Supply Chain Management MidTerm
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
ABC Analysis
What: Categorizes products total consumption (price * volume)
Manufacturers use it to allocate limited inventory planning resources (daily planning of A items)
Retailers use it to allocate planning resources but also to decide what items to drop (C items)
Inventory management
can use ABC analysis
lower inventory carrying cost = increase cash flow, risk reduction, faster response to market changes, decrease interest expense, leaner supply chain
Demand planning
Used to help better manage inventory with fewer stock out and less excess inventory/holding cost
Use tech and data (Point of sale data) to make forecasting better —> and plan demand better
S&OP
Forecasting across sales. Operations, Finance and Supply chain management
It is very hard to achieve bc of each groups different objectives
Demand Shaping
Pushing the market twoard certain product
Methods like Buy one Get one
Toyota Production System (TPS)
A manufacturing management system reduces wast (inventory, set up time)
Key Processes: Utilizing front line workers, Value stream map, JIT/Pull, Pro active continue improvement
Six Sigma
A process improvment method that reduces variation
Patriots best super bowls
Super Bowel 51 (2017)
Epic comeback
First super bowl to be decided at overtime
Lady Gaga Performed
Set Up Time
Non Value added
Reducing set up time can increase capacity
Just in Time (Jits)
Producing what is needed when its needed
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Theory
What: Determine the optimal amounts of each order
Why: minimize total cost
Process Mapping
Best way to see inefficiencies and get rid of the bottle neck
Visualize process into individual small steps
Functional Product
Is a “need” product like groceries
Easy to forecast —> low tock outs
Cost is King
Low Margins
Long life cycle
Low Variety
Is a good fit for Just in time
Efficient Supply Chain
Firm schedule/info flow
Low cost
Low Inventory
Innovative Product
Is a “want” products
Difficult to forecast
Short lead time
High Margins
High variety
May also be called fashion
Poor fit for Just in time
Responsive SC
Flexible schedule
Differentiation
Short Lead times
Buffer inventory/capacity
Make to order
When manufacturing and supplies are waiting on stand by waiting for order to come in
Example: when you order food from restaurant the chef has the ingredients but doesn’t make the food until you order
An example of a pull system bc an order has to pull products through supply chain
Make to stock
Forecasting how much you think you can sell
Example: when you go to a clothing store and their is already a certain amount of inventory you can select from (there is no back what we have is what we have)
Push system bc we are pushing our inventory onto customers even though they haven’t yet laced orders
Engineer to order
Making a customized product for each order can’t finish product design until customer tells you what they want; everything is triggered by a customer order
Example: Commissioning a piece of art the artist can not start the process until the customer lets them know what type of art they want how big and so on
A pull system bc the item has to be pulled through the supply chain
Theory of Constraint (TOC)
Find/Relive bottleneck
Total Landed cost
The total price of a product once it has landed on a customers door
You get it by adding the original price with all the transportation cost custom duties and ect
Total Quality Management (TQM)
A structured approach to overall management
Process Analysis
A set of activities which take inputs (materials or info) and transform into an out put
Inventory management
2nd most important in supply chain
Can use ABC analysis & EOQ (TAC)
Lower inventory carrying cost
Increase cash flow
faster response to market change
risk reduction
decreased interest expense
leaner supply chain
Return On Assets (ROA)
ROA = Profit as percentage of sales × Asset turnover = Profit before taxes × Sales
Sales Total assets
Standard Work
Hard because no one likes change and resits
Don’t like loss of freedom
Remember the physicians and Cortez (either get with the program or get out)
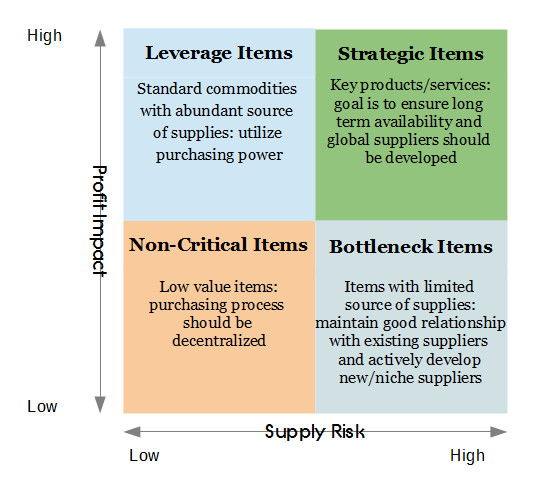
Supplier Selection
Use “K matrix” to decide
Want to have trustworthy suppliers
Supplier Management
Tactical side of Sourcing— supplier scorecards , expediting, etc
Change Management
Challenges
Training/Qualified
Transition Ramp Up/Ramp Down
Loss of relationship/Working procedures
Inevitable start up cost/revenue
Economy of Scale
Lower costs with higher volume due to spreading fixed costs
when you make a lot of a product, it's cheaper to make each individual unit.
Diseconomy of Scale
Getting bigger leads to higher costs per unit, which can reduce overall efficiency and profitability.
Category Strategy
Determine the types of products you have and how to best source them for maximum profit and minimized supply risk —> Use K Matrix