3.6 - government debt, budgets, financing
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
government (national/ public) debt
amount of money that a government owes to lenders outside of the government itself
accumulation of deficits minus surpluses
government budget
plan of a country’s revenues and expenditures over a period of time
balanced budget
expenditures = tax revenues
(*rarely happens)
budget deficit
expenditures > tax revenue
(*happens very often )
financed by borrowing
budget surplus
expenditures < tax revenue
financing government debt with borrowing
borrowing withing country
borrowing from foreign countries
*great need for borrowing during recession to finance
borrowing allows for continued spending without increasing taxes
sustainable debt
level of debt where government has
enough revenues to meet its debt obligations (interest + repayment of borrowed amount)
without accumulating arrears (overdue debt payments)
while also allowing economic growth to continue at an acceptable level
ways of borrowing
issuing bonds
directly from financial institutions
issuing bonds explanation
certificate that promises to pay interest at various intervals until the moment it is repaid to the bondholder.
holder of bond = lender
financial investors (individuals, firms, banks) have incentive to buy bonds because income they receive
issuers of bond = borrowers
measurement of debt
debt-to-GDP ratio
share of rGDP od the borrowing country
costs of high levels of debt
debt servicing costs → payment that must be made in order to repay the amount of the loan + interest
poor credit ratings
debt servicing costs explanation
debt servicing costs ↑ = opportunity costs↑ = money to spend on social services and infrastructure ↓
when debt is from foreign lenders they must be repaid in foreign currencies
governments to pay use exports revenue
hence less money for imports
foregone imports = opportunity cost → negative consequences for economic growth
poor credit rating explanation
high credit rating
pay back loans in full and on time without difficulties
low credit rating
difficult to find investors
difficult to borrow from financial institutions
impacts of higher taxation and lower government spending
to achieve budget surpluses
increased income inequality
lower private investment
loss of market confidence
possibility of debt trap
lower economic growth
reasons for increased taxation and decreased spending being politically unpopular
reduced gov. spending and investment may lead to
fall in AD
fall in r GDP
deflationary gap
hence → increased debt-to-GDP ratio
increased income inequality explained
government debt ↑ = bonds issued ↑ = income distribution inequality ↑
buyers of bonds tend to be higher income people
when governments pay them interest it does it through tax revenues
transfer of income away from low income tax payers towards high income
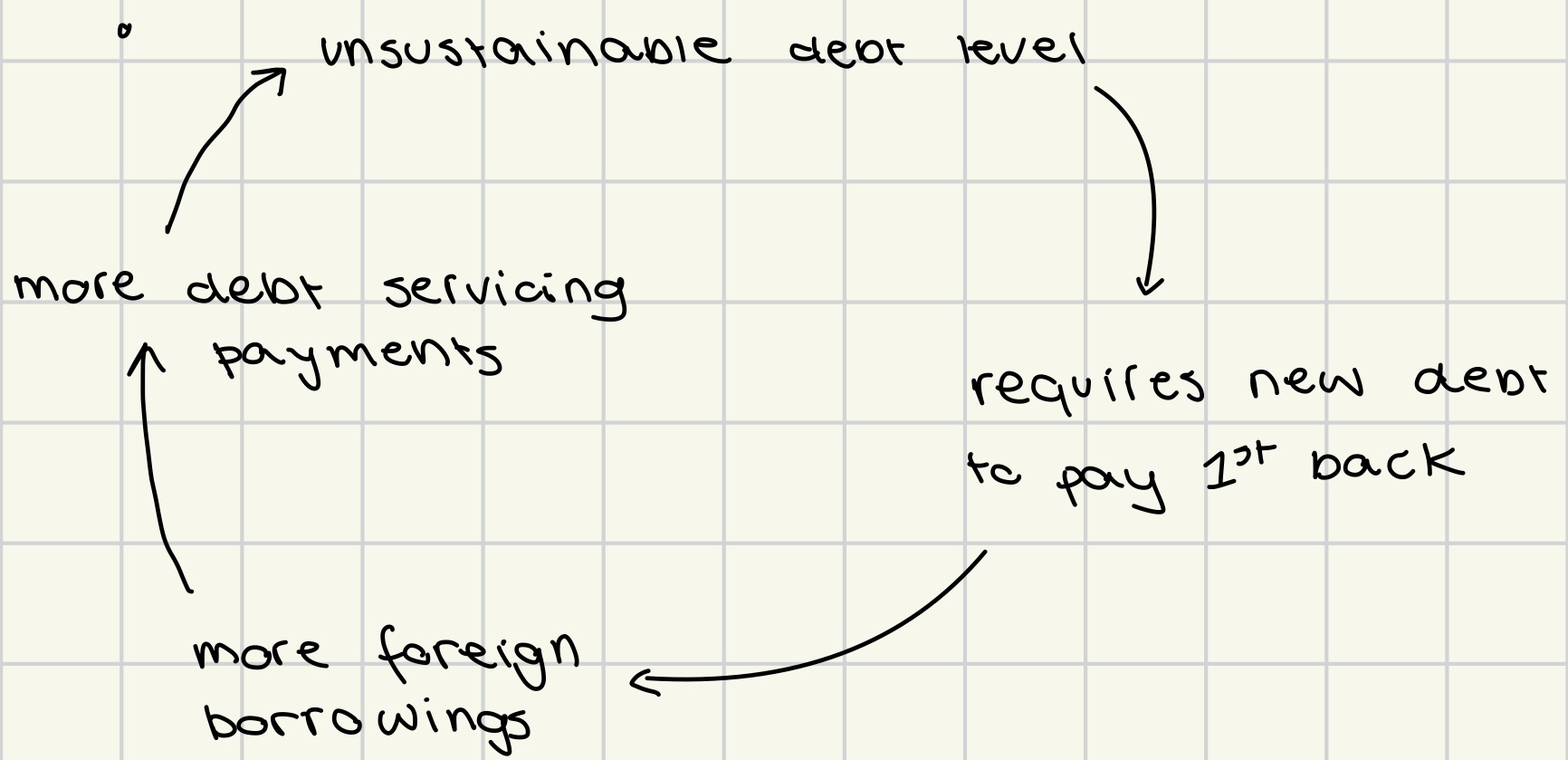
debt trap
country most keep on taking new loans in order to pay back the old ones