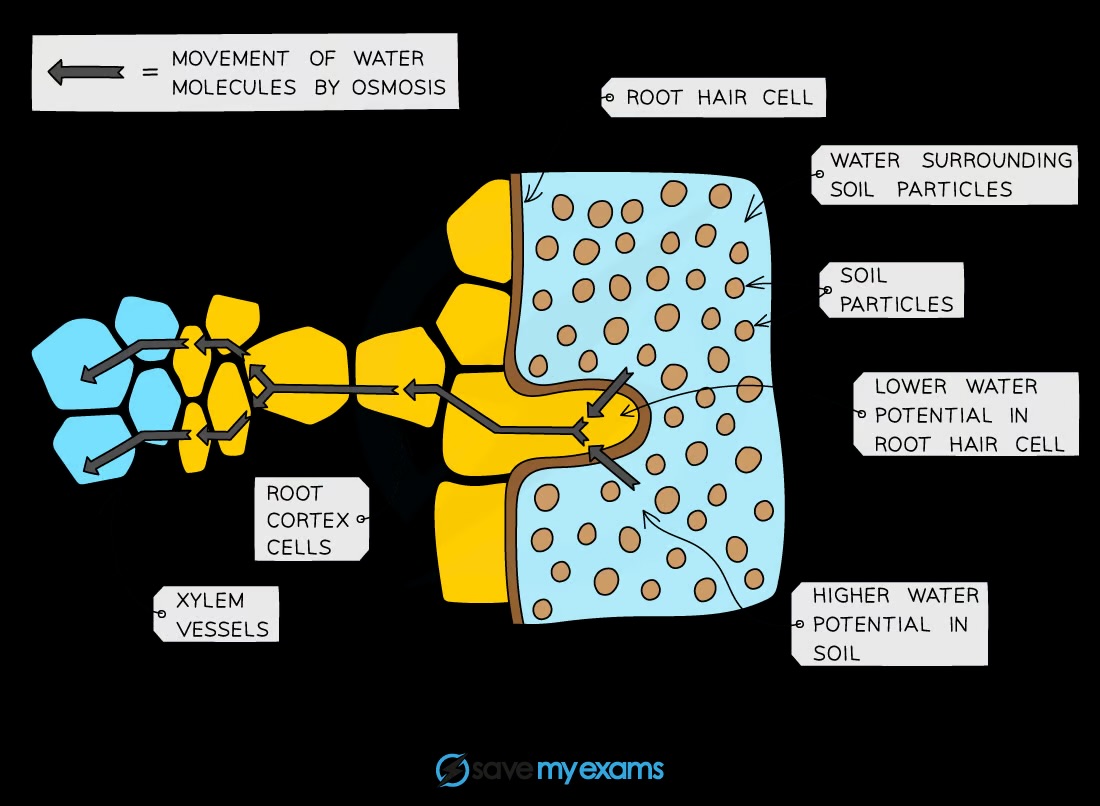
What are root hair cells and their function?
Root hair cells are cells that extend from the root epidermis and increase surface area for water and mineral ion uptake

How do root hairs increase the uptake of water and minerals?
Their large surface area allows for greater absorption of water and mineral ions from the soil
What is the pathway taken by water through a plant?
Water moves from root hair cells → root cortex cells → xylem → mesophyll cells in the leaf
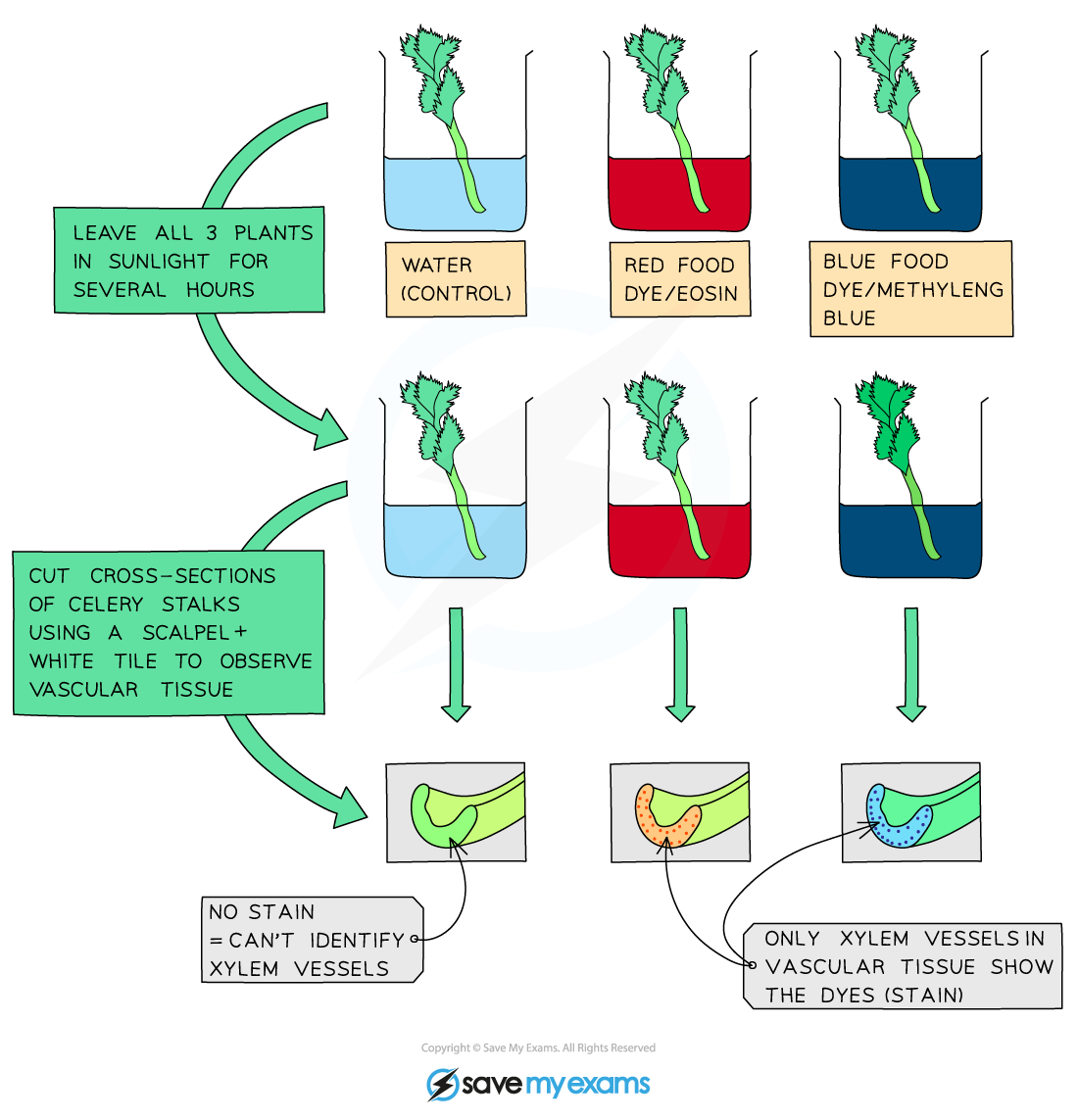
How can the pathway of water in plants be investigated?
By using a suitable stain to observe the movement of water through the plant
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour from the leaves of plants
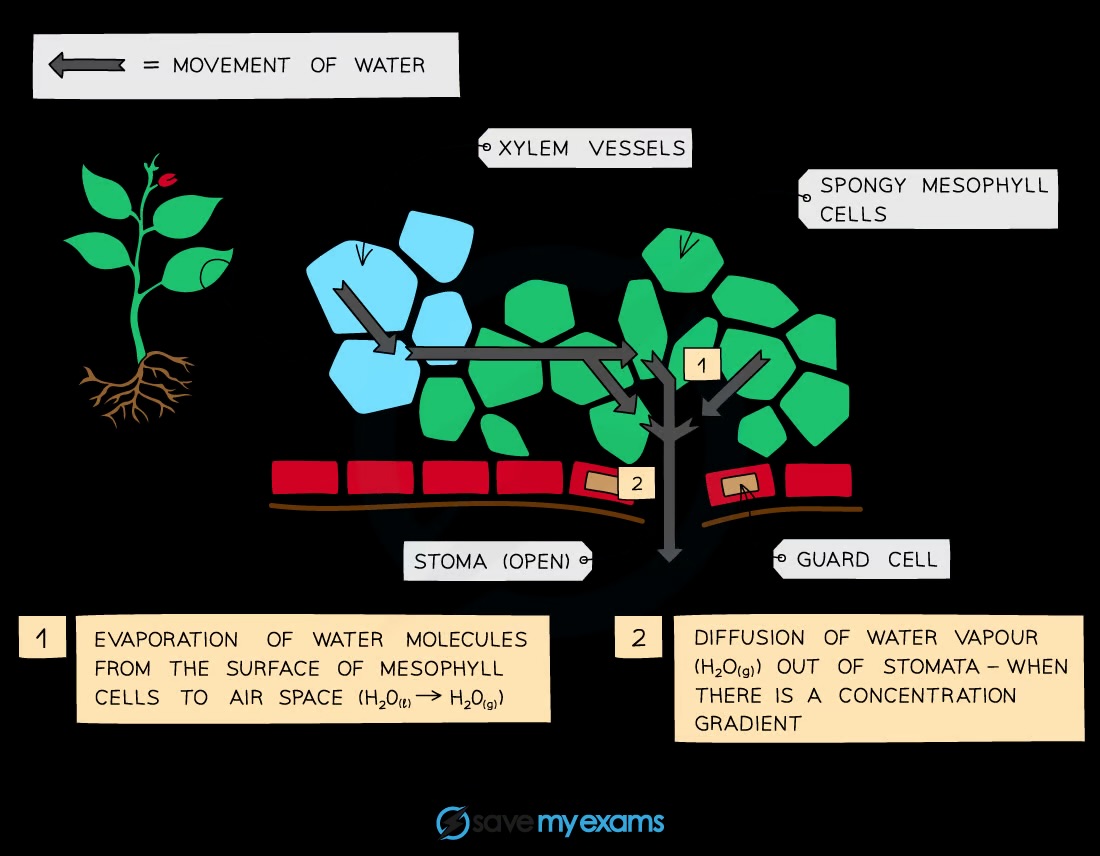
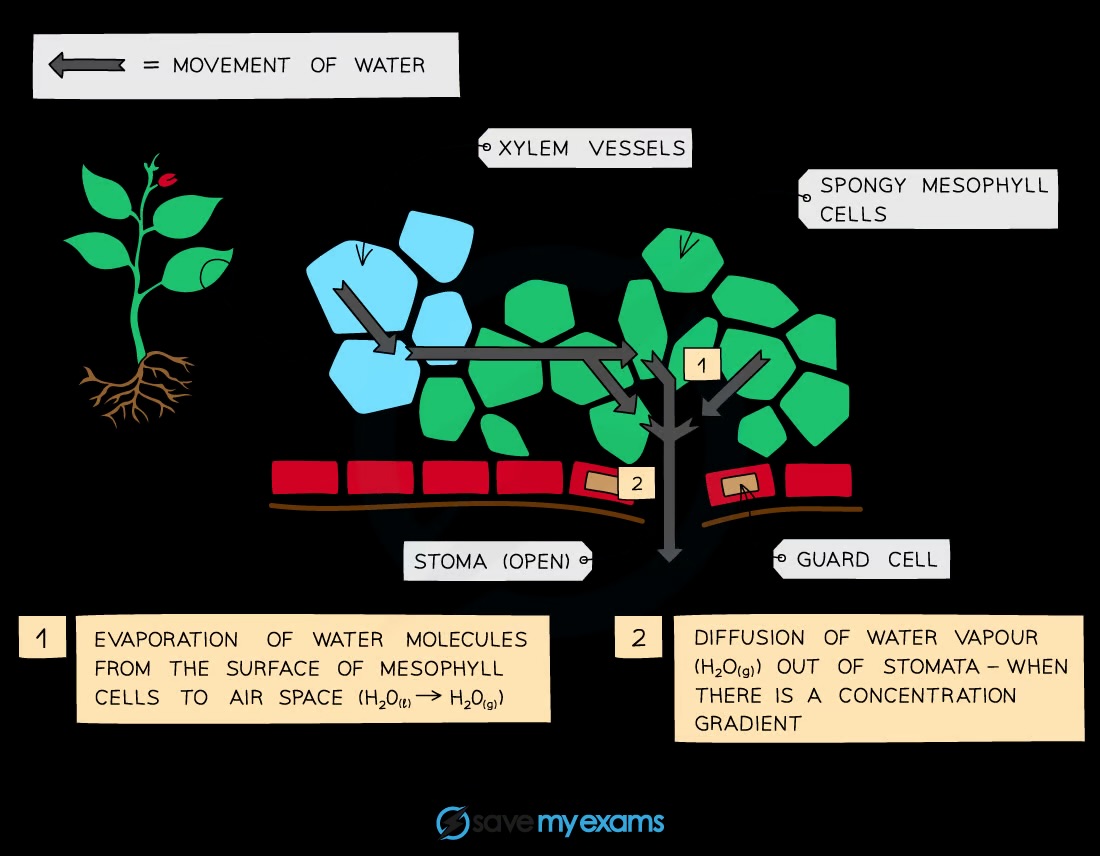
How does water evaporate in the leaf?
Water evaporates from the mesophyll cells, moves into the air spaces, and diffuses out through the stomata as water vapour
What factors affect the rate of transpiration?
Temperature and wind speed
How is water vapour loss related to the leaf structure?
Water vapour loss is influenced by the large internal surface area provided by air spaces between mesophyll cells and the size and number of stomata
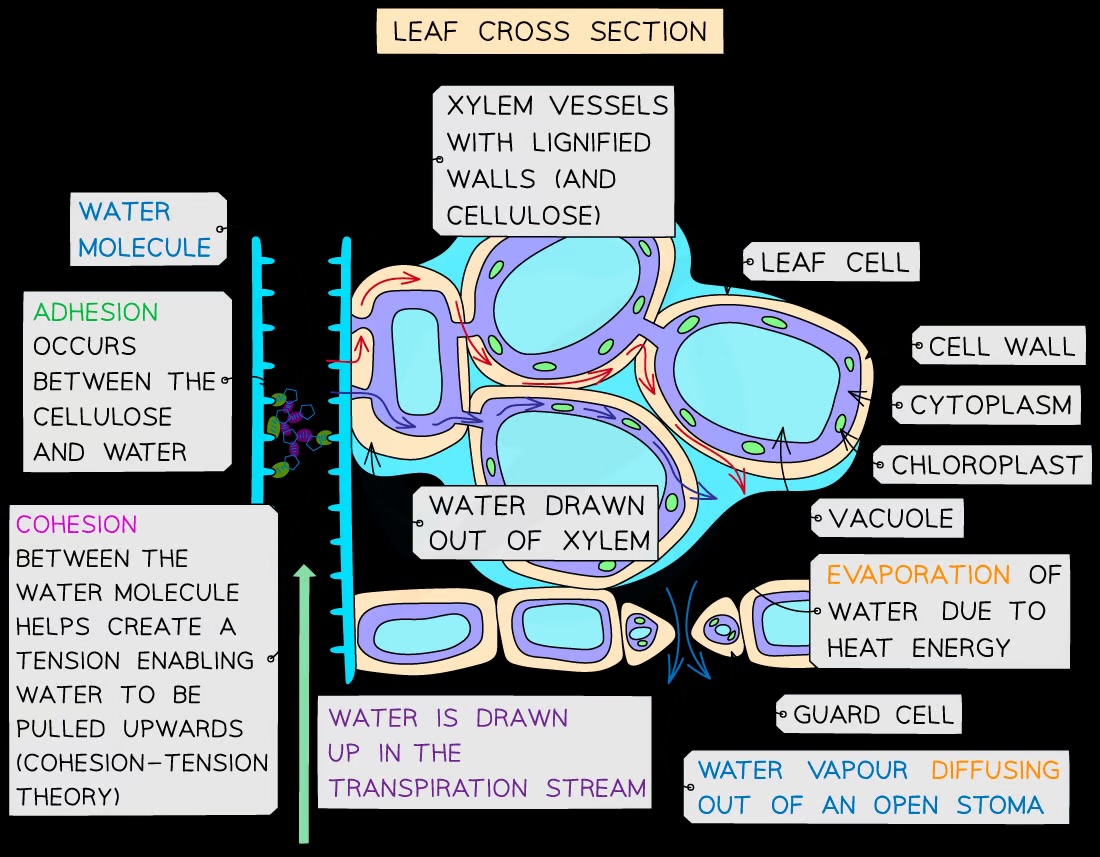
What is the mechanism that moves water upwards in the xylem?
Transpiration pull, where water molecules are drawn upwards due to attraction between molecules
What factors affect the rate of transpiration?
Temperature, wind speed, and humidity
What causes wilting in plants?
Wilting occurs when there is excessive water loss through transpiration, leading to a reduction in turgor pressure
What is translocation in plants?
The movement of sucrose and amino acids in the phloem from sources to sinks
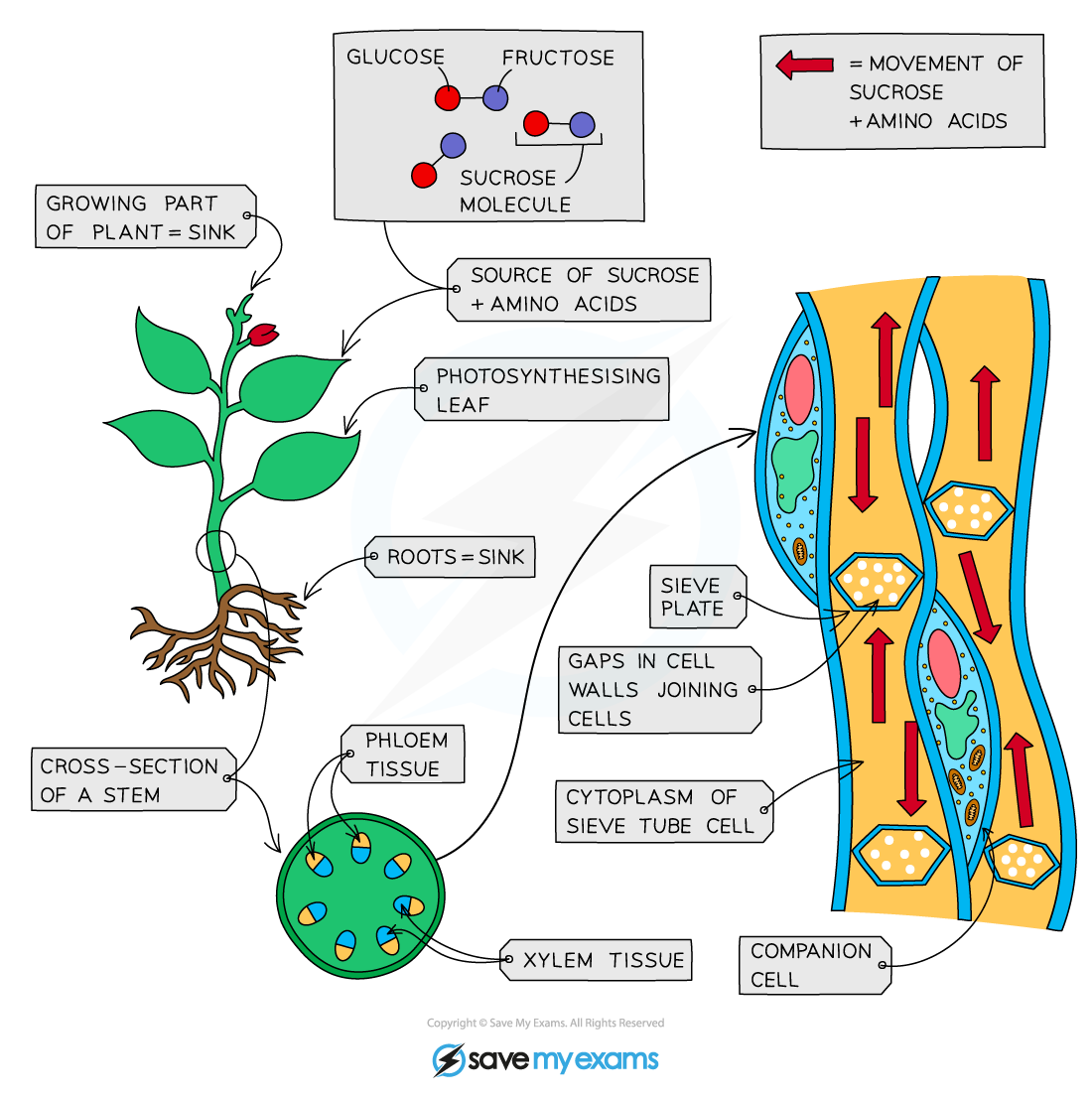
What are sources in plants?
Parts of the plant that release sucrose or amino acids
What are sinks in plants?
Parts of the plant that use or store sucrose or amino acids
Why can some parts of a plant act as both a source and a sink at different times?
Some parts can store or release sucrose or amino acids depending on the plant’s needs at different times