Chapter 2 - Chemical components of cells
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
polymer
Long molecule made by covalently linking multiple identical or similar subunits (monomers).
Subunit
A monomer that forms part of a larger molecule, such as an amino acid in a protein or a nucleotide in a nucleic acid. Can also refer to a complete molecule that forms part of a larger molecule.
The distribution of elements in the Earth's crust differs from
the human body
Humans: lots of H
Earth: lots of O
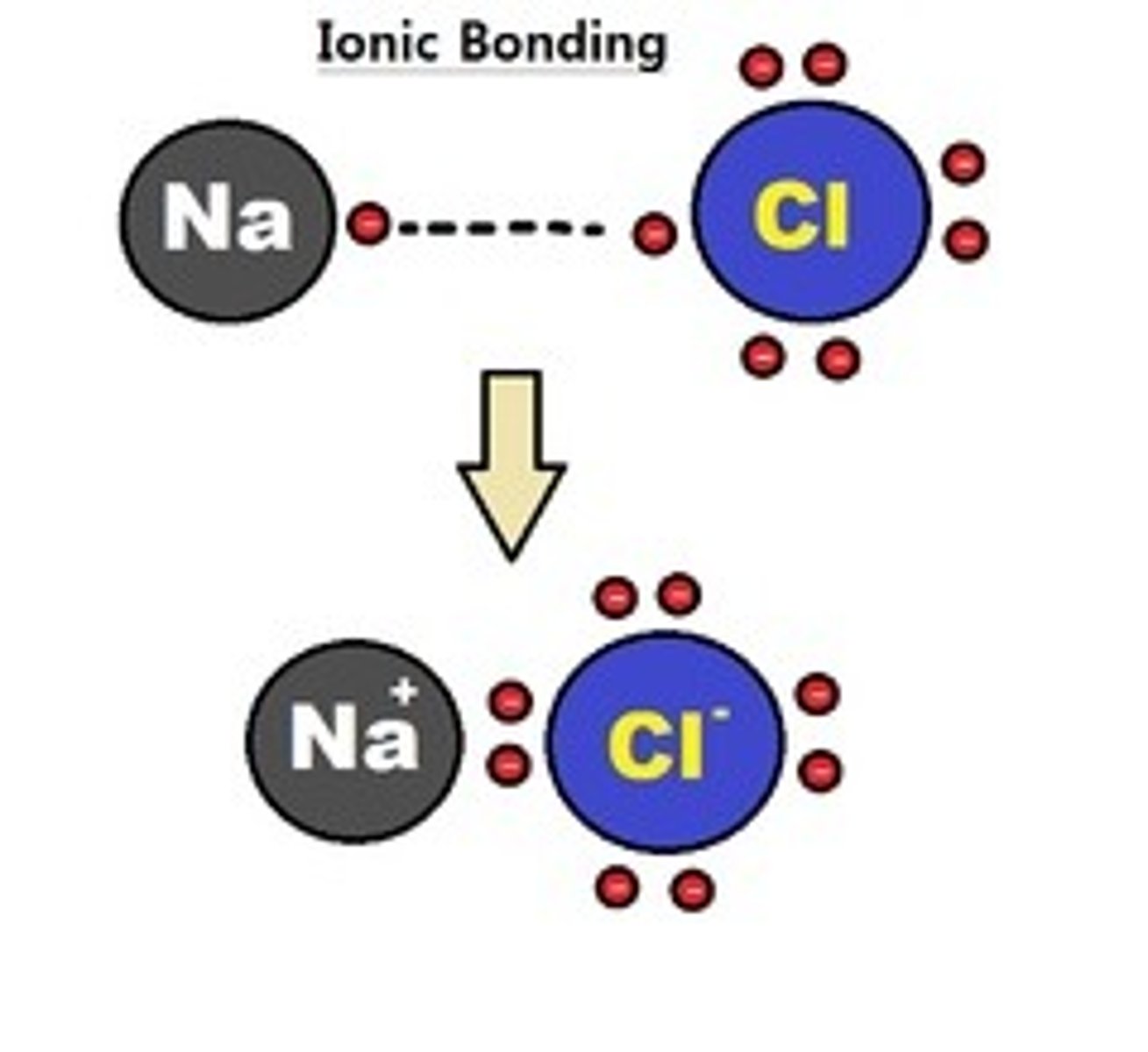
ionic bond
electrons are donated
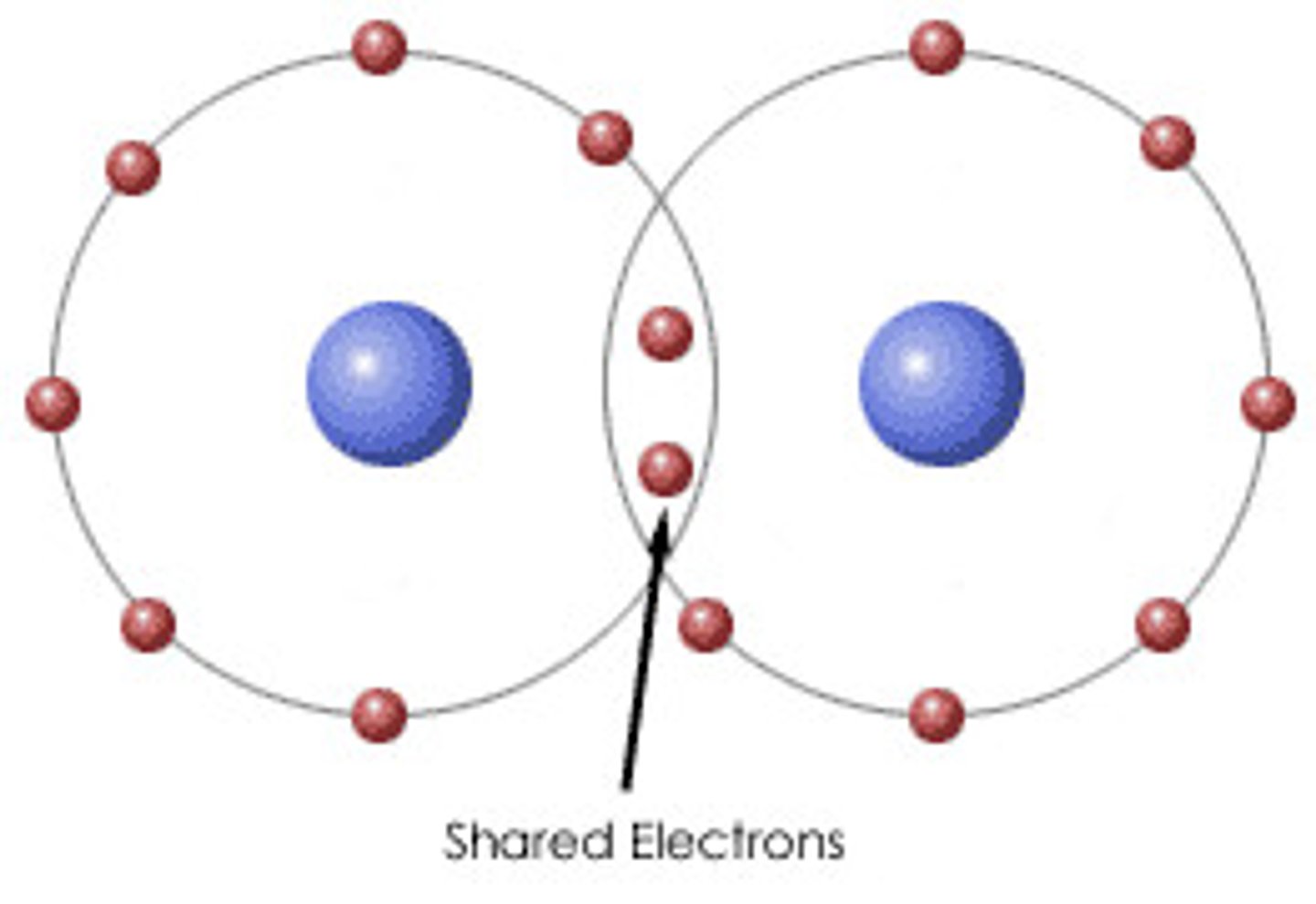
covalent bond
electrons are shared
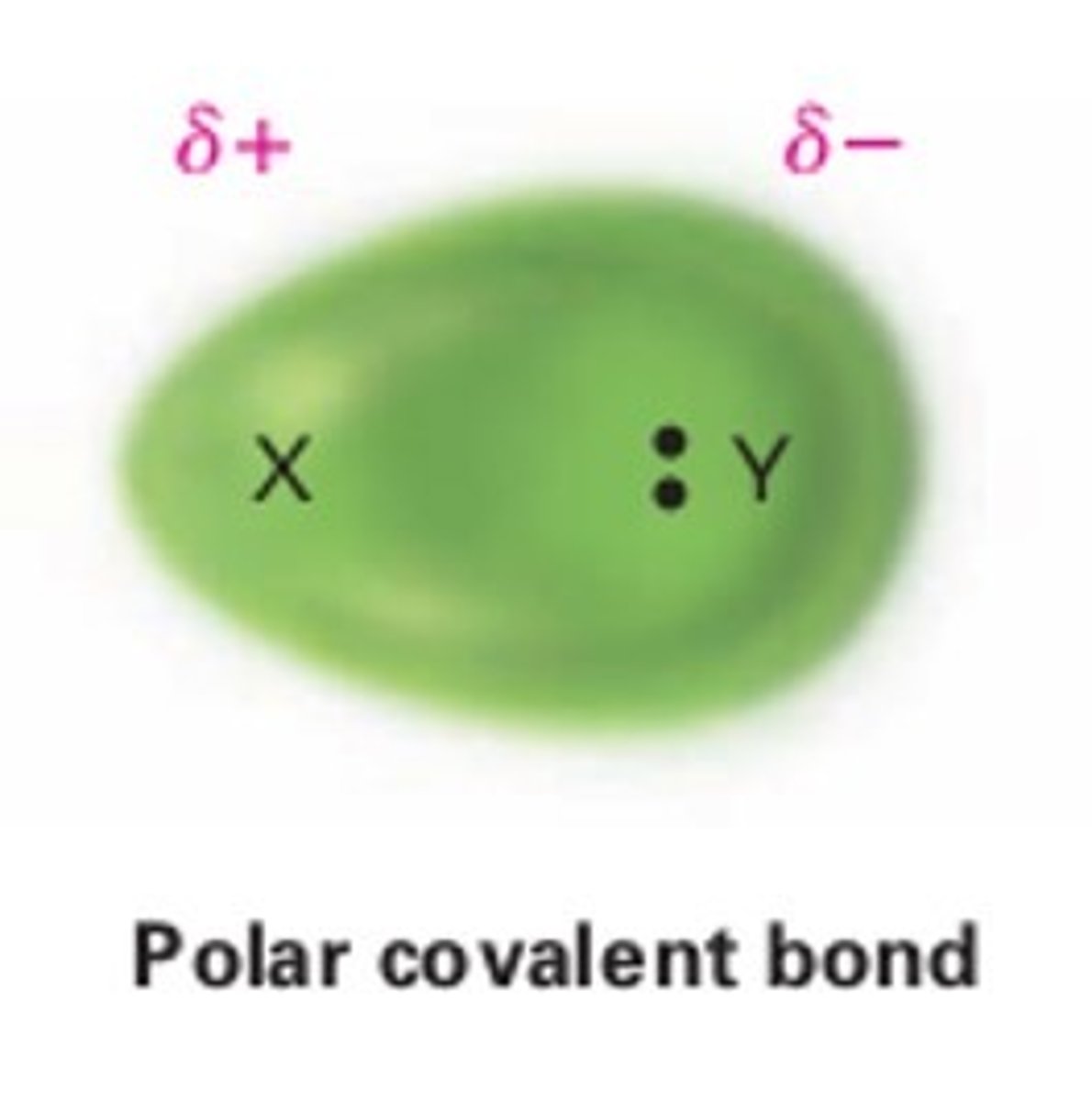
electrons in covalent bonds are shared
unequally (partially neg or pos)
noncovalent bond
does not involve the sharing of electrons; singly are relatively weak, Examples are hydrogen bonds and van der Waals attractions.
hydrophobic force
A noncovalent interaction that forces together the hydrophobic portions of dissolved molecules to minimize their disruption of the hydrogen-bonded network of water;
acid
releases a proton when dissolved in water and created hydronium ions, lowering pH
base
accepts a proton when dissolved in water, usually nitrogen containing purines in DNA/RNA
methyl
--CH3
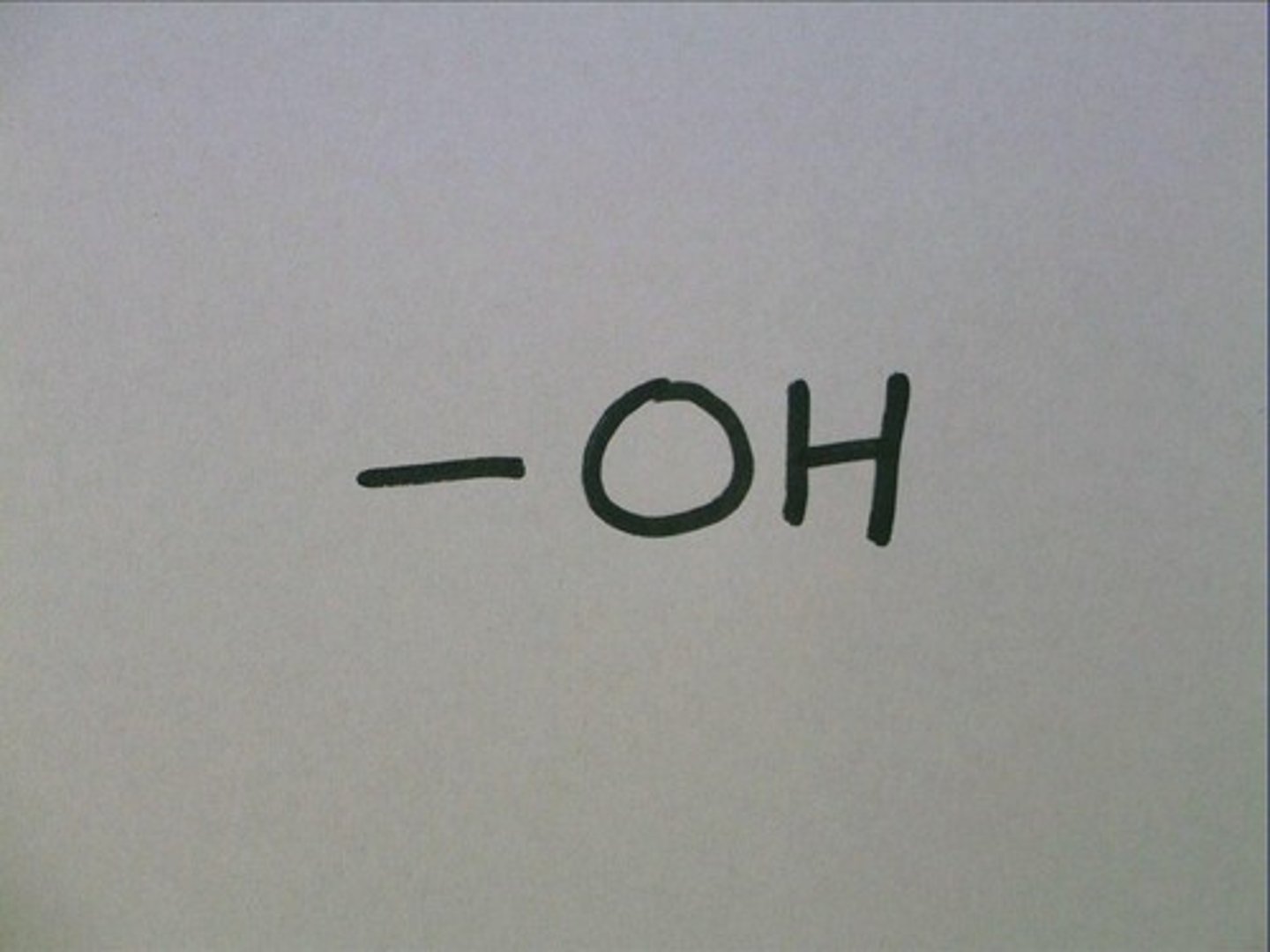
hydroxyl
--OH
carboxyl
--COOH
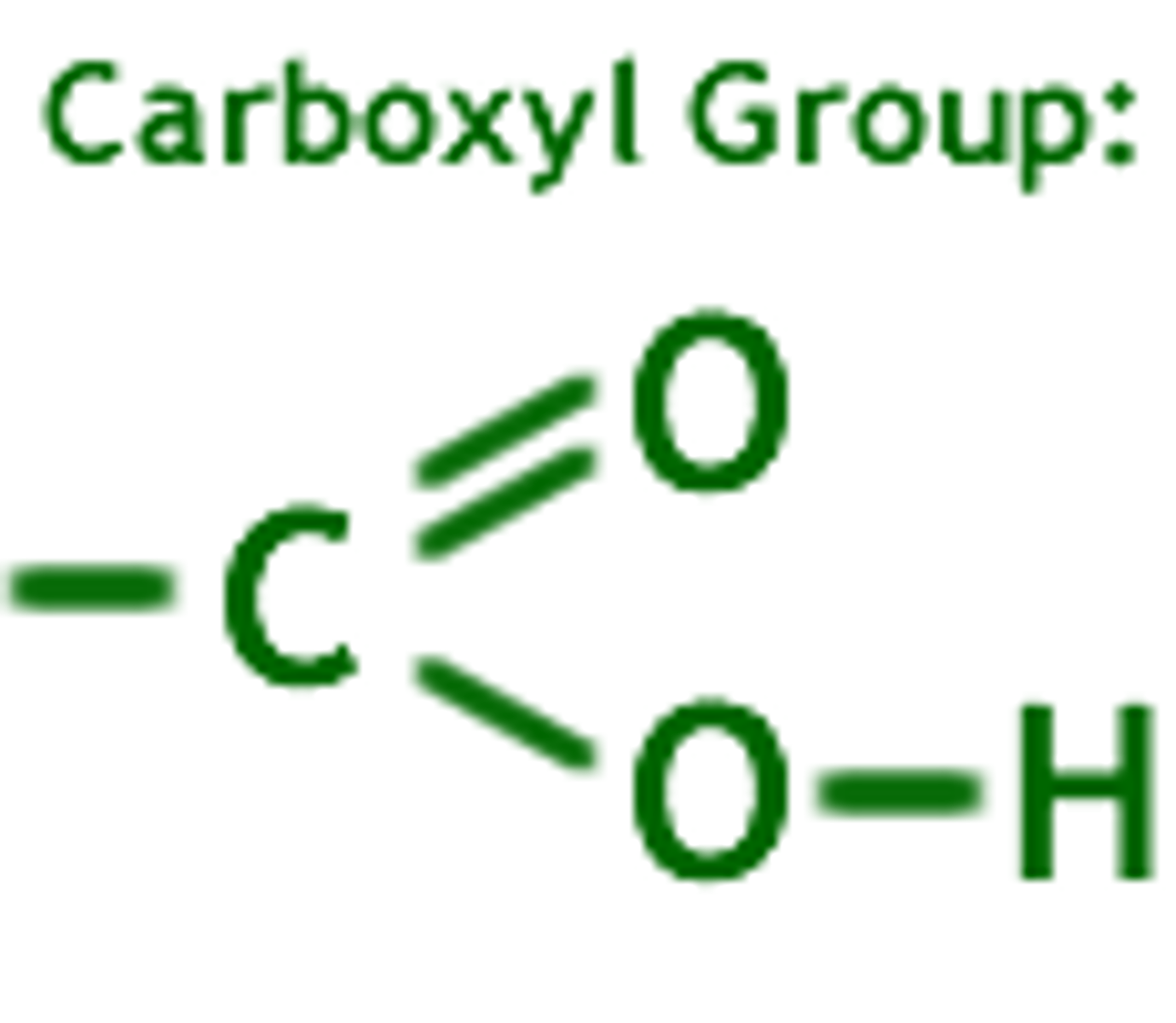
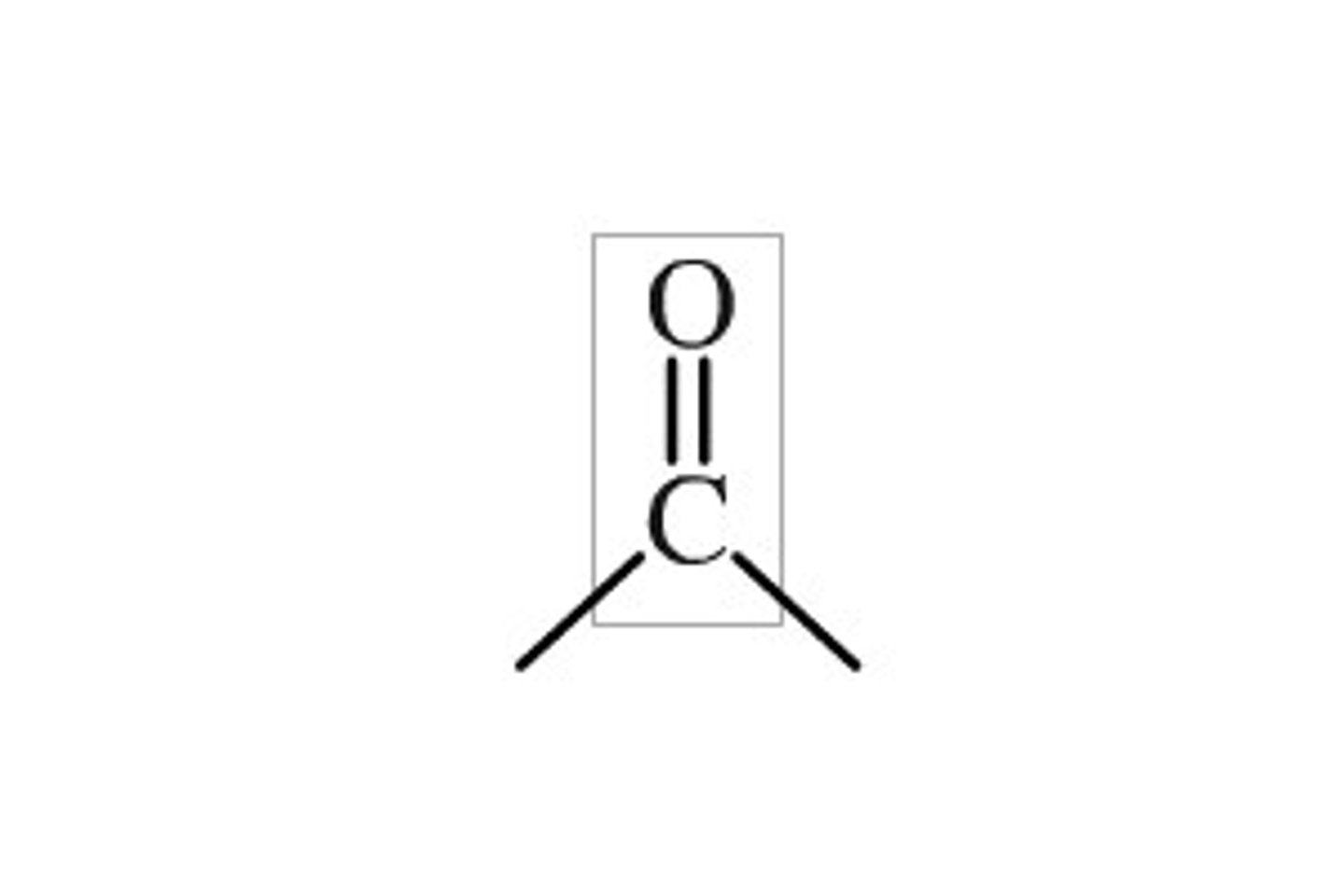
carbonyl
--C=O
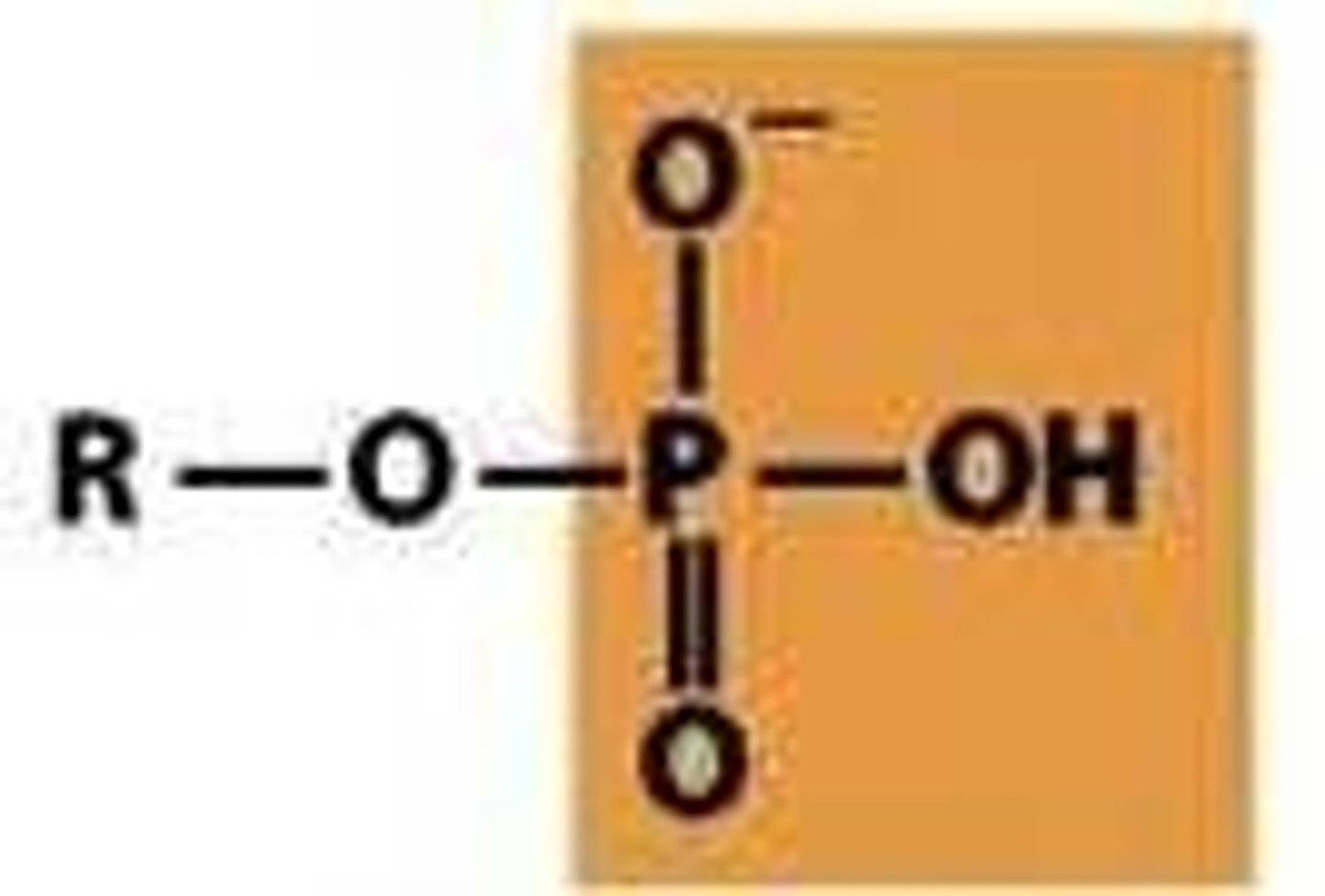
phosphoryl
PO3 2-
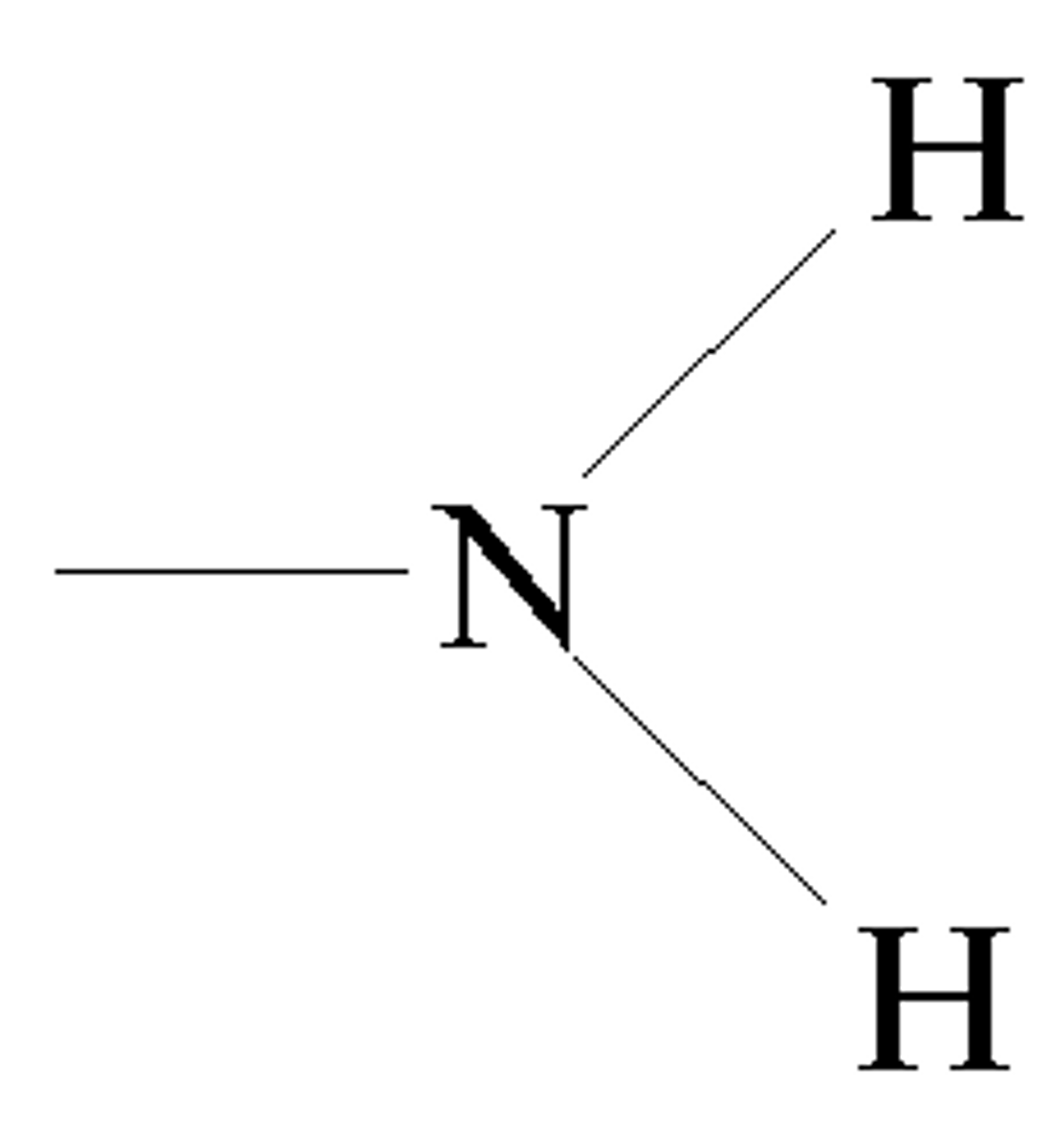
amino
-NH2
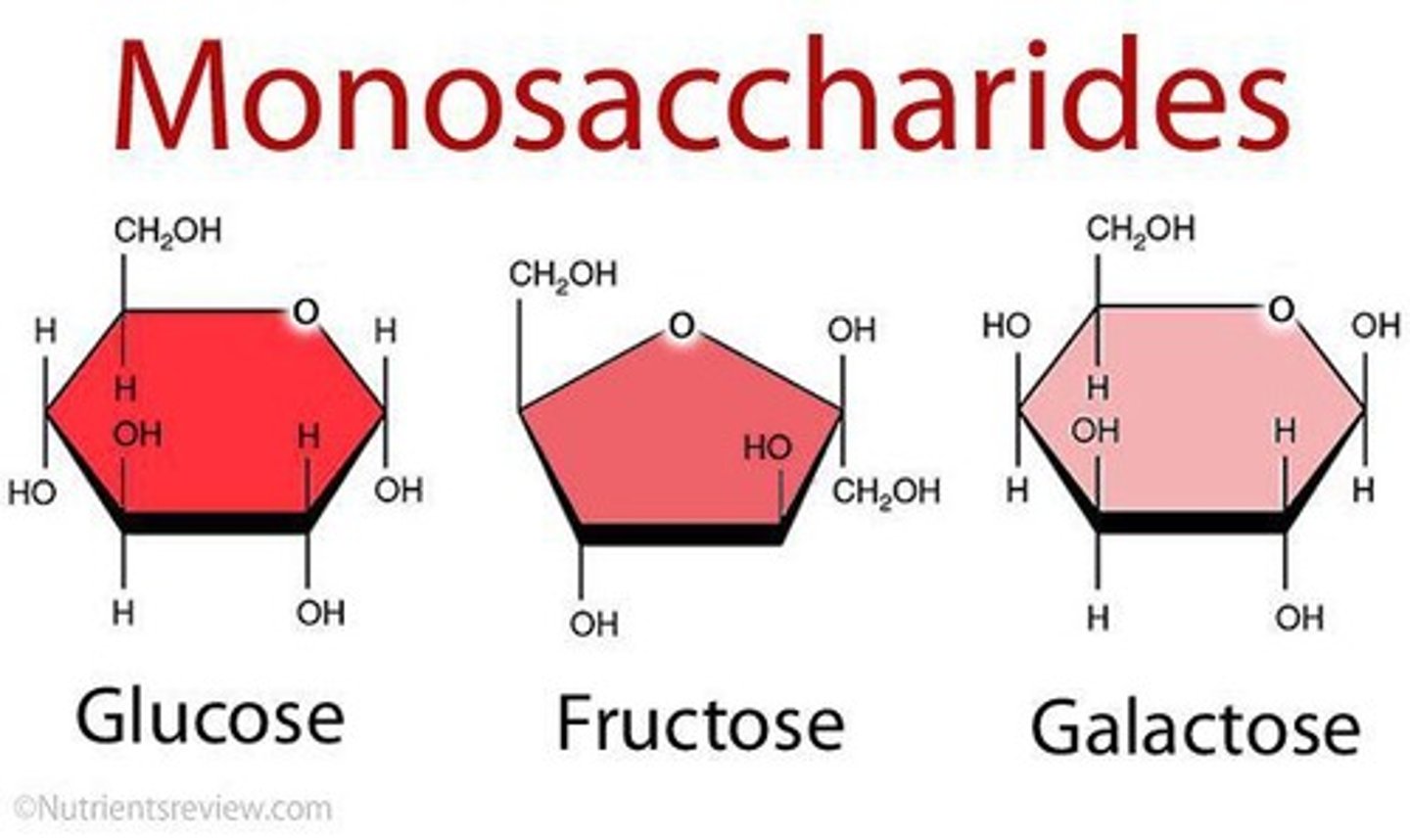
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide or sugars (glucose) --OH
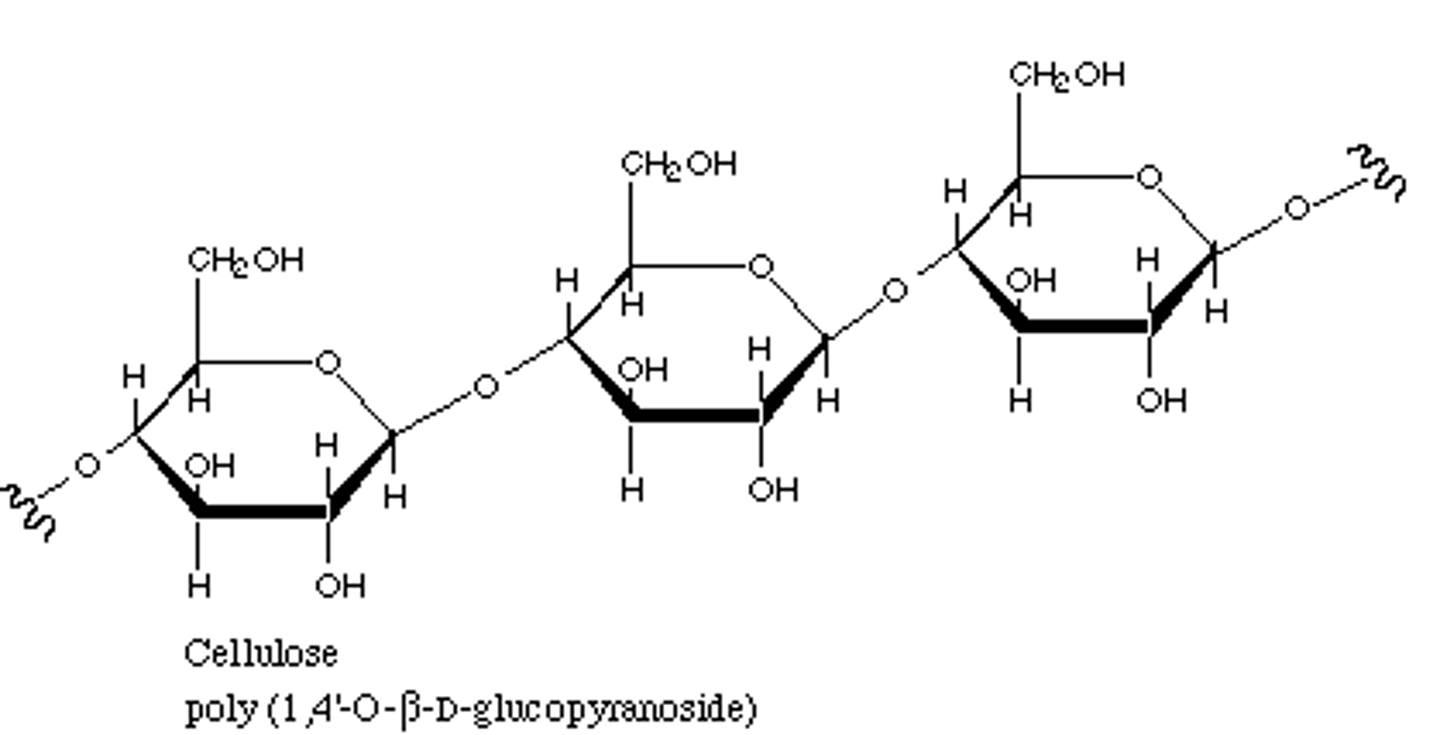
carbohydrate polymer
disaccharide, polysaccharide (sucrose, glycogen, starch)
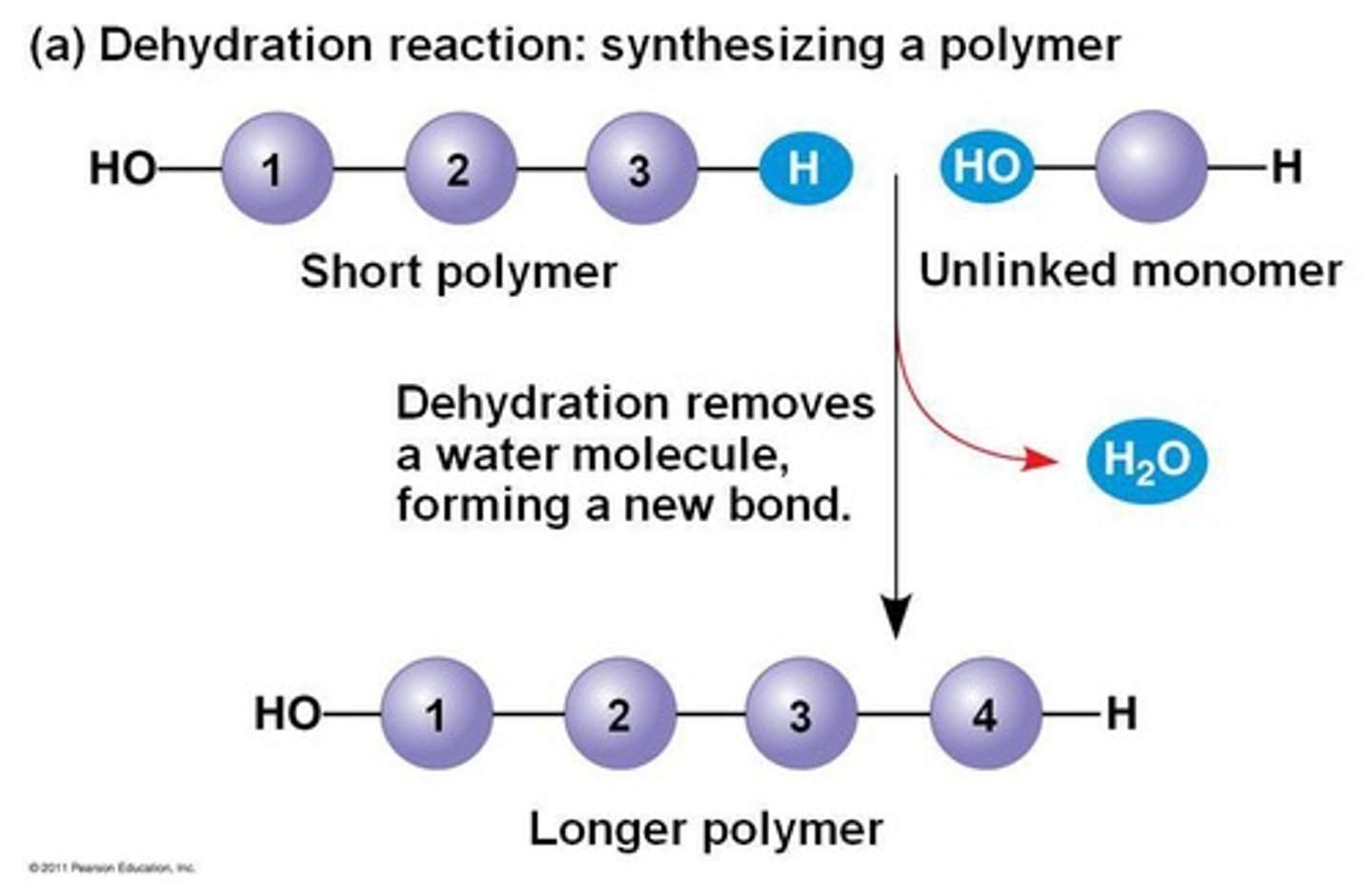
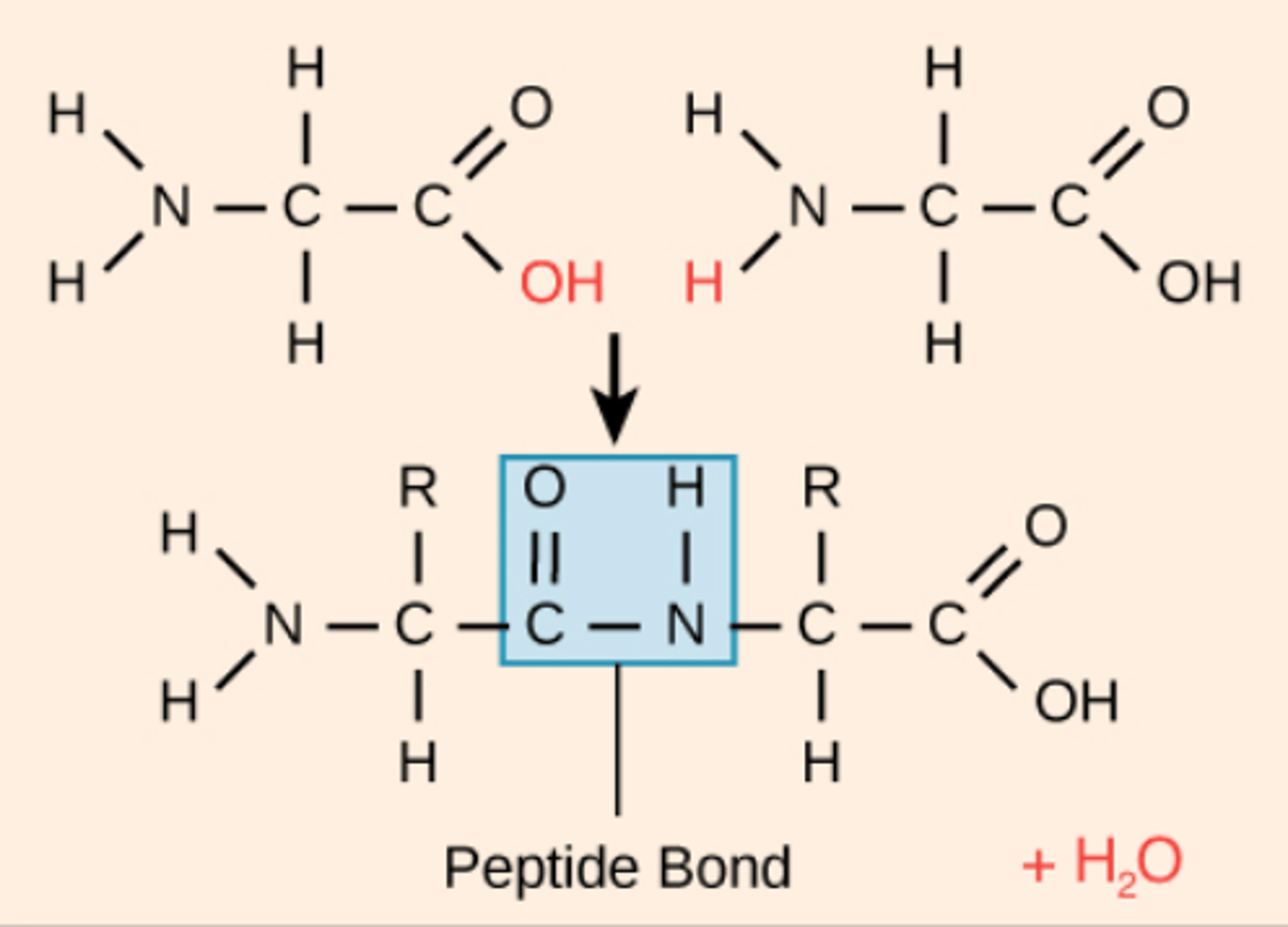
condensation reactions
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule, BUILDS
--energetically unfavorable
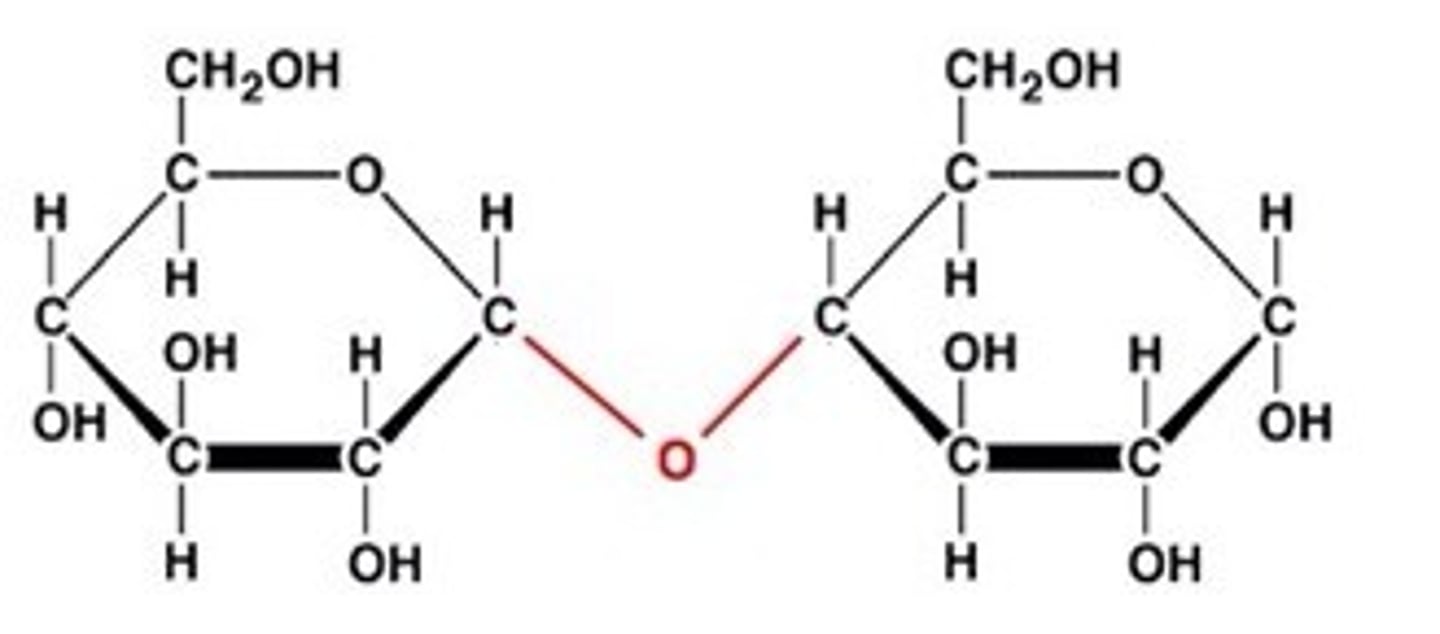
glycosidic bond
covalent bond between two monosaccharides
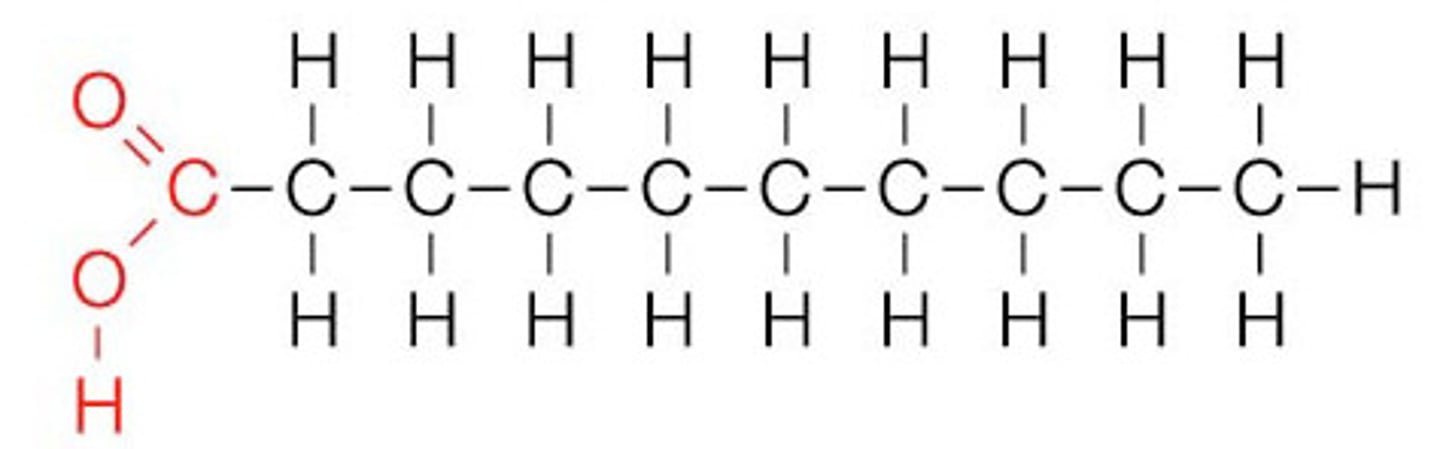
fatty acid/palmitic acid structure
1. long hydrocarbon chain and is hydrophobic
2. carboxyl group (--COOH) and acts as an acid, and in aqueous it is --COO- and is hydrophilic and reactive
fatty acids have both
hydrophobic and hydrophilic components
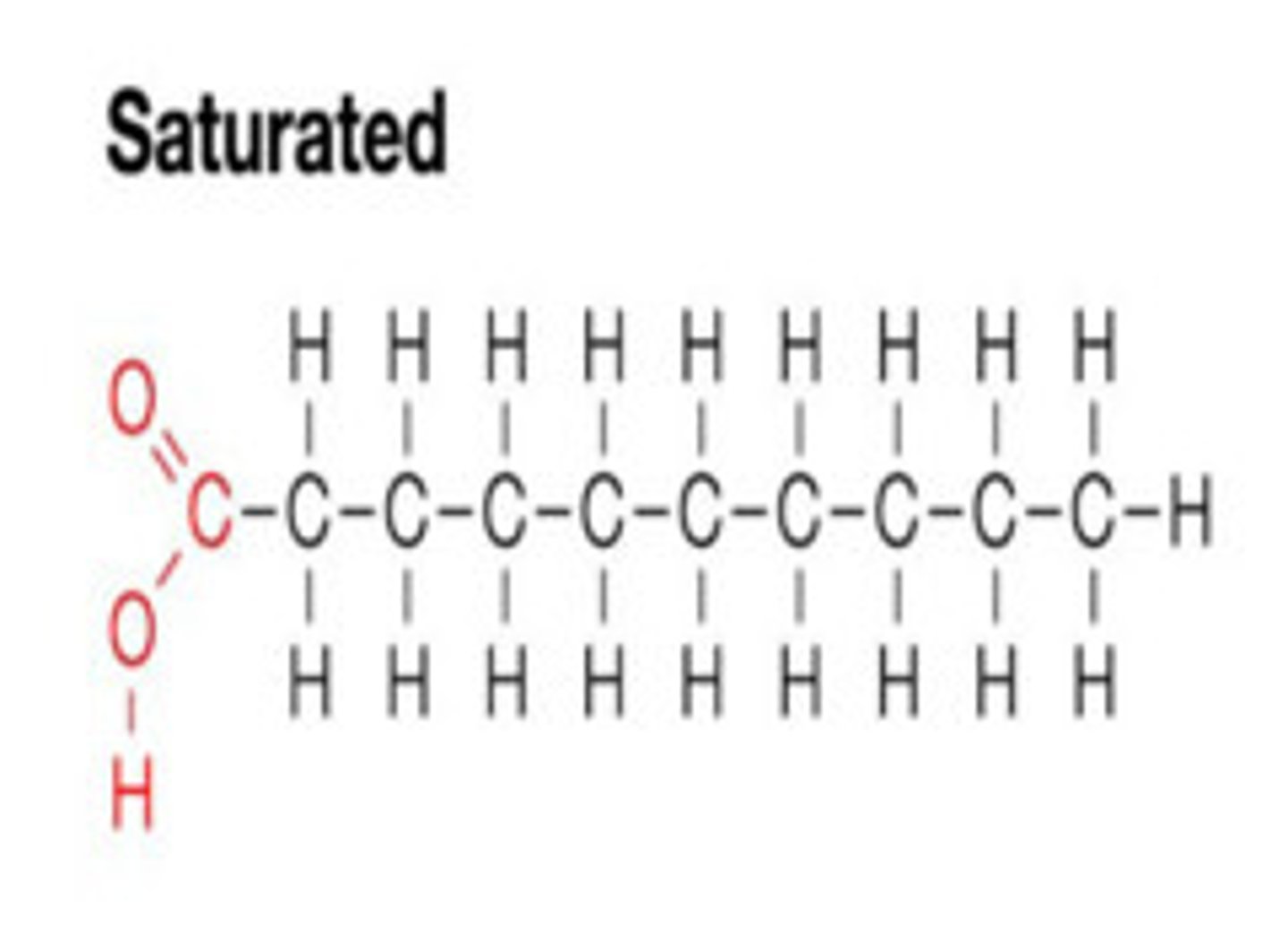
saturated palmitic acid
max number of H and NO double bonds
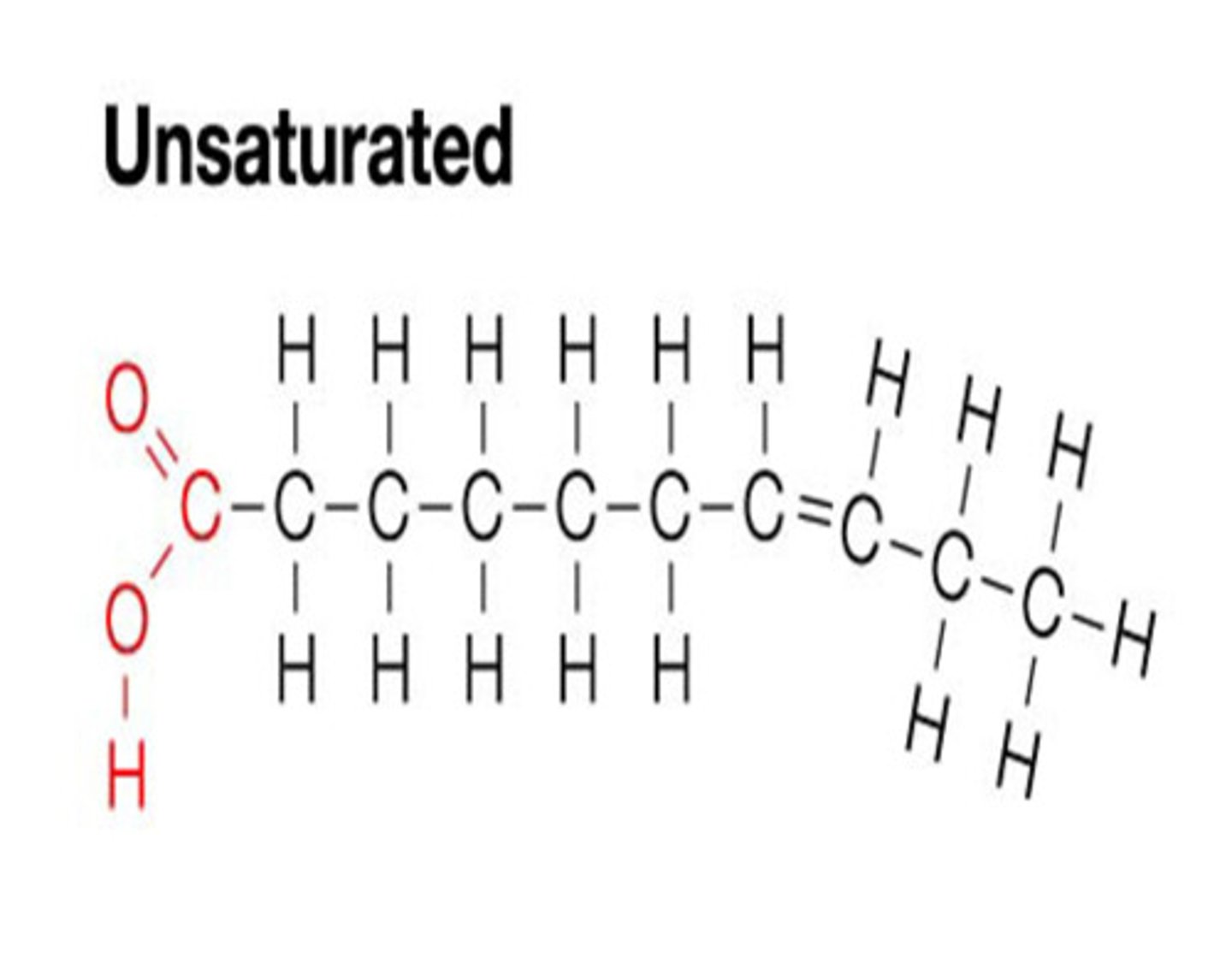
unsaturated palmitic acid tails
one or more double bonds and created kinks
-cannot pack together
fatty acids are stored as
glycerol in the cytosol
lipids are insoluble in
water (hydrophobic)
lipids are soluble in
fat and nonpolar organic solvents like benzene
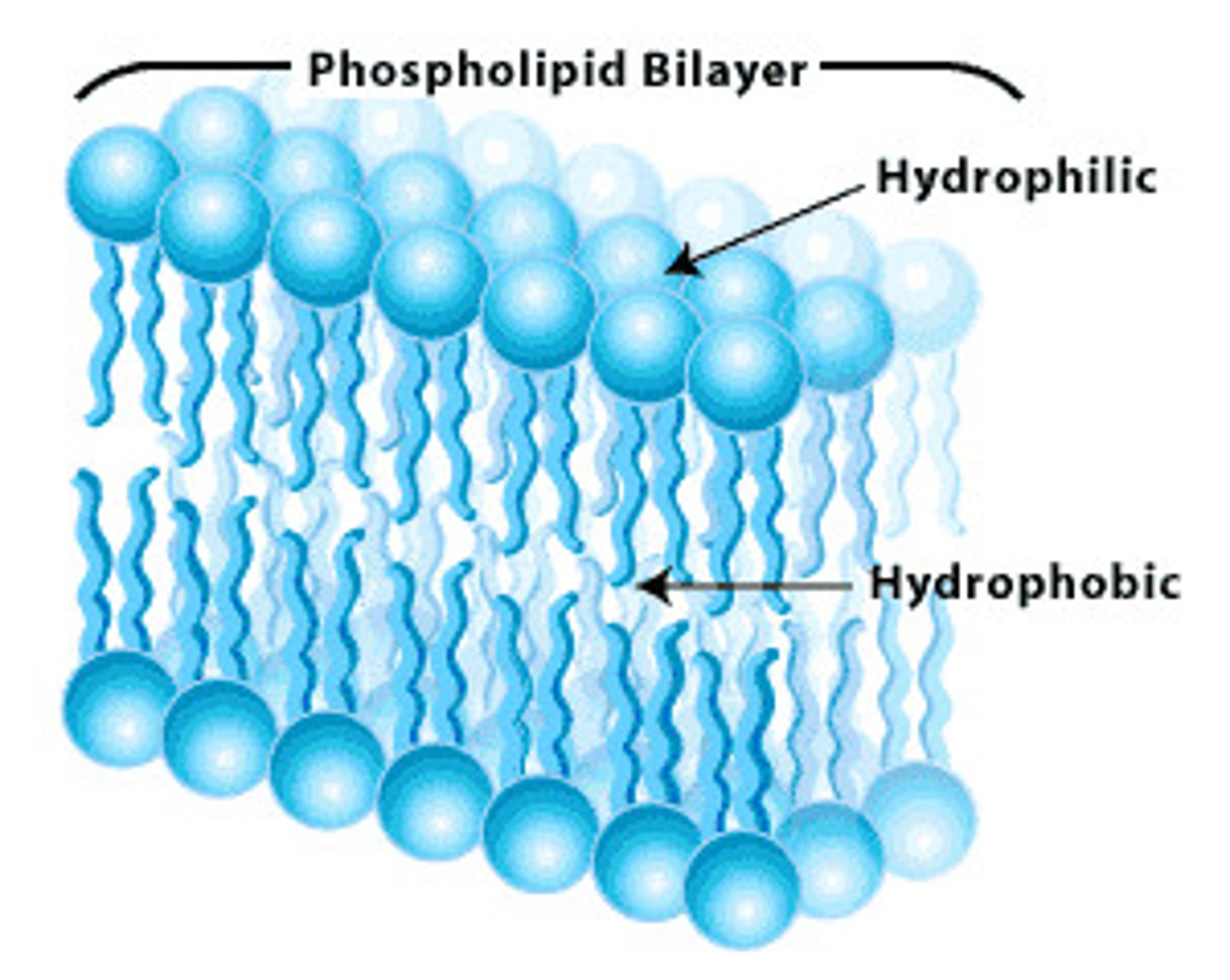
phosopholipid bilayer
hydrophilic head facing towards aqueous environment and hydrophobic fatty acid tails facing inwards
fatty acid groups
--OH and -COOH or -COO-
amino acids are the monomers
proteins
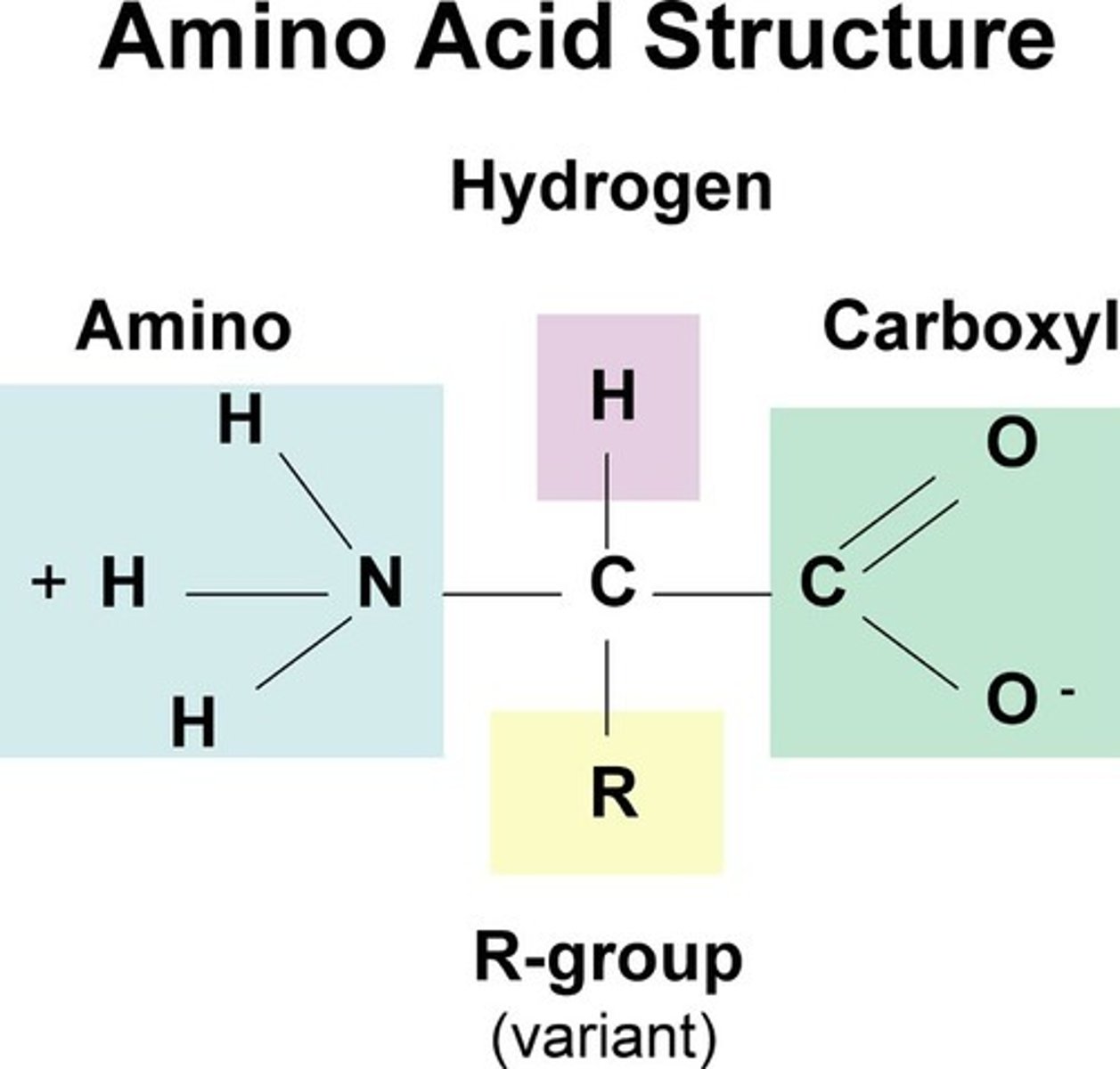
all animo acid groups
-COOH and --NH2
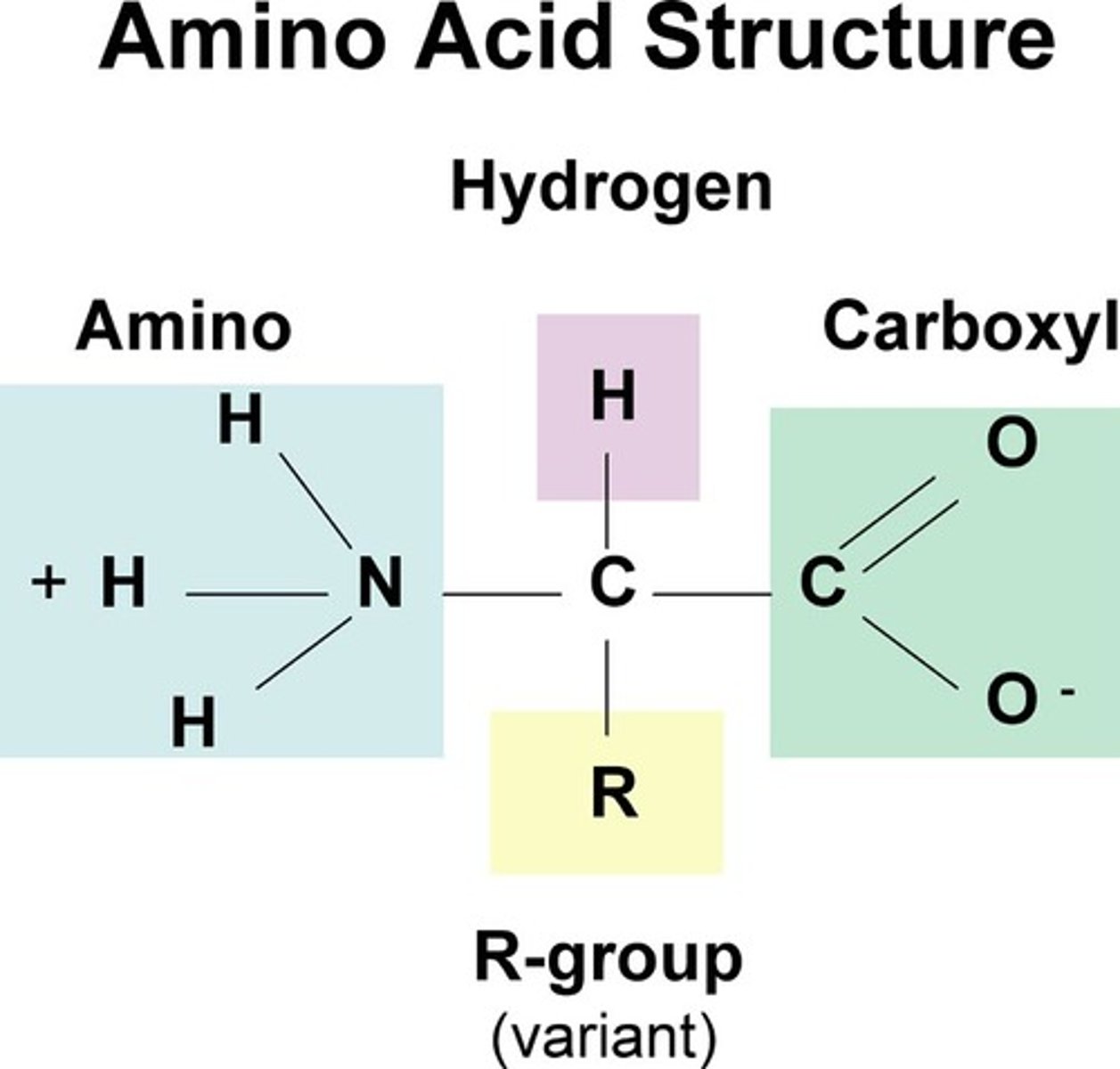
protein is a polymer made of
monomers of animo acids
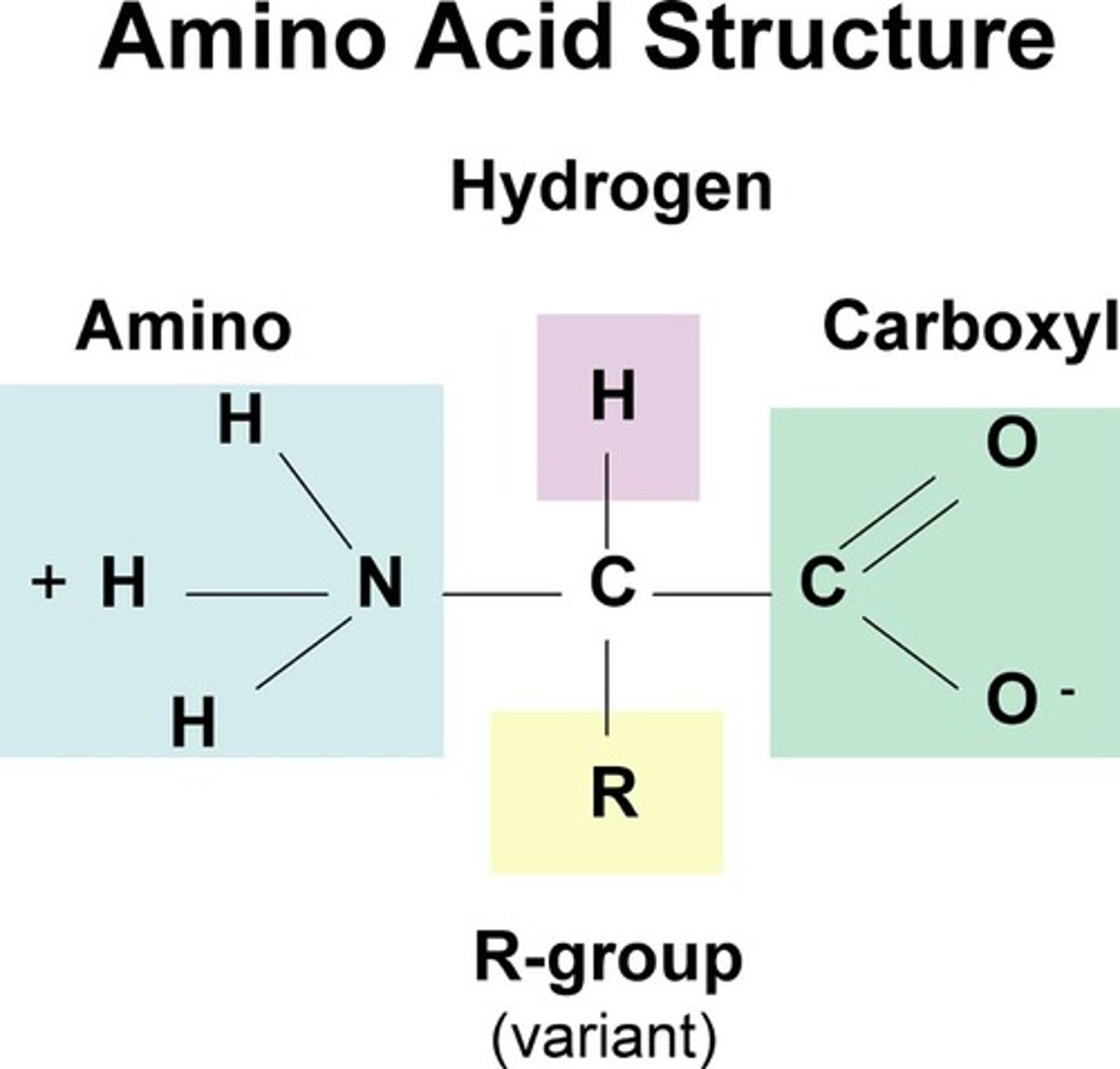
peptide bonds
Covalent bonds linking amino acids in proteins.
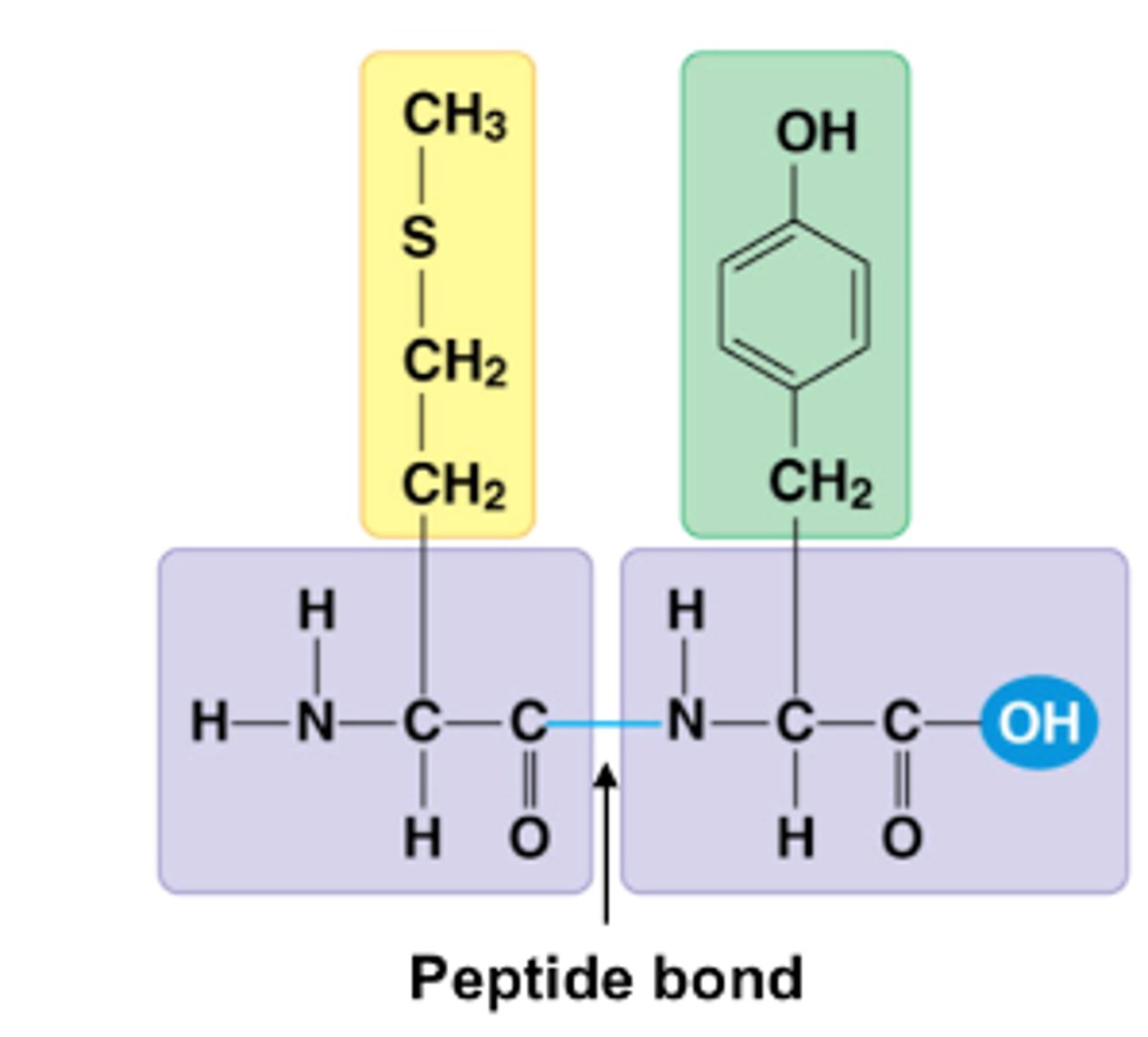
peptide bonds are formed by
condensation bonds
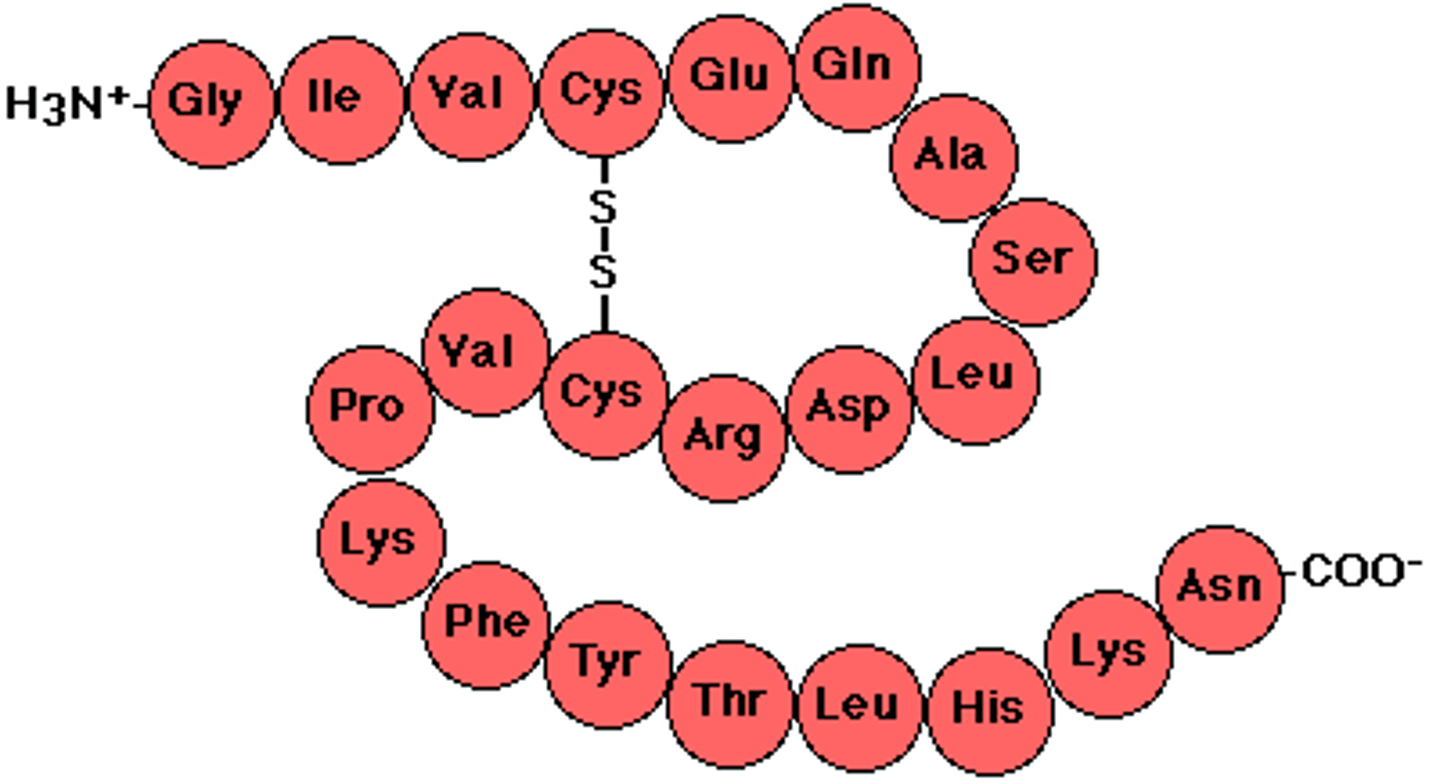
polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
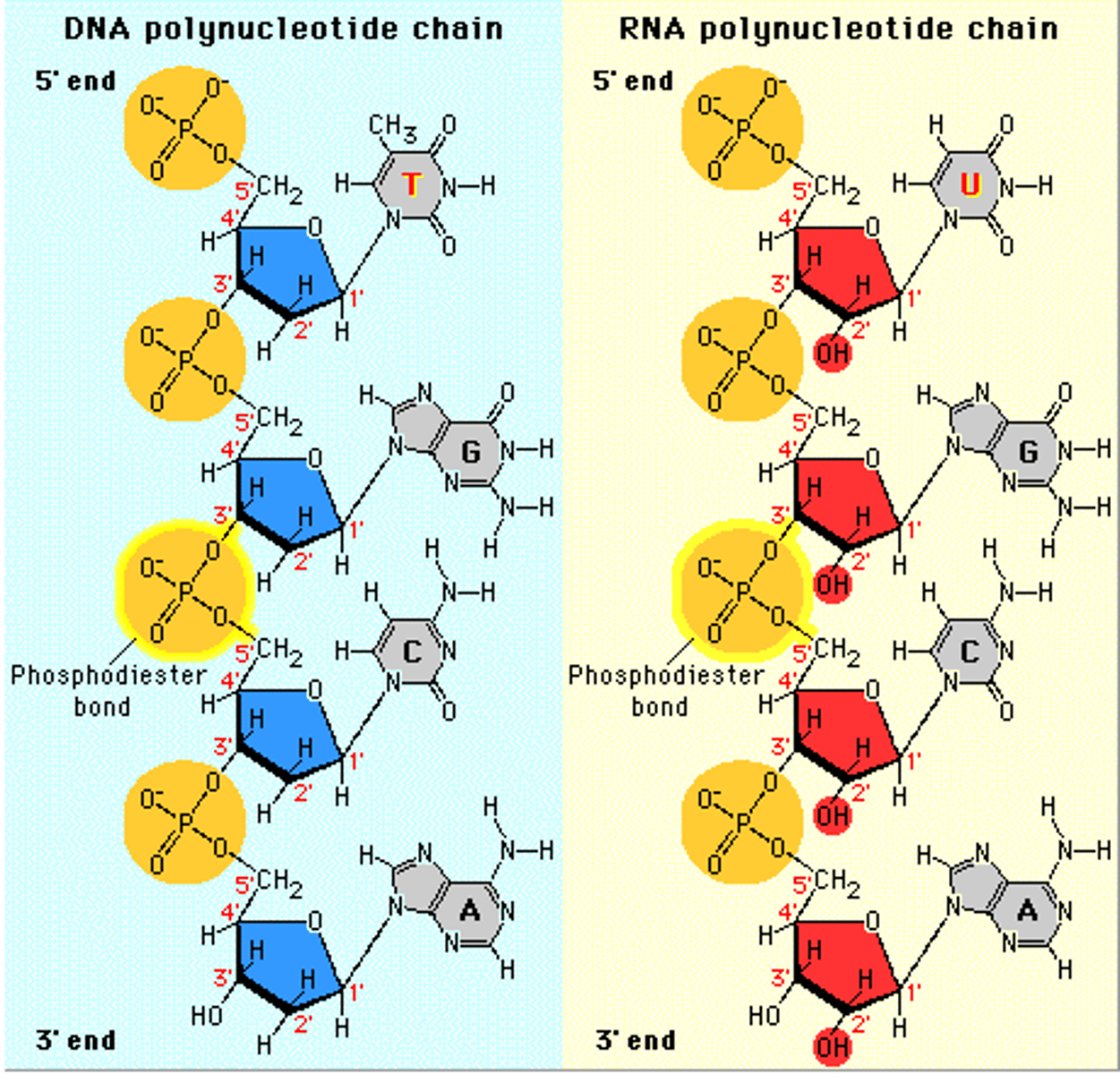
nucleic acid monomers
nucleotides
nucleic acids polymers
DNA and RNA, polynucleotides
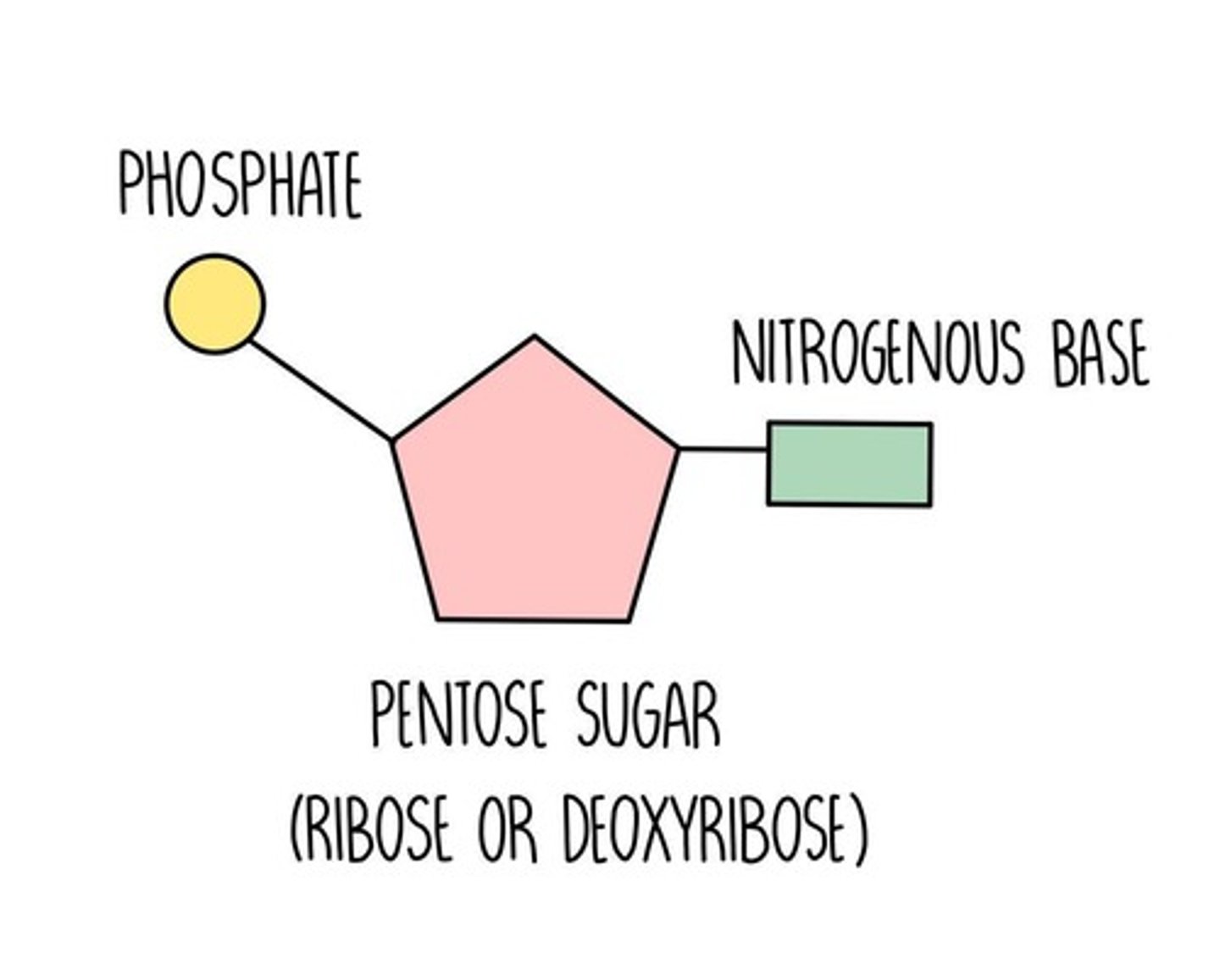
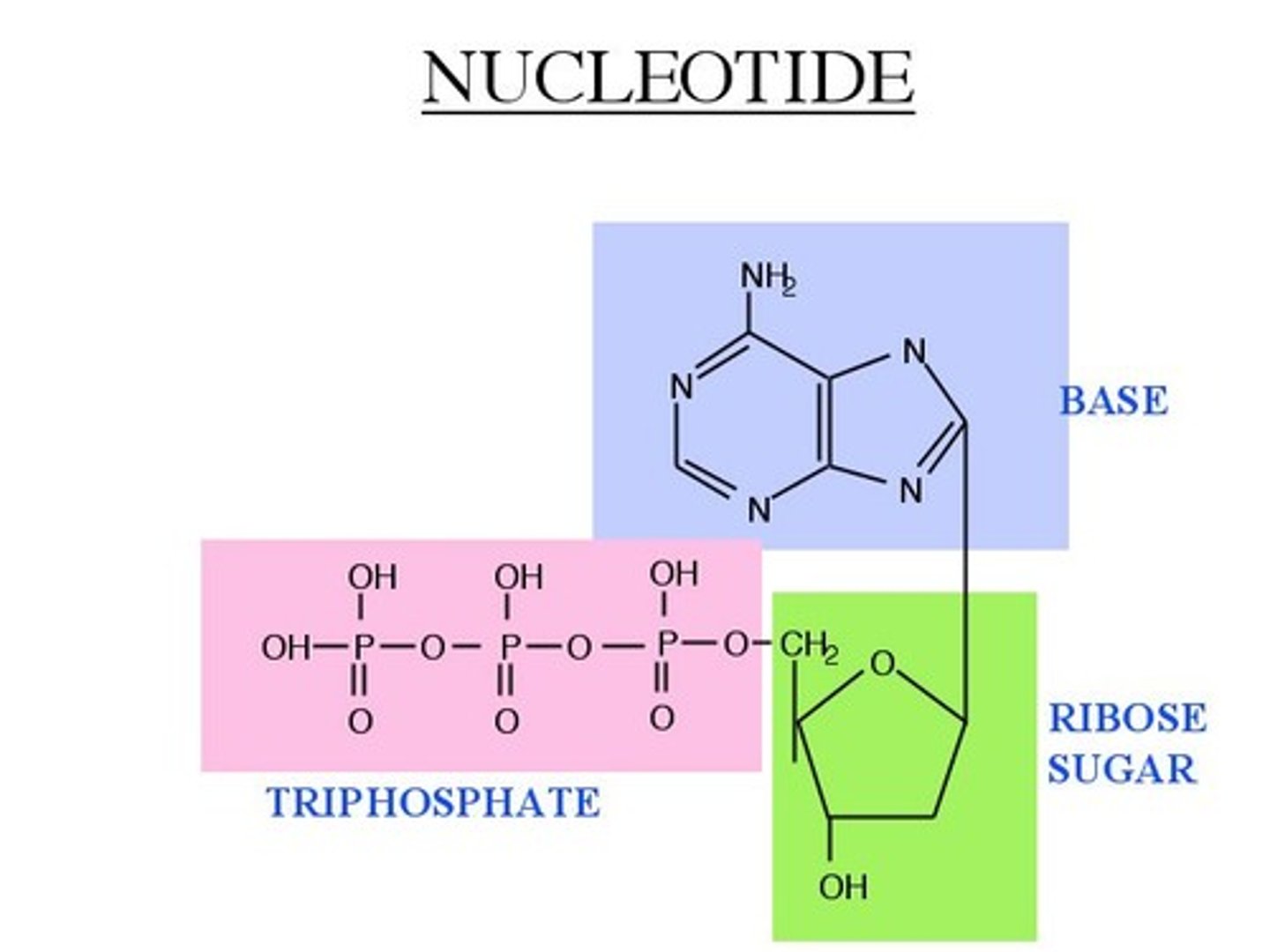
nucleotide structure
5 carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), phosphate group, nitrogenous base
ribonucleotides
Nucleotides containing ribose sugar (RNA monomer)
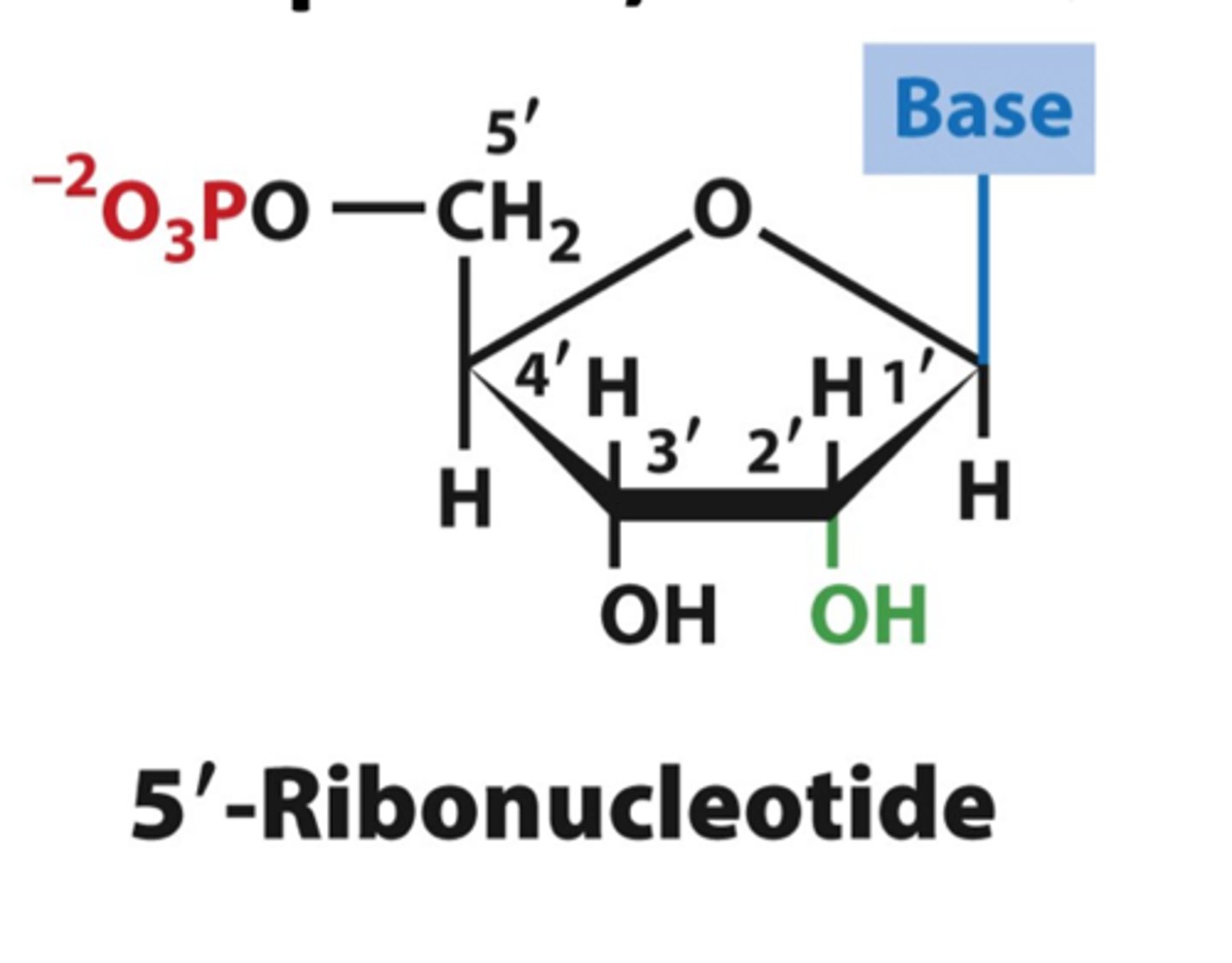
deoxyribosenucleotides
nucleotides containing deoxyribose sugar (DNA monomer)
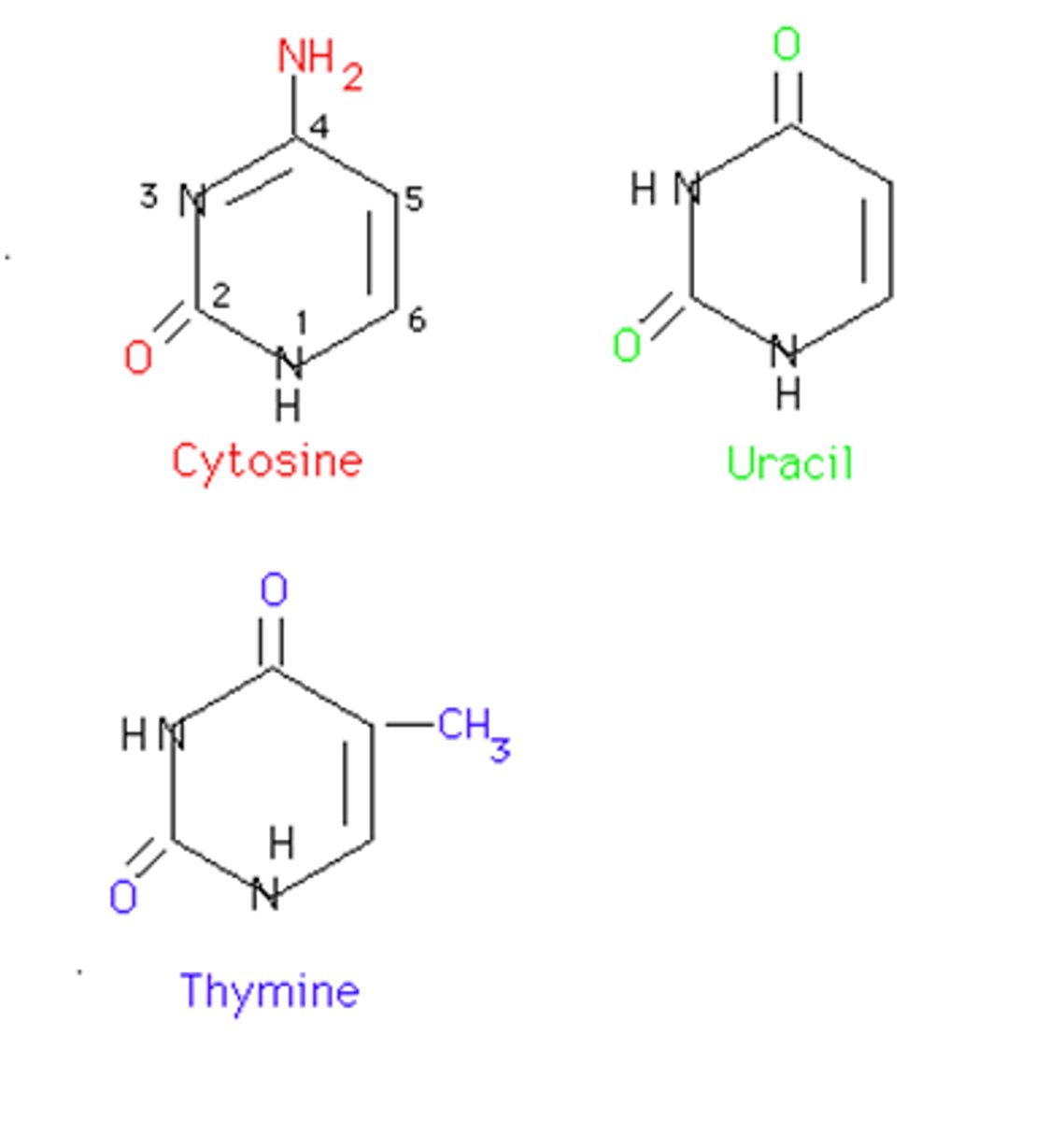
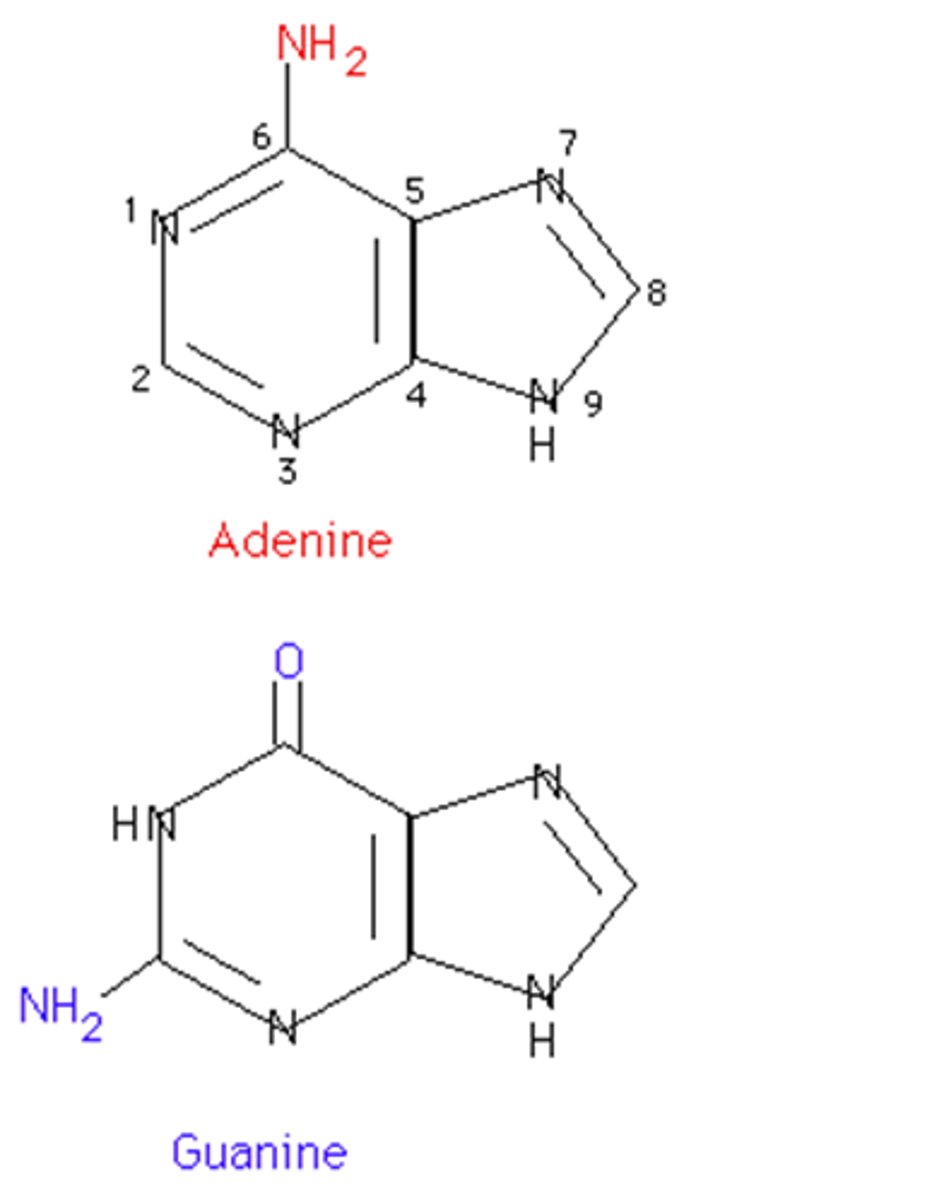
Pyrimidines
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil derived from 6-ring pyrimidine ring
purines
Adenine and Guanine 5-ring
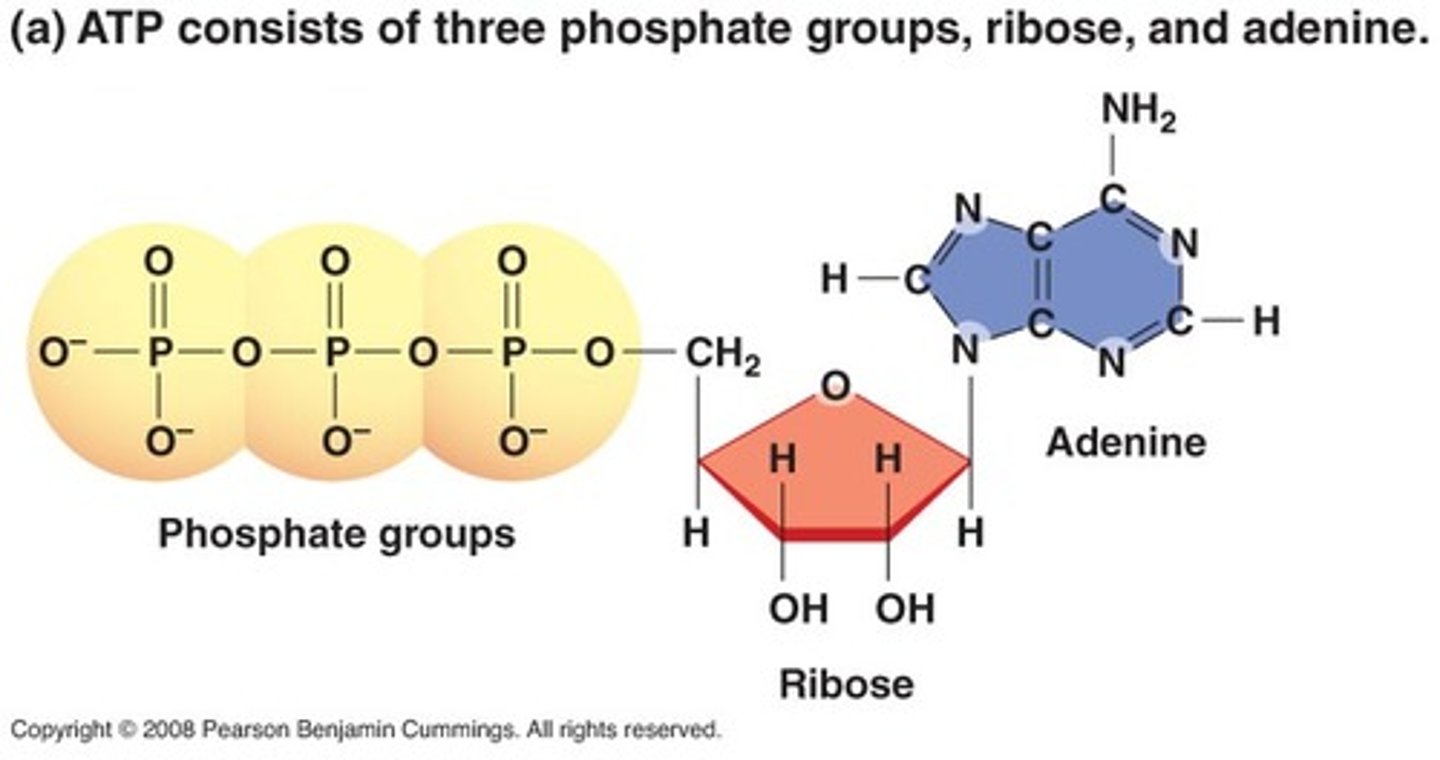
ATP structure
adenine (nucleotide), ribose, 3 phosphate groups
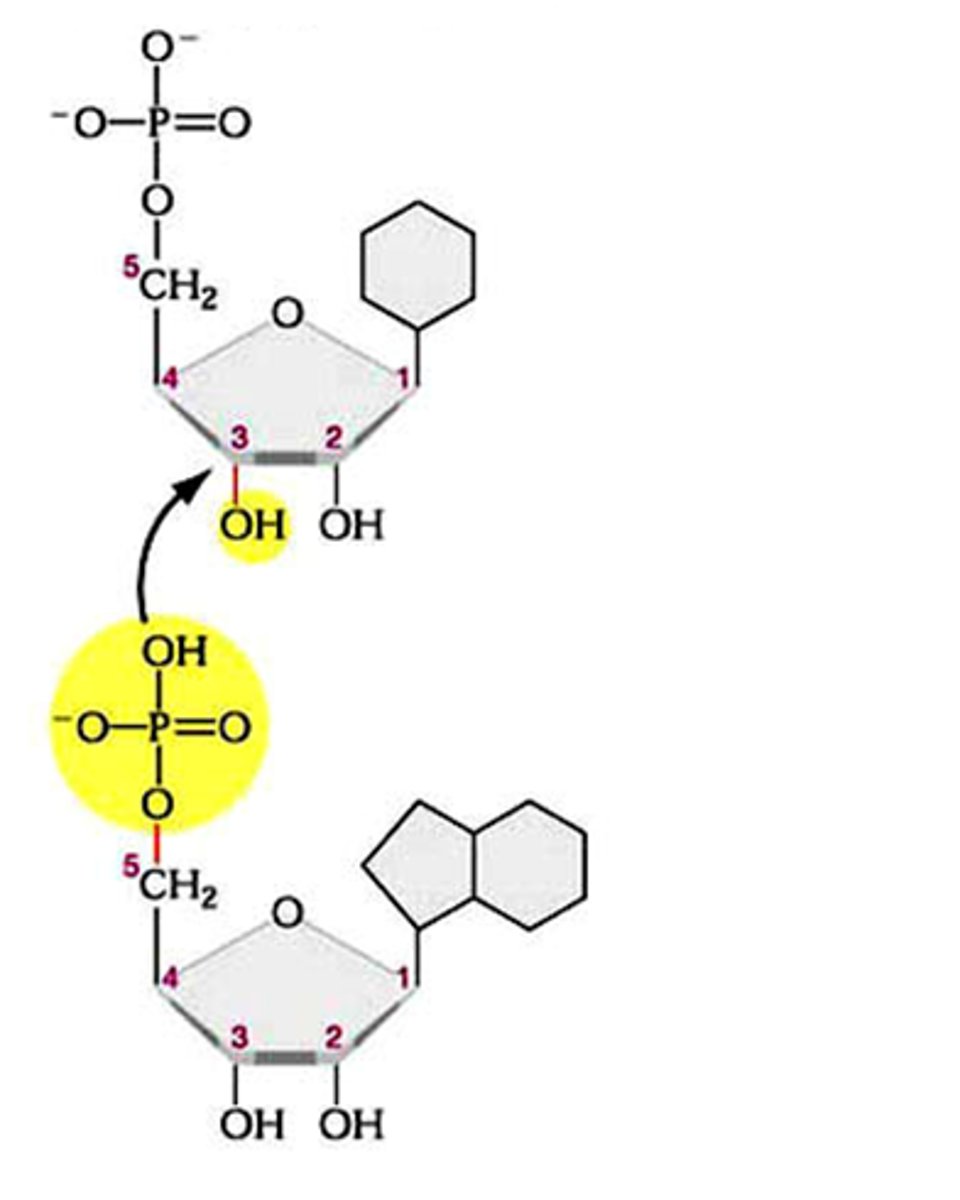
phosphodiester bonds
Bonds between phosphate group and pentose sugar in nucleic acids.
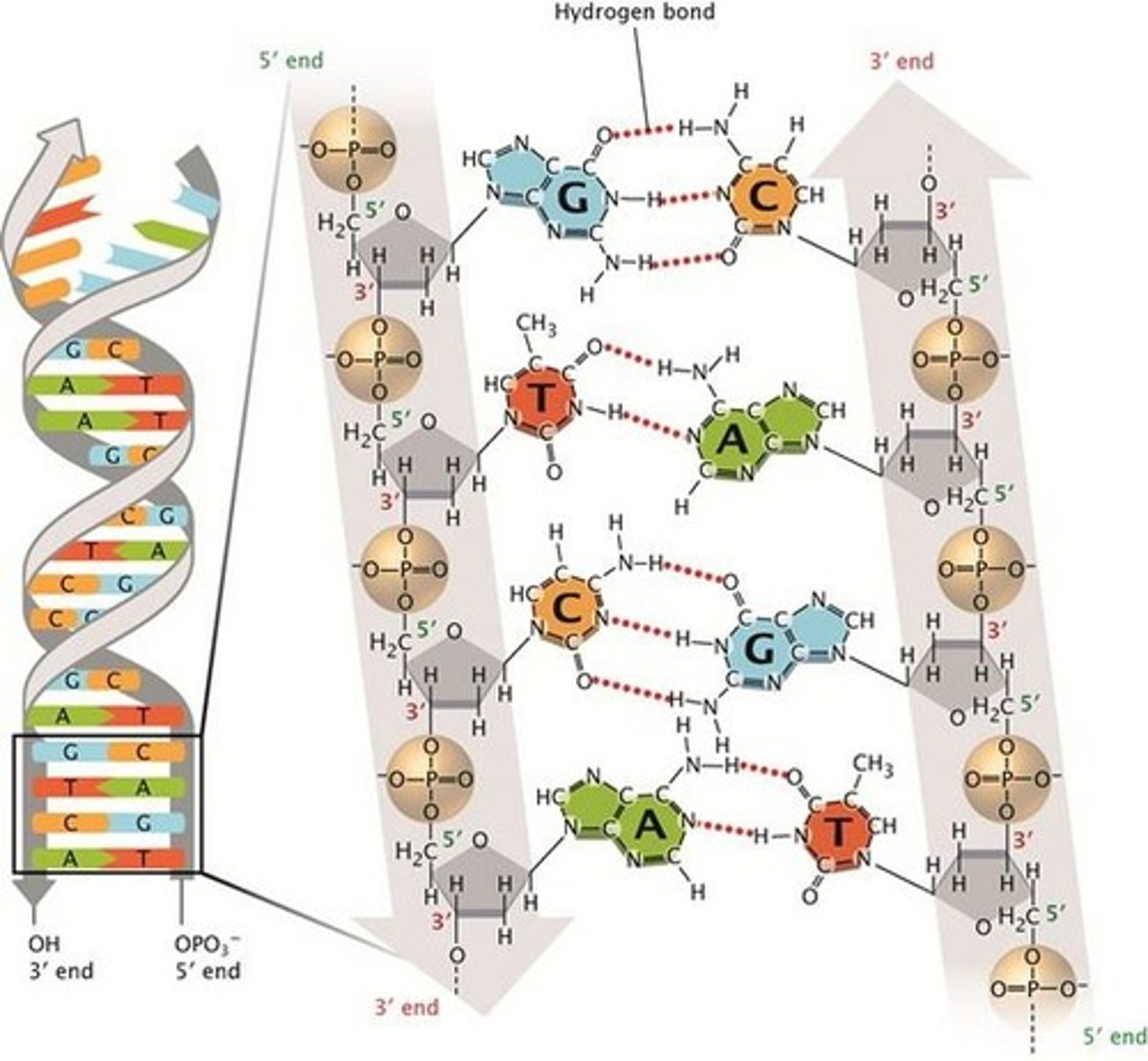
DNA double helix structure
composed of 2 polynucleotide chains that run in opposite directions and held together by H bonds between bases
polymers grow by
Addition of a monomer onto one end of the polymer chain by condensation rxn
the function of polymers are determined by
sequence of monomers/subunits
shape and sequence of macromolecules determines
the function
what is needed to form a macromolecular assembly such as a ribosome
covalent and noncovalent bonds
nucleotides function
-energy transfer (ATP)
-forma RNA and DNA molecules
How is protein, RNA, and DNA molecules formed
from monomers/subunits by condensation reactions
noncovalent bonds
Weak chemical bonds in which no electrons are shared
Ex: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals
how do protein chains fold?
noncovalent attractions
how do macromolecules bind to other molecules?
noncovalent attractions
electrostatic attraction
the attraction between positive and negative charges Ex: ionic bonds and polar covalent bonds