Membranes and Transport
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Define plasma membrane
Structure common to all cells. It acts as a barrier where all cells must cross to enter or leave the cell thus achieving selective permeability. This means that the plasma membrane can selectively allow certain particles to pass through based on size, charge, and polarity.
Factors that contirbute to rate of simple/faciliated/diffusion and active transport
Compare and contrast protein pumps and protein channels
Protein pumps: Requires ATP to transport molecules against electrochemical graident. Binds to molecule being transported, changes shape, and then release to otherside of membrane
Protein channels: Passive transport/faciliated diffusion. Allows fast movement of molecules across membrane. Can be gated (open to certain stimuli like certain ion) or open.
List the function of cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
Cell surface protein type that binds cells with other cells or extracellular matrix (collagen proteins/structural supporting structures)
Different CAMs present in different types of cell-cell junction
Outline the requirements of osmosis and how osmosis works
Requires:
solute concentration gradient
Semipermeable membrane
Solute that can’t pass through membrane
How it works:
Passive movement of water from area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration (or low osmarlity to high osmolarity)
Continues until concentration gradient is equalized
Oultine the role of aquaporins
Water channel pore (protein) in membrane
Reasborption of water in collecting ducts of kidneys
Provide permament channels for diffusion of water molecules
Some water molecules can pass through tiny spaces between phospholipid molecules
What factors influence the selectivity in membrane permeability
Particle Size (big molecules can not simply diffuse through the membrane)
Polarity
Charge
Concentration gradient
Channel proteins
Pump Proteins
State the difference between a lipid bilayer and the double membrane of many organelles
Lipid bilayer is fundamental structural component of cell membranes while double membrane is a specialized feature of certain organelles with unique functions.
Uncharged particles
Nonpolar molecules
Small polar molecules
Large molecules
Charged molecules
the movement of particles from region of higher concentration to lower concentration through transmembrane proteins.
Passive movement (no ATP required)
Distinguish between diffusion and facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion doesn’t require a
Both do not require ATP (passive movement).
Active uptake is highly selective
Involves pump molecules
List the two different types of transport proteins and their structure
Channel (pore) proteins:
Carrier proteins: Changes shape to transport substance across membrane. Ex: protein pumps and electron carriers
Integral proteins- Embedded in plasma membrane layer and permanently attached. They are called transmembrane protein because they move across. They are amphipathic because it have a hydrophobic section at the centre (fatty acid) and a hydrophilic section at the ends.
Peripheral proteins- Temporarily associated with the membrane’s surface by interacting with integral proteins or phospholipids. Hydrophilic.
Conformational change
Energy input needed in ATP
Against the gradient (low to high instead of high to low concentration)
State the structure and function of glycoproteins and glycolipids
Glycoproteins: Cell markers or antigens for cell-to-cell recognition such as ABO blood group antigens that reject different blood types.
Glycolipids:
Accepted view of the structure of the plasma membrane, compromising a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded. It is fluid because components like lipids and proteins can move laterally (sideways) and mosaic because proteins are scattered around.
Describe the importance of membrane fluidity
Proteins can move and function correctly
Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points so membranes are fluid and thefore flexible at regular temperature of cell
What are the factors of lipid bilayer’s fluidity
Shorter chains in lipids = increase fluidity and permeability because shorter chains have weaker van der Waals force which makes the membranes less rigid and more flexible
Longer chains in lipids = decrease fluidity because it gives more interaction between tails of the phospholipids = more tightly packed and less fluid membrane
Define homeoviscous adaptation
Adaptation to cell membrane lipid composition to maintain its membrane fluidity.
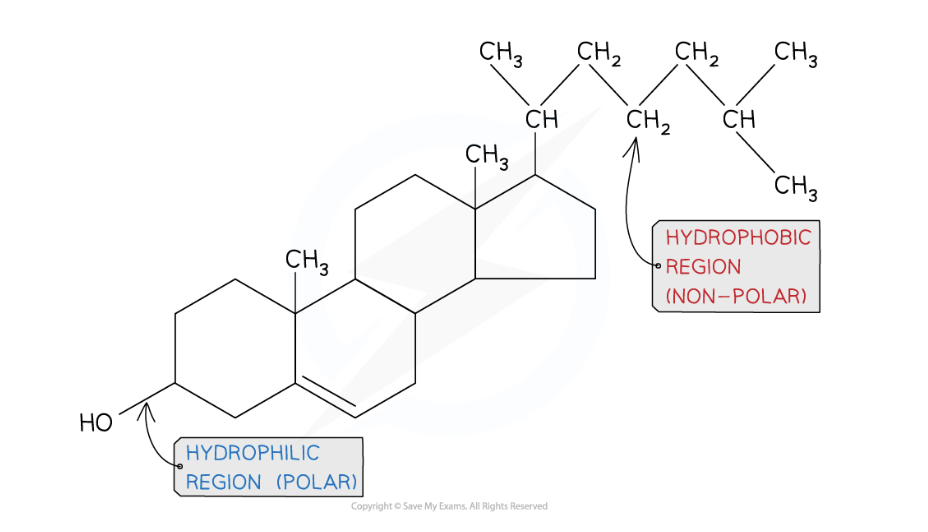
Detail how cholesterol help maintain membrane fluidity
Cholesterol is a lipid hormone that restricts the fluidity of the plasma membrane by stablizing the cell membrane at low/high temperatures. It disrupts the close-packing of phospholipds to increase flexibility at low temperatures (stronger bonds) and holds them together at high temperatures (less stronger bonds).
It can also act as a barrier by fitting in spaces between phospholipids because it is hydrophobic region that fits between the hydrophobic fatty acid tails in the centre, preventing water-soluble substances from diffusing across the membrane.
Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis
Endocytosis: Transports mateirals into cells. Plasma membrane engulfs material to form a small sac around it.
Phagocytosis: Bulk intage of solid material by cell (phagocytes). Vacuoles are called phagocytic vacuoles. They engulf bacteria by phagocytic white blood cells.
Pinocytosis: Bulk intake (large quantitiy of material) of liquids
Exocytosis: Materials are removed from/out of cell. Vesicles are fused to cell membrane and release contents outside of cell. Example of this pancreatic cells.
Outline the functions of voltage-gated channels and provide some examples
Operates in response to chemical or electrical sstimuli such as active potential in neurons.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Distinguish the characteristics of cell-adhesion molecule (CAM) and extracellular matrix (ECM)
Cell-adhesion moleucles (CAMs)
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
Define ligand gated channels
Transmembrane channel protein that open in response to binding of chemcial messengers such as hormone or neurotransmitters.
Oultine the steps of the sodium-glucose cotransporter
Type of co-transporter protein that involves in combination of faciliated diffusion and indirect active transport (uses energy releases by