B4 MUSCLES
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What’re the 3 types of muscles found in the body?
cardiac
skeletal
smooth
What’re features of skeletal muscles?
function is locomotion
cells are striated
contraction is voluntary and conscious
have regular arrangement so the muscle contracts in one direction
contraction is rapid
short length of time contracted
What’re features of cardiac muscle?
function is pumping blood through the heart
cells are specialised striated
contraction is involuntary
cells branch and interconnect to allow efficient transfer of impulses so brings about simultaneous contraction
contraction is intermediate
intermediate length of time contracted
What’re features of smooth muscle?
function is to line blood vessels, digestive tract and uterus
cells are unstriated
contraction is involuntary
no regular arrangement as different cells can contract in different directions
contraction is slow
can remain contracted for a relatively long time
How are skeletal muscles attached to bone?
by tendon
How do skeletal muscles work?
can only pull
antagonistic pairs work together
agonist contracts while antagonist relaxes
What is the structure of the skeletal muscle?
composed of many highly specialised muscle fibres bound by connective tissue
What’re features of muscle fibres?
surrounded by a thin cell membrane (sarcolemma)
nuclei is found beneath the sarcolemma
sarcoplasm contains a large number of mitochondria
cell contains a large number of myofibrils which run parallel to eachother (surrounded by the sarcoplasmic reticulum)
What’re features of myofibrils?
made up of myofilaments
myofilaments are divided into thick (myosin) and thin myofilaments (actin)
myofilaments are arranged into sarcomeres
What is the structure of a sarcomere?
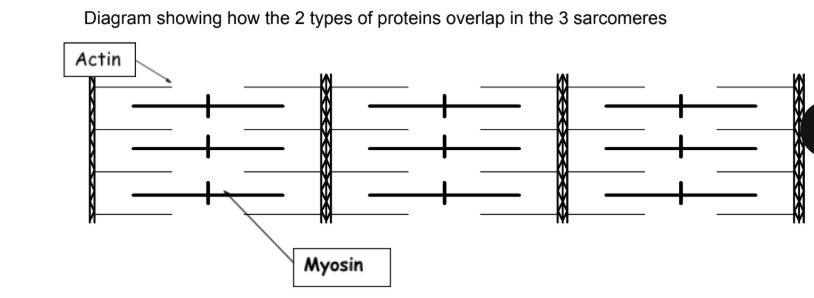
What happens to the Z lines and the I band when the muscle contracts?
they decrease in length
What happens to the A band when a muscle contracts?
stays the same length
What is the A band, Z line, M line and I band?
A band- dark region which contains the entire length of myosin
Z line- boundaries of the sarcomere
M line- central line of the sarcomere
I band- light region which contains only actin filaments
What is the structure of an actin filament?
thin filaments in sarcomere which has a binding site for myosin head, when the muscle is relaxed the binding site is covered by tropomyosin
What is the structure of myosin?
thick filaments in sarcomere that have hinged globular heads so they can move back and forth. each myosin has a binding site for actin and a binding site for ATP
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum where they bind to the tropomyosin protein, change its shape and exposes the binding site
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
molecule that releases the energy for muscle contraction. it bindsss to myosin which releases ATP causing the myosin head to bend
What is the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
a protein on actin filament which blocks the actin-myosin binding site at rest
What occurs in the sliding filament theory?
calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
calcium ions bind to protein receptors on the tropomyosin, which are complementary to the calcium ions causing the tropomyosin to move
this exposes the myosin-head binding sites on the actin filament
myosin heads bind to actin binding sites and form cross bridges
each myosin head contains ATP which is hydrolysed into ADP and Pi by ATPase, causing a power stroke which pulls the actin filament a short distance
a new ATP attaches to myosin head which breaks the cross bridges and separates it from the actin
this process repeats moving the actin along a bit more each time
What is the role of ATP in the sliding filament theory?
hydrolysis of ATP causes myosin heads to bend
attachment of new ATP molecules causes myosin heads to detach
What is phosphocreatine?
stored by muscles
donates a phosphate to ADP to regenerate ATP in the short term
phosphocreatine can be regenerated utilising ATP when it can be supplied via respiration
What’re the 2 types of muscle fibres which skeletal muscles are made up of?
slow twitch
fast twitch
What’re features of slow twitch muscle fibres?
slow speed of contraction
found in large proportions in muscles used for posture
slow rate of fatigue
good for endurance activities
energy is released slowly through aerobic respiration so have many mitochondria and are surrounded by capillaries to supply oxygen and glucose
red due to myoglobin
What’re features of fast twitch muscle fibres?
faster, stronger speed of contraction
found in large proportions in muscles used for fast movement
fast rate of fatigue
good for short bursts of speed
energy is released quickly by anaerobic respiration using glycogen, so they have fewer mitochondria and capillaries
paler in colour due to no myoglobin
How are slow twitch fibres adapted?
uses aerobic respiration to regenerate ATP, so have many large mitochondria
high concentration of myoglobin to act as an oxygen store
very closely associated with a large number of capillaries to provide an oxygen supply
less extensive sarcoplasmic reticulum as fewer calcium ions required
less glycogen as glucose is broken down fully
How’re fast twitch fibres adapted?
use anaerobic respiration (phosphocreatine) to regenerate ATP
fewer, smaller mitochondria
low concentration of myoglobin
fewer capillaries associated with fibres
extensive sacoplasmic reticulum as more calcium ions are required at one time for rapid intense contraction
more glycogen as more glucose required as aerobic respiration yields less ATP per glucose