233 Unit 1 Ch 1 - Intro to A&P and the Human Body
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Anatomy
The study of body structure
Physiology
The study of body function
ex: how muscles contract
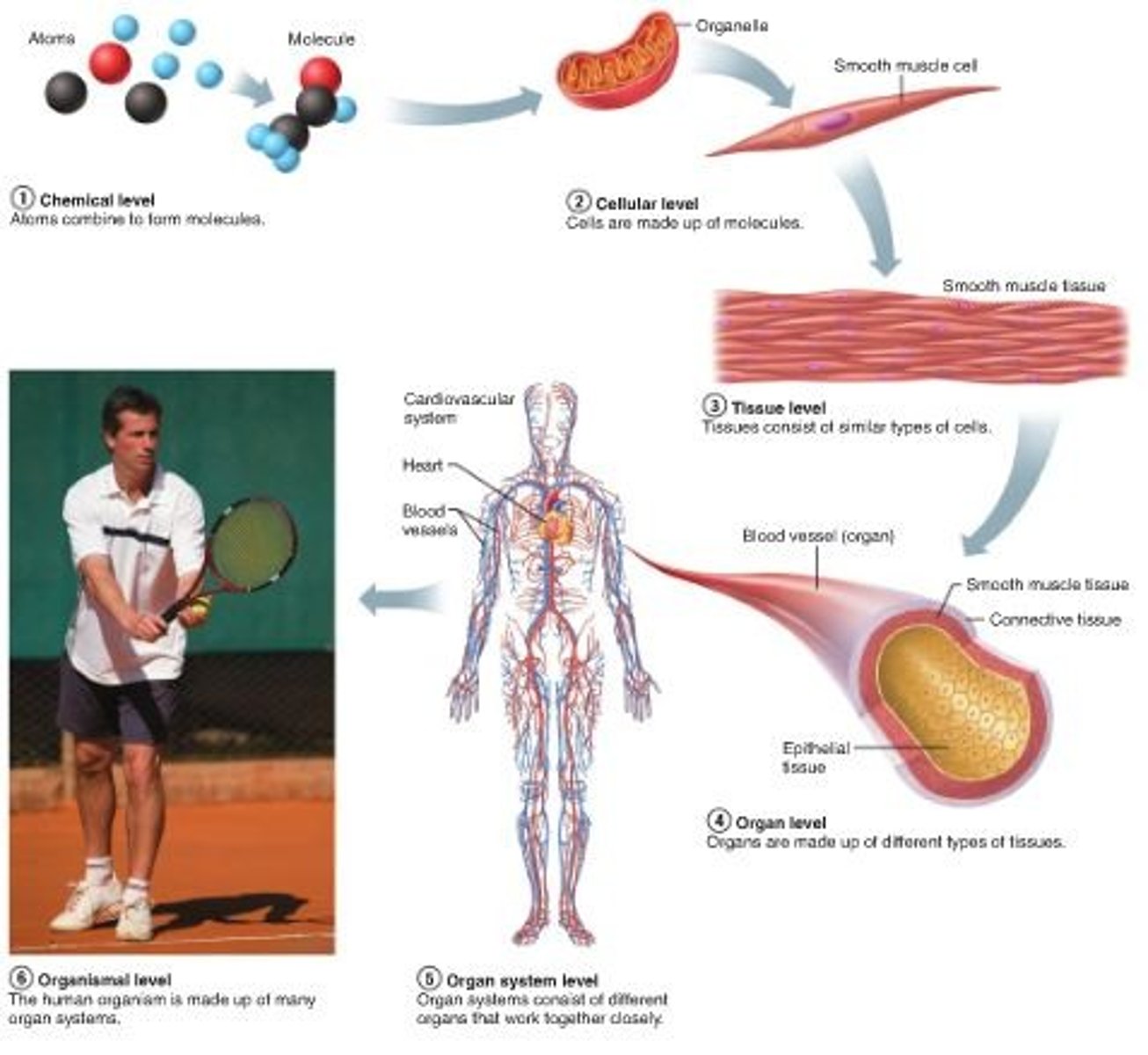
Describe the levels of organization in the human body (be able to put these in order)
1. Chemical Level (simplest/ smallest)
2. Cellular level
3. Tissue level
4. Organ level
5. Organ system level
6. Organism level (largest/ complex)
integumentary system
protects against environmental hazards; helps control body temperature
skeletal system
Provides support and protection for tissues
Muscular System
provides movement
nervous system
controls body activites
Endocrine system
secretes hormones and helps regulate body activities
cardiovascular system
transports oxygen, nutrients throughout body--also picks up CO2
lymphatic system
Defense against infection and disease
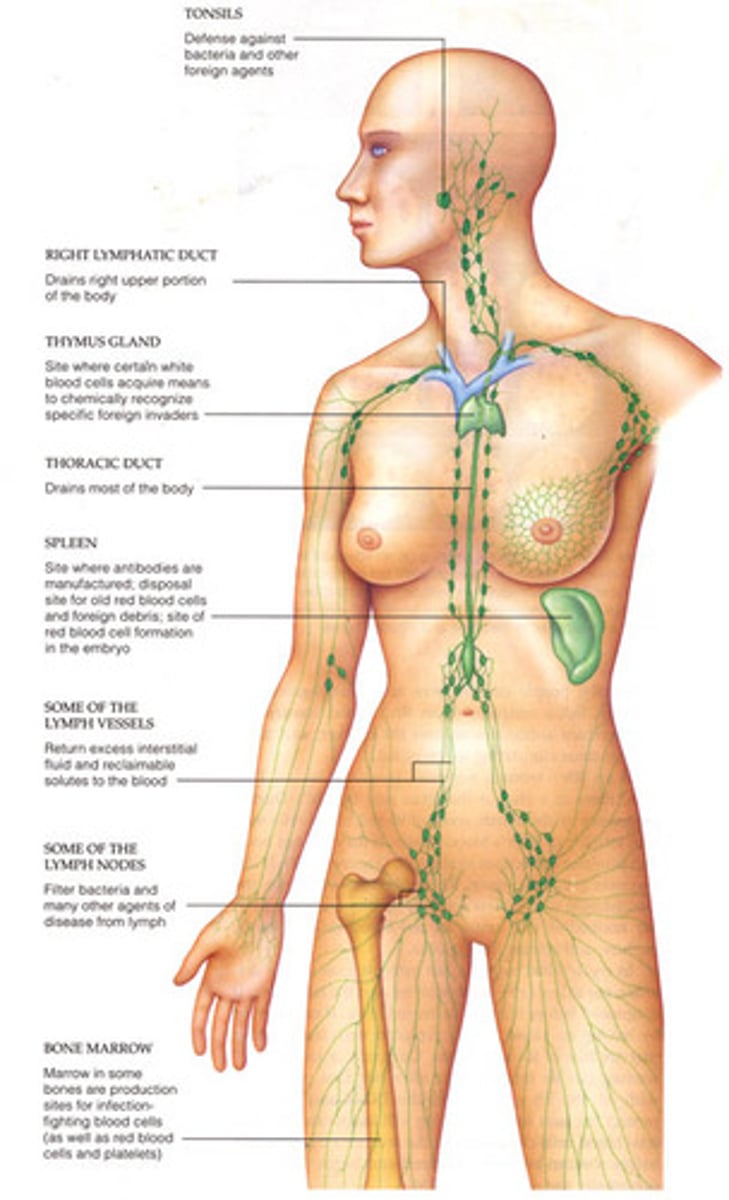
Respiratory System
Brings oxygen into the body & gets rid of CO2 out of body

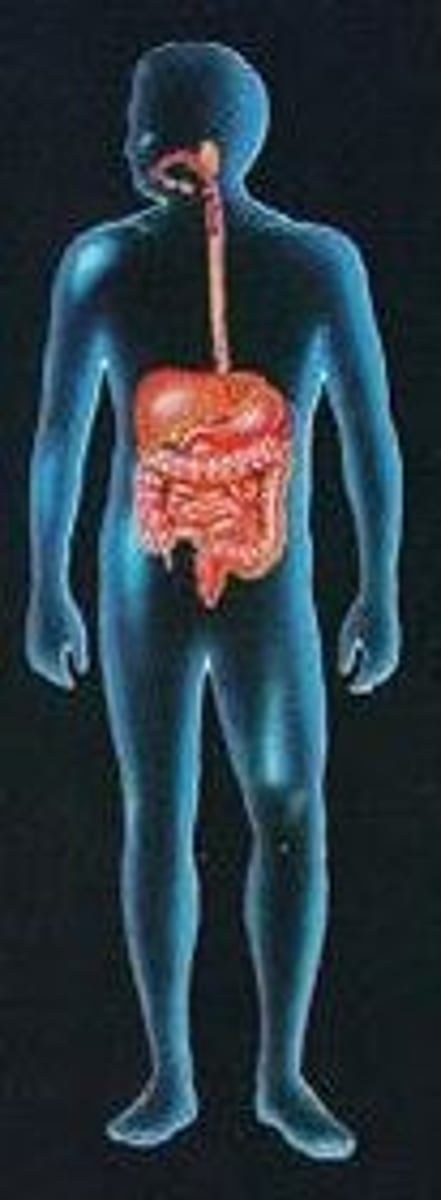
digestive system
Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients, conserves water and energy
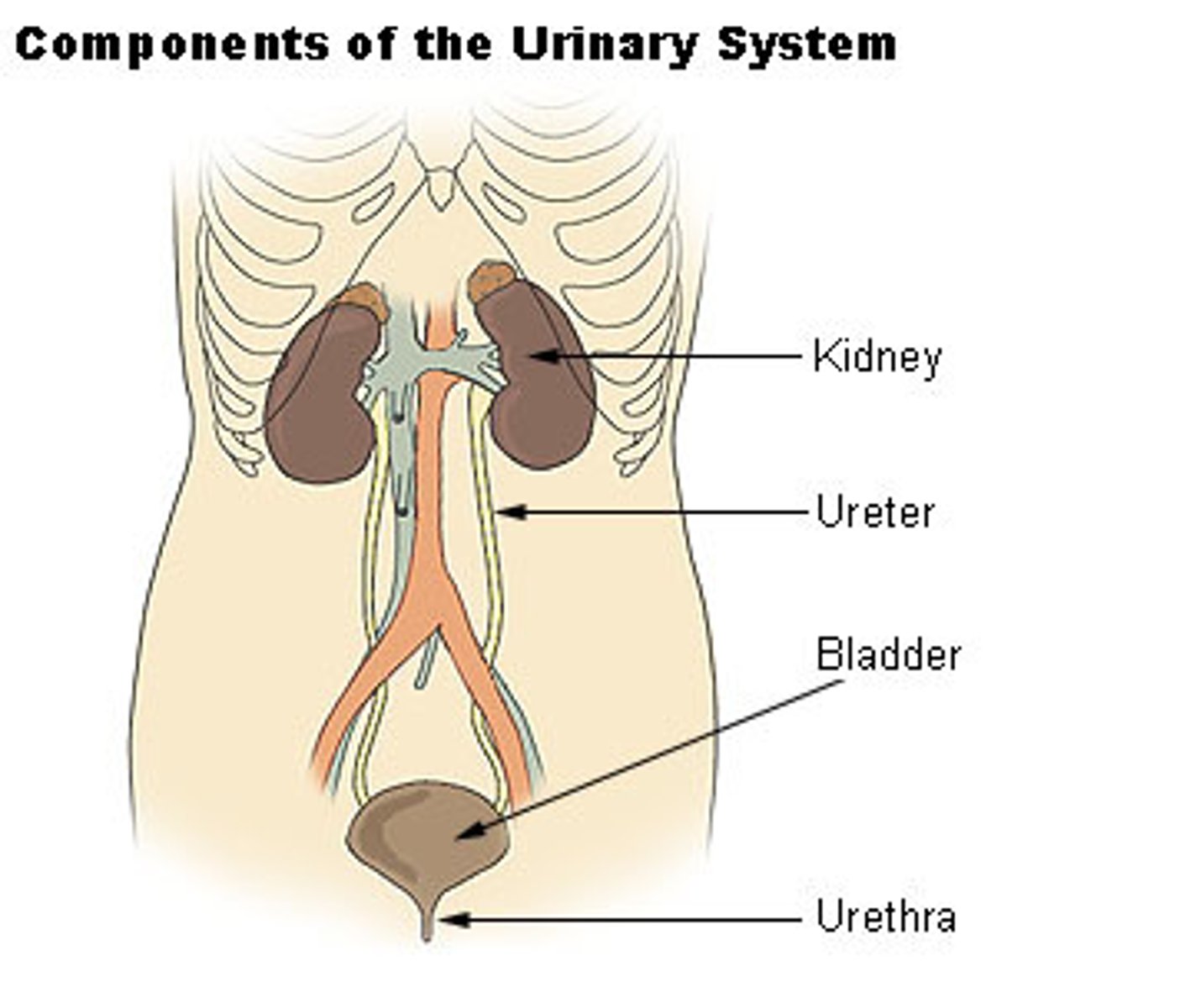
urinary system
eliminates water, salts, and waste
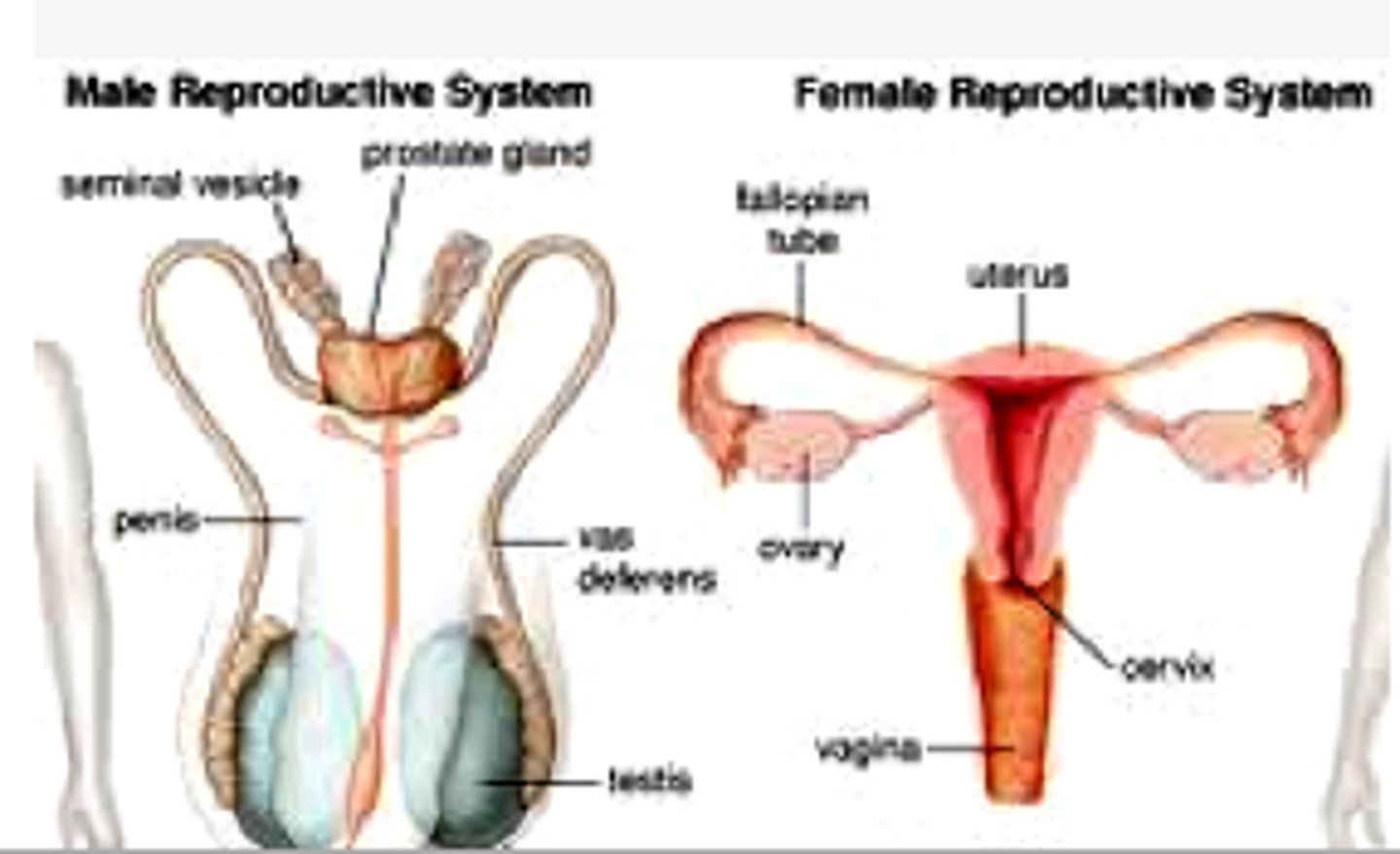
reproductive system
Reproduce offspring- produce female and male gametes
Homeostasis
All body systems work together to maintain a stable internal environment within NARROW limits
ex: body temp, fluid balance
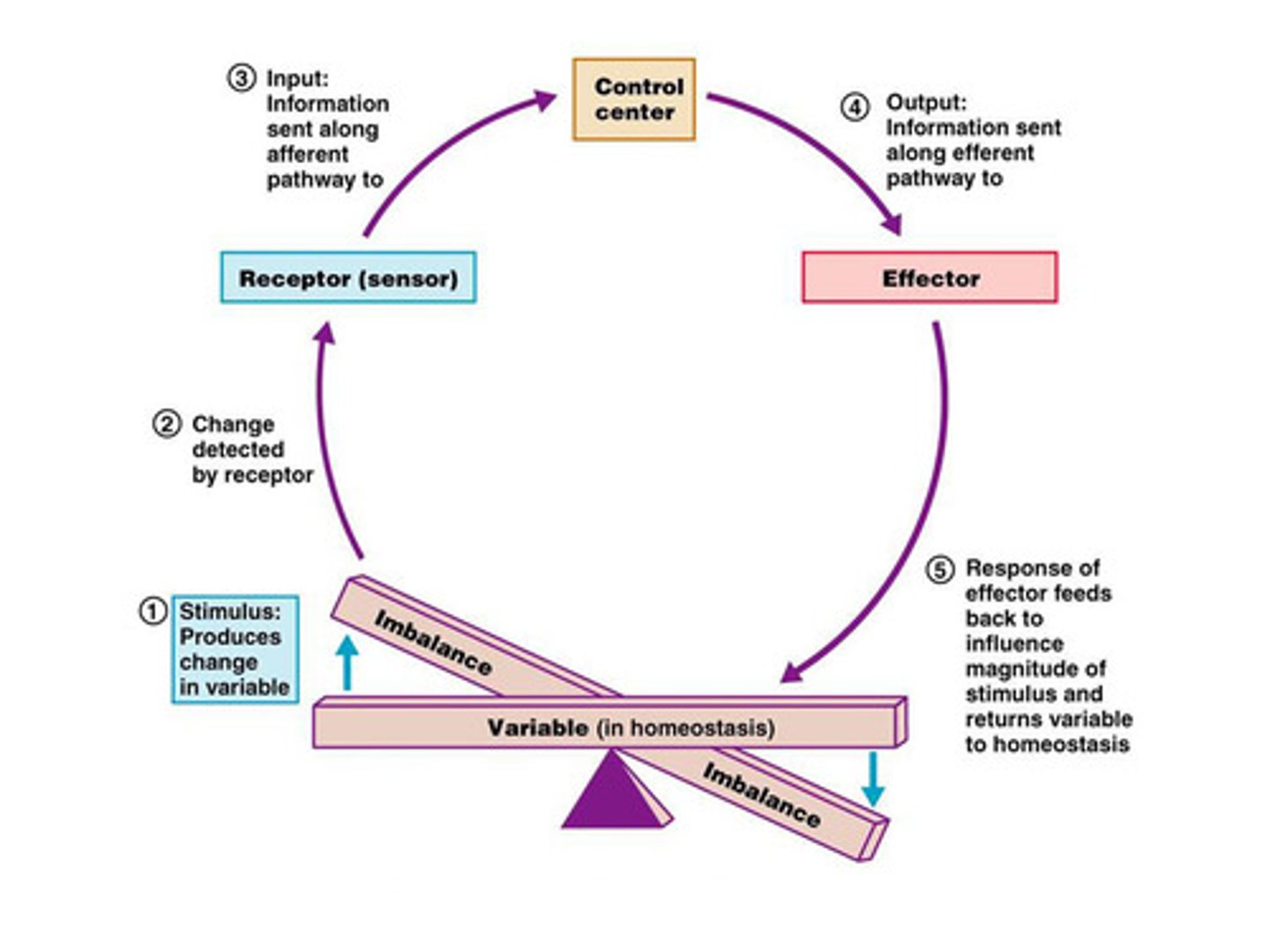
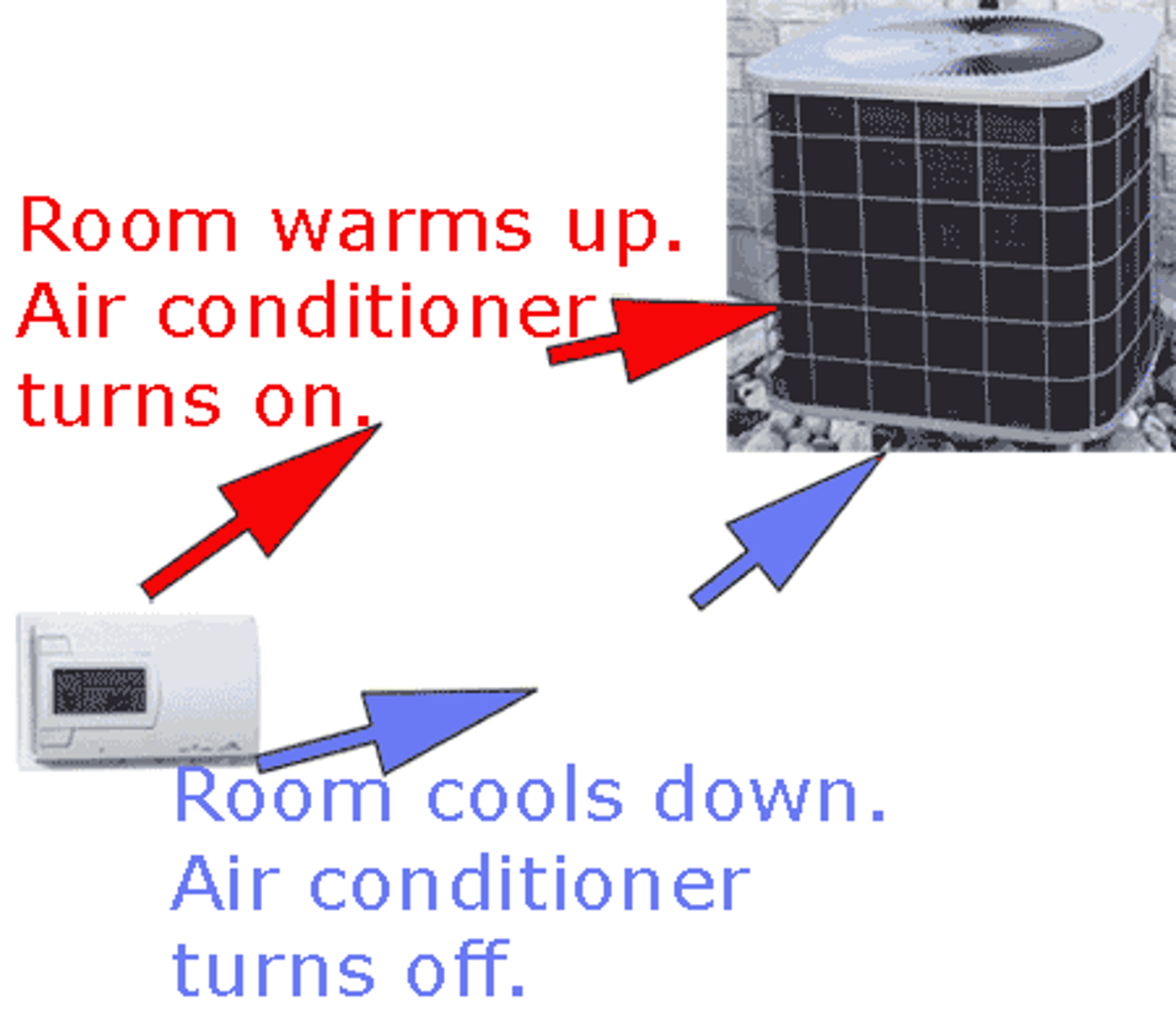
negative feedback
REDUCE the change or output: the body responds by bringing conditions back to a stable state / within normal limits. EX: a fever--your body sweats to cool off to bring temperature down
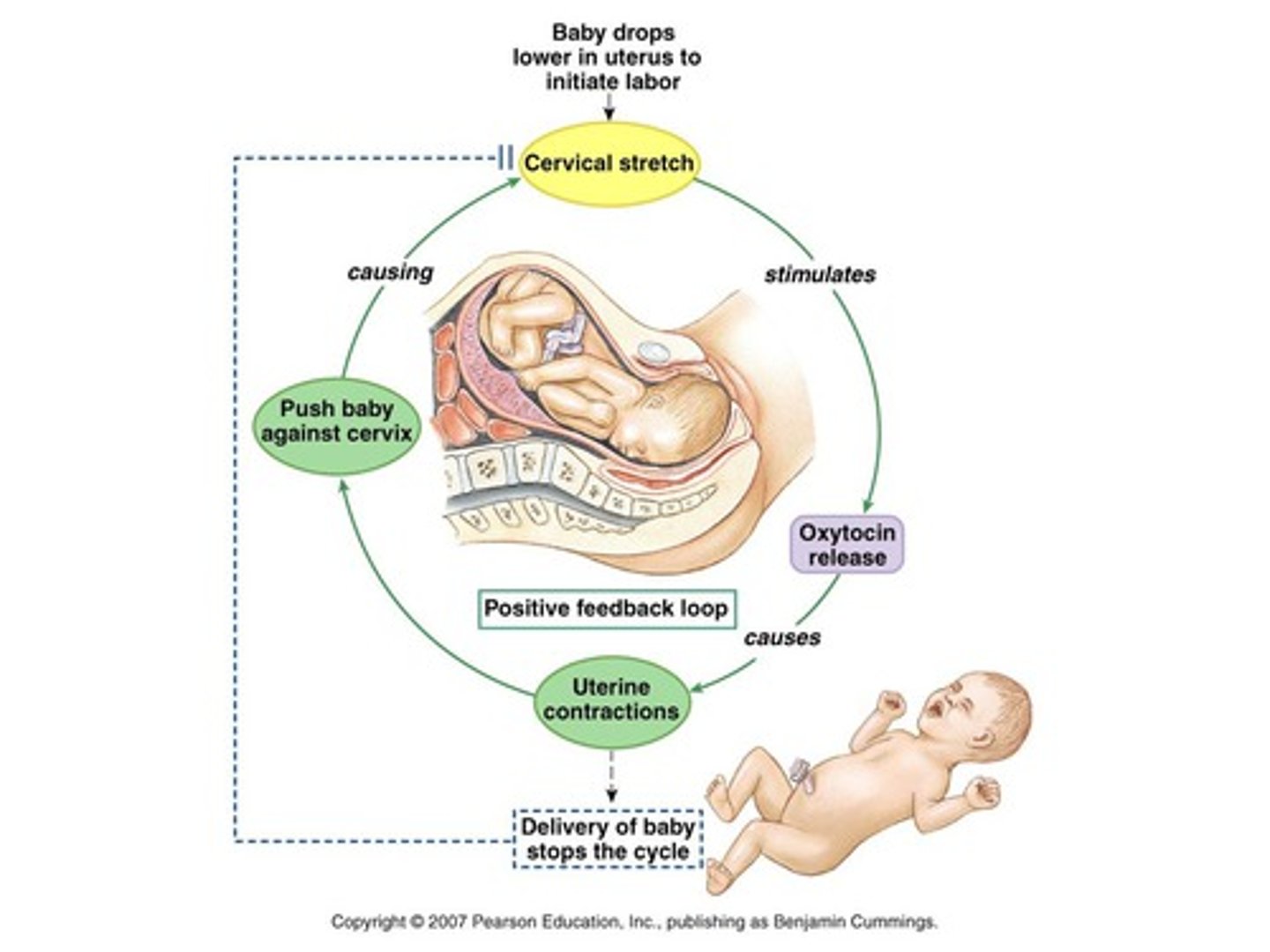
positive feedback
INCREASES or amplifies the stimulus AWAY from normal state or limits:
ex: Childbirth (amplified contractions until birth of baby), blood clotting (amplified clotting factors released until bleeding stops)--positive feedback is rare in humans
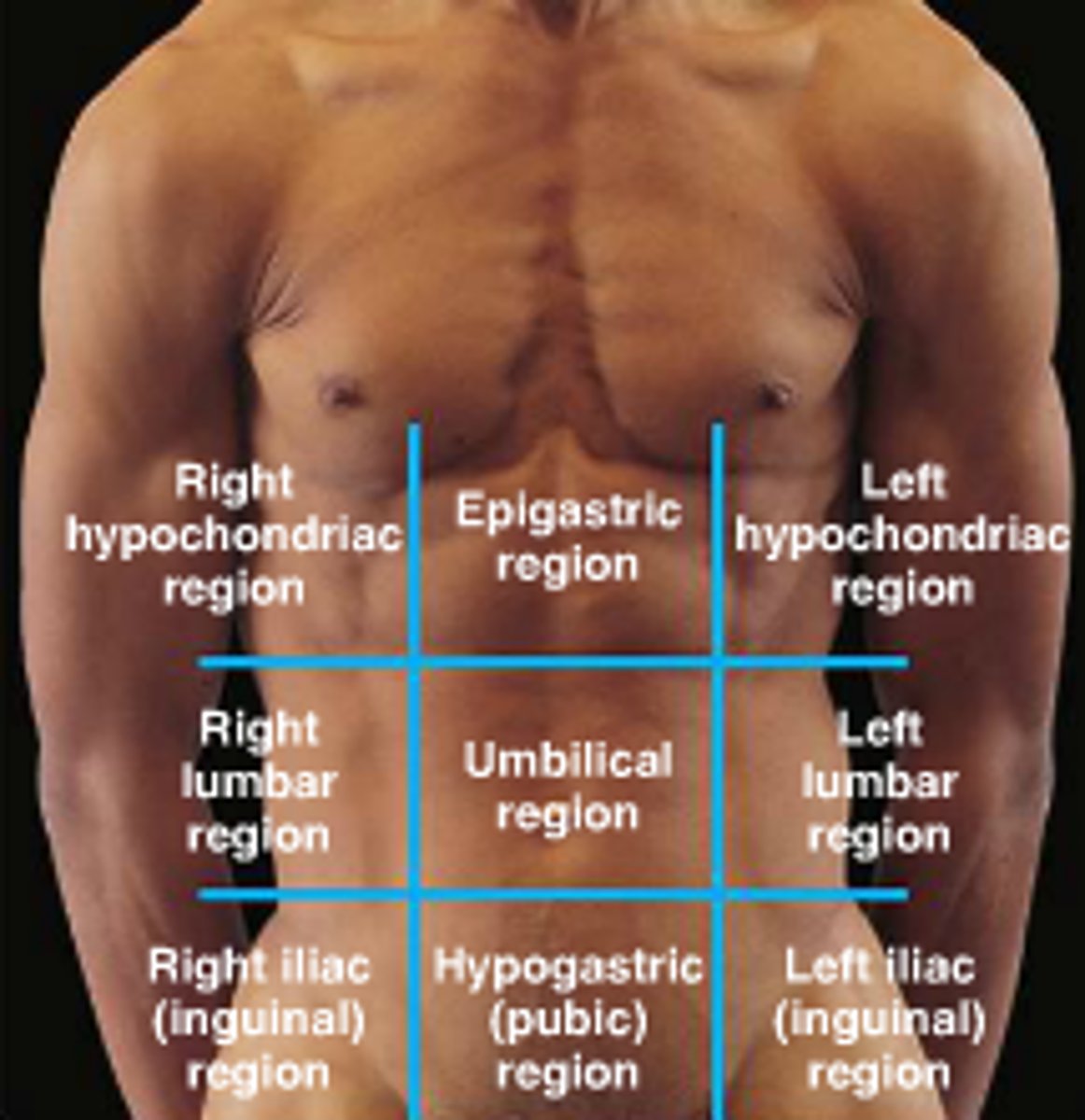
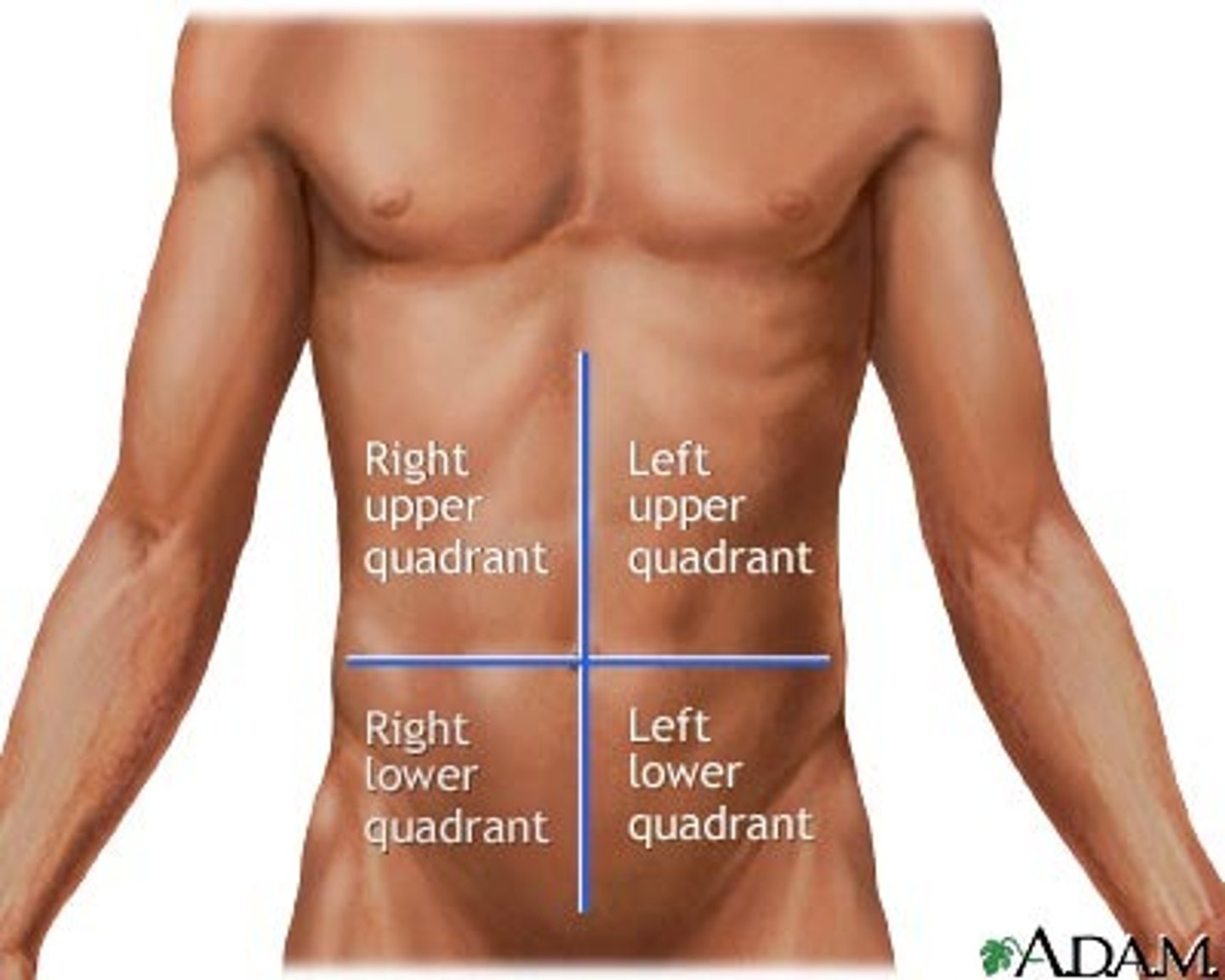
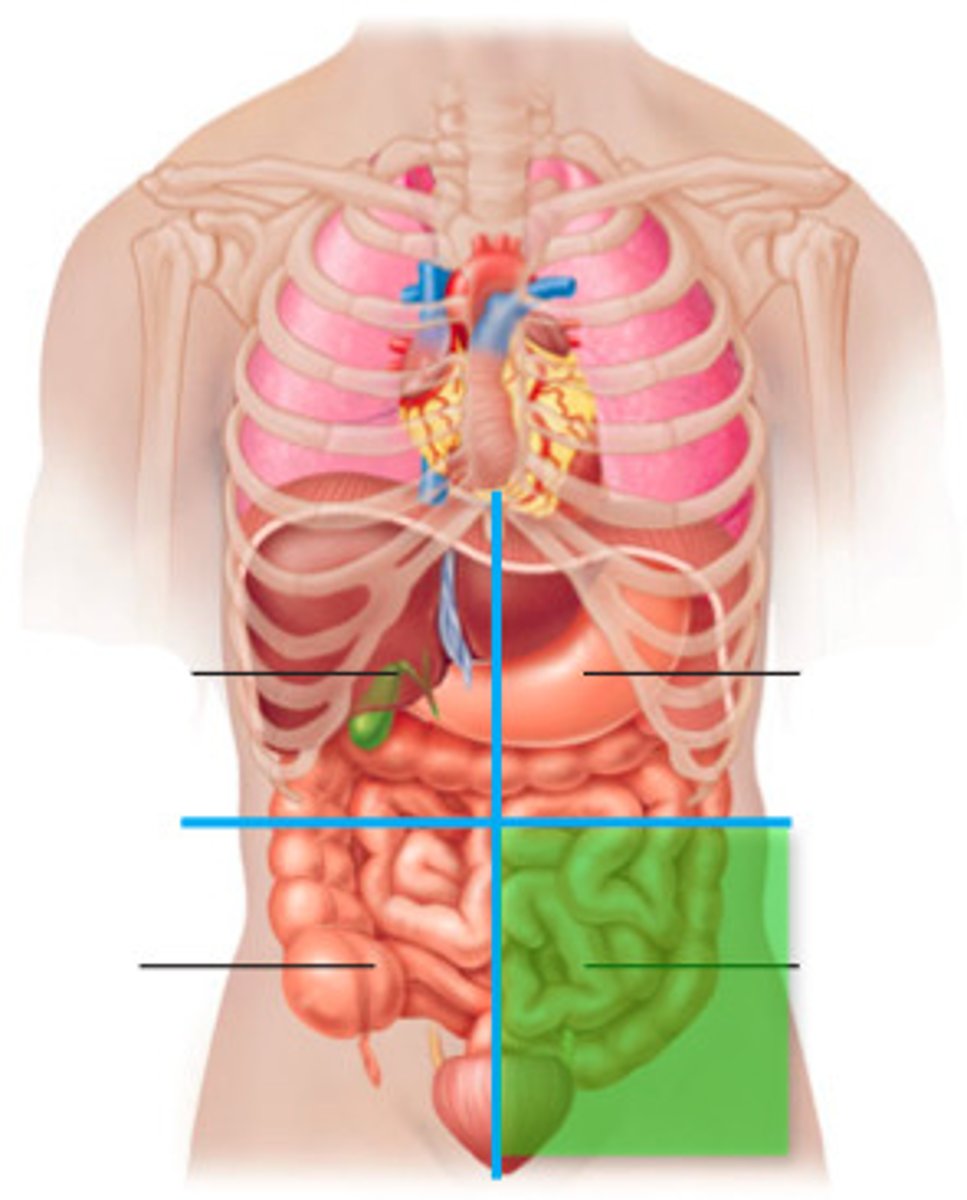
abdominopelvic regions
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Where is the appendix? Where is the liver? Where is the stomach?
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into superior and inferior portions
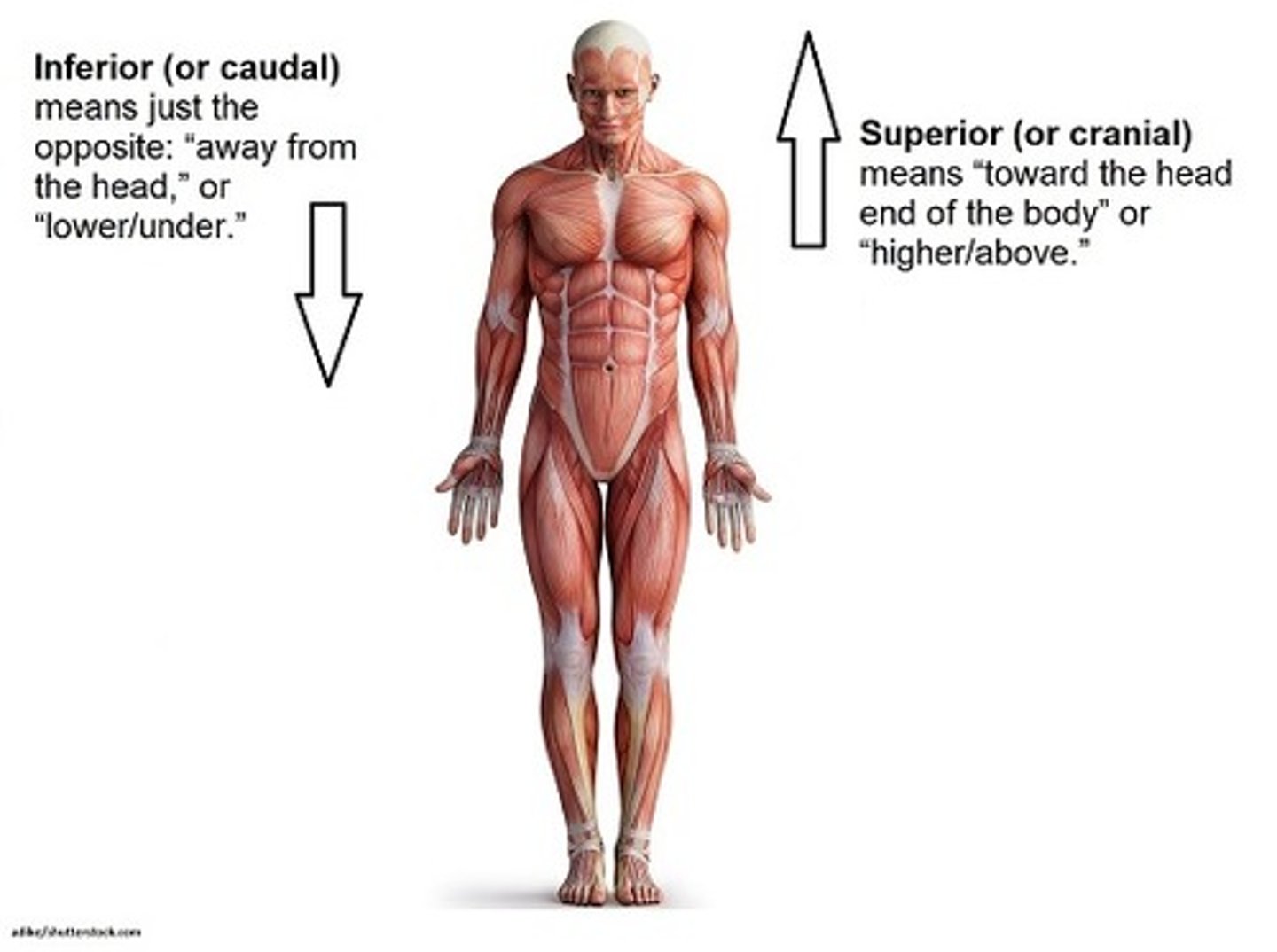
Superior
above (towards head)
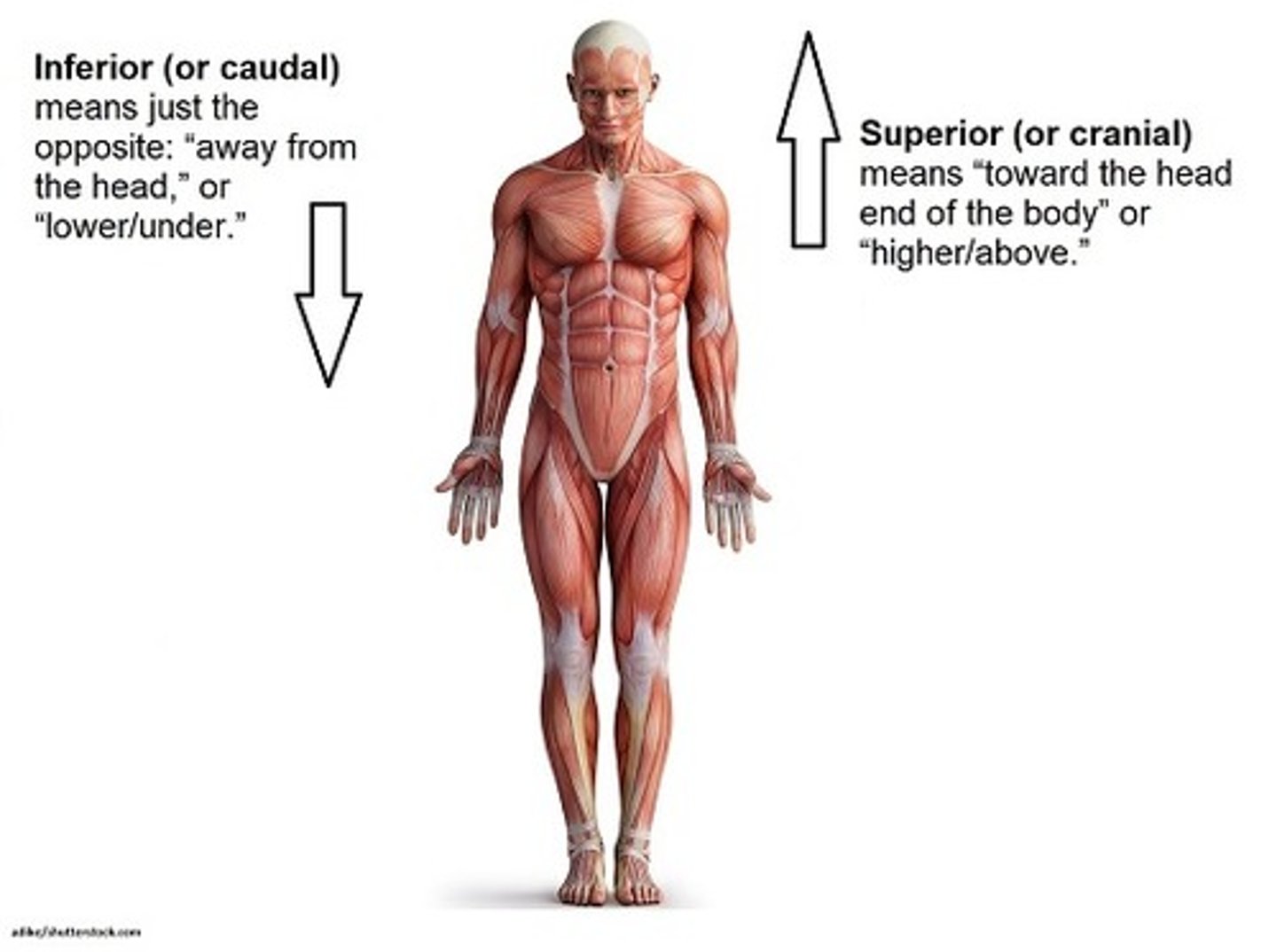
Inferior
lower (away from head)
frontal (coronal) plane
vertical plane dividing the body or structure into anterior and posterior portions
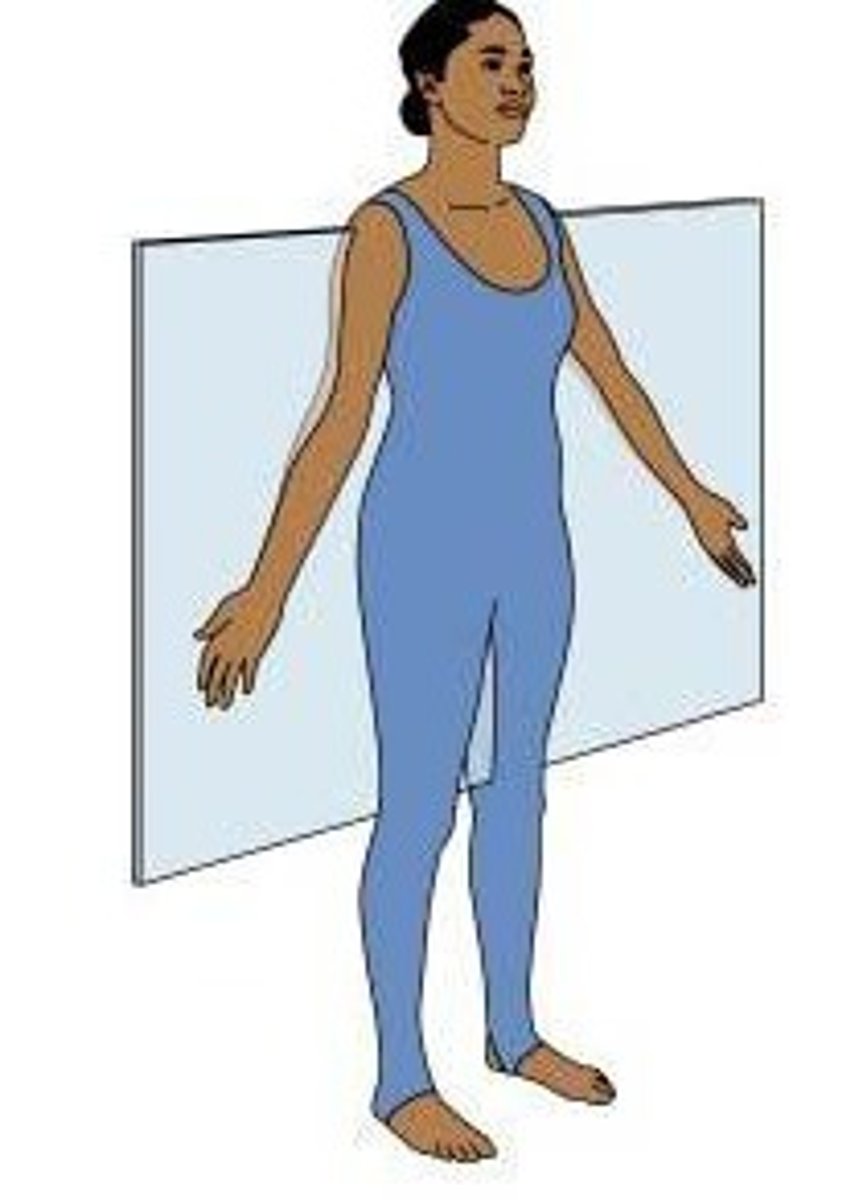
Anterior
front of the body (= ventral)
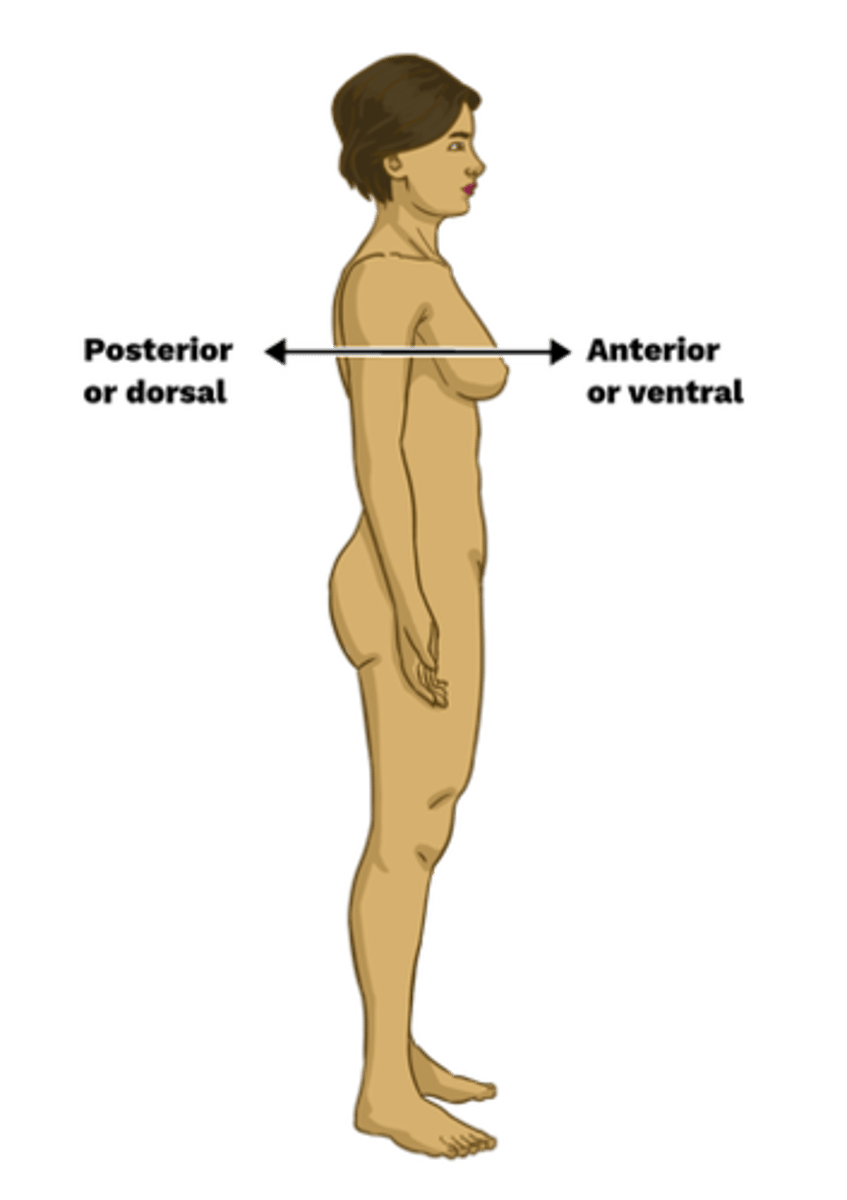
Posterior
back of body (= dorsal)
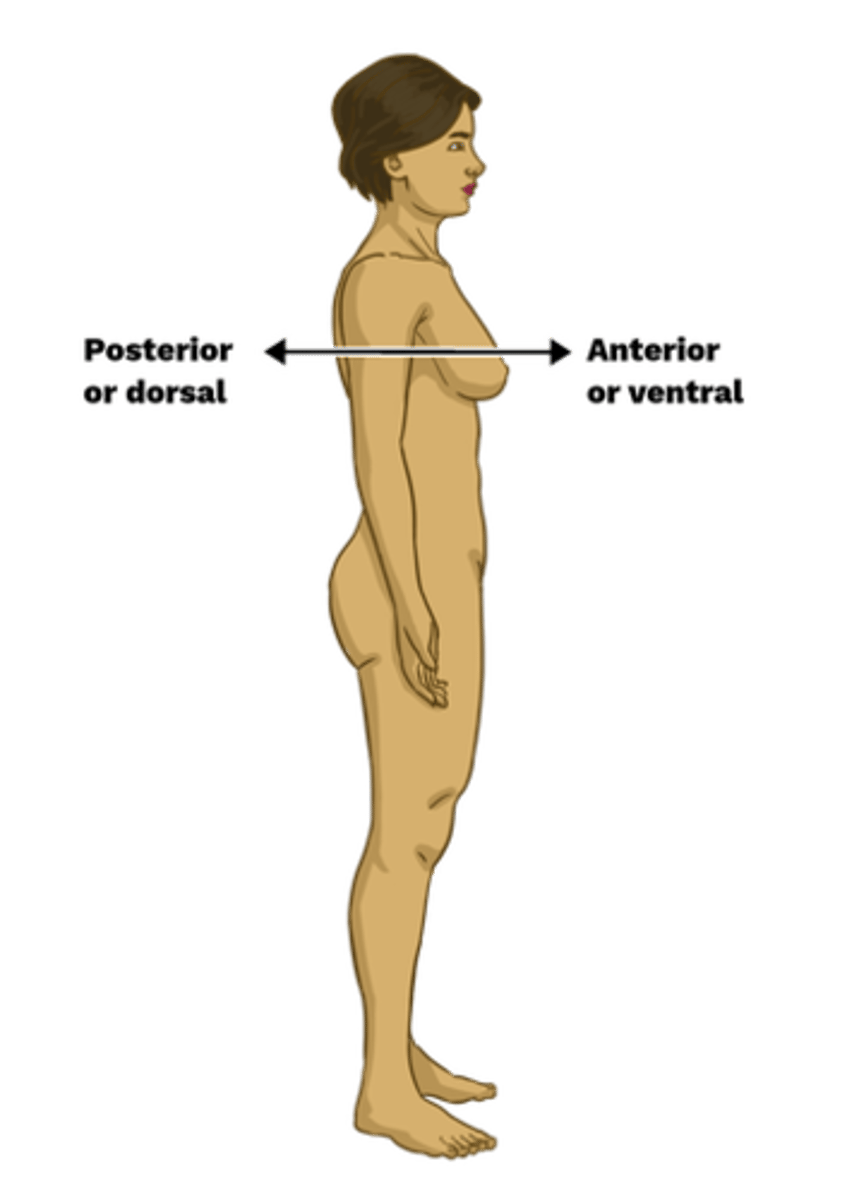
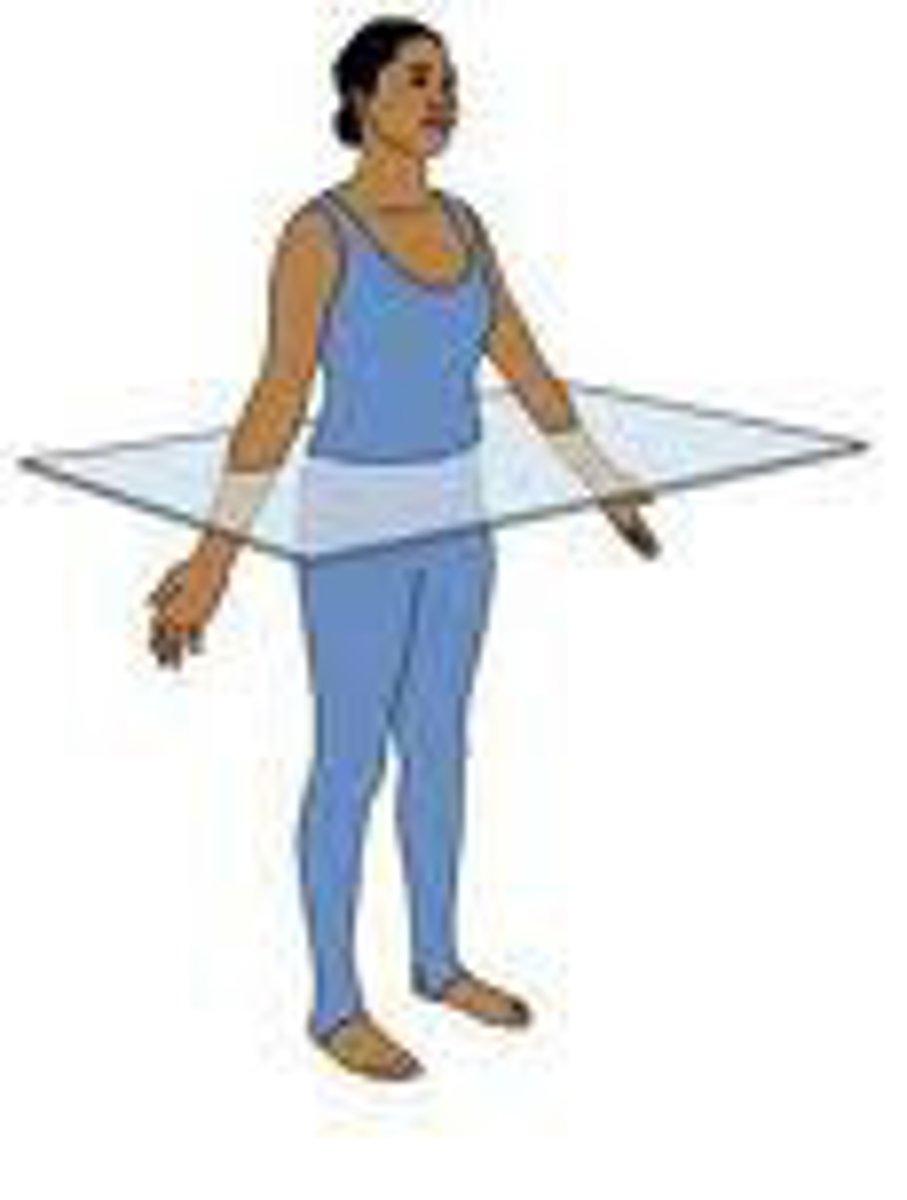
sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions
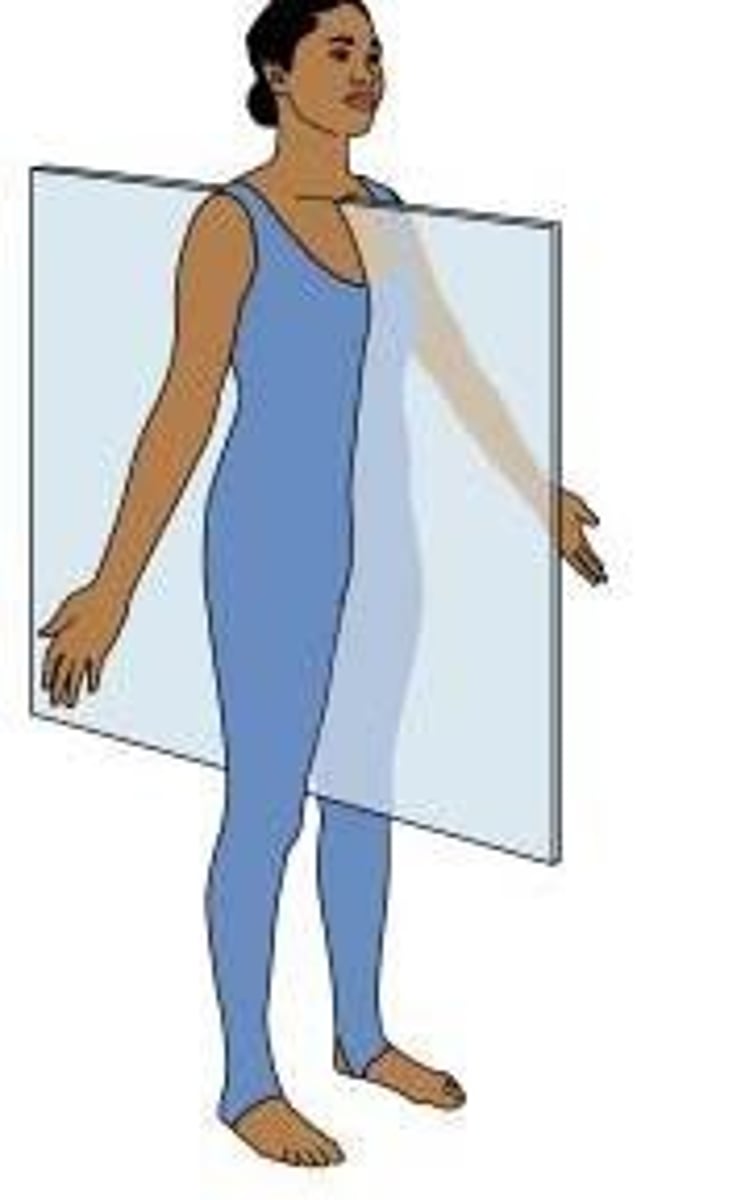
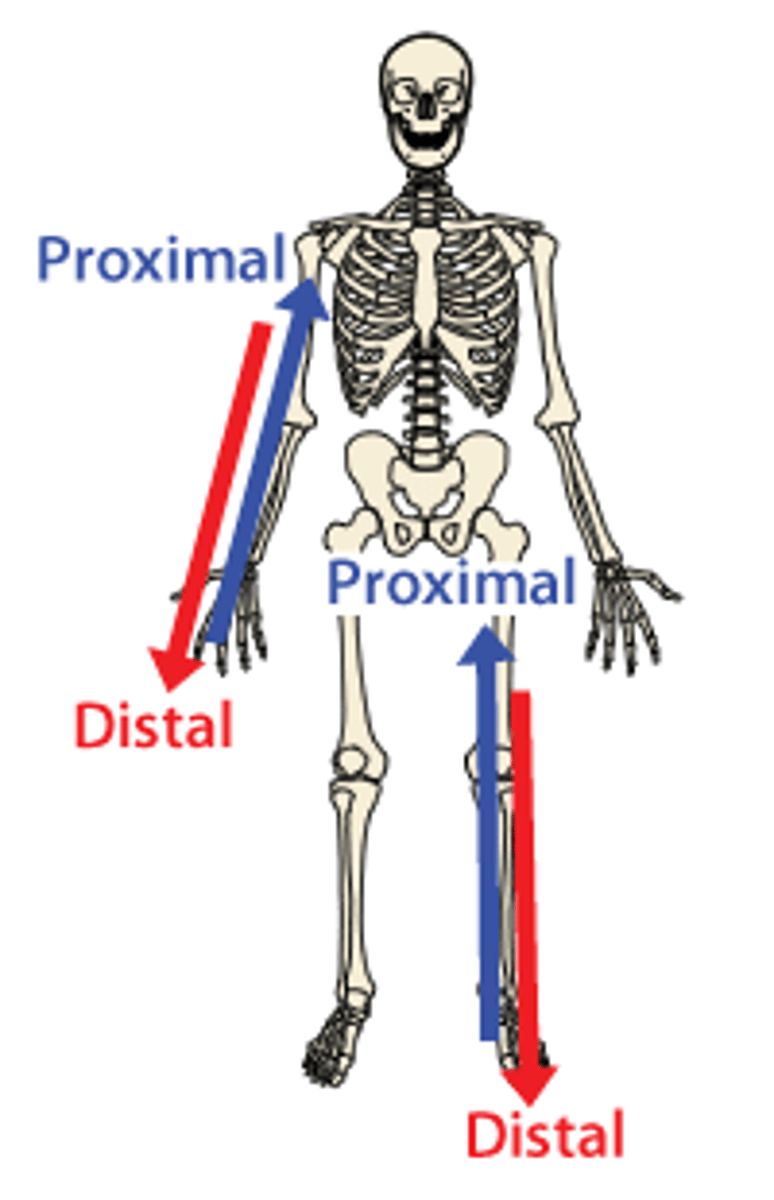
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment (usually closer to trunk of body). Example, the elbow is proximal to the wrist. The toe is distal (more distant) to the knee.
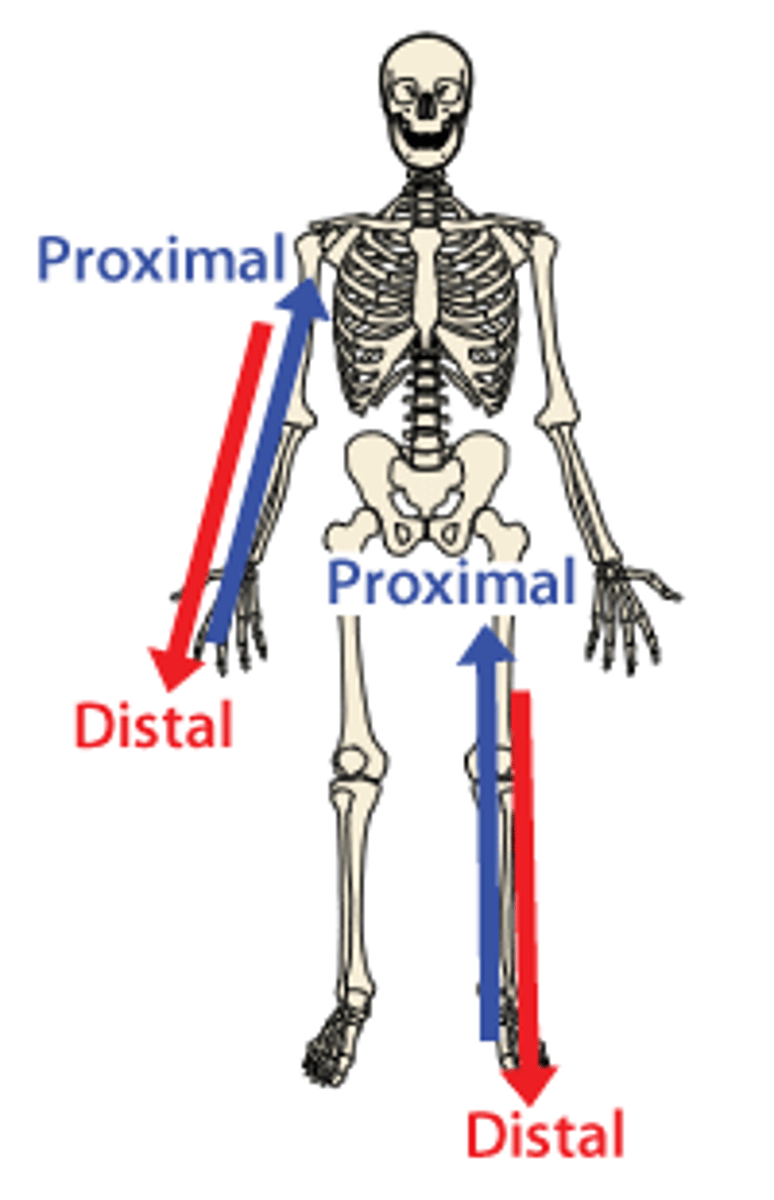
Distal
away from the point of attachment
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body (the radius is lateral to the ulna, the ears are lateral to the nose).
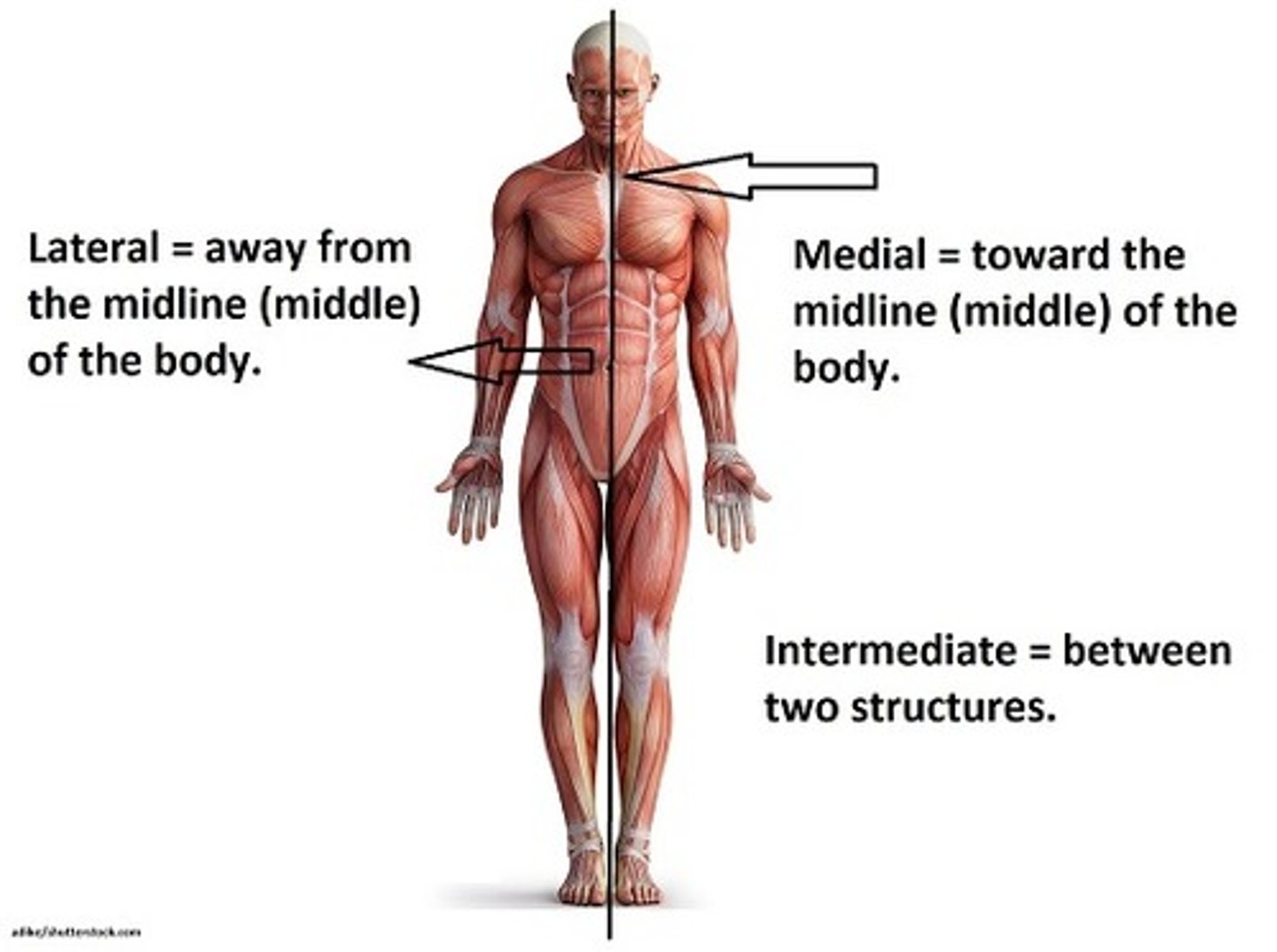
Medial
Toward the middle of the body. Example, the umbilicus is medial to the ilium. The mouth is medial to the ears.
body cavities
spaces within the body that contain and protect internal organs
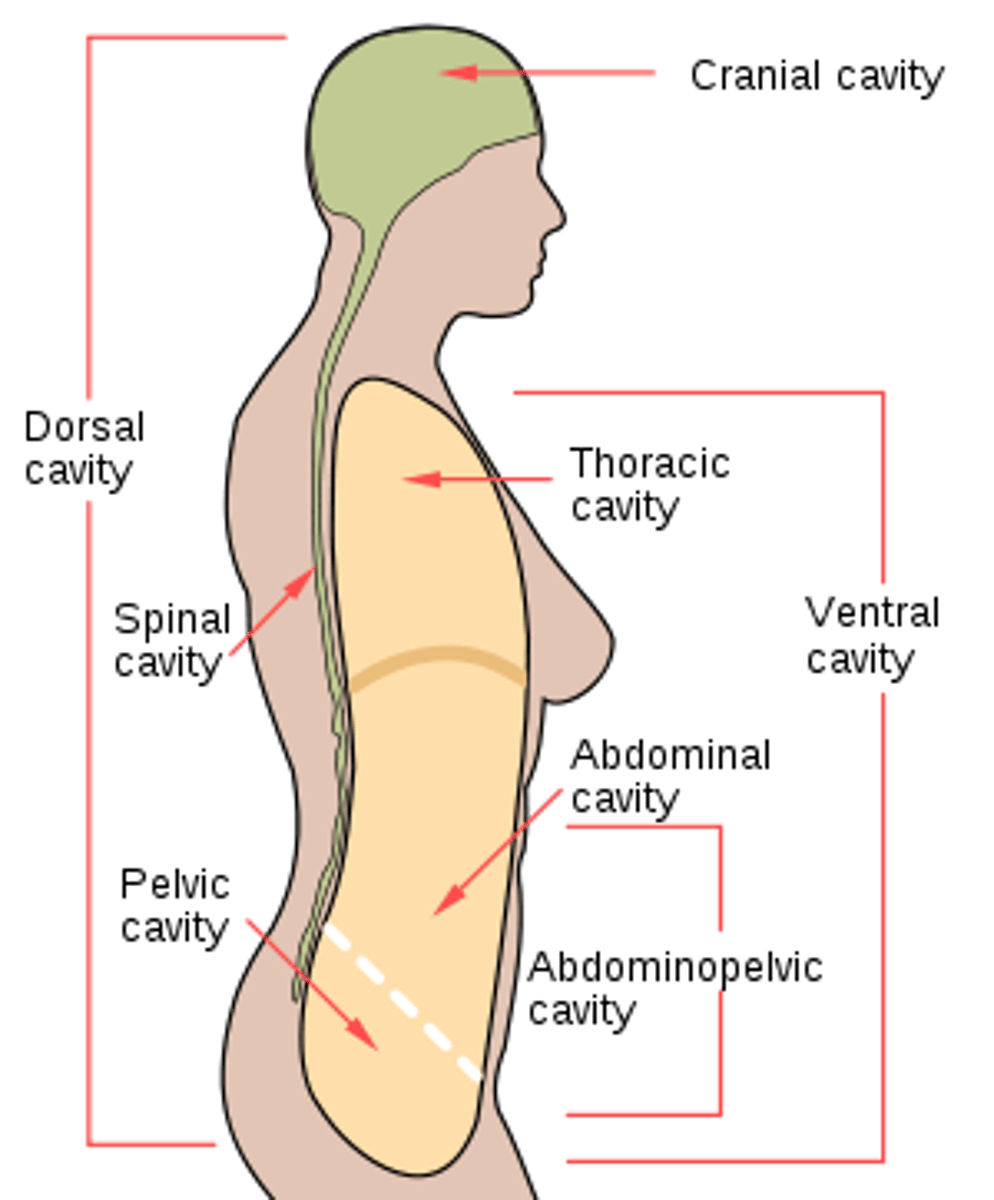
ventral body cavity
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
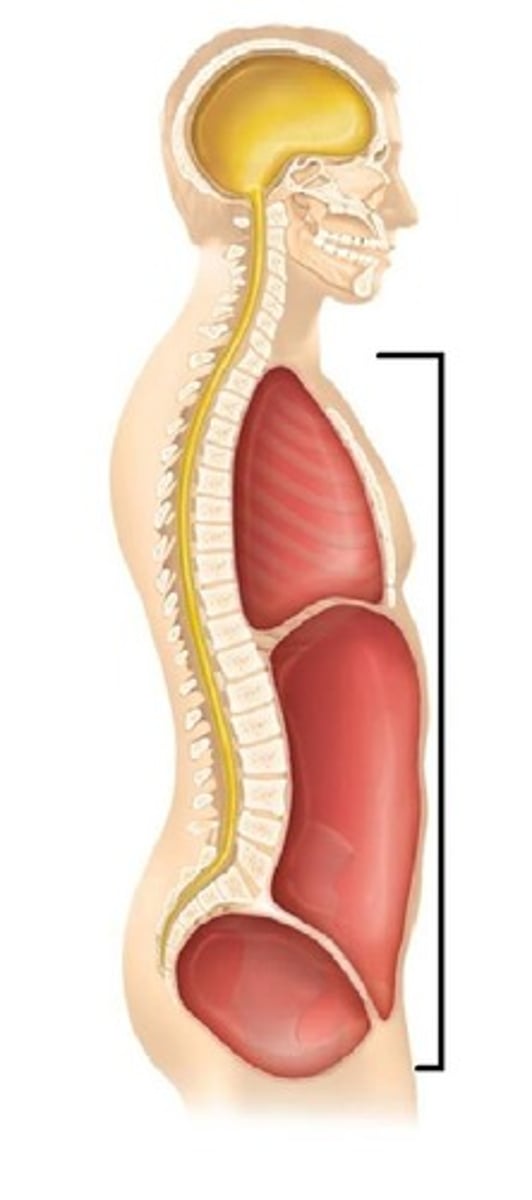
thoracic cavity
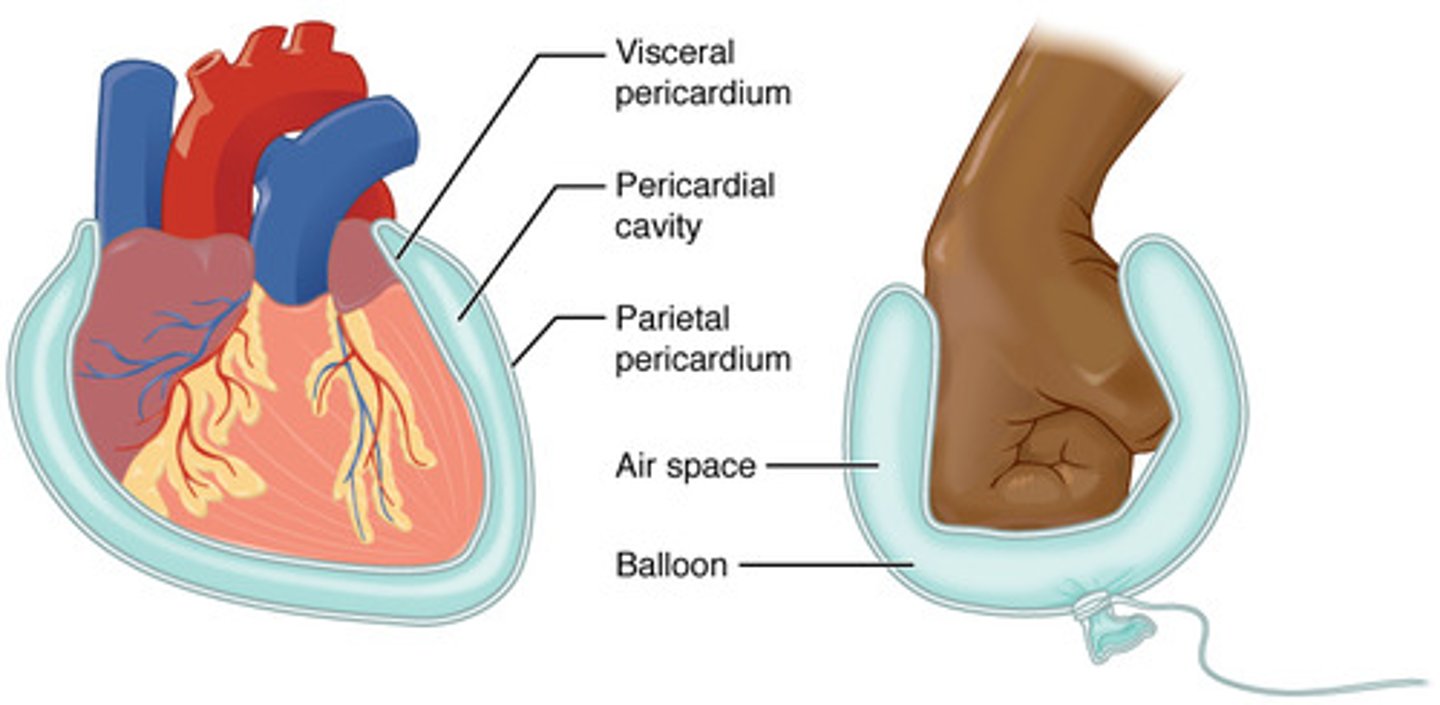
superior to diaphragm, pleural and pericardial cavities
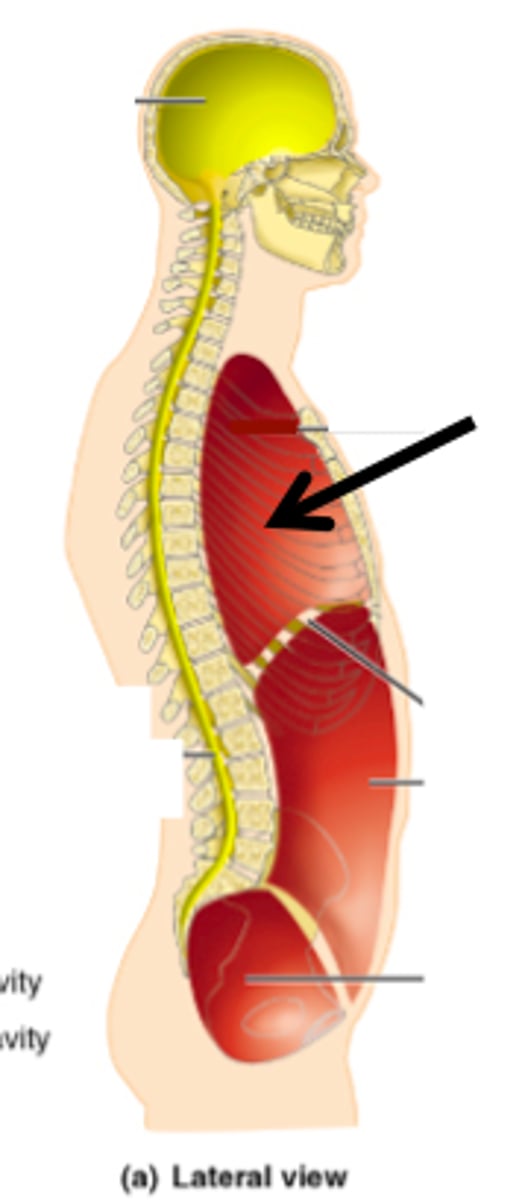
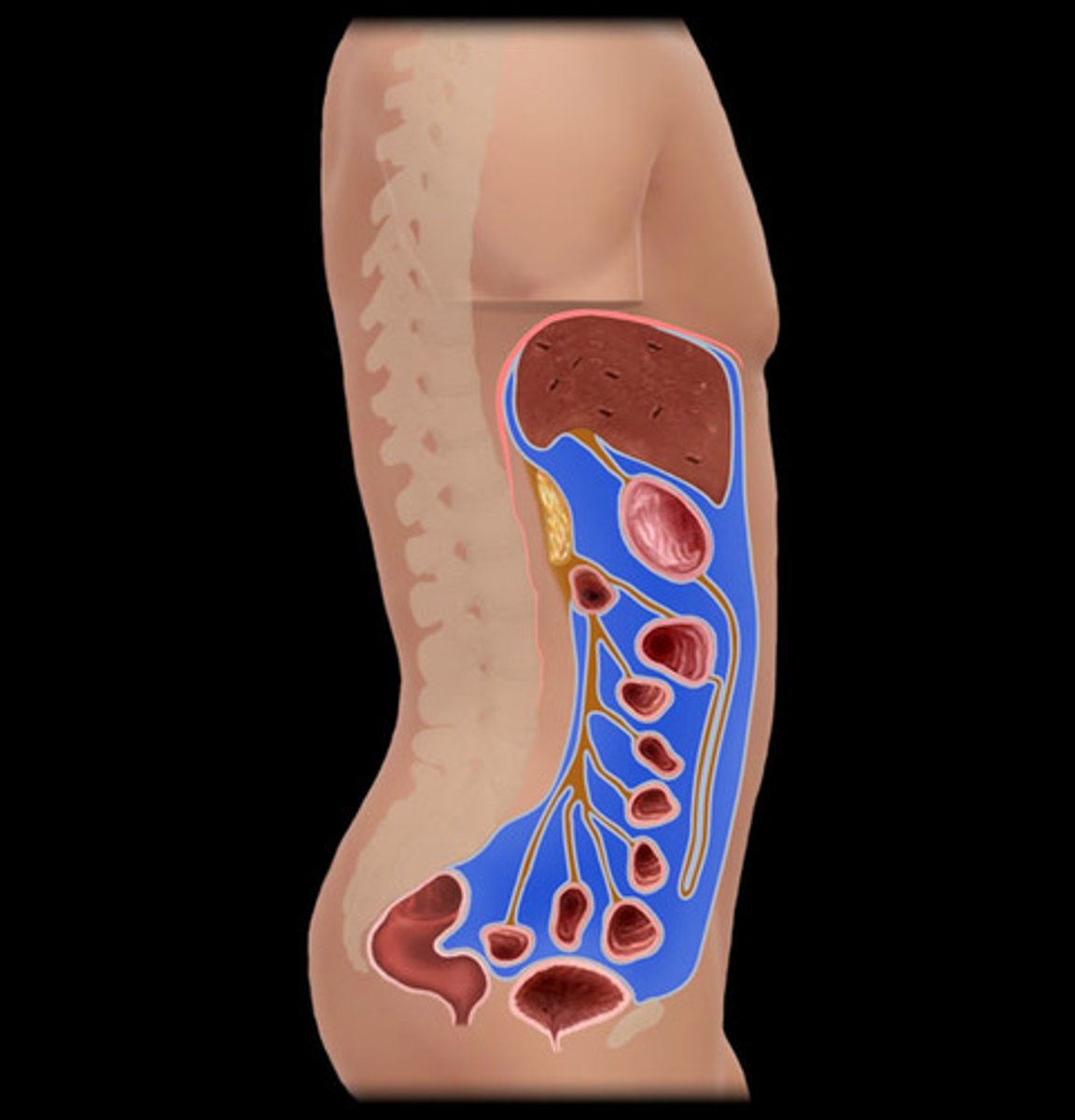
peritoneal cavity
Sometimes also called abdominal cavity or upper abdominal cavity. The space within the abdomen that contains the intestines, the stomach, and the liver. It is bound by thin membranes (the parietal and visceral peritoneum).
pelvic cavity
Inferior portion ; Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
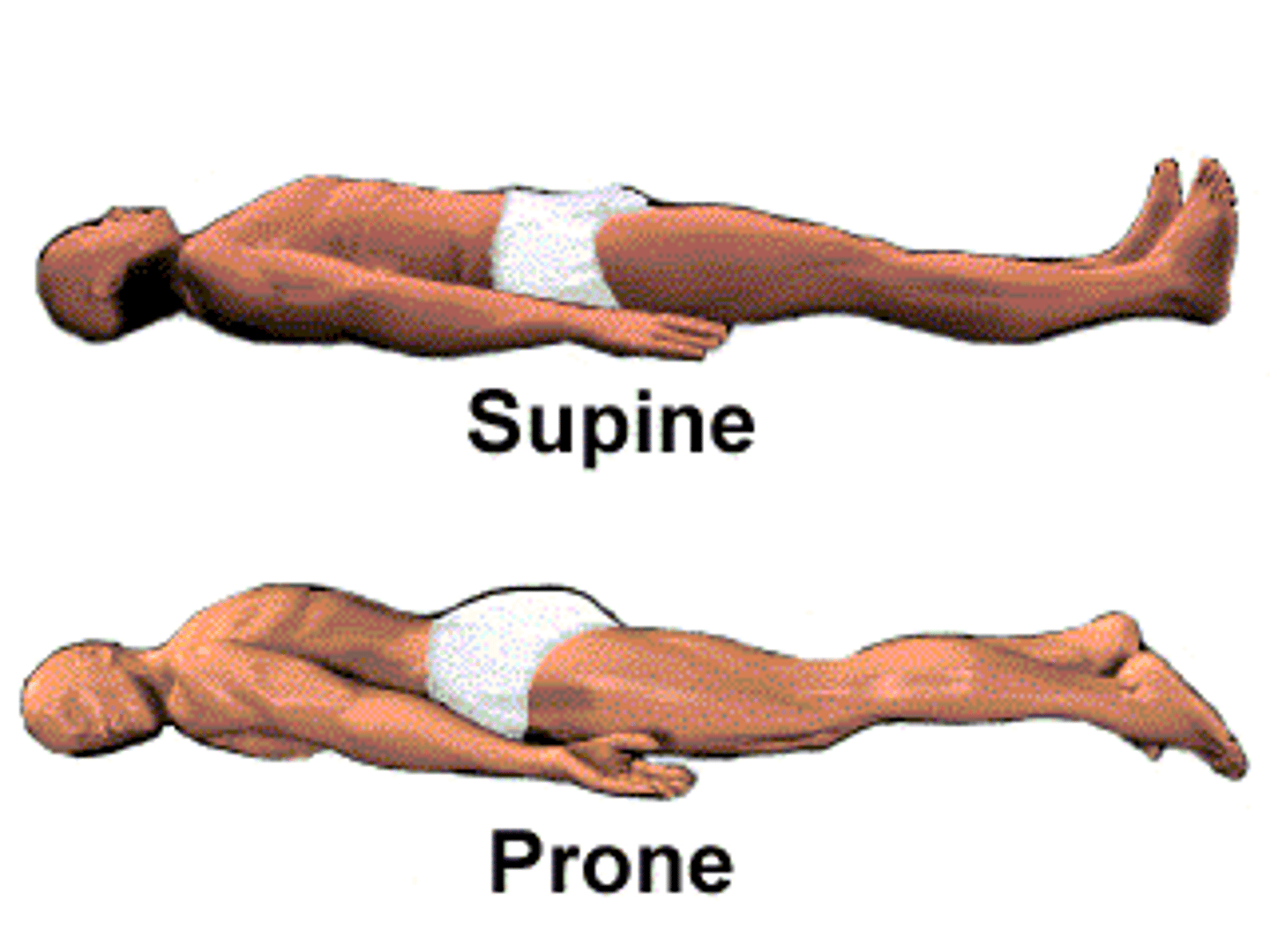
Supine and Prone Positions
Supine: Lying face up
Prone: lying face down
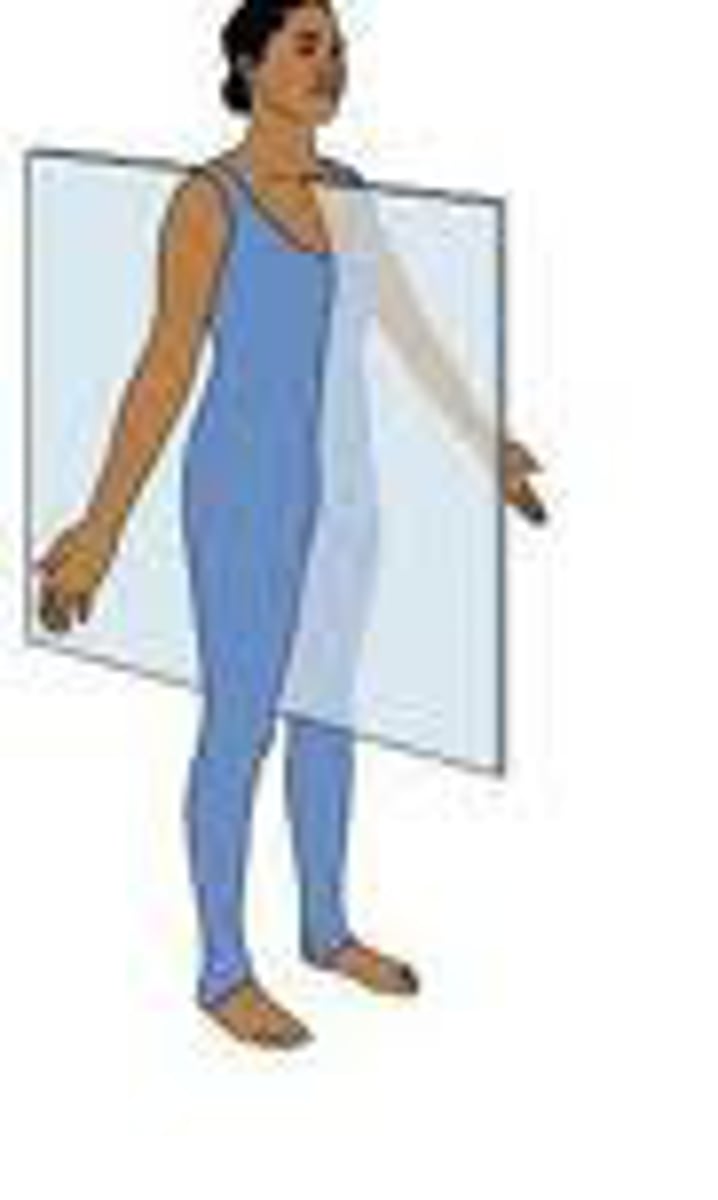
Midsagital (median) plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
parasagittal plane
Divides body into unequal right and left sides
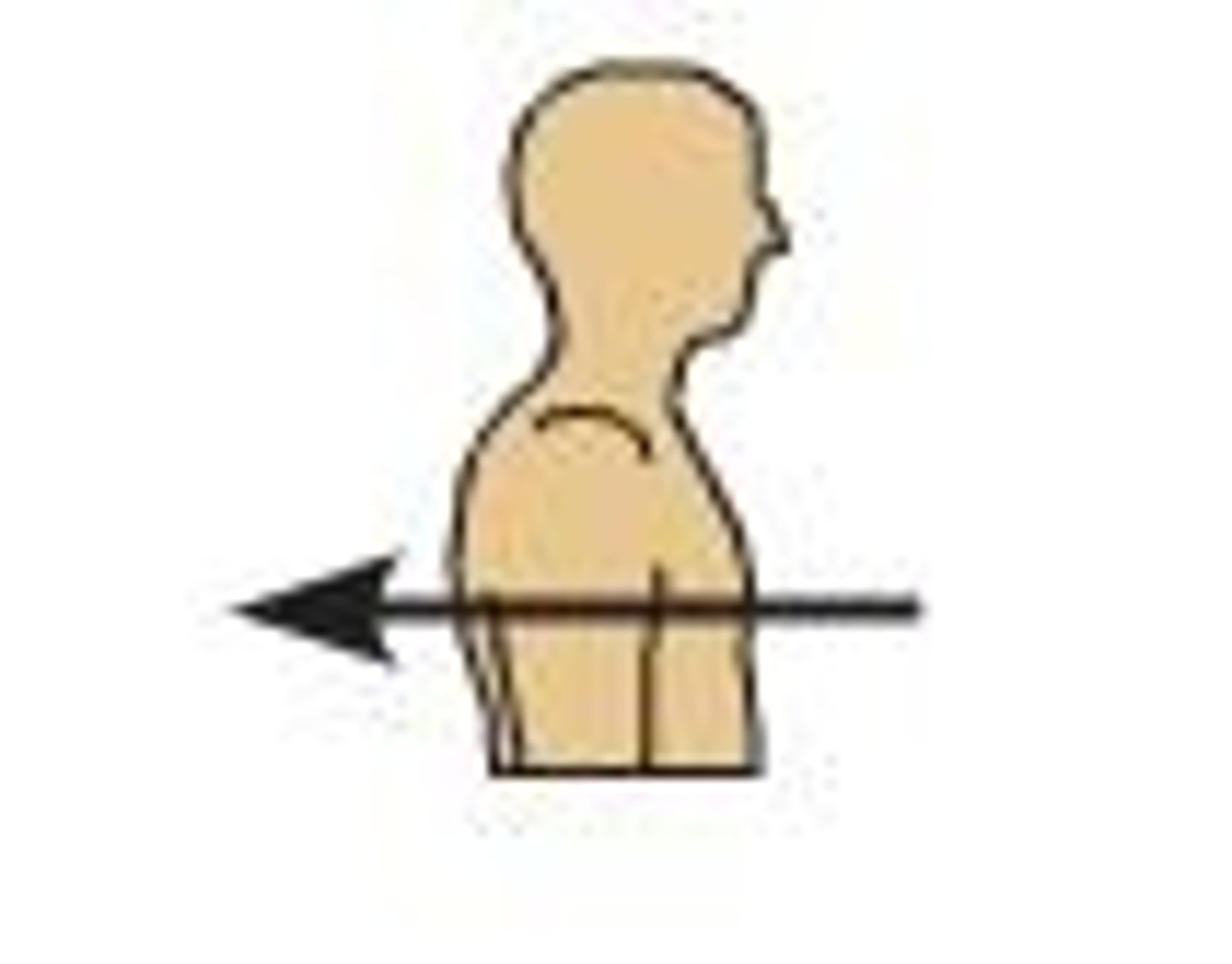
Dorsal
back or posterior (in humans)
Ventral
anterior or towards the front (in humans)
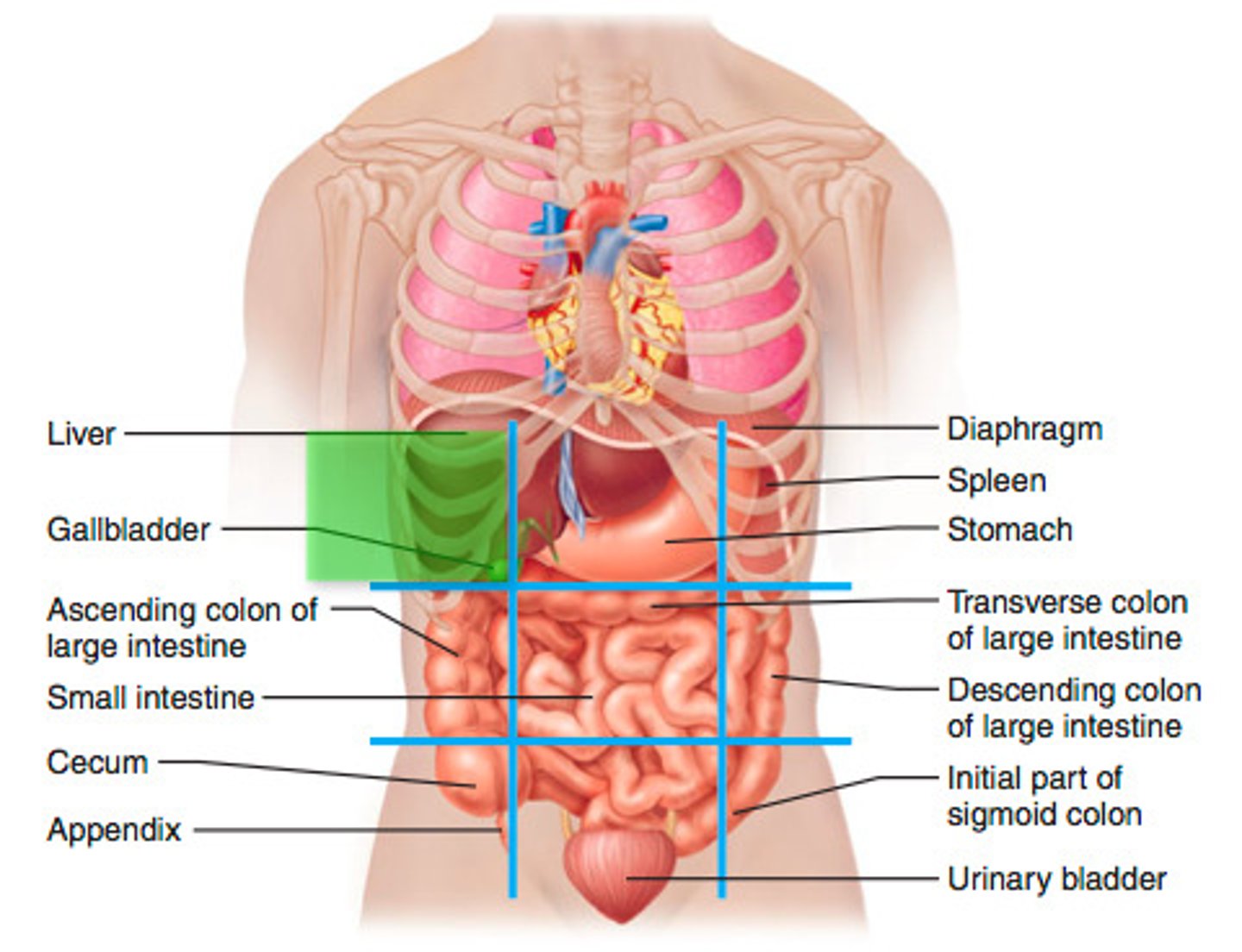
Right Hypochondriac region
liver, gallbladder (hypo= under, chondro = cartilage/ribs)
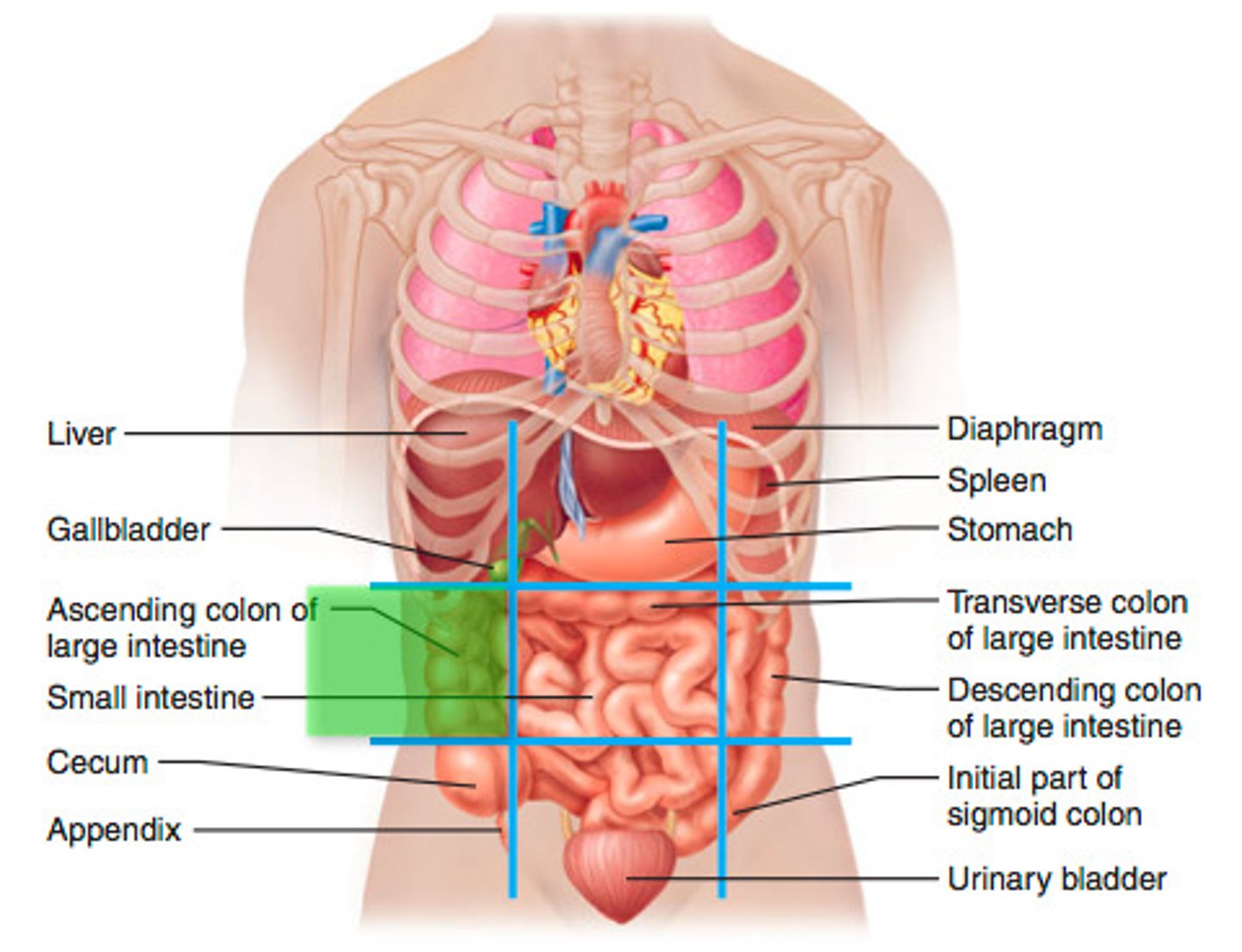
right lumbar region
ascending colon of large intestine, small intestine
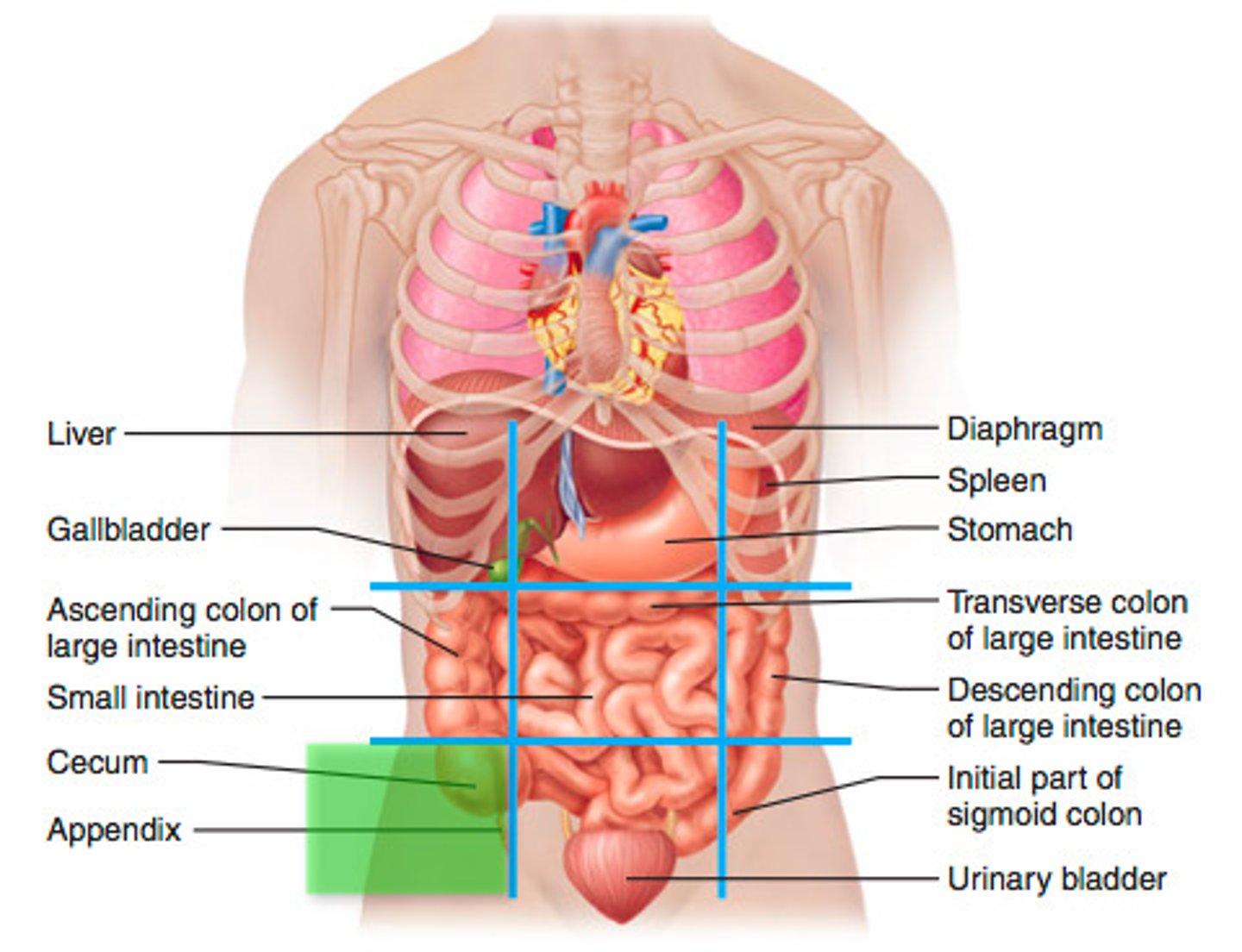
right inguinal region
cecum, appendix
left hypochondriac region
diaphragm, spleen (hypo= under, chondro = cartilage/ribs)
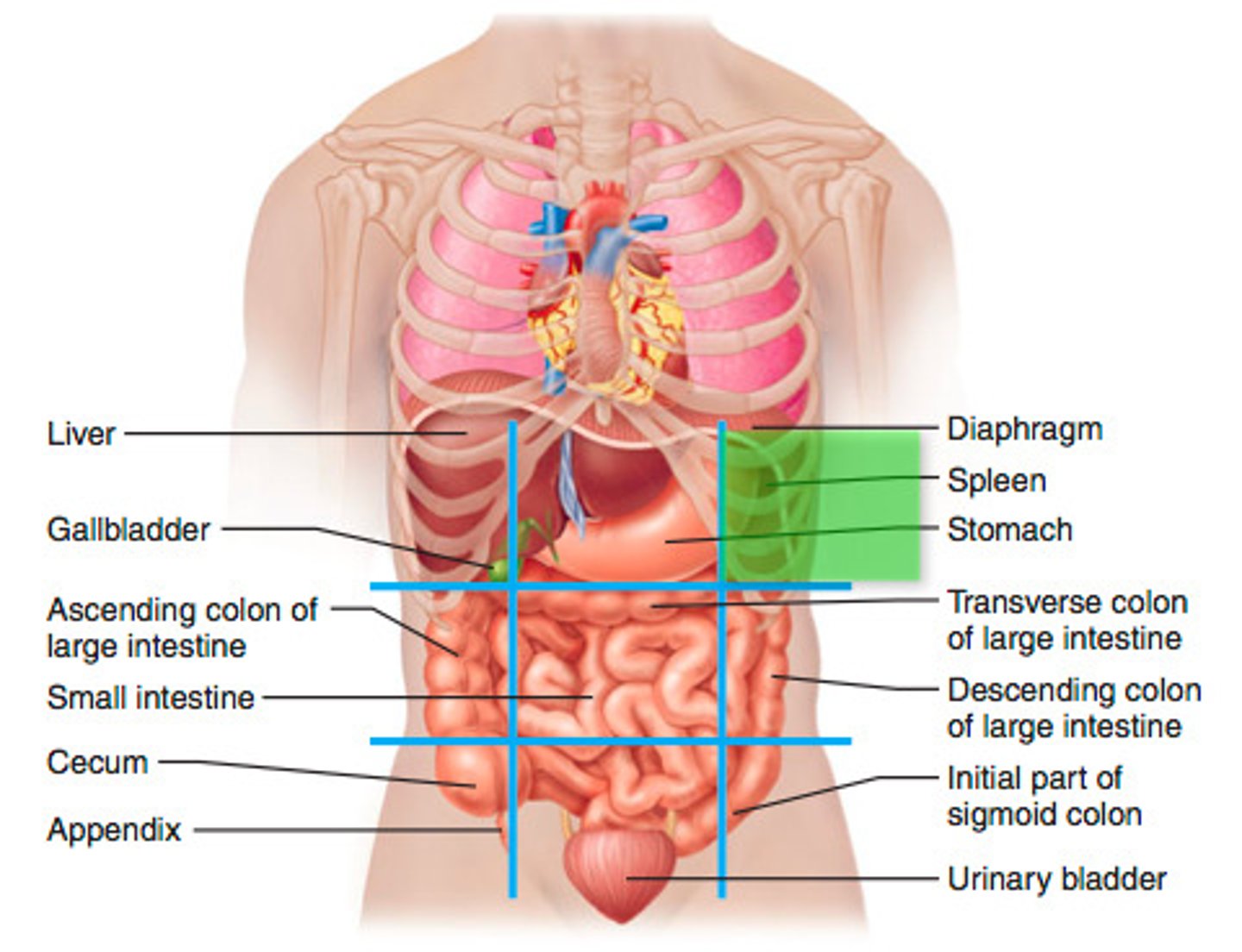
Left lumbar region
descending colon and transverse colon of large intestine
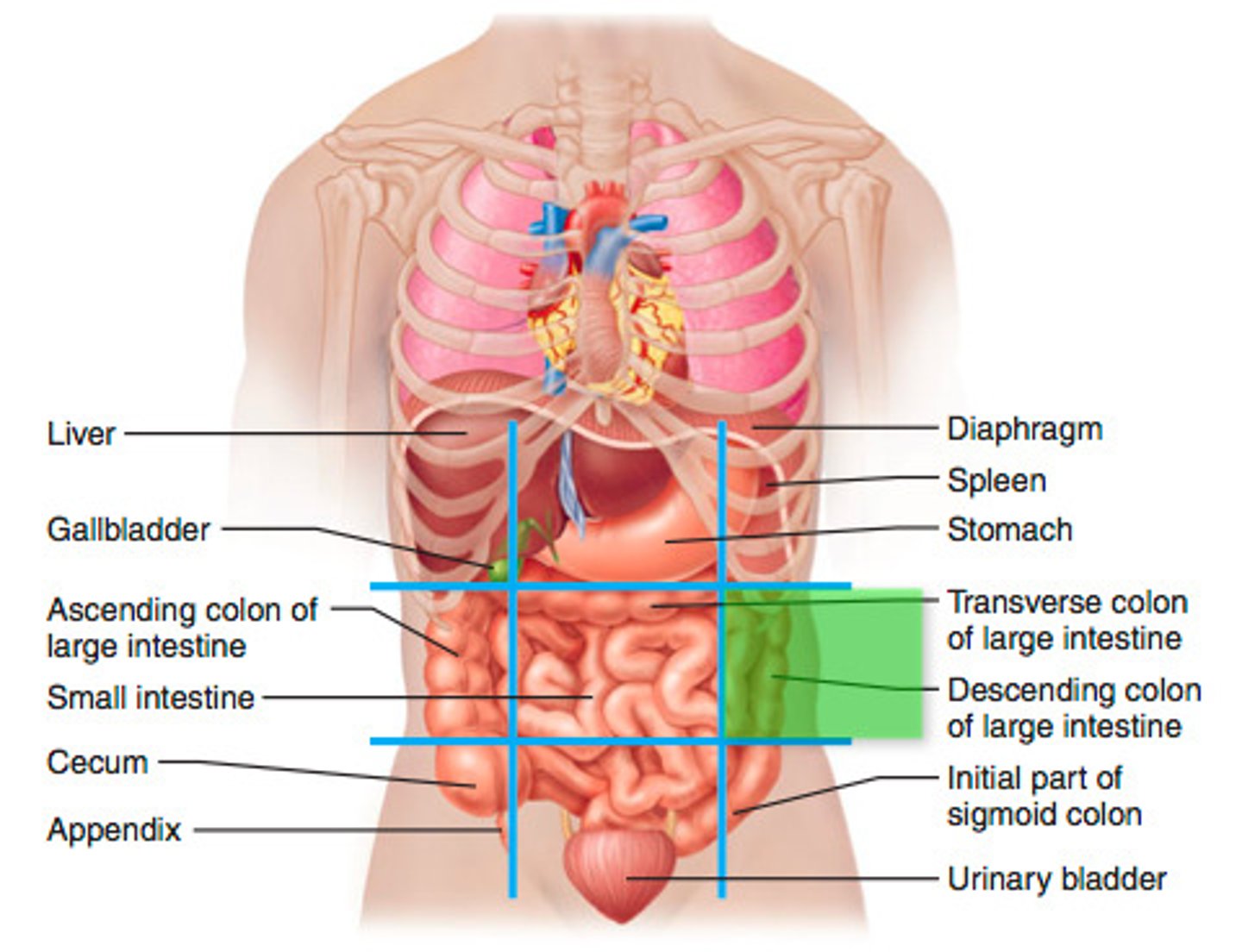
Left inguinal region
sigmoid colon, urinary bladder
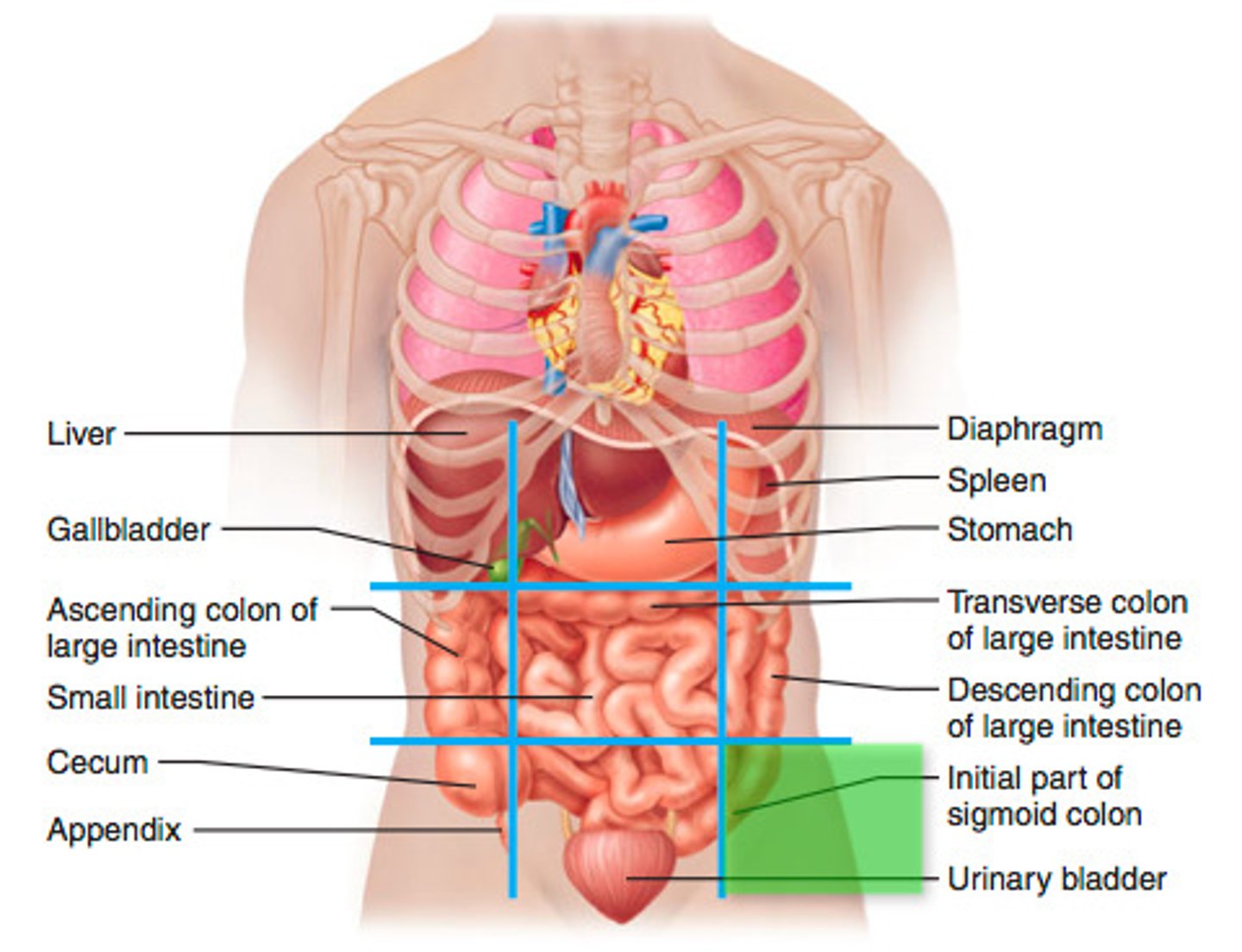
epigastric region
Stomach, liver (epi = on top of, gastric = stomach)
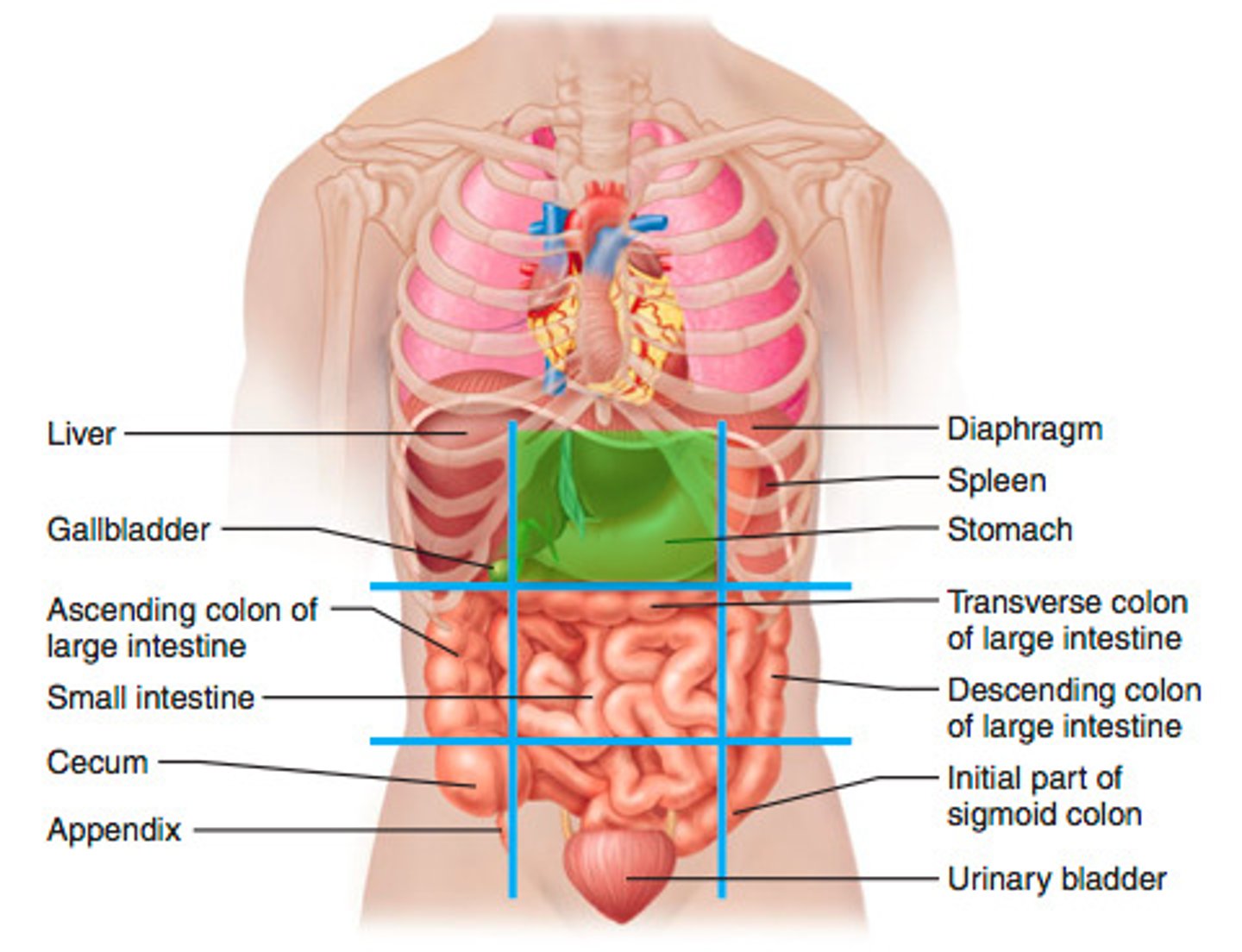
umbilical region
small intestine, transverse colon
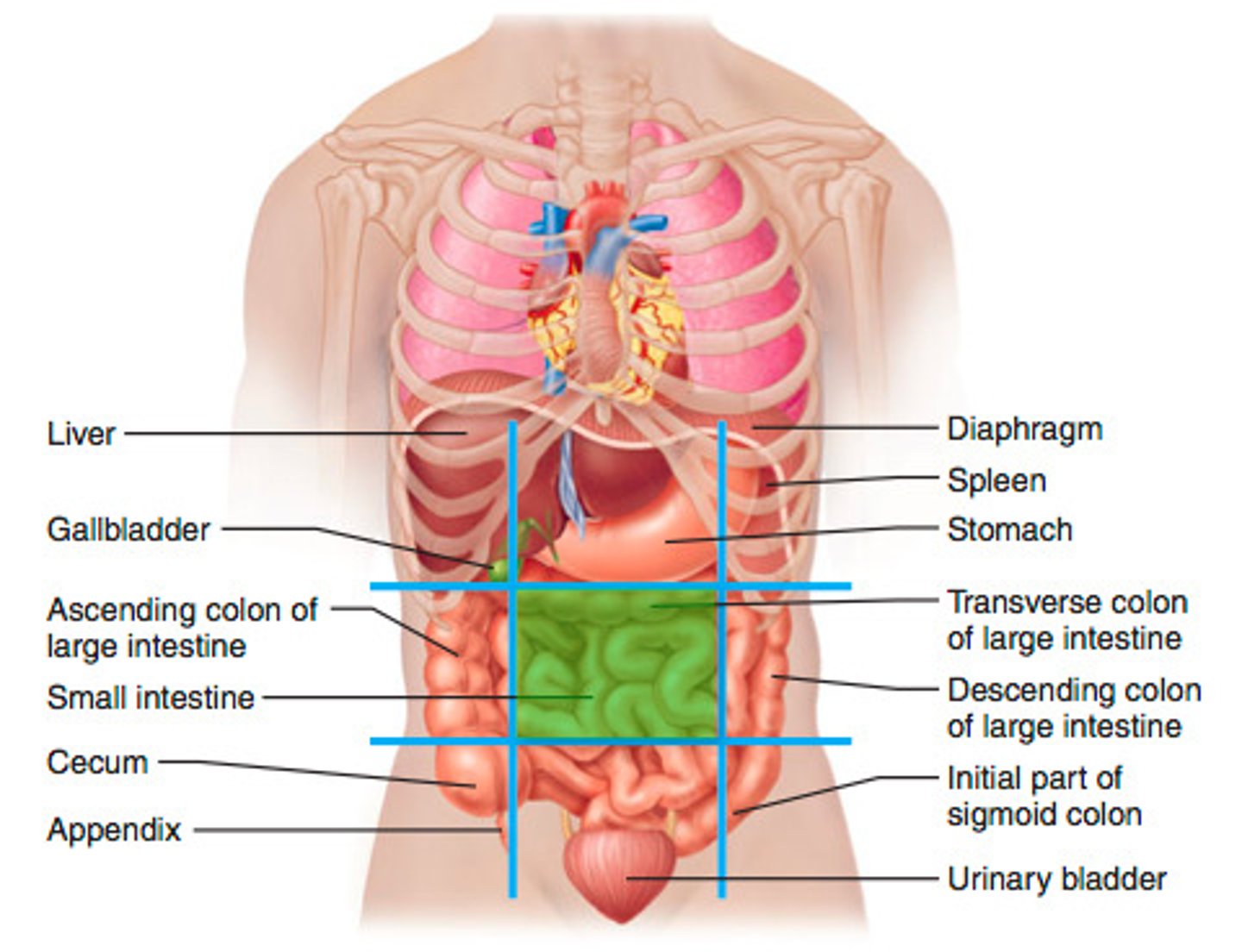
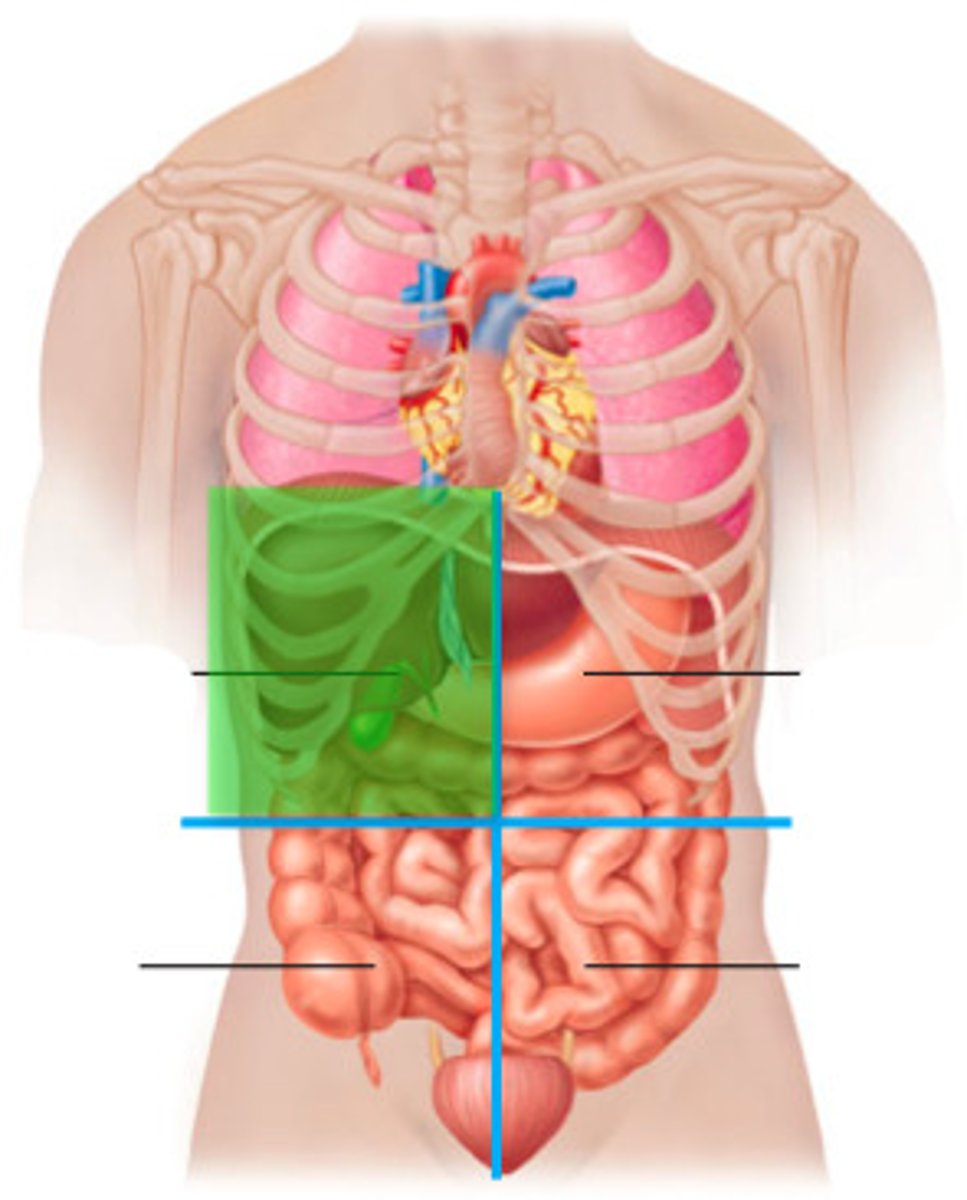
hypogastric (pubic) region
bladder, small intestine, colon (hypo= under/ inferior , gastric = stomach)
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Liver, stomach
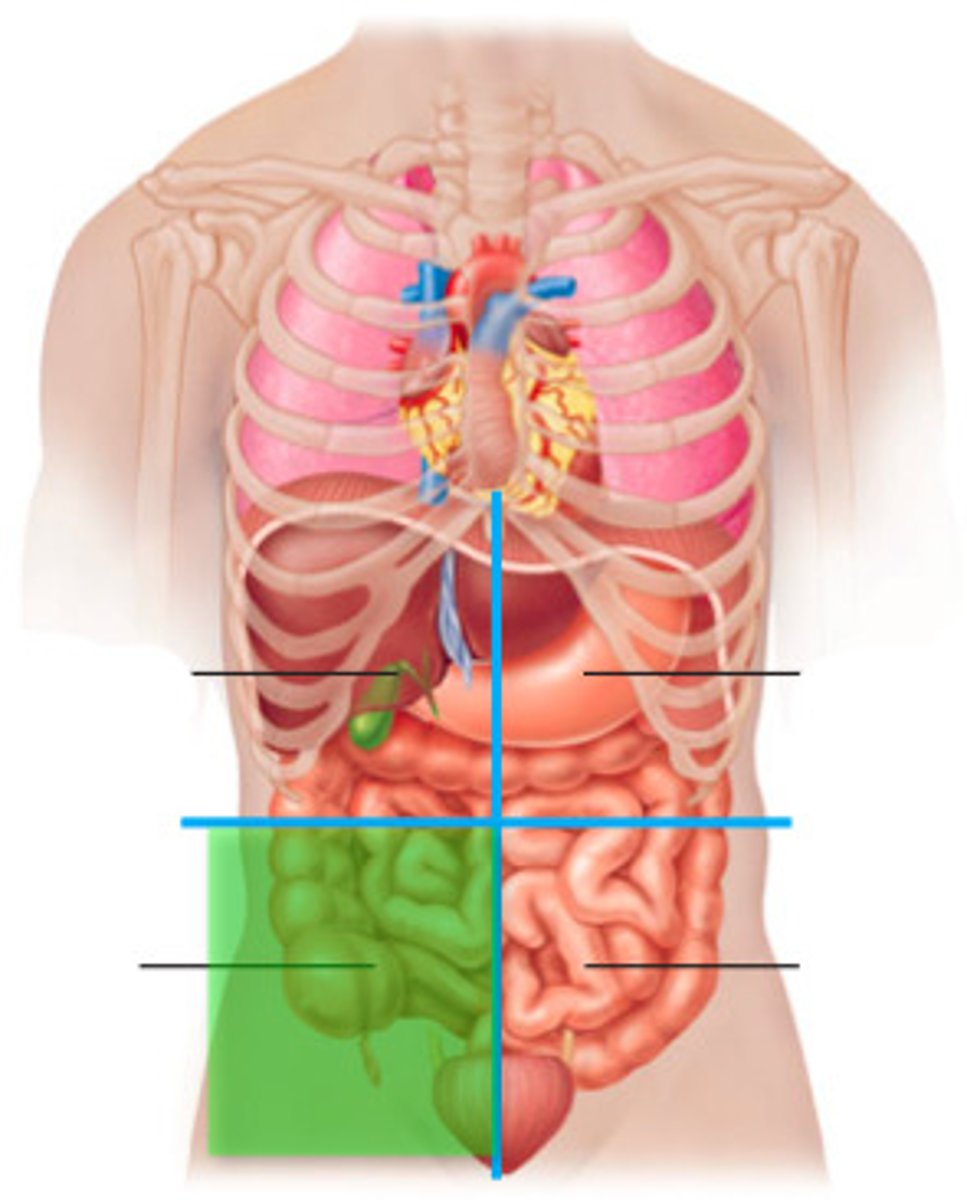
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
cecum, appendix, large intestine
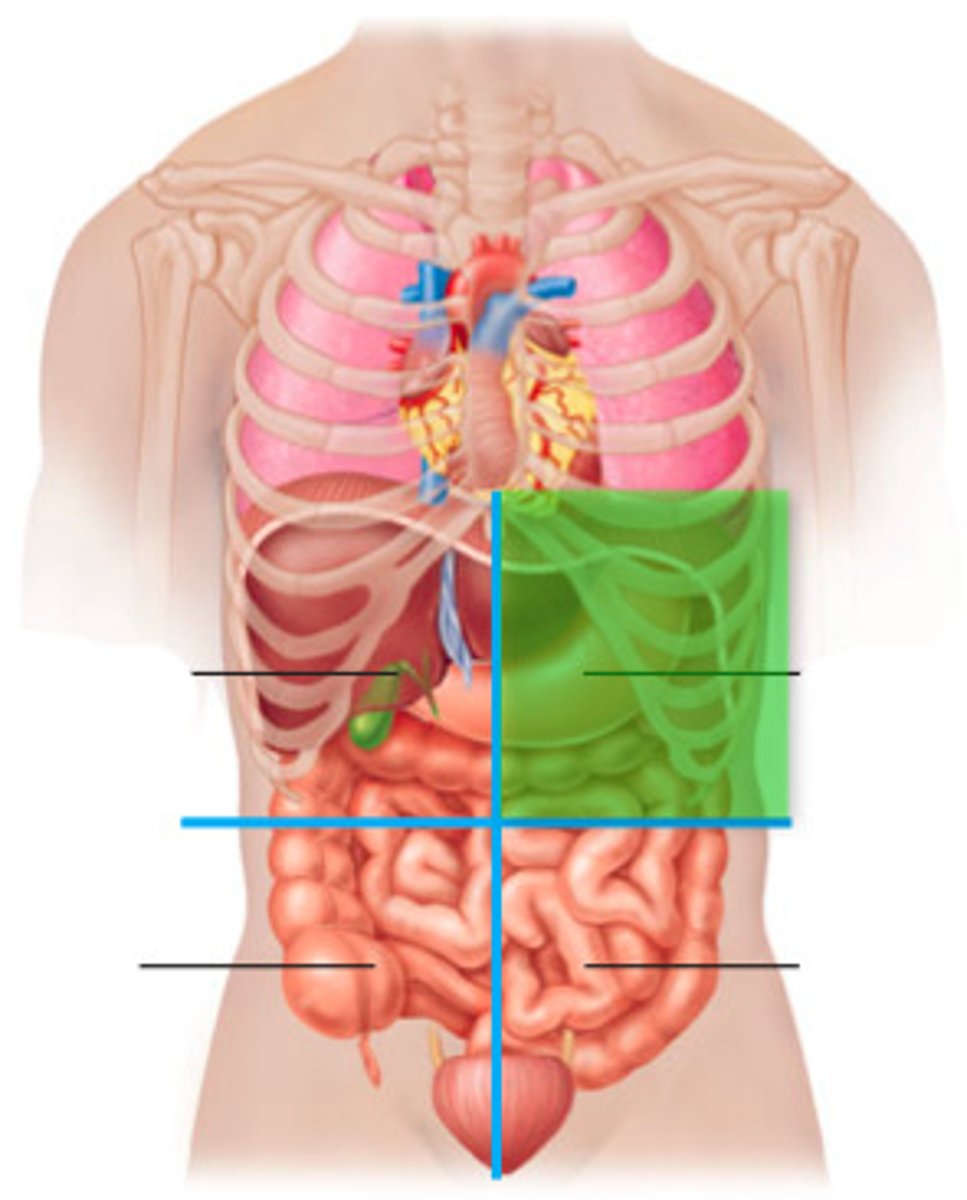
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
spleen, liver, pancreas, stomach
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
small intestine, large intestine, left ovary, left Fallopian tube, left ureter
serous membranes (serosa)
Serous membrane (or plural, serosa) is a thin membrane lining the organs and inner walls of body cavities. These membranes secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding (reduce friction) between the organs and body walls as they rub against each other.
Gastra
stomach
Myo
Muscle
Cyst
bladder, hollow
Dys
painful, difficult, abmormal
neur
nerve
otic
ear, having to do with the ear (for example, an ear infection is called otitis)
anabolic steroids
synthetic variants of the male hormone testosterone
Effects of anabolic steroids
increase muscle mass, infertility, liver tumors, severe acne, hair loss
Hypothermia
abnormally low body temperature (if you are out in the cold you can have hypothermia, which is dangerously low body temperature)
Hyperthermia
abnormally high body temperature (people have recently died during heat waves from hyperthermia)
Which organ system includes organs which secrete hormones, such as the thyroid, pancreas, and pituitary glands?
Endocrine System
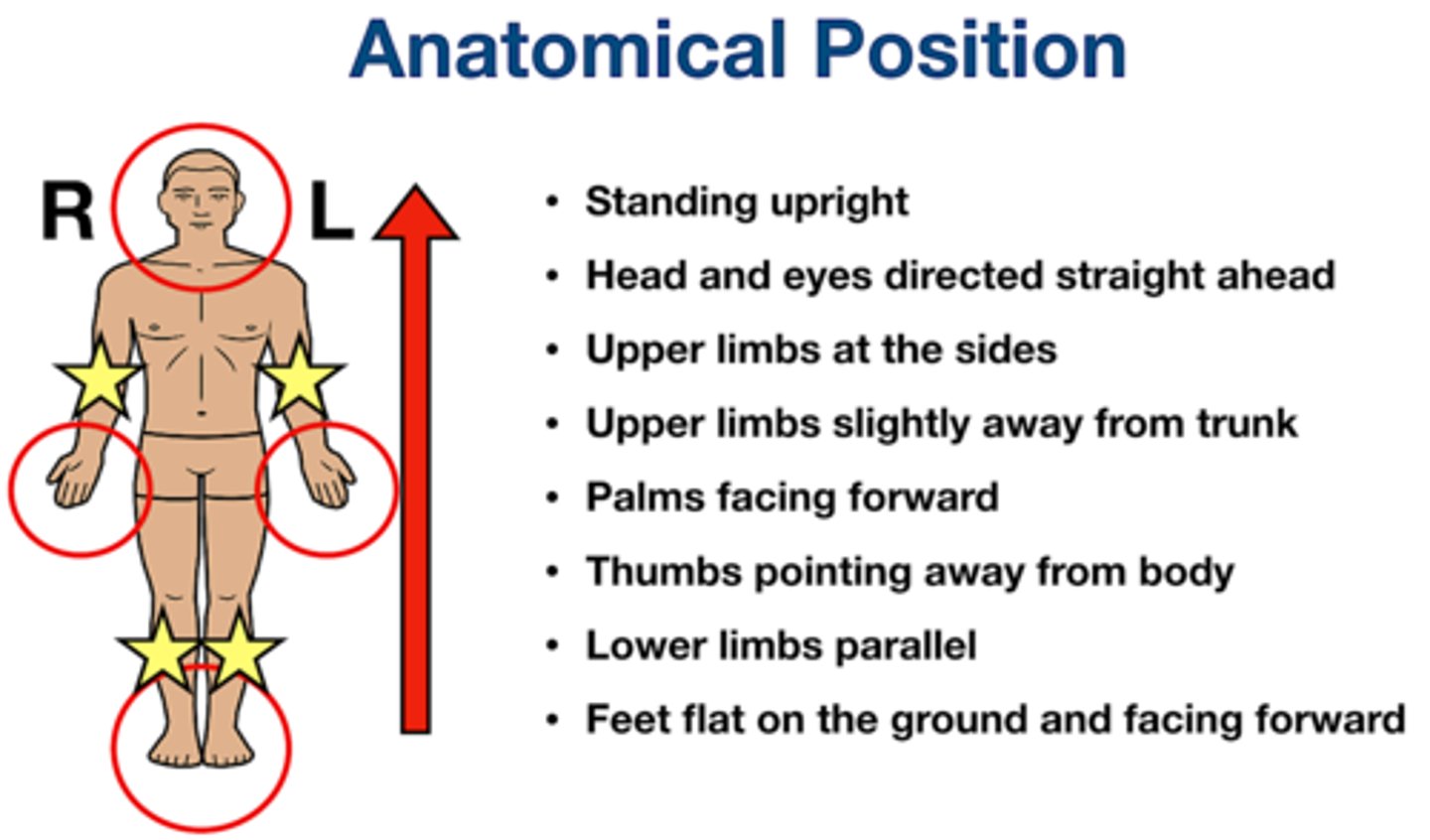
Define or draw anatomical position.
Briefly explain the homeostatic mechanism that takes place when your body gets too hot, such as from a high fever?
Your body systems work together to help the body maintain a stable internal temperature. If body temperature rises, blood is directed to the skin. This allows more blood to flow near the skin's surface. Heat is given off by the skin into the surrounding air. Sweat is produced; when the sweat evaporates, it helps to cool the body. Rapid breathing can also help the body eliminate excess heat. Together, these responses to increased body temperature explain why you sweat, pant, and become red in the face when you exercise hard.

The study of large body structures, visible to the naked eye, such as the heart is called ________ anatomy.
gross
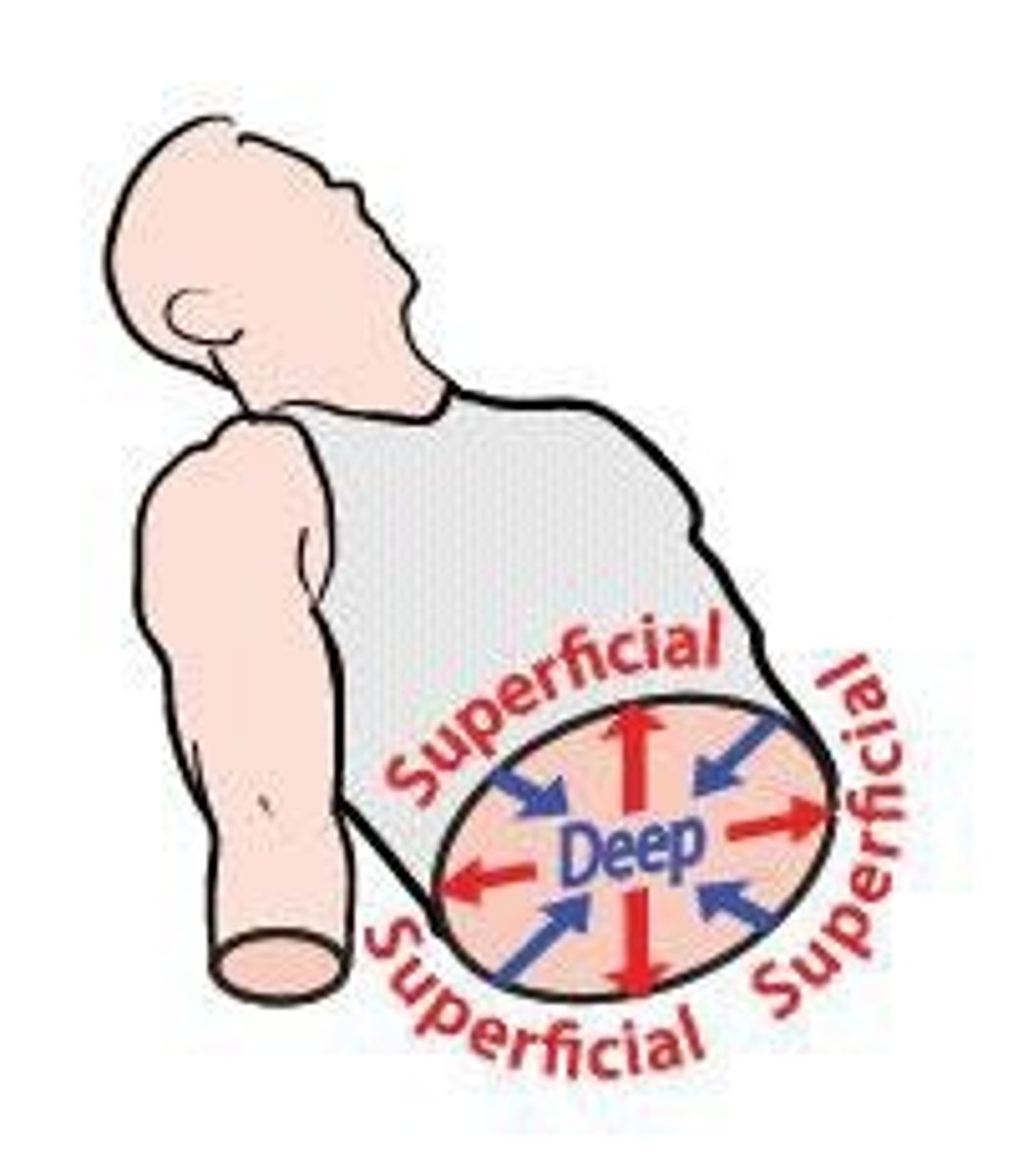
superficial
near the surface (example, the sternum is superficial to the heart )