high performance computing module 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
module one
Last updated 10:46 AM on 9/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
what is high performance computing?
a collection of multiple interrelated disciplines which include:
\-application programs
\-performance and metrics
\-high performance computing systems
\-supercomputing problems
\-application programming
\-application programs
\-performance and metrics
\-high performance computing systems
\-supercomputing problems
\-application programming
2
New cards
what are some examples of applications for high performance computing?
3
New cards
what is the definition of high performance computing?
\
\
achieve the greatest computing capability possible at any point in time and technology while engaging in a class of electronic machines called supercomputers.
4
New cards
what is the purpose of HPCs?
derive answers to questions which can’t be addressed alone through empiricism, theory, or standard computers.
5
New cards
where can HPC be applied?
climate and weather prediction simulations, geo-sciences (seismic simulations), manufacturing and material science, health and pharmaceutical development.
6
New cards
how can HPC performance be measured?
time number of operations, ‘FLOPS’ (floating point operations per second), efficiency.
7
New cards
What are some of the magnitudes for FLOPS?
anywhere from kilo to exa. mega= million, giga = billion, tera = trillion, meta = quadrillion, exa = quintillion.
8
New cards
What is an alternative to FLOPS to measure HPC performance?
the length of time it takes for a computer to solve a specific problem (like a benchmark).
9
New cards
what is the High Parallel Linpack?
It is an algorithm which runs specific calculations ot solve a set of linear equations in dense matrix form.
10
New cards
What is the most visible part of a supercomputer?
hardware
11
New cards
what are nodes in a supercomputer?
thousands of nodes, or individual servers, are connected together in order to solve problems in parallel and solve them quicker.
12
New cards
What are some key differences between a standard computer and a supercomputer?
Organization: supercomputers maximize interconnectivity and scale for thousands of component resources.
Scale: A supercomputer is significantly larger than a standard computer and allows for logical parallelism.
\
Parallelism: problems are divided in parallel in order to solve different parts of a problem at the same time and converge to a solution more quickly.
Scale: A supercomputer is significantly larger than a standard computer and allows for logical parallelism.
\
Parallelism: problems are divided in parallel in order to solve different parts of a problem at the same time and converge to a solution more quickly.
13
New cards
TRUE or FALSE?: each individual node has its own OS.
true
14
New cards
TRUE or FALSE?: APIs expose and exploit application parallelism.
true
15
New cards
TRUE or FALSE?: The design of specific algorithms allows a supercomputer to divide problems efficiently.
true
16
New cards
What was the origin of supercomputing?
simulating problems in nuclear physics.
\
it was developed to track large systems of particles consisting of different species which interacted with each other and were not in equilibrium; the lack of equilibrium made it difficult to compute and calculate analytically.
\
HPC was also used to solve some partial-differential equations and model the climate using linear algebra. it is currently used to simulate stochastic systems and graph problems.
\
it was developed to track large systems of particles consisting of different species which interacted with each other and were not in equilibrium; the lack of equilibrium made it difficult to compute and calculate analytically.
\
HPC was also used to solve some partial-differential equations and model the climate using linear algebra. it is currently used to simulate stochastic systems and graph problems.
17
New cards
How can you use application programming?
programming interfaces such as differnt languages, libraries, and tools
18
New cards
What do proramming languages used for HPC focus on?
performance
19
New cards
Why is it important for HPC languages to focus on performance?
using efficient languages allows for the execution of parallel tasks and synchronisation between them (such as sharing and allocating resources).
20
New cards
Which are the most used HPC languages today?
Fortran, C, C++, Java, Python.
21
New cards
Whhat is fine-grained parallelism?
It is a process run in multiple-thread shared memory system programming interfaces like OpenMP and Clik++.
22
New cards
What are some applications of HPC?
Fraud detection and market data analytics, oil and gas distribution, accelerating production and manufacturing, molecular dynamic simulation, personalized medicine, identifying and modelling climate change.
23
New cards
What are the components of system hardware?
processor cores and memory units (PMs) connected to a network and persistent storage.
24
New cards
What are the components of an OS?
a system-wide OS connected to I/O object storage and software which is connected to the lower-level persistent storage. The OS also contains many different lightweight kernels.
25
New cards
What do the runtime systems contain?
user threads, global address spaces.
26
New cards
what are the key aspects that different HPC from other computers?
HPCs are designed for high computational capacity and speed whereas standard computers are designed for more general purposes.
27
New cards
what is the peak performance?
the maximuum rate at which operations can be accomplished theoretically by the hardware resources of a supercomputer. it is measured in units of flops.
28
New cards
how is peak performance calculated?
clock rate provided by the device technology. hardware parallelism is determined by the computer architcture.
29
New cards
why can’t you ever actually reach the peak performance of an HPC?
the idea situation cannot be reached, when you are running an application the code may not be optimized and parallelization may not be efficient enough to reach peak performance. peak performance is calculated based on benchmarks.
30
New cards
what is scalability?
the ability for a system to handle more work as the size of a computer or app grows.
31
New cards
what is strong scaling?
the problem remains the same while the number of processors is increased. this mitigates the workload per processor. this type of scaling is used for long-running CPU-bound.
32
New cards
What is Amdahl’s law?
the speedup is limited by the fraction of the serial part for the software which is not amenable to parallelization.
33
New cards
what is weak scaling?
both the number of processors and the problem size are increased, the workload per processor remains constant. this scaling is used for large memory-bound applications where the required memory can’t be satisfied by a single unit, or node.
34
New cards
What does SLOW stand for?
Starvation, Latency, Overhead, Waiting
35
New cards
What is starvation?
an absence of work and poor distribution of tasks.
36
New cards
what is latency?
the lag, or time it takes for information to travel from one part of the supercomputer to another via local memory access or the execution pipeline.
37
New cards
What is overhead?
additional work beyond what is actually required to perform the tasks which can weigh the system down. Overhead can be caused by poor task scheduling. it can be helped by control parallelism through synchronization and support communication.
38
New cards
What is control parallelism?
the consecutive execution of different instruction streams in order to optimize a solution.
39
New cards
What is waiting (in the context of performance degradation)?
A part of the system can wait for shared resources to
40
New cards
How can you improve performance?
via hardware scaling, parallel algorithms, performance monitoring, work and data distribution, task granularity control, etc.
41
New cards
What is the key to performance improvement?
performance measurement and profiling.
42
New cards
43
New cards
What are the key requirements for HPCs?
\-parallel processing
\-scalability
\-high-speed interconnection
\-reliable storage
\-efficient cooling
\-fault tolerance
\-scalability
\-high-speed interconnection
\-reliable storage
\-efficient cooling
\-fault tolerance
44
New cards
what is parallel processing?
coordination of multi-processor operations.
\
\
45
New cards
what is scalability?
capability for the system to grow without disruption to system function.
\
\
46
New cards
what is high-speed interconnection?
allows for fast data transfer between components.
47
New cards
what is reliable storage?
large and fast data storage which is reliable for access.
\
\
48
New cards
what is efficient cooling?
maintaining an optimal temperature allows the system to function even through intensive processing.
\
\
49
New cards
what is fault tolerance?
can handle errors without significant work loss.
\
\
50
New cards
What three key disciplines does HPC incorporate?
technology, methodology, and application.
51
New cards
What is the principal defining property of HPC?
assurance of delivered performance for an end-user application.
52
New cards
What is Moore’s law?
the prediction by Intel cofounder Gordon Moore that devicetransistor density would increase by a factor of two every 2 years.
53
New cards
What are benchmarks?
specific problems to compare and asses different HPC systems and capabilities
54
New cards
what is HPC architecture?
the organization and functionality of HPC components and the logical instruction set presented to computer programs and compilers.
55
New cards
What are some properties of HPC architecture which determine performance?
\-speed of components
\-paralleism, number of components that can operate simultaneously
\-efficiency of component use in degree of utilization
\-paralleism, number of components that can operate simultaneously
\-efficiency of component use in degree of utilization
56
New cards
TRUE or FALSE? HPC performance is directly related to the speed of its components.
true
57
New cards
what is bandwidth?
how much data is transferred per unit of time
58
New cards
what is latency in the context of communication speed?
how long it takes data to move across a network
59
New cards
What are some of the physical limits of parallelism?
speed of light, atomic granularity, Boltzmann constant
60
New cards
How can you you measure the efficiency of a system?
sustained performance divided by the peak
61
New cards
What is a power issue in HPC?
the speed or processor cores is in part proportional to their clock rate and the greater the clock rate the more energy needs to be applied.
62
New cards
What are the key properties that determine performance of an HPC architecture?
speed of components, parallelism and efficiency
63
New cards
What are the main types of Flynn’s taxonomy of parallel architectures?
SISD- single instruction and single data stream
SIMD- single instruction multiple data stream
MIMD- multiple instruction multiple data stream
MISD- multiple instruction single data stream
SIMD- single instruction multiple data stream
MIMD- multiple instruction multiple data stream
MISD- multiple instruction single data stream
64
New cards
What is the reliability problem?
The larger the system the greater the amount of faults.
65
New cards
What are hard faults?
breakage in hardware such as damaged cores and memory, communications means, secondary storage, and control
66
New cards
What are soft faults?
intermittent failure that can happen due to environment.
67
New cards
What are software errors?
flawed coding in either the OS or the user-end application
68
New cards
What is programmability?
How difficult it is to write or develop a complex application code
69
New cards
What are some contributing factors to programmability?
\-processor core and system architectures
\-programming models and language ease of use
\-effectiveness of system software
\-programming models and language ease of use
\-effectiveness of system software
70
New cards
What are memory technologies used for?
storing, accessing, and changing data.
71
New cards
What are some examples of data types which can be stores in memory?
bools, chars, strings, ints, floats
72
New cards
What are some example of memory technologies?
\-Magnetic storage- hard disk and tapes
\-NVRAM- fast disk
\-Dynamic RAM- main memory
\-Static RAM- core registers
\-NVRAM- fast disk
\-Dynamic RAM- main memory
\-Static RAM- core registers
73
New cards
What does the Von Neumann Computer Architecture look like?
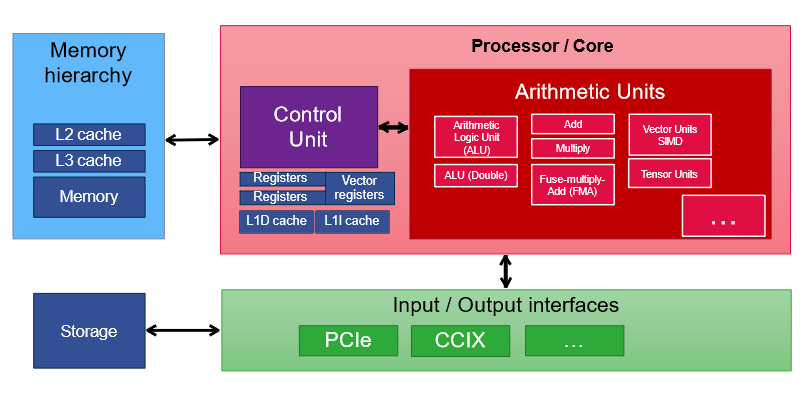
74
New cards
How does HPC architecture exploit its enabling technologies?
It minimizes the time to approach a solution, minimizes throughput of operations, and serves the class of computations associated with large and usually numeric-intensive applications.
75
New cards
which architecture of flynn’s taxonomy is most used and why?
MPMD- it parallelizes tasks more efficiently.
76
New cards
What are some facets of Von Neumann architecture?
\-Defined in 1940
\-Uses an ALU, registers, processors and main memory unit
\-A load operation reads a word from memory and places its value into a register to be used by the ALU.
\-Uses an ALU, registers, processors and main memory unit
\-A load operation reads a word from memory and places its value into a register to be used by the ALU.
77
New cards
What is true about commodity clusters?
\-is a form of HPC assembled from commercially manufactured subsystems
\-cluster node is a computer that can be directly employed individually as a pc
\-provides economy of scale to increase performance to cost dramaticallt compared to custom designed MPPs of the same scale
\-cluster node is a computer that can be directly employed individually as a pc
\-provides economy of scale to increase performance to cost dramaticallt compared to custom designed MPPs of the same scale
78
New cards
What is the difference between SNP, MPP, and Commodity Clusters?
Commodity clusters became the standard, SMP/MPP followed suit by parallelizing. CCs and MPPs
79
New cards
what is true about MPPs clusters?
they use message passing by a system area network
\
\
80
New cards
What are commodity clusters?
It isd a group of integrated computer systems. standard components used for PCs
asrchetupe of the conventional scalable HPC system used as a model
\
asrchetupe of the conventional scalable HPC system used as a model
\
81
New cards
Is a commodity clusert integration network employed together or separately?
Separately
82
New cards
What is the architecture of a commodity cluster?
you have different nodes that each have their own processor and have their own RAM attached. you have
83
New cards
How are the processors in a node interconnected?
Using message-passing interfaces like OpenMP.
84
New cards
How are nodes in a cluster connected?
Via a network using a MPI.
85
New cards
What is a big issue with hard drives?
They’re nowhere near as fast as SSDs.
86
New cards
How have the use of standard components from PCs impacted scalability, affordability, and adoption of HPC systems in various sectors?
they’re significantly cheaper, but they might not be as fast because they aren’t the state of the art components
\
\
87
New cards
What are the main elements of a supercomputer?
\-a node (standalone computer), which is the major processing and memory component used for computations.
\
\-a system area network, or SAN. it is a communication channel that interconnects all the nodes together into a single distributed computing system. it supports data message passing between nodes.
\
\-the host (login node), which is a special node dedicated to supporting user services such as login accounts, administration, resource allocation and scheduling. users log into the host node through an institution’s LAN.
\
\-secondary storage which is connected to via a network.
\
\-a system area network, or SAN. it is a communication channel that interconnects all the nodes together into a single distributed computing system. it supports data message passing between nodes.
\
\-the host (login node), which is a special node dedicated to supporting user services such as login accounts, administration, resource allocation and scheduling. users log into the host node through an institution’s LAN.
\
\-secondary storage which is connected to via a network.
88
New cards
Why are clusters so skewed on the top500?
they’re cheaper, but although they are cheaper they are not the best performing.
89
New cards
What are the differences between a core, a socket, and a processor?
the socket is where you put the processor, the processor will manage threads, and the core is a virtual processor within the processors (for optimization purposes).
90
New cards
What is the SAN?
main network connecting the nodes
different from custom network such as intel omnipath
\
different from custom network such as intel omnipath
\
91
New cards
what is secondary storage?
hard drives or SSDs connected to each node, although sometimes secondary storage can be replaced by diskless nodes or NVRAM.
\
a storage subsystem has its own controllers and can even have its own network.
\
it can access an external storage system through a LAN and share information with other systems. RAID is a protocol used to avoid disk failures.
\
a storage subsystem has its own controllers and can even have its own network.
\
it can access an external storage system through a LAN and share information with other systems. RAID is a protocol used to avoid disk failures.
92
New cards
What is the throughput computing modality?
the efficient execute of independent jobs that require minimal comunication or coordination
93
New cards
What is the message passing modality?
a modality which requires a significant amount of communicaiton and coordination within the application to speed up the time to the solution. Because of this, it uses distributed memory for communication.
94
New cards
What is the shared-memory multiple-thread applications (SMMTA) modality?
A modality in which apps are restricted to shared memory. An example of this modality is the OpenMP programming tool.
95
New cards
What is performance profiling?
A way to determine how good a supercomputer is at performing its tasks.
96
New cards
What does a module contain?
contains the language, compiler, debugging tools, basically like having an IDE inside the module.
97
New cards
True or False?: HPLs are CPU-intensive.
true
98
New cards
Why would you use the HPLC benchmark?
Linpack is commonly used to rank supercomputers on the TOP500 list, assessing peak performance.
99
New cards
Why would you use the HPC Challenge benchmark?
This suite contains seven different benchmarkscatering to various memory access patterns andworkload types, making it suitable for a widerange of computational tasks
100
New cards
Why would you use the HPCG benchmark?
It is designed for applications withworkloads that are not represented by HPL,especially those involving sparse systems ofequations.