CT 1-2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
the number of x-rays detected by each detector
what is the CT quantum mottle directly related to?
describes the noise resulting from the finite number of x-rays used to make an exposure
what is the quantum mottle in x-ray?
computerized axial tomography
define CAT
computed tomography
define CT
x-rays that pass through patients body
what does CT measure?
computer to perform complex mathematics
what is needed to make CT into images?
x-ray tube produced a thin, focused beam of x-rays (pencil beam) that passed through a single detector, moved across the patient at 1 degree and 5 min/image
describe the first CT scanner
fan beam (x-ray beam shaped like paper fan) with multiple detectors in a straight line, moved across the patient at 5 degree angle and about 20 sec/image
describe 2nd generation scanner
fan beam with multiple detectors along a curve, tube and curved array of detectors rotate around the patient, and 1 sec/image
describe 3rd generation scanner
fan beam with multiple detectors encircle patient, tube rotates around patient, and < 1 sec/image
describe 4th generation scanner
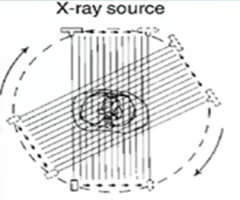
1st generation (parallel beam)
this shows what type of CT scanner?
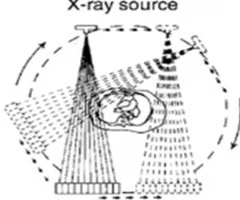
2nd generation (fan beam)
this shows what type of CT scanner?
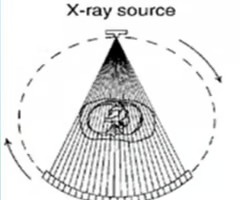
3rd generation (fan beam rotate only)
this shows what type of CT scanner?
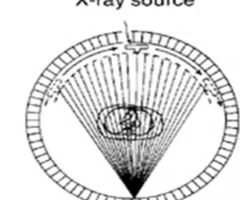
4th generation (fan beam stationary circular detector)
this shows what type of CT scanner?
reduced time required for exam and increases clinical applications
why were continuous rotation scanners a good development?
allows for continuous rotation of x-ray tube assembly
what is a slip ring?
slip rings
what is the reason for rotation speed?
slip rings
why dont we need power and data cables for 4th generation scanners?
stationary metal contacts through which electrical signals and power are transferred to and from the rotating slip ring
what are electrical brushes?

eletrical brushes
what is in the image?
collects info from multiple anatomical slices in each rotation of the x-ray tube
what is a multi-row scanner?
more anatomical coverage in less time
why are multi-row scanners better than single?
MDCT or MSCT (parallel or 3rd gen)
what detectors can be multi-row?
x-ray beam shape similar to a cone that spreads out like a fan along the table
describe cone beam
cone
what type of beam is now standard?
Electron beam CT; scanner that has no x-ray tube allowing it to have fast scan time
what is EBCT?
cardiac and coronary artery imaging
what is EBCT good for imaging?
when the electron beam strikes the anode
how is an x-ray beam generated on an EBCT?
a fusion of PET and CT image
what is PET/CT
attenuation correction and anatomical clearity
why do we do PET/CT?
size and spacing of detectors
size of focal point
reconstruction filters
what are factors contributing to spatial resolution of a CT?
with small bars of acrylic and then imaged
how is CT spatial resolution checked?
mA
what effects image contrast most?
images slice thickness
spatial resolution
linearity of CT numbers
high and low contrast
what does monthly/quarterly CT phantom do?
verification of tube output and detector response at different kVp and mA settings
what does a CT warm up do?
tube warm-ups
fast calibrations
CT phantom
what QC must be done for CT
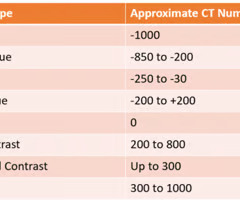
1000
what is bone hounsfield unit?
-1000
what is air housfield unit?
0
what is water hounsfield unit?
1000 * (Uij-Uwater/Uwater)
Hu =
tissue attenuation values
what do hounsfield units express?
mA
what increases contrast resolution
slice thickness
rotation speed
table motion
what decreases patient dose?
mA and kVp
what increases patient radiation dose?
kVp, mA, slice thickness, more x-rays per detector, increase beam intensity, decrease pitch
what decreases CT noise?
30-150 kV
what is average kVp range?
50-400 mA
what is average mA range?
helical ro spiral; multislice
what types of CTs have pitch? which have beam pitch?
table moves 2 mm every 1 mm of detector width
what is implied with a collimator pitch of 2
increase number of x-rays at each energy level
what does higher mA values do?
right, more
as kVp gets higher it stretches the energy spectrum to the ______ (left, right) by generating ______ (less, more) higher energy x-rays
energy transferred to x-ray in bremsstrahlung interaction
define kVp
step and shoot for the heart
what is multi-slab axial?
full circle around a small region of interest
what is axial scanning
full circle but scanner moves continuously
what is helical scanning?
ceramic material
cadmium tungstate
bismuth germinate
what can CT detectors be made out of?
50-150 kV
at what kV are electrons accelerated toward the anode?
causes it to release electrons via thermionic emissions
why does the filament circuit need to be heated?
heating the filament wire from electrical resistance
what does the activation of a cathode filament circuit cause?
no, stationary usually
do the brushes move with the slip rings
each ring is electronically conductive and provides circuit path over 360 degrees of rotation and has electrical contact with brushes between the rotating rings
describe the arangement of slip rings
electrical swivel
what is another name for slip ring
measured x-ray photon information that must be processed/ reconstructed to form CT images
what is CT raw data?
by absorption (never leave body) or scattering (interact with structures and change direction)
what are 2 ways x-ray photons are attenuated
reduction in the number of photons in the x-ray beam as it passes throguh the tissues in patients body
define attenuation
bremsstrahlung radiation
how are majority of x-rays produced?
x-ray produced as a result of an electron colliding with or passing near nucleus of an atom
define bremsstrahlung
x-ray produced as a result of an electron in target replacing one ejected by a fast moving incoming electron
define characteristic radiation
electron in target is kicked out, another electron of target atom moves into that location and releases excess energy (x-ray)
what happens if the electron collides with an electron?
directly collide with nucleus
come near nucleus
collides with another electron
what are some ways the electron can interact with the target?
tungsten becasue has high number of electrons (high atomic number) and very high melting point
what is a CT target made out of and why?
electrons are accelerated at very high speeds towards a target
how does a CT work?
traumas and evaluate extent of damage
what are some reasons to CT orthopedic?
kidney stones, blockages, abnormal growths
what are some reasons to CT the urinary tract?
cysts, abscesses, infection, bleeding, tumors, aneurysms, diverticulitis, appendicitis,
what are some reasons to CT the abdomen?
infections, cancer, PE, aneurysms, cardiac, coronary artery
what are some reasons to CT the chest?
see facial bones and sinuses
what are some reasons to CT the head?
there isnt one federally
what is the CT dose limit?
x-rays indirectly produce ion pairs in tissues as they pass through which can interact with chemical systems in the body causing DNA damage
what is x-ray damage?
cause detrimental changes in the atoms and molecular processes
what can ionizing radiation do to the body?
ionizing radiation
what is the disadvantage of CT?
easily stored
accurately reproduced from stored data
electronically transferred to another facility
easily manipulated and processed
what are the advantages of digital information?
information expressed in a continous fashion
define analog
information expressed in terms of discrete numbers
define digital
< 0.5%
what percentage can a CT differentiate density differences?
differentiate tissues in body from each other
what is the greatest advantage of a CT?
axial
all slices are considered
perpendicular to axis which travels from anterior to posterior in patient
what are coronal slices
perpendicular to the axis which travels from left to right in the patient
what are sagittal slices?
perpendicular to the axis which travels from head to foot in patient
what are transverse slices?
sections made by cutting anything at right angles to any axis
what are cross sections?wh
linear accelerator treatment table
what type of table is used for radiation therapy?
oncology to verify patient positioning prior to receiving radiation therapy
what is cone beam most commonly used for?