Biological membranes
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
Fluid mosaic model
Theory of cell membrane structure with proteins embedded in a sea of phospholipids
Explain why some cells don’t take up a solution during active transport
EQ
Cells are dead
No ATP to take up stain
Describe the effect of high temperatures on the structure of the yeast cell membranes
EQ
Phospholipids vibrate more
More gaps in membrane
Bilayer becomes more fluid
Describe the arrangement and functions of two named components of a cell surface membrane
EQ
Proteins for facilitated diffusion
Barrier to polar and large molecules
What is meant by cell signalling
EQ
Communication between cells
Explain how cell surface membranes contribute to the process of cell signalling
EQ
Exocytosis
Glycoproteins have receptors
Shape of receptors adn signal are complementary
Cell surface membrane allows century of some signal molecules
State one role of membranes inside cells
EQ
Site for enzyme attachment
List 3 components of cell surface membrane
EQ
Phospholipids
Proteins
Cholesterol
Active transport definition
EQ
Movement of molecules from a low to high concentration
ATP required
State 2 examples of active transport in cells
EQ
Ions into root hair cells
H+ ions out of companion cells
What mechanism is involved in this
Calcium ions entering a nerve cell down a concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion
Describe the route that water molecules take through the cell surface membrane
EQ
Between phospholipids
Through aquaporins
Explain why plant cells don’t burst when they are left in pure water
EQ
Cell wall provides strength
Explain why facilitated diffusion requires no energy
EQ
Uses only the kinetic energy of a particle
Down concentration gradient
Via protein channels
Explain why glucose cannot pass through a membrane by simple diffusion
EQ
Too large
Phospholipids act as a barrier
State and explalin how one property of the phospholipid bilayer contributes to the stability of the membrane
EQ
Hydrophobic fatty acid tails point inward to form bilayer
Outline the roles of membranes within cells
EQ
Compartmentalisation
Site of chemical reactions
Explain the role of the membrane in the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Hold ribosomes
Compartmentalisation
Where do the independent variable and the dependant variable go on a table?
EQ
IV first column
DV second column
Suggest and explain why a low PH might cause the red pigment to leak out the beetroot cells
EQ
Denatures proteins
Membrane permeability is reduced
Outline how students could modify their investigation to get a more accurate value for the pH at which the red pigment begins to leak out the beetroot cells.
EQ
Use PH buffer with range with smaller intervals
Test more values between x and y
Explain why progesterone can move across membranes
EQ
Non polar so diffuses through phospholipid bilayer
What 3 molecules have up ATP
Adenine
Ribose
Phosphate groups
How does the fluid mosaic model describe the structure of a plasma membrane.
EQ
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophobic tails inwards
Hydrophilic heads outwards
Explain how the structure of phospholipid molecules allows for the formation of plasma membranes
EQ
Hydrophilic phosphate heads facing outwards
Hydrophobic fatty acid tails point inwards
Phospholipid bilayer
Describe the structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
EQ
Phospholipid bilayer
Covered with ribosomes
Cisternae
For which macromolecules foes a plant need both nitrogen andd phosphorous
EQ
DNA
How would flooding affect the soils water potential
EQ
Lower water potential
What type of graph is needle for absorbance and concentration of ethanol axis
Line graph
Explain how carrying out replicates would improve an investigation
EQ
Calculate mean
Improvement repeatability
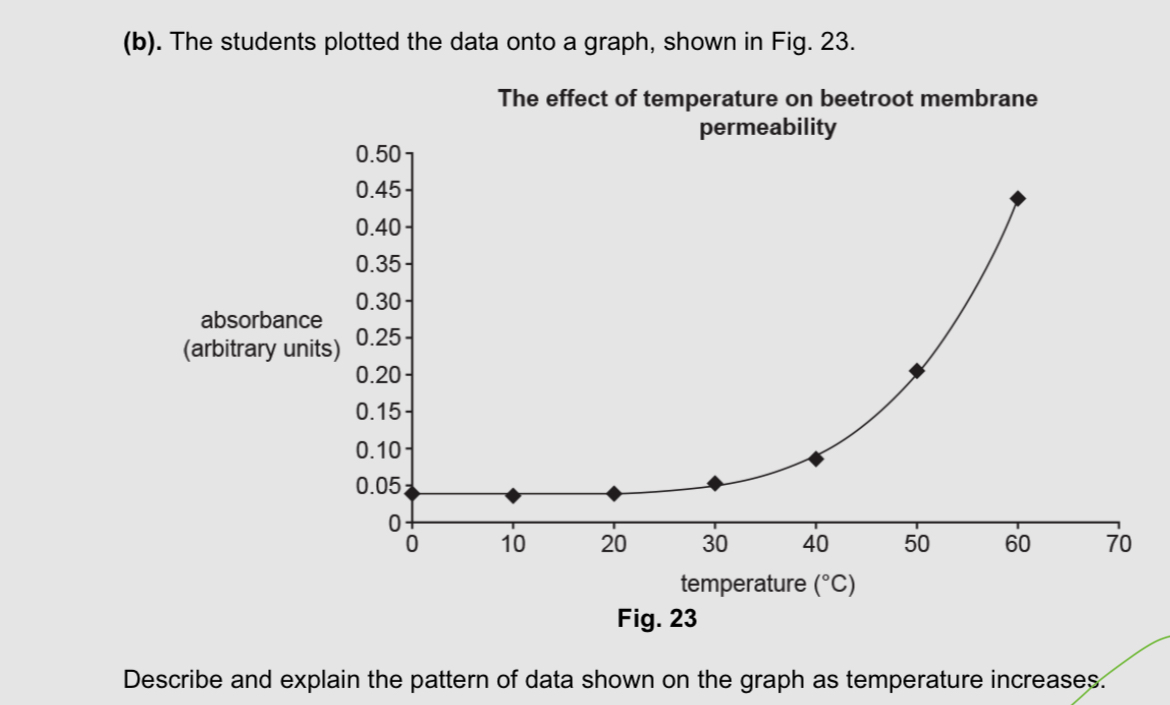
As temperature increases the absorbance increases
Pigment leaves the cell
Temperature doesn’t increase much from 0 to 30
How would using smaller intervals improve an investigation
EQ
More accurate
What do you have to remember when a question asks why something can pass through a membrane
EQ
Can DIFFUSE through phospholipid bilayer
How do you make a practical more precise
EQ
Repeats to calculate a mean
Smaller intervals
What should you include in a hypothesis?
Anomalies
General trend of graph
How do you increase the thickness of a Viking tube?
EQ
Use 2 visiting tubes
What is the role of a universal indicator?
EQ
Measure end point
Where does the DV and IV go on a graph?
EQ
IV-x axis
DV-y axis
How can you improve the VALIDITY of data?
EQ
Repeats
Smaller intervals
One control variable-most prominent
How does using smaller intervals increase the validity of data?
EQ
Allows trend to be identified more clearly
Effect of boiling on a plasma membrane so…
EQ
Damages plasma membrane
No osmosis
how you can modify a procedure to improve accuracy
EQ
Test smaller intervals of ——-between — and ——
Explain the effect of ethanol on a plasma membrane
EQ
Dissolves phospholipid bilayer
No osmosis
How can students reduce the uncertainty of their data
EQ
Use more accurate apparatus
Explain the importance of osmosis in plant support
EQ
Water enters vacuole
Pressure against cell wall
Turgid cells support plant cells
Uncertainty of a ruler
2 uncertainties
So double value they give you
HIGHER WATER POTENTIAL
HIGHER SOLUTE POTENTIAL
If a questions asks you to describe two solutions compositions
Suggest a practical error in an osmosis experiment that could have caused an anomaly
EQ
Inadequate drying
More mass of one than other different pieces
How do you use data to determine the water potential of a potato
Data-concentration and change in mass
EQ
No change in mass when water potential of solution is identical to water potential of potato
Analysis of data
Plot graph of concentration against sucrose and find where intercepts x acis
What is a limitation of a practical procedure in an investigation of changing surface area of a potato cube?
EQ
Inconsistency of surface area-difficult to cut smaller cubes accurately
Why is rate of movement of molecules from a plasma membrane to the center of living cells often greater than seen in procedures
EQ
Involvement of cytoskeleton
What other factor will change if you change the concentration of sucrose solutions?
EQ
Water potential
Why do you use line graphs

EQ
Water bath
Timer
What is dialysis tubing
Partially permeable membrane like tube


Outline the method that the students would use to carry out an investigation into the effect of temperature on the diffusion rate in their model cells
EQ
Add 25cm3 of glucose solution to the dialysis tubing
Knot the tubing
Place in a water bath and remove the sample after 10 minutes
Add Benedict’s to test for glucose
Repeat for different temperatures
Evaluate questions remember:
Refer to control variables
Refer to why data is correct
Refer to why data is incorrect
Refer to any reasons why the data would be incorrect-COMMON EXAMPLE IS SAMPLE SIZE
State how hydrogen peroxide could affect the plasma membrane
EQ
Changes fluidity of the membrane
Denatures proteins
Beetroot investigation of temperature and absorbency control variables
EQ
Shape of beetroot
Volume of ethanol
Type of beetroot
Why do you have to control the variety of the beetroot in experiment?
EQ
To control pigment concentration as different beetroots have different water potentials
Formula for serial dilutions
EQ
Concentration 1 x volume 1 = concentration 2 x volume 2
Rearrange for different values
What is the volume 2 in serial dilution formula?
EQ
Total volume that you need to make each serial dilution to
What is the concentration 2 in the serial dilution formula
EQ
Concentration you are trying to make for the next serial dilution

EQ
A
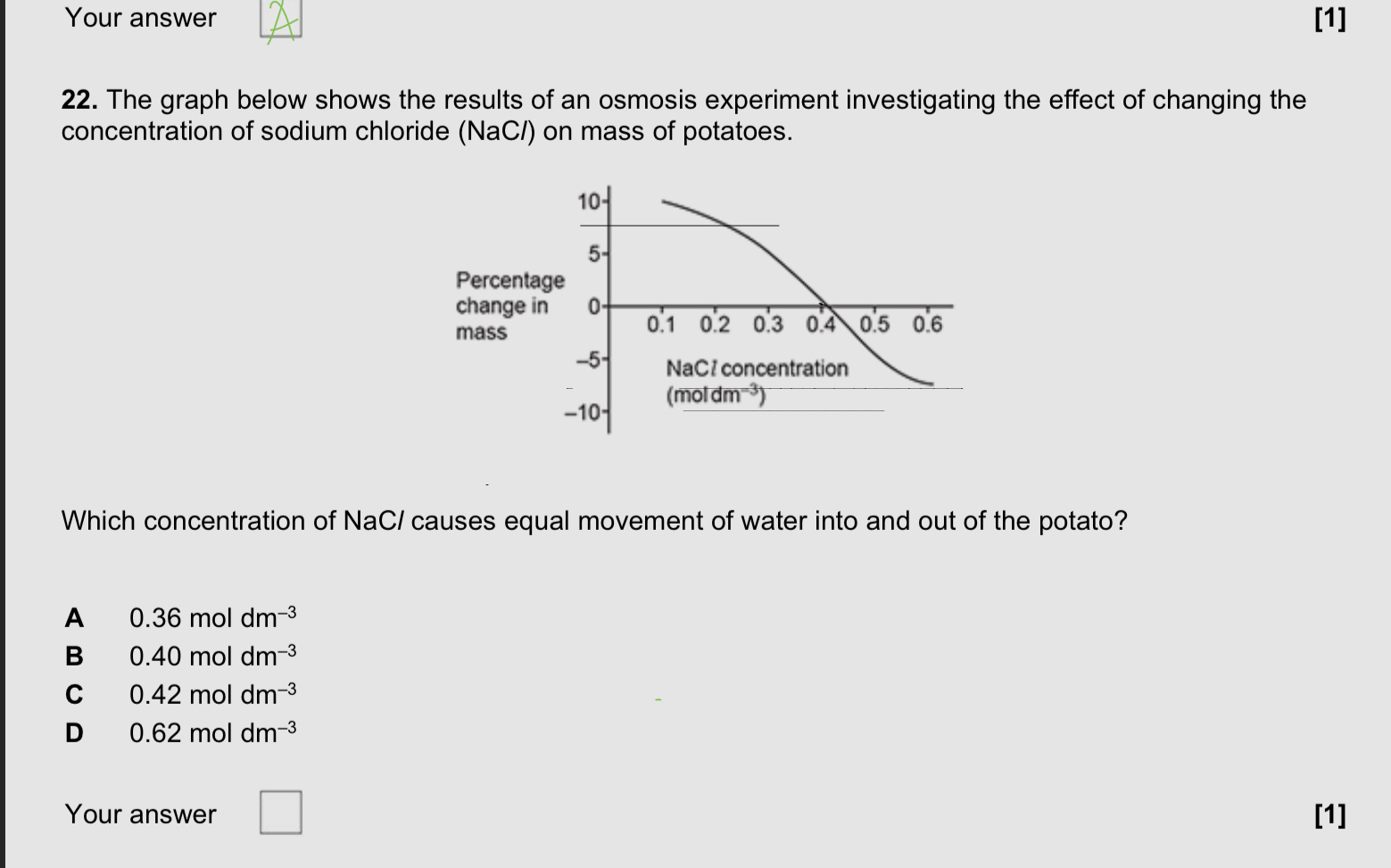
EQ
C
How does frozen beetroot affect the percentage absorbance and why?
EQ
Percentage absorbance is higher
Ice damages membrane
Where do the labels go on a graph of percentage absorbance -colorimeter experiment
EQ-sort of
Concentration of substance on y axis
Absorbance on x axis
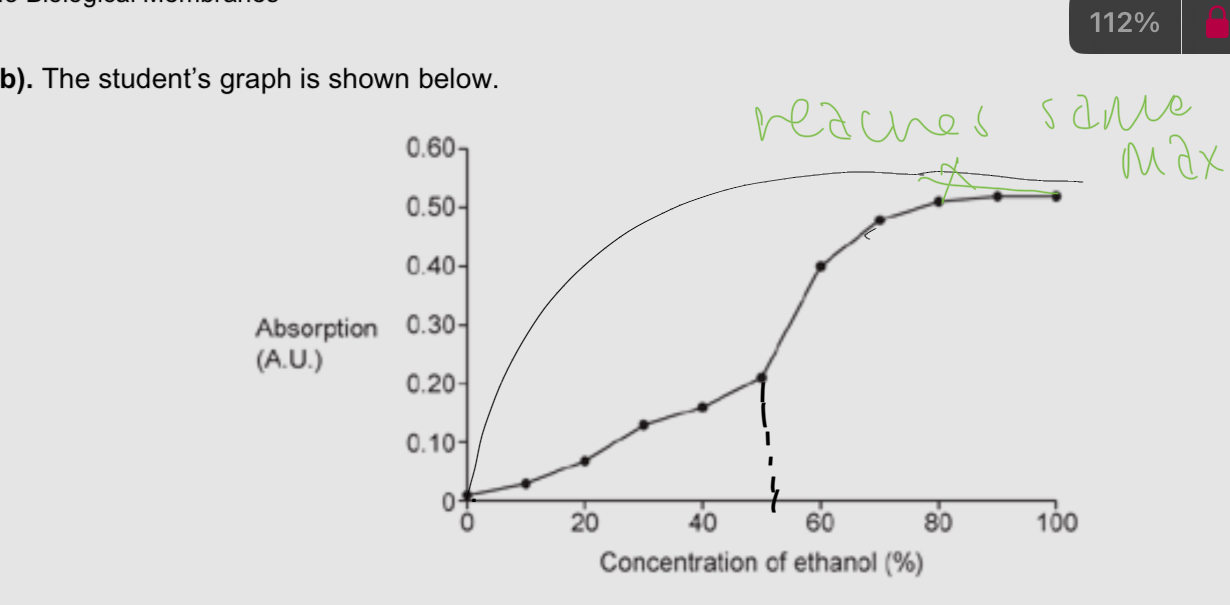
Explain the shape of this graph
EQ-beetroot experiment
Ethanol increases the permeability of the membrane
Levels off as no more pigment is released
Effect of cholesterol on a membrane at higher temperatures
EQ
Decreases fluidity

EQ
Solution lowers water potential of soil
Water moves out of cells by osmosis
How are mineral ions transported into a plant?
Where are they transported to?
EQ
Active transport of minerals into the xylem
What does a proportional graph mean?
EQ-sort of
As one value increases the other increases by the same factor
Glycolipid
Phospholipid chain with a. Chain of carbohydrate molecules attached
What is an intrinsic protein
Integral protein
Glycoprotein
Protein with a chain of carbohydrate molecules attached
Are phosphate groups polar
Yes
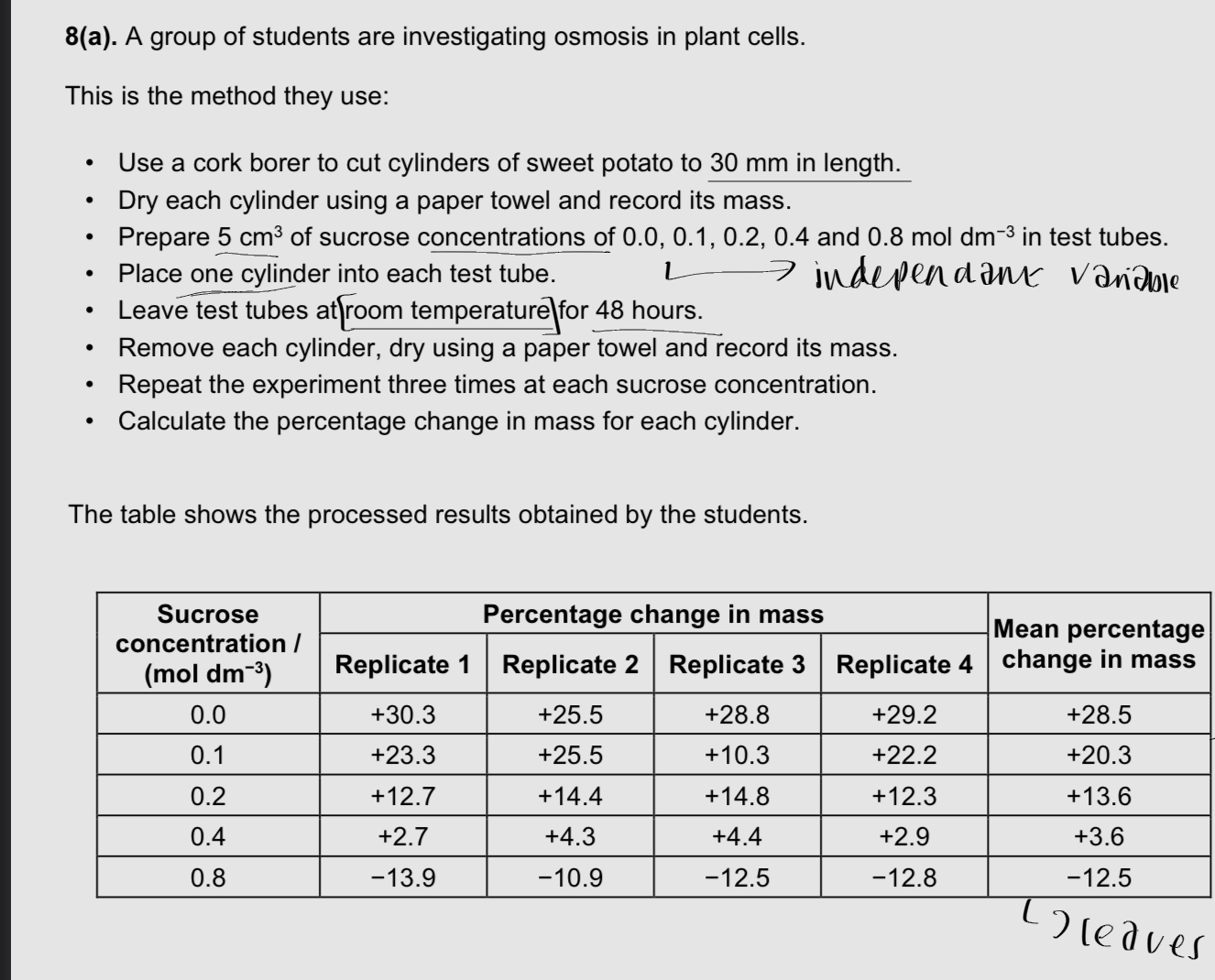
Explain the difference between the mean results obtained at the 0.0 mol dm-3 and 0.8 mol dm-3 sucrose concentrations
EQ
Gain in mass at 0.01mol due to higher water potential inside cells
Mean loss at 0.8 due to lower water potential than inside cells
How do anomalies affect the precision of data
EQ
Reduces repeatability of the data
Increases standard deviation of data
Plasma membrane
Cell surface membrane
What do you have to remember when doing serial dilutions
EQ
Mix the contents after adding water and solution
Describe the plasmas membrane
Partially permeable
If a question asks how you compare 2 sets of data how do you do this
EQ
Draw 2 graphs
Draw a line of best fit for both graphs
Analyse
Roles of membranes at surface of cells
Separates cells components from external environment
Regulates transport of materials in and out of cell
CELL SIGNALLING
site of chemical reactions

B
Find surface area to volume ratio
Greatest surface area to volume ratio diffuses the fastest
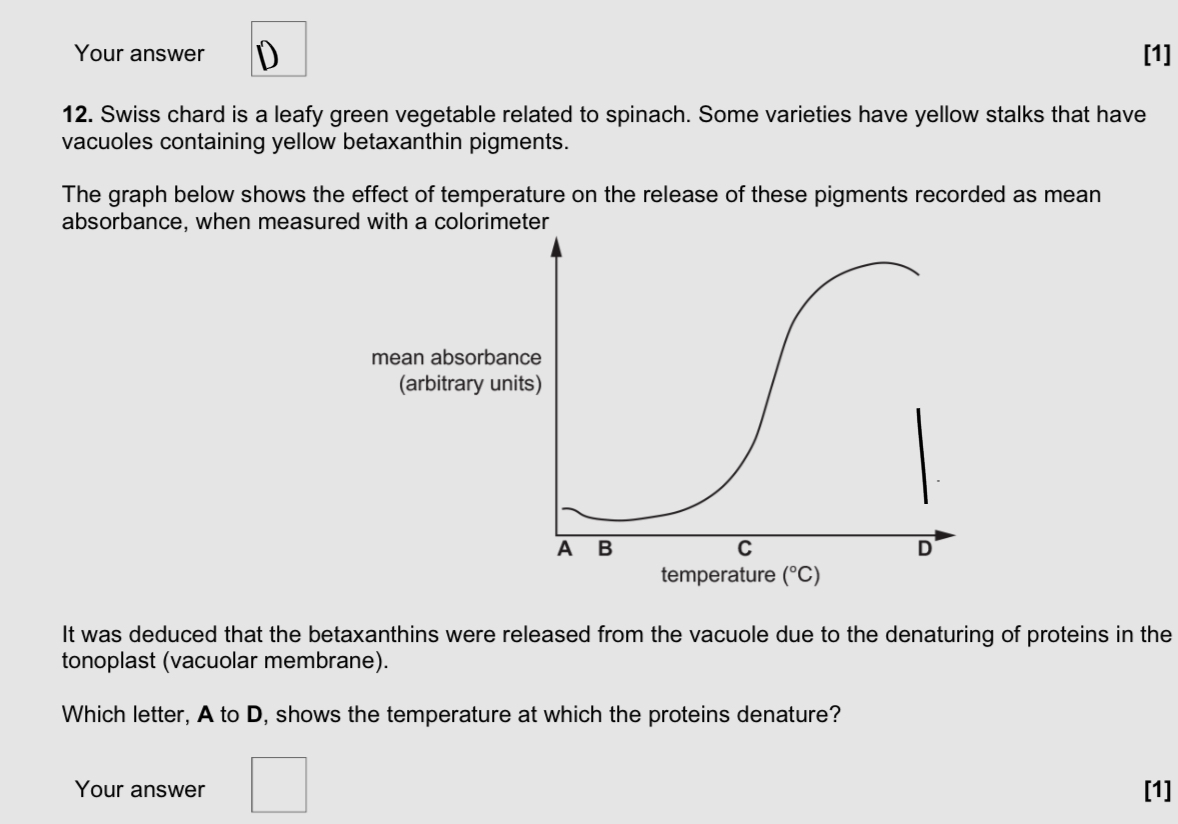
C
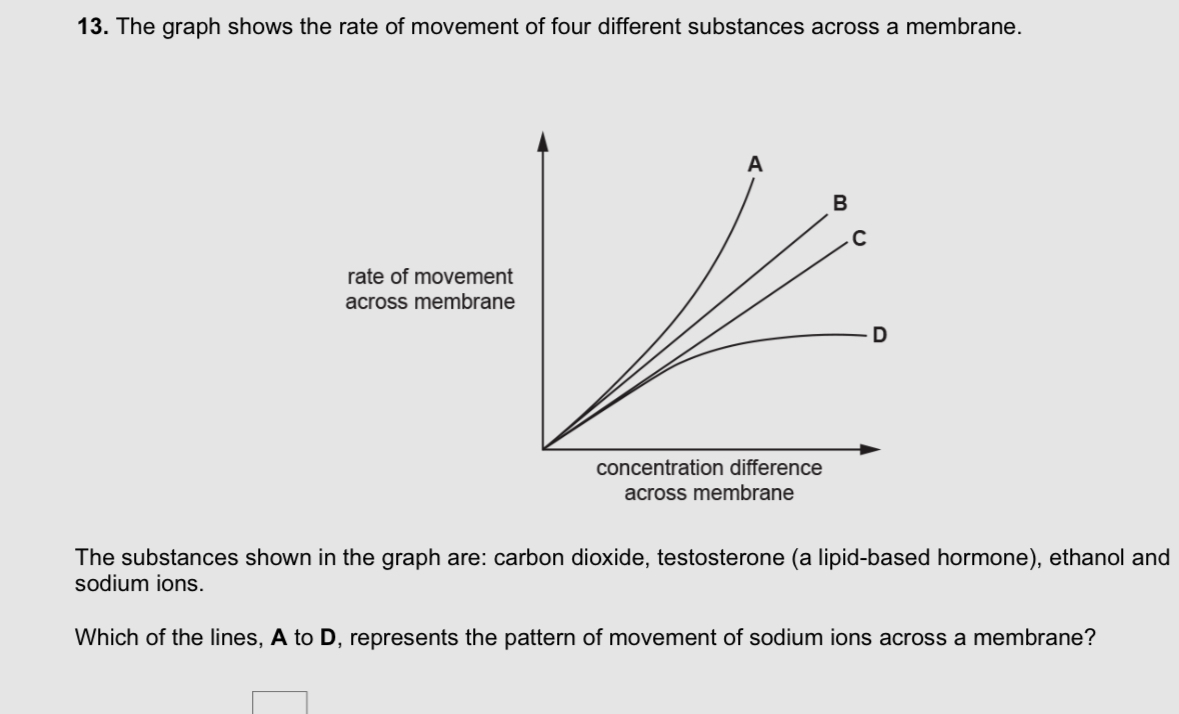
D
Which does cell to cell signalling:
Intracellular membranes
Extracellular membranes
Extracellular only
What is the effect of cholesterol dependant on
EQ
Temperature
At lower temperatures how does cholesterol affect the fluidity of a membrane
EQ
Increases fluidity
What goes on the axis on a percentage absorbance temperature graph for beetroot experiment?
EQ
Percentage absorbance on x axis
Temperature on y axis
Where are receptors on steroid hormones and why are they there?
EQ
Inside cells as steroids can cross the plasma membrane
How do you calculate percentage uncertainty with these 2 values
Mass uncertainty
EQ
Uncertainty per instrument
Divided by
Change in mass
Multiplied by 100
Why do plasma membranes have antigens at the surface of cells
So that immune system recognises the cell as itself
Purpose of plasma membranes inside cells
Chloroplasts-reactions of photosynthesis
Small intestine-digestive enzymes on plasma membrane
Why are there digestive enzymes on the plasma membrane of epithelial cells in the small intestine
Catalyse breakdown of sugars
What type of proteins are the channel and carrier proteins
Integral proteins
Why are glycocalyx on the outside of the membrane
Very hydrophilic and attract water with dissolved solutes helps cells interact with water environment
Glycocalyx definition
Carbohydrate molecules