Temperate Deciduous Forests & Mississippi River
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:27 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Alfisols
deciduous forest soils, typically rich in nutrients and organic matter from annual leaf inputs
\- soil richness contributed to forest conversion to agriculture, with causing effects on soil productivity
\- replacement of nutrient generating processes with fertilizers; organic, then inorganic → nutrients, micronutrients, no contribution to soil structure
\- old-growth of deciduous forests essentially gone, secondary forests still cover large portions of the eastern U.S.
\- soil richness contributed to forest conversion to agriculture, with causing effects on soil productivity
\- replacement of nutrient generating processes with fertilizers; organic, then inorganic → nutrients, micronutrients, no contribution to soil structure
\- old-growth of deciduous forests essentially gone, secondary forests still cover large portions of the eastern U.S.
2
New cards
Amphipoda - shredder
contribute to nutrient recycling and provide high-quality food for a variety of animals
3
New cards
Beetles (Coleoptera):
larvae primarily wander the stream bottom scavenging for dead organisms, detritus, or other food particles that get lodged between rocks or in deep pools.
4
New cards
detritus
waste or debris of any kind
5
New cards
Bergman’s Rule
The more North a population of native deer are, their antlers get bigger
6
New cards
Brook Charr
* native TDF trout
* usually wait for food to drift by (drift feeding)
* can be anadromous in coastal streams
* sensitive to changes in water quality
* extirpated from many low-pH streams (Al3+ toxicity)
* started to decline due to Rainbow Trout, so Brook Charr would swim to headstreams not watersheds
* usually wait for food to drift by (drift feeding)
* can be anadromous in coastal streams
* sensitive to changes in water quality
* extirpated from many low-pH streams (Al3+ toxicity)
* started to decline due to Rainbow Trout, so Brook Charr would swim to headstreams not watersheds
7
New cards
Brown Trout
* widespread stocking has reduced the distribution of Brown Trout in many eastern streams to small headwater reaches
* maintaining/restoring native Brown Trout is a conservation priority in several states
* maintaining/restoring native Brown Trout is a conservation priority in several states
8
New cards
Stocking
raising fish in hatcheries and then releasing them into waters that already have some wild fish
9
New cards
Buffering capacity of water
water’s ability to get the pH the same even though other acids and bases are added
The primary buffering system in freshwater is the **bicarbonate buffering system**
The primary buffering system in freshwater is the **bicarbonate buffering system**
10
New cards
Caddisflies (Trichoptera)
* considered to be a shredder and collector
* shreds material then uses that to make “armor” to protect from predators
* those that collect do the same but they build with the items they find not shred
* shreds material then uses that to make “armor” to protect from predators
* those that collect do the same but they build with the items they find not shred
11
New cards
Canopy layer
* made up of the overlapping leaves and branches of the trees, usually 25-40m
* usually interrupts 15-30% of water during a rainfall> water evaporates before reaching the soil
* usually interrupts 15-30% of water during a rainfall> water evaporates before reaching the soil
12
New cards
Co-evolution
* when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection
* mussels start as a parasite so they would attach to fish to survive> gaining adaptations that allow bypass of the fish's innate immune system
* mussels start as a parasite so they would attach to fish to survive> gaining adaptations that allow bypass of the fish's innate immune system
13
New cards
**Collateral damage during harvesting:**
* lead to Reduced Impact Logging (RIL) which was beneficial
* careful road planning
* tree-felling directions (cut a tree so it falls in the direction you plan)
* vine removal
* careful road planning
* tree-felling directions (cut a tree so it falls in the direction you plan)
* vine removal
14
New cards
CPOM, FPOM, DOM
* coarse particulate organic matter (CPOM)
* fine particulate organic matter (FPOM)
* dissolved organic matter (DOM)
* make up the food web in headwater streams
* fine particulate organic matter (FPOM)
* dissolved organic matter (DOM)
* make up the food web in headwater streams
15
New cards
Cutthroat Trout
trout that has been restored using techniques like barriers, and rotenone (piscicide)
16
New cards
Decapoda (crayfish important)
* in the shredder group
* crawfish have claws, which makes it easier to shred
* crawfish strongly influenced macro-invertebrate numbers and leaf litter breakdown
* crawfish have claws, which makes it easier to shred
* crawfish strongly influenced macro-invertebrate numbers and leaf litter breakdown
17
New cards
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
* is one of the most important water quality parameters in freshwater systems and has become an increasingly important concern in several marine systems around the world.
\
* DO levels are inversely related to temperature,
* as temperature goes up, DO levels go down, as warm water cannot hold as much oxygen as cold water
\
* Oxygen does not dissolve easily in water, ranging from 0-14.6 mg/l.
\
* we rarely see DO levels over 10 mg/l in natural systems
\
* DO levels are inversely related to temperature,
* as temperature goes up, DO levels go down, as warm water cannot hold as much oxygen as cold water
\
* Oxygen does not dissolve easily in water, ranging from 0-14.6 mg/l.
\
* we rarely see DO levels over 10 mg/l in natural systems
18
New cards
Dobsonflies (Megaloptera)
* considered to be predators
* larvae control the populations of aquatic invertebrates by consuming them
* larvae control the populations of aquatic invertebrates by consuming them
19
New cards
Dragonflies (Odonata) and Damselflies (Odonata)
considered to be the predators
20
New cards
Drift-feeding
* Wait for food to drift by
* fish that drift feed are considered predators
* fish that drift feed are considered predators
21
New cards
Edge species
* species that tend to eat or dwell on the edge of the forest
22
New cards
example of edge species
white-tailed deer
23
New cards
Endangered Colorado River fishes
* Colorado Pikeminnow
* Bonytail
* Razorback Sucker
* Flannelmouth Sucker
* Bonytail
* Razorback Sucker
* Flannelmouth Sucker
24
New cards
Colorado Pikeminnow, Bonytail, Razorback Sucker, Flannelmouth sucker
all endangered but are experiencing restoration using techniques like;
* **migration barriers** (prevent recolonization)
* **piscicide**
* **restocking** (breeding and releasing the offsprings)
* **genetic identification** (allows fishers to see how many strains of one fish there are)
* **culture** (managing fish and their environment while in captivity)
* **migration barriers** (prevent recolonization)
* **piscicide**
* **restocking** (breeding and releasing the offsprings)
* **genetic identification** (allows fishers to see how many strains of one fish there are)
* **culture** (managing fish and their environment while in captivity)
25
New cards
Evapotranspiration
* signifies the amount of rainfall that is lost to the processes of:
* evaporation (mostly from the ground)
* transpiration (movement of water from the roots through leaf stomata)
* (often used in forest and watershed biology) **Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration**
**Act – or Pittman-Robertson Act:**
* evaporation (mostly from the ground)
* transpiration (movement of water from the roots through leaf stomata)
* (often used in forest and watershed biology) **Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration**
**Act – or Pittman-Robertson Act:**
26
New cards
Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Act – or Pittman-Robertson Act
* passed by Congress in 1937 to provide funding for the restoration and management of sport birds and mammals.
* Funds for this Act are collected in the Department of the Treasury from:
* an 11% excise tax paid by manufacturers on sporting arms, ammunition, and archery equipment
* a 10% tax on handguns.
* Funds for this Act are collected in the Department of the Treasury from:
* an 11% excise tax paid by manufacturers on sporting arms, ammunition, and archery equipment
* a 10% tax on handguns.
27
New cards
Flashy hydrograph
* depicts sharp vertical jumps and equally steep vertical declines
* river discharge increases rapidly over a short period of time, indicating rainwater reaches the river very quickly. This means the river is more likely to flood.
* higher elevation would imply lower temperatures, less evapotranspiration, greater rainfall, steeper slopes, and shallow soils → greater runoff
* river discharge increases rapidly over a short period of time, indicating rainwater reaches the river very quickly. This means the river is more likely to flood.
* higher elevation would imply lower temperatures, less evapotranspiration, greater rainfall, steeper slopes, and shallow soils → greater runoff
28
New cards
Forested versus urban stream hydrographs
* rainwater gradually builds and either absorbs into the soil or run off (not flashy though)
* flashy is rather quick and leaves no time for the water to absorb into the soil> river could flood
* flashy is rather quick and leaves no time for the water to absorb into the soil> river could flood
29
New cards
Functional feeding groups
shredders, collector/gatherers, collector/filterers, predators
30
New cards
shredders
* important first step in organic processing
* poor food source
* create small organic particles colonized by bacteria and \n fungi, “peanut butter on the cracker”
* (think crawfish)
* poor food source
* create small organic particles colonized by bacteria and \n fungi, “peanut butter on the cracker”
* (think crawfish)
31
New cards
Collector/gatherers
* search for enriched organic particles as energy source
* (think crane fly/ mosquito hawk)
* (think crane fly/ mosquito hawk)
32
New cards
33
New cards
Collector/ filterers
* trap food particles carried by the current
* (black flies)
* (black flies)
34
New cards
Predators
* take advantage of herbivore production
* invertebrates usually active search predators
* fishes include searchers and drift-feeders
* (dragonflies)
* invertebrates usually active search predators
* fishes include searchers and drift-feeders
* (dragonflies)
35
New cards
Glochidia
* what mussel embryos develop to
(they are parasitic)
(they are parasitic)
36
New cards
Ground layer
* mosses, lichens
(any vegetation on bottom of trees)
(any vegetation on bottom of trees)
37
New cards
Groundwater
* when groundwater and rainfall collects > percolation (slow passage of a liquid through a filtering medium) occurs
* groundwater is important for waterflow in headstreams
* groundwater is important for waterflow in headstreams
38
New cards
Hardwoods
* wood type deciduous forest contain
* used to make furniture and musical instruments
* used to make furniture and musical instruments
39
New cards
Herbaceous layer
* consists of grasses and forbs and ferns
* non-woody plants without a perennial stem,
* usually goes to 1 m
* non-woody plants without a perennial stem,
* usually goes to 1 m
40
New cards
High-grading problem with selective harvesting
genetic selection prefers untouched trees
(un-harvested sub-optimal trees)
(un-harvested sub-optimal trees)
41
New cards
Hydrology
* how water moves
* TDF has a complex hydrology -> increased biodiversity and productivity
* can be altered from watershed development
* when a combination of water quality and hydrology changes -> higher order streams lower in the watershed are affected
* TDF has a complex hydrology -> increased biodiversity and productivity
* can be altered from watershed development
* when a combination of water quality and hydrology changes -> higher order streams lower in the watershed are affected
42
New cards
Inorganic fertilizer
* nutrients/ micronutrients
* no contribution to soil structure
* no contribution to soil structure
43
New cards
Interception
common when rain falls on a forest -> leaves and branches intercepts the rain and makes it fall to the ground slower
44
New cards
Intermittent (ephemeral) stream
* cease to flow every year or at least twice every five years
* aquifer development could could affect headwater stream ecosystems
* aquifer development could could affect headwater stream ecosystems
45
New cards
Key deer
* distinct sub species to the native white-tailed deer
* declined to 25 individuals in 1940 due to the Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Act -> National Key Deer Refuge established in 1950
* 800 by 2008
* declined to 25 individuals in 1940 due to the Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Act -> National Key Deer Refuge established in 1950
* 800 by 2008
46
New cards
Mayflies (Ephemeroptera)
* collector/gather
* move nutrients around which maintains other aquatic communities
* move nutrients around which maintains other aquatic communities
47
New cards
**Migration barrier for trout restoration**
limit recolonization of restored stream reaches (**kept the stream native.. No invasive species**)
48
New cards
Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act
* fostered from U.S. Forest Service (1903) and the U.S. Park Service (1916)
* important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for White-tailed deer
* important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for White-tailed deer
49
New cards
National Wildlife Refuge System
* established in 1903 (Roosevelt) at Pelican Island
* consistent growth through the 20th century;
* >560 National Wildlife Refuges in operation today
* aims to conserve wildlife
* consistent growth through the 20th century;
* >560 National Wildlife Refuges in operation today
* aims to conserve wildlife
50
New cards
Oak, maple, elm, hickory common trees
the characteristic hardwood trees (make furniture or instruments) in TDF
51
New cards
Old-growth forests
* forests that have developed over a long period of time..essentially free from catastrophic disturbances
* old growth in deciduous forests are essentially gone
* old growth in deciduous forests are essentially gone
52
New cards
Organic fertilizer
rich in nutrients from leaves
53
New cards
Perennial stream
usually gets discharge (volume of water moving down a stream) year-round
54
New cards
Piscicide
* poison that kills fish
* (Rotenone)
* (Rotenone)
55
New cards
Quality Deer Management (QDM)
non-profit wildlife conservation organization dedicated to ensuring the future of white-tailed deer, wildlife habitat, and our nation's hunting heritage
56
New cards
Rainbow trout
* a large trout native to the Pacific seaboard of North America
* It has been widely introduced elsewhere, both as a farmed food fish and as a sporting fish.
* Most remain in streams, but some migrate to lakes and some to the sea
* caused problems with Brook Char
* It has been widely introduced elsewhere, both as a farmed food fish and as a sporting fish.
* Most remain in streams, but some migrate to lakes and some to the sea
* caused problems with Brook Char
57
New cards
Reduced impact logging (RIL)
beneficial; careful road planning, tree-felling directions, vine removal
58
New cards
Rotenone
* one of two piscicides approved for use in the U.S
* It is derived from a family of S. American plants
* interferes with fish mitochondrial function
* was used to kill invasive fish in headwater streams and restore Native Brook Trout
* It is derived from a family of S. American plants
* interferes with fish mitochondrial function
* was used to kill invasive fish in headwater streams and restore Native Brook Trout
59
New cards
Ruminant
* an even-toed ungulate mammal that chews the cud regurgitated from its rumen.
* cattle, sheep, antelopes, deer, giraffes, and their relatives
* have 4-chambered stomachs
* cattle, sheep, antelopes, deer, giraffes, and their relatives
* have 4-chambered stomachs
60
New cards
Runoff, infiltration, percolation
* **Runoff**- the movement of landwater to the oceans (slope/soil type/ how complex the ground is \[rugosisty\])
* chiefly in the form of rivers, lakes, and streams;
* consists of precipitation that neither evaporates, transpires nor penetrates the surface to become groundwater
* **Infiltration**-into,
* **Percolation**-down through
* chiefly in the form of rivers, lakes, and streams;
* consists of precipitation that neither evaporates, transpires nor penetrates the surface to become groundwater
* **Infiltration**-into,
* **Percolation**-down through
61
New cards
Scrapers
* adapted for feeding on periphyton (biofilm)
* (algae, diatoms, bacteria, draped organic particles)
* (algae, diatoms, bacteria, draped organic particles)
62
New cards
Secondary forests
* a forest or woodland area which has re-grown after a timber harvest..until a long enough period has passed so that the effects of the disturbance are no longer evident
* Still cover a large portion of the eastern U.S.
* Still cover a large portion of the eastern U.S.
63
New cards
Shade-tolerant trees
* trees that can grow in the shade
* are produced in uneven aged management
* are produced in uneven aged management
64
New cards
Shrub layer
* includes both shrubby vegetation and seedling trees
* grow to 3 m
* grow to 3 m
65
New cards
Snags
* standing dead trees that contribute significantly to forest habitats for wildlife.
* It has been estimated that snag habitat provides cover, food, and breeding habitat to over 1,000 species in the U.S.
* It has been estimated that snag habitat provides cover, food, and breeding habitat to over 1,000 species in the U.S.
66
New cards
Softwoods
* low density wood fibers and used for structural lumber \n ex: coniferous trees
67
New cards
Stoneflies (Plecoptera)
* shredder/predator
* about 2,000 species of insects
* the adults of which have long antennae, weak, chewing mouthparts, and two pairs of membranous wings
* the nymph resembles the adult but lacks wings and may have external gills on various parts of its body
* The nymph feeds on plants, decaying organic matter, and other insects;
* the nymphal stage lasts from one to four years
* and the adults live several weeks
* about 2,000 species of insects
* the adults of which have long antennae, weak, chewing mouthparts, and two pairs of membranous wings
* the nymph resembles the adult but lacks wings and may have external gills on various parts of its body
* The nymph feeds on plants, decaying organic matter, and other insects;
* the nymphal stage lasts from one to four years
* and the adults live several weeks
68
New cards
Stream baseflow
* results from precipitation that infiltrates into the soil and eventually moves through the soil to the stream channel
* particularly important in many streams for maintaining baseflow as well as stream temperatures and gravel spawning beds (salmonids)
* particularly important in many streams for maintaining baseflow as well as stream temperatures and gravel spawning beds (salmonids)
69
New cards
Stream discharge (volume; velocity x cross sectional area)
* stream discharge is based on the volume of water
* when the discharge is high, velocity is high as well (more damage)
* when the discharge is high, velocity is high as well (more damage)
70
New cards
Stream hydrograph
* rainfall event shows through characteristic discharge (volume) through time
* can be reflect human influence on water
* can be reflect human influence on water
71
New cards
Stream order
\
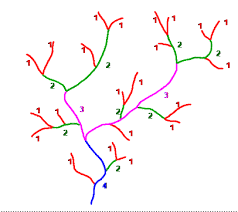
72
New cards
Subsurface flow of rainfall
* depending on slope and soil composition
* infiltrated water can move downslope to a stream channel in a relatively quick process aka subsurface flow of rainfall
* infiltrated water can move downslope to a stream channel in a relatively quick process aka subsurface flow of rainfall
73
New cards
Throughfall and stemflow – effective
rainfall
rainfall
* **Throughfall**: after rainfall -> un-intercepted drips
* **Stemflow**: gravity, together it’s called effective rainfall and is available for runoff (slope, soil type, rugosity, etc.)
* infiltration (into) and percolation (down through)
* **Stemflow**: gravity, together it’s called effective rainfall and is available for runoff (slope, soil type, rugosity, etc.)
* infiltration (into) and percolation (down through)
74
New cards
Traditional deer management
* Protection of females with buck only harvest
* polygynous species makes this management approach problematic for controlling population size
* polygynous species makes this management approach problematic for controlling population size
75
New cards
Transpiration
* movement of water from the roots through the leaf stomata
* low humidity/higher temperatures and greater wind speeds tend to increase transpiration rates thus reducing runoff to the stream
* low humidity/higher temperatures and greater wind speeds tend to increase transpiration rates thus reducing runoff to the stream
76
New cards
True flies (Diptera)
collector-gathers
77
New cards
Understory layer
* 3 -25 m
* young dominant trees
* smaller species
* young dominant trees
* smaller species
78
New cards
Uneven-aged management
* the result of selective harvesting and creates shade-tolerant trees
* habitat diversity and minimizes erosion
* results from selective harvesting
* habitat diversity and minimizes erosion
* results from selective harvesting
79
New cards
U.S. Forest Service
* 1903 (Roosevelt and Pinchot) improved land management and critical habitat for White tailed deer
* fostered important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for WTD,
* (Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act)
* fostered important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for WTD,
* (Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act)
80
New cards
U.S. Park Service
* 1916 improved land management and critical habitat for WTD
* fostered important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for WTD,
* e.g., Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act
* fostered important federal legislation that improved environmental conditions for WTD,
* e.g., Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act
81
New cards
Variable retention harvesting
* an approach to harvesting based on the retention of structural elements or biological legacies, harvesting preferred,
* maintains age diversity, snags coarse woody debris, and genetically superior trees.
* maintains age diversity, snags coarse woody debris, and genetically superior trees.
82
New cards
Water yield to streams
* in coniferous forest water yields to streams with extensive clearcutting activity -> water yield to streams increases substantially
* less so in deciduous forests (less intensive harvesting)
* less so in deciduous forests (less intensive harvesting)
83
New cards
Wetland Reserve Program
* was a major land retirement and habitat restoration/conservation program established by the **1990 Farm Bill.**
* continued a major paradigm shift in the U.S. that began in the 1970s
* whereby the goals of federal funding programs shifted from converting freshwater wetlands to agricultural croplands to protecting and enhancing wetlands on private land.
* continued a major paradigm shift in the U.S. that began in the 1970s
* whereby the goals of federal funding programs shifted from converting freshwater wetlands to agricultural croplands to protecting and enhancing wetlands on private land.
84
New cards
White-tailed Deer
* 17 subspecies
* ruminant
* bergmann's rule
* tremendous recreational value
* crashed in 1850-1900s
* T. Roosevelt founded the boone and crockett club and established the hunter ethics
* huge population increases through the 1900s
* Lacey Act (1900)
* development of state wardens
* Aldo Leopold’s Game Management in 1933
* wildlife biologists trained in the 1940s- 50s
* ruminant
* bergmann's rule
* tremendous recreational value
* crashed in 1850-1900s
* T. Roosevelt founded the boone and crockett club and established the hunter ethics
* huge population increases through the 1900s
* Lacey Act (1900)
* development of state wardens
* Aldo Leopold’s Game Management in 1933
* wildlife biologists trained in the 1940s- 50s
85
New cards
Wilderness Act of 1964
* preserve and protect certain lands “in their natural condition”
* “secure for present and future generations the benefits of wilderness.
* “secure for present and future generations the benefits of wilderness.
86
New cards
Benthos
* the flora and fauna found on the bottom or in the bottom sediments/ of a sea/ lake/ or other body of water
* loss a lot of sedentary bentos during eutrophication of the Mississippi River
* refers to infaunal (in) and epifaunal (on) animal assemblages associated with lake and ocean substrates
* The benthos community is composed of a diversity of
* macrobenthos (>1 mm in length)
* meiobenthos (0.1-1.0 mm)
* microbenthos (
* loss a lot of sedentary bentos during eutrophication of the Mississippi River
* refers to infaunal (in) and epifaunal (on) animal assemblages associated with lake and ocean substrates
* The benthos community is composed of a diversity of
* macrobenthos (>1 mm in length)
* meiobenthos (0.1-1.0 mm)
* microbenthos (
87
New cards
Coastal wetland ecosystems services
* storm protection
* erosion protection
* wildlife habitat
* fisheries production
* nutrient and sediment filter
* carbon sequestration
* recreation
* erosion protection
* wildlife habitat
* fisheries production
* nutrient and sediment filter
* carbon sequestration
* recreation
88
New cards
Storm protection
barrier islands are critical buffers that reduce inland storm damage
89
New cards
Erosion protection
vegetation around marshes resist coastal erosion from currents/tides
90
New cards
Wildlife habitats
coastal marshes provide food and habitats for resident and migratory wildlife
91
New cards
Fisheries production
75% of commercial and recreational species marsh dependent
92
New cards
Nutrient and Sediment filter
filters the dirt from going to the Gulf
93
New cards
Carbon Sequestration
* the trees reduce flooding
* Filter pollutants before they reach the water
* stabilize stream banks and help reduce erosion and sediment pollution
* Filter pollutants before they reach the water
* stabilize stream banks and help reduce erosion and sediment pollution
94
New cards
Recreation
the marsh provides lots of education and fishing opportunities for humans
95
New cards
Coastal wetland loss
* subsidence
* sea level rise
* saltwater intrusion
* sediment deprivation from MR levees
* sea level rise
* saltwater intrusion
* sediment deprivation from MR levees
96
New cards
subsidence
sinking
97
New cards
sea level rise
when land sinks, water rises
98
New cards
saltwater intrusion
* to reduce the chances of flooding:
* canals were built to drain water..
* However, saltwater would run inside the canals and affect the freshwater fish and species (BAD)
* canals were built to drain water..
* However, saltwater would run inside the canals and affect the freshwater fish and species (BAD)
99
New cards
sediment deprivation
sediment starvation over the last half-century has shifted an accretion/erosion equilibrium towards marsh loss
100
New cards
Coastal wetland restoration projects
* ridge restoration
* oyster reef development
* shoreline protection
* barrier island restoration
* marsh creation
* MR water/sediment diversions
* oyster reef development
* shoreline protection
* barrier island restoration
* marsh creation
* MR water/sediment diversions