Topic 8 - Mutations
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Mutations
Change in an organism's DNA sequence
What are the main causes of mutation?
Errors during DNA, chemicals, radiation (e.g.mutagens)
What causes point mutations?
Errors during DNA replication
What is the function of DNA Polymerase?
It's capable of proofreading and detecting any mismatch of nucleotide pairing
Mismatch repair proteins
secondary mechanism for repairing mismatch if not fixed by DNA polymerase
detect the mismatched base and remove it from the newly synthesized strain via nuclease action
Point mutations
characterized by their affection to protein sequence
Types of point mutations: silent, missense, nonsense
What are silent mutations?
Mutations that have NO EFFECT on the protein sequence (undetectable) because multiple codons code for the same AA
What are missense mutations?
Mutations that result in AA SUBSTITUTION
What are nonsense mutations?
The MOST HARMFUL mutations that results in premature stops due to the substitution of an AA for a stop codon (they stop translation)
Why are premature stops harmful?
They result in nonfunctional proteins alongside smaller sized proteins
Why does the substitution of AAs with different characteristics harmful to proteins?
It stops function + misfolds protein
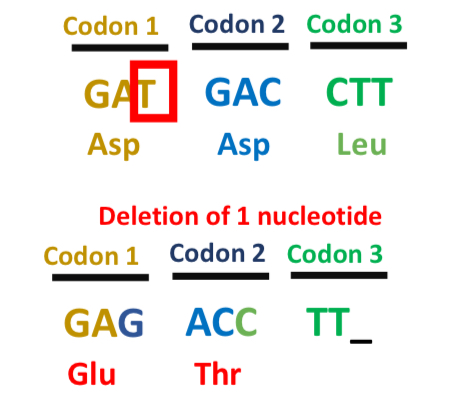
What are frame shift mutations?
Mutations that shift the reading frame via the insertion/deletion of nucleotides
NOT ALL INSERTIONS/DELETIONS CAUSE THESE MUTATIONS
What is the mechanism(s) of DNA repair?
Primary: DNA Polymerase
Secondary: Mismatch repair proteins
What are resolvers of DNA mutation?
nucleotide excision, mismatch repair proteins, DNA polymerase
What are initiators of DNA mutation?
silence, missense, nonsense, frameshift
How can UV exposure cause DNA mutations?
It can cause adjacent thymines to form covalent bonds which can be replicated incorrectly by DNA polymerase, causing frameshift or point mutations
What is nucleotide excision?
When nuclease removes a single strand of DNA which contains dimer that is to be repaired by DNA Polymerase
DNA Polymerase synthesizes (fixes hole/gap in DNA left by nuclease) a new strand using the opposing strand as a template
DNA Ligase forms the final phosphodiester bond between the new DNA(‘5) and old DNA(‘3)