BIOA101 FINAL EXAM S2
1/193
Earn XP
Description and Tags
updated so it should cover all the notes. 2023. if you study this you owe me $5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
Fixity of Species
There is one creation, and that creation of all living and non living thing happened once and were created in the form we see them today.
Great Chain of Being
European idea that every species was a link on a chain extending from lowest forms to humans and on to spiritual beings. All links and been designed at the same time during creation and would never change.
Once all the links were discovered and described, the meaning of life would be revealed.
DNA structure
DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix and joined by hydrogen bonds, between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine
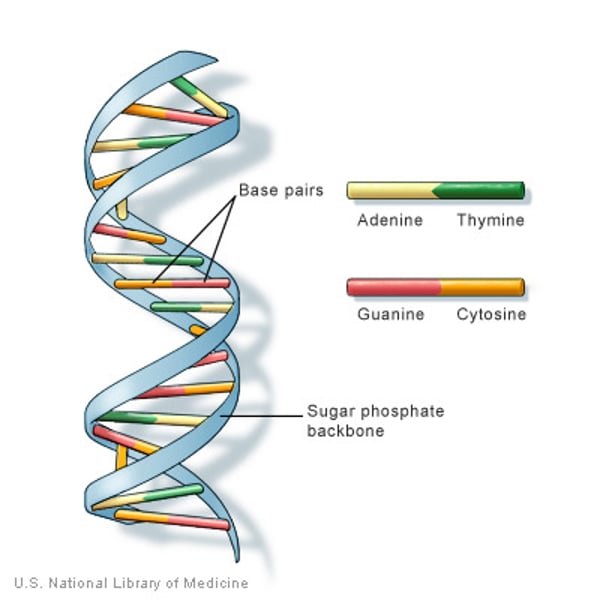
What are the two main functions of DNA?
Replication and Protein synthesis (transcription and translation)
Somatic cells are ______________
Diploid (46)
Gametes are __________
Haploid (23)
Mitosis is _____________
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells, each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
Meiosis is ___________
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
What are some examples of a recessive trait?
Sickle Cell Anemia
Cystic Fibrosis
Albanism
What are some examples of a dominant trait?
Huntington's Disease
Brachydactyly (digits look like toes)
Microevolution
Change in allele frequencies within a population or species
Macroevolution
Change in allele frequencies above a species level eg. between species
What are the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions?
No mutation takes place.
No genes are transferred to or from other sources (no immigration or emigration takes place).
Random mating is occurring.
The population size is very large.
No selection occurs.
Why is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium a null hypothesis?
Because it can be used to describe statistically significant deviations from the Equilibrium. If the deivation is significant, then the gene frequencies are changing and evolution is occurring.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
What are the two types of natural selection?
1. Directional selection
2. Balancing selection
What is directional selection?
Selection that acts to move the mean of a population in one particular direction
What is balancing selection?
Selection that maintains variation in a population, most commonly through heterozygote advantage.
What is phenotypic plasticity?
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
Bergmann's Rule (body size)
Relationship between body mass and surface area: warm-blooded animals that live in cold areas are bigger than those that live in warm areas
Allen's Rule (body shape)
The principle that an animal's limb lengths are heat-related; limbs are longer in hot environments and shorter in cold environments (to maximize heat retention/loss).
What do you get if you have a lack of vitamin D?
Rickets
Why did people further away from the equator lose the darkness of their skin?
High levels of melanin (dark skin) existed to absorb the high levels of UV from the sun. Once they moved to places with less sun, the high levels of melanin were no longer needed as there was not as much UV to absorb.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Acclimatisation
Change that takes longer to come back into affect in the face of stress. Stress removed = revert back to normal.
Developmental acclimatisation
When stress occurs during a period of growth and development, the organism tends to adapt developmentally to the stress (if they can). They do not revert back when the stress is removed.
Main characteristic of high altitude
Low oxygen
What is the initial response of a human to high altitude?
Increase in respiration (acclimatisation)
What is the response of a human to high altitude for an extended period of time?
Body makes more red blood cells to carry oxygen (developmental acclimitisation)
What are the effects of hypoxia?
headaches, tunnel vision, fainting, increased heart rate, difficulty sleeping, bad dreams often about suffication
What are the two costs associated with acclimatisation to high altitude?
1. Increased rates of infant mortality, premature birth and miscarriage
2. Lethargy and reduced activity
Name the three Macronutrients
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
Name the two micronutrients
Vitamins and Minerals
What is the function of protein?
To build and repair tissue
What is the function of carbohydrates?
To supply and store energy to the body
What is the function of lipids?
To store energy and contribute to cell structure
What are the function of vitamins and minerals?
Essential for body growth and function - joints, bones, immune support, eye health, digestion
What are the water soluble vitamins?
Vitamin B (meat and dairy) and Vitamin C (fruit and vege)
What are the fat soluble vitamins (can be stored)?
Vitamin A, D, E, K
What three factors determine the human diet?
1. Biological factors - availability to food, climate, weather, fauna, landscape etc
2. Cultural factors - food and status
3. Social factors - consumption patterns, poverty and abundance, social status
What are the three parts of fossil evidence that shows the evolution of diet?
1. The size of the teeth (molar size, canine size)
2. Dental Microwear (pit size and striations)
3. Mandible shape and Sagittal crest (bite force and muscle activity during chewing)
What is auxology?
The science of human growth and development
What is growth?
An increase in mass or number of cells
What is development (biological)?
Differentiation of cells into different tissues and their maturation
What are the four factors that affect growth and development?
1. Genetics
2. Hormones (HGH or somatotropin - hormones that stimulates growth, cell reproduction/generation)
3. Inter-population variation: variation in regards to stature, development of teeth etc.
4. Environment: nutrition, infection etc.
How does bone growth occur?
Start as cartilage model and then ossify into hard, mineralised bone
Endochondral bone formation
bone tissue replaces a cartilage model of a bone; most bones form in this fashion
Epiphysis
End of a long bone (rounded end)
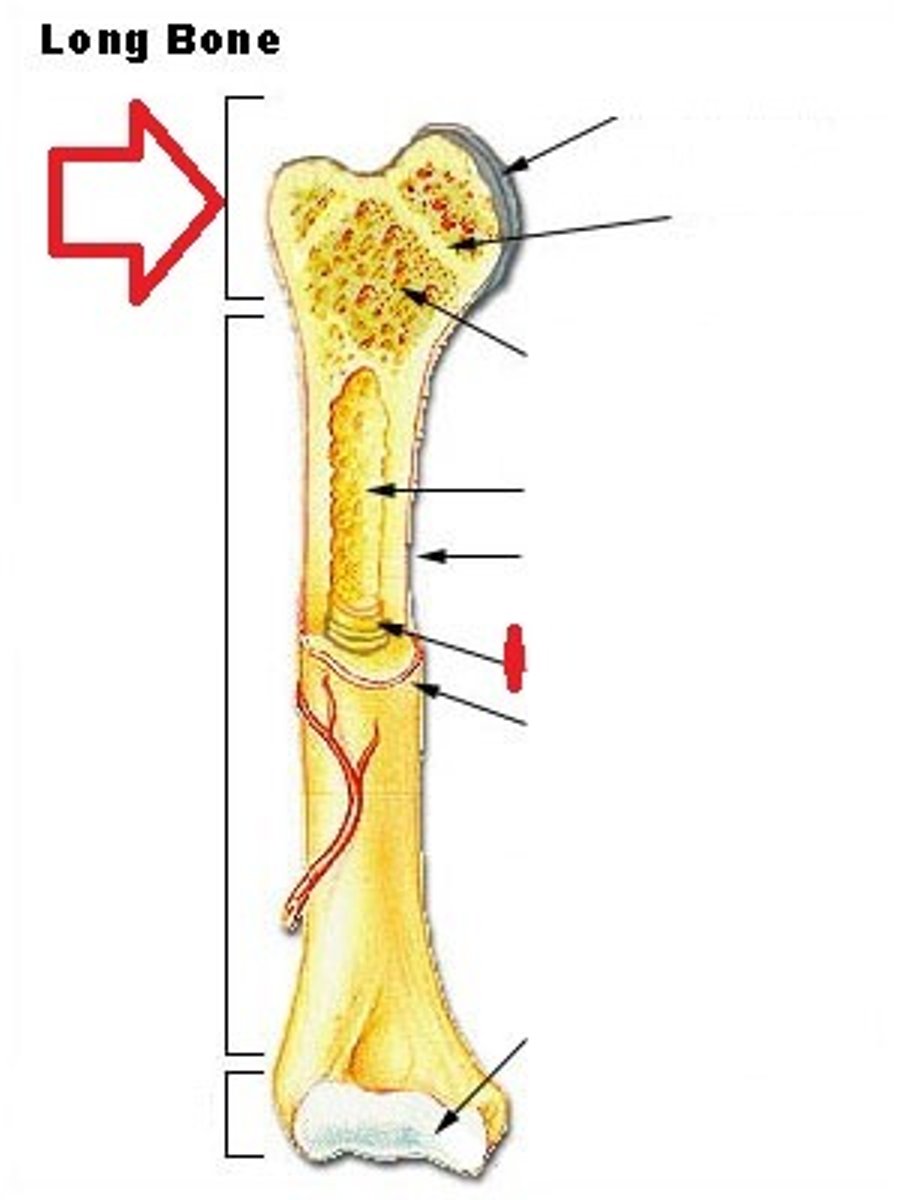
Growth Plate
the area just below the head of a long bone in which growth in bone length occurs; the epiphyseal plate.
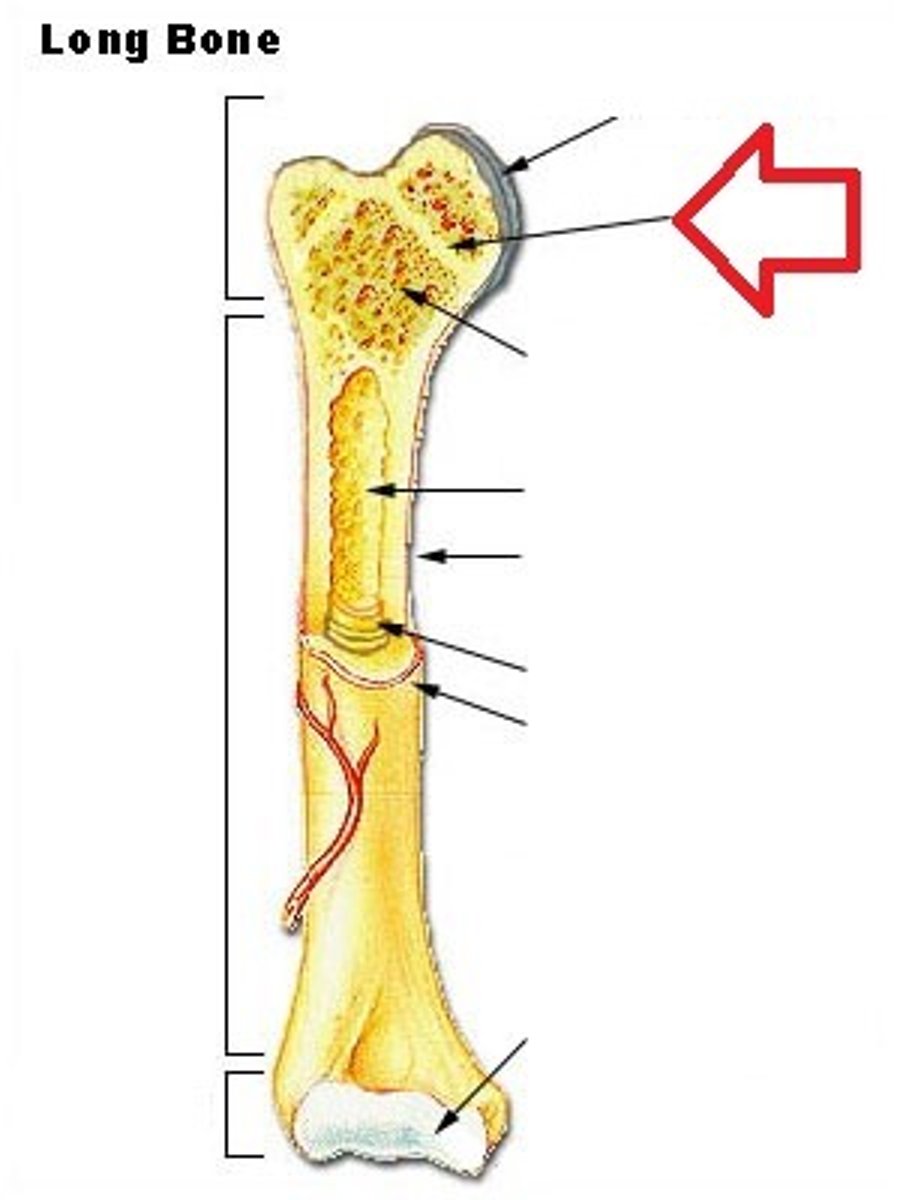
How do you work out how old/what growth stage an individual is at (with a long bone)?
Look at the epiphyseal fusion - how much the parts of the bone are fused
How to determine age in a human?
Look to see what bones are fused
What do you use to age an infant/child?
- Dentition: length of roots, adult tooth presence
- Long bone lengths
- Epiphyseal fusion - how fused the bones are
- Morphological changes in bones
Characteristics to define a primate:
- Petrosal bulla - in all primates
- Forward facing eyes
- Grasping hands and feed
- Nails instead of claws
- Generalised body plan - not just for one thing
- Generalised dentition - not just for one diet
- Large brain relative to body size

What gives primates a visual advantage?
Enclosure of the orbits: primates have a full ring or socket enclosing the eye for protection
What is the problem with having a large brain?
It takes lots of energy to run, so you need to consume lots of calories to have the energy for it to run
What characteristics do Strepsirhines have?
- Wet nose
- Curly nostrils
- Long snout
- Tapetum Lucidum
- Post-orbital opening
- Unfused mandible
- Generally asocial
- Generally nocturnal
What primates are in the Strepsirhine category?
Lemurs, Lorises, Pottos, Galagos

What characteristics do Haplorhine's have?
- Dry nose
- Straight Nostrils
- Reduced snout
- No Tapetum Lucidum
- Post-orbital closure
- Fused mandible
- Generally social
- Generally diurnal
What primates are in the Haplorhine category?
Baboons, Gorillas, Apes, Orangutans, Chimpanzees, Tarsiers

What are some characteristics of Old World primates?
- Downward facing nostrils
- Range of body sizes (1.5 - 35kg)
- Two premolars
- Some species terrestrial
- Ischial callosities (like on baboons)
- Bilophodont Molars (two ridges)
What are some characteristics of New World primates?
- Flat Nose
- Sideways facing nostrils
- Three premolars
- All species arboreal
- Prehensile tails - can grab things (only some)
- Not bilophodont molars
What are ischial callosities?
Hard sitting pads on the bum, related to support while in sitting position
Why are Old World Monkeys more diverse?
Have had to adapt to a wide range of environments (tropical forests, grassland, snow areas etc), and range from arboreal to terrestrial forms. This has led to a wide range of diversity in anatomy and behaviour.
Name three key figures in the study of primate behaviour:
1. Louis and Mary Leaky
2. Jane Goodall
3. Dian Fossey
What is Socioecology?
The ecological study of social behavior
What is sociobiology?
How behaviour relates to evolutionary history
Proximate
How a behavior occurs or is modified
Ultimate
Why the behaviour occurs or exists
What are some advantages of being social?
- access to mates
- food
- lower risk of predation
What are some disadvantages of being social?
- more mate competition
- more competition for resources
- greater risk of disease
What are the six primate social systems?
1. Solitary
2. Fisson-fusion
3. Pair-bonded
4. multiple-male, multiple-female
5. One female, multiple-male
6. One male, multiple-female
What are the four primate mating systems?
1. Monogamy
2. Polygyny
3. Polyandry
4. Promiscuity
Alloparenting
A common behavior in many primate species whereby individuals other than the parents hold, carry, and in general interact with infants.
Allogrooming
Behaviour of grooming other members of the same social groups
What are voluntary ways Primates communicate?
Gesture, body position, facial expressions, vocalisations
What are involuntary ways Primates communicate?
Scent, pheromones
What is referential communication?
The ability to use sign/symbol/sound to refer to something else. It is a learned behaviour.
eg. alarm calls to tell others which predator is around and how to escape it
Gestural Communication
Facial expressions, postures, gestures
Facial Expressions
- often communicating in the context of competition
- negotiating access to resources
- signal threat or submission, reduce number of actual fights.
Is altruism high or low cost
Low cost and reciprocal altruism fairly common
Name three types of altruism in primates
1. Grooming
2. Food sharing
3. Co-operative killings
Why are primate models used?
There is lots of similarities between human and primate vulnerability to disease and response to medicine.
What can we study using primate models?
- early hominin social structure
- evolution of cognition
- evolution of human behaviours
- ecology of early humans
What is the ape that is closest relative to humans?
Chimpanzee (Pan).
Why can apes not talk?
- high larynx and wrong vocal tract shape
What are the issues with animal language studies?
They can be biasedly interpreted by humans and the observer effect can happen; where the observer is potentially giving cues without recognising it.
What are the three main examples of tool use in apes?
Using leaves for drinking
Termite fishing with sticks
Spear use
What colours would humans identify first and second?
Black and White
What colour would humans identify third?
Red
What colour would humans identify fourth?
Blue, Green or Yellow
What colour would humans identify last?
Brown
What it dangerous about inbreeding?
It increases the likelyhood of expression of lethal or debilitating recessive genes
What is the Westmark hypothesis?
- also called Reverse Sexual Imprinting
People who live in close proximity during the first six years of their lives become desensitized to sexual attraction and are not attracted to each other.
Why do Taiwanese sim-pua marriages not do so well?
The boy is sent to live with his future wives family from a very young age and they are raised as children together. This causes them to become desensitized to sexual attraction and are not as attracted to each other.
What is paleoanthropology?
The study of hominid evolution and human life as revealed by the fossil record - looking at both biological and behavioural (cultural) differences.
What are hominins?
Includes all the bipedal hominini, back to the divergence of the great apes.
What are the characteristics of the human foot?
Large heel, ankle developed for walking, stiff midfoot for leverage, abducted big toe in line with the other toes.
What are the characteristics of the ape foot?
Small heel, ankle adapted for climbing, flexible midfoot, grasping big toe
When did the first hominins arise?
6-7 million years ago.
What dating methods are used in paleoanthropology?
Stratigraphic dating - layers of sediment, debris and rock can tell you how long the bones have been in the ground for.