Evolution and Human Behavior 01:070:201 Cronk | Test 2
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Sexual reproduction
two parents combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
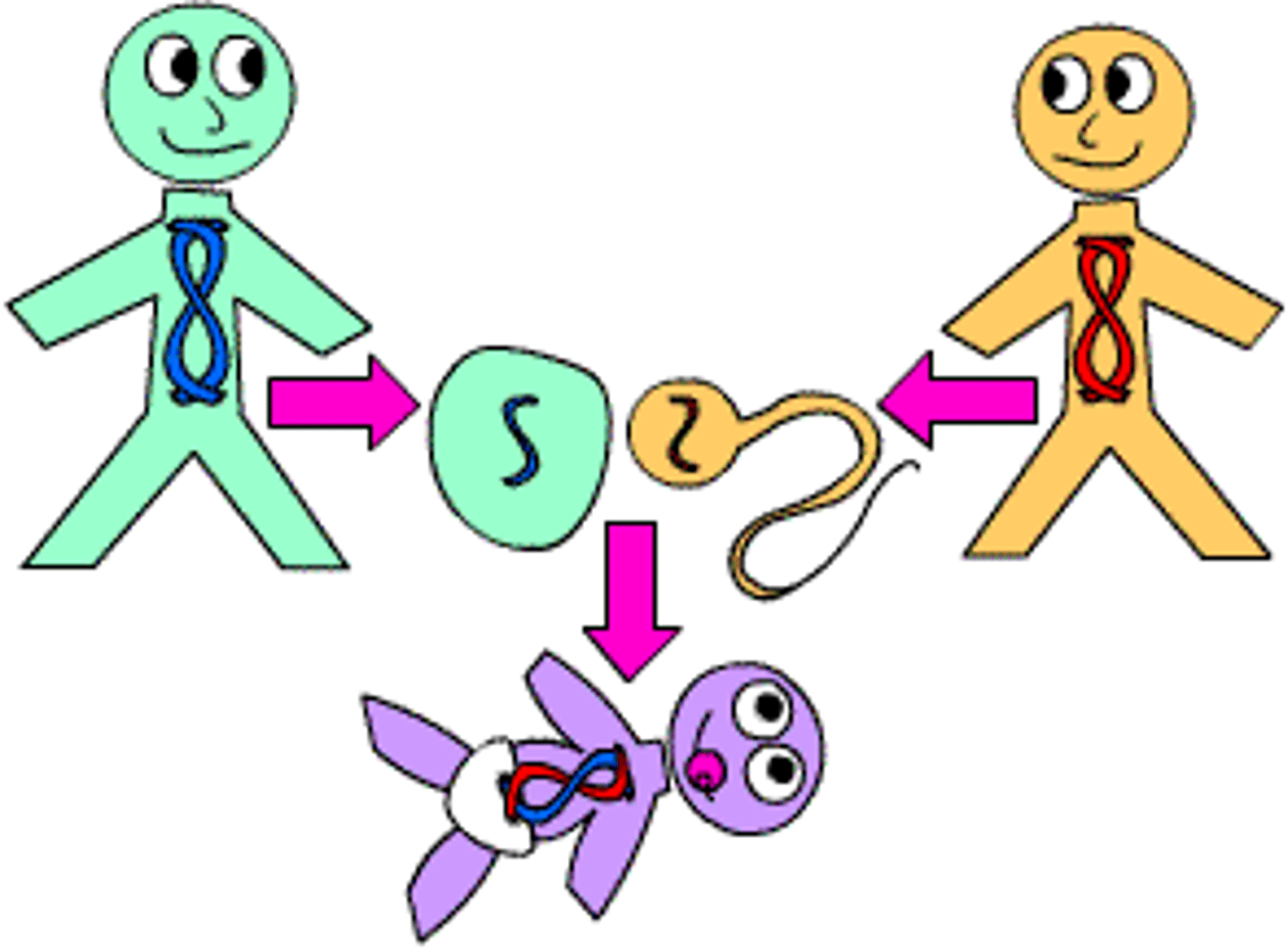
Asexual reproduction
process by which a single parent reproduces by itself
Polyandry
multiple male mates/husbands
i.e. the jicama
uncommon in humans as a marriage system

Feminized male faces
males with relatively feminine facial morphology will be preferred when parental investment is important and likelihood of conception is low
Engagement ring study
American men pay more when buying rings for younger women
Key to low WHR
more gluteofemoral fat; it is especially important for the fetal nervous system (including brain development)
Effects of sperm competition on male behavior and physiology
external position of testes and epididymis, was believed that internal testes would cause sperm to be weaker
Sim pua marriages in Taiwan
children betrothed to each other are also raised together, leading to unhappy marriages and lower reproductive rates
believed that by raising children together as siblings they would want to wed, though this resulted in them not wanting to have sex, less reproduction
Indirect care
providing resources; buying the groceries, cooking
Costs of sexual reproduction
males unable to produce offspring; only half of each parent's genome passed onto offspring, disrupting successful parental genomes
Costs of mating
not having to find a mate would save time and energy
Costs of recombination
successful combinations of genes are lost when recombination occurs during meiosis; genes get mixed up due to meiotic process; run the risk that offspring will be lower quality than parent
Cost of meiosis
half your genome is lost when you make a gamete (sperm/egg)
Benefits of sexual reproduction
sexual reproduction produces a greater chance of variation within a species than asexual reproduction would
this variation improves the chances that a species will adapt to his environment and survive
Red Queen effect; pathogen stress
Gametogenesis
making of gametes
Red Queen effect
sex makes organisms moving targets for pathogens; pathogens can evolve much more quickly than their hosts, if a pathogen evolves the ability to attack you and if you reproduce asexually, it will also be able to attack your offspring; if you reproduce sexually, then your offspring aren't identical to you, so they have a fighting chance against the pathogen; sex is more common and sexual selection is more intense where pathogens are a problem
females often prefer males that have signs of being healthier and having fewer parasites; to maintain relative fitness, each population must constantly adapt to the other
Daphnia magna, a facultative sexual crustacean, and Pastuera Ramosa, a bacterial parasite
more asexual Daphnia than sexual Daphnia become infected
the offspring of asexual Daphnia are infected at the same rate as their mothers, but the rate of infection among sexually produced offspring decreases
among those infected, infestation rates increase among asexually produced offspring but remain the same among sexually produced offspring
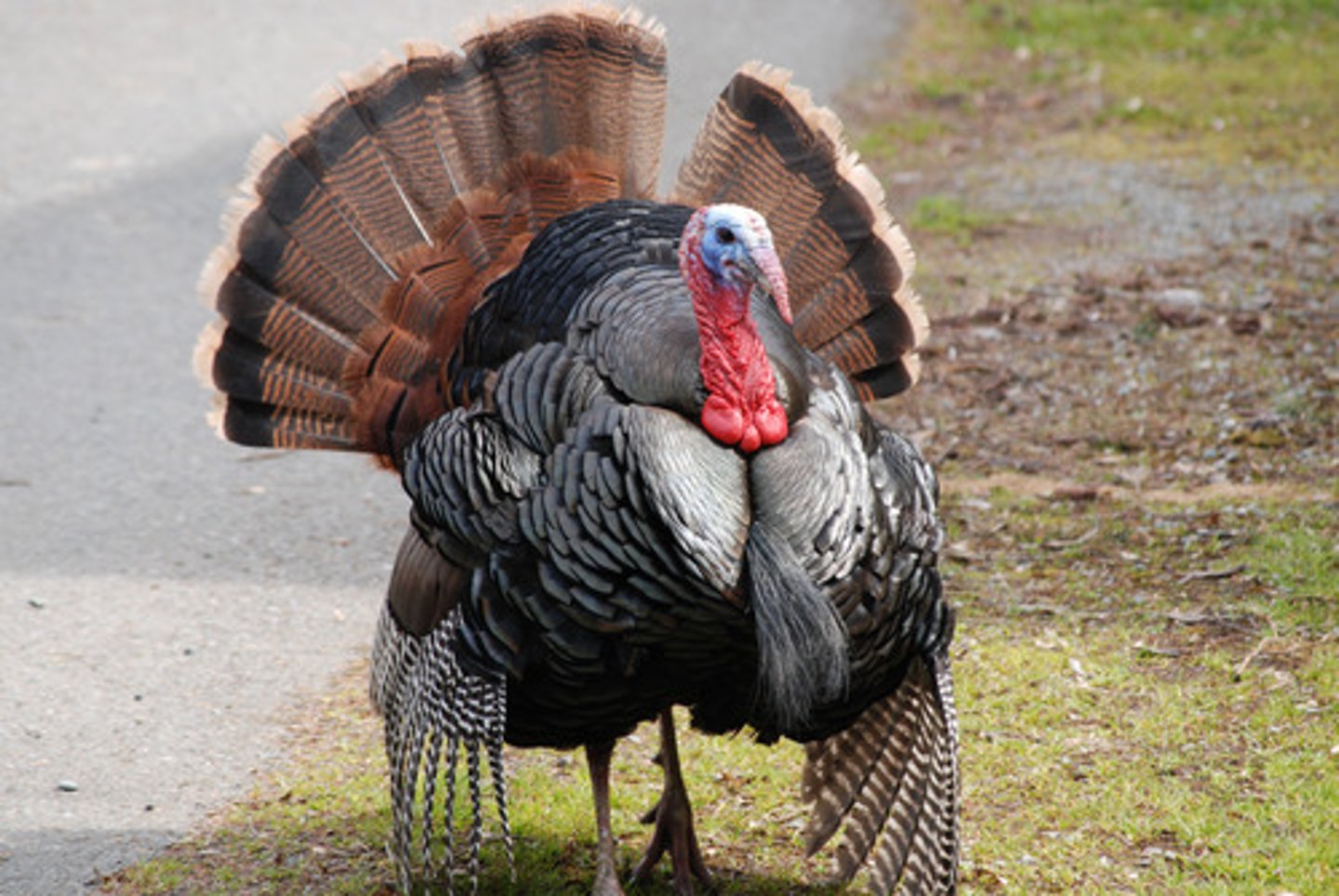
Wild turkey
example of Red Queen effect; female wild turkeys prefer males (toms) longer snoods and wider crowns because such men have fewer parasites than others

Pathogen stress
pathogens and diseases encountered by a species shape the development of species' values and qualities
Sexual dimorphism
how different males and females are of a species are in terms of their reproductive strategies may be roughly indicated by how different they are physically
(di-morph = two-bodies)
Mixed mating strategies
few of either sex will be able to offer potential mates high levels of all desirable qualities, some might have good genes but be poor investors and vice versa; males and females may have mixed strategies in terms of what they offer and what they seek in mates
Anisogamy
"not same-size gametes"
refers to a difference in gamete size in males and females; eggs large and costly, sperm small and cheap
Divergent selection
populations of the same species evolve different traits due to varying environmental pressures, leading them to adapt in distinct ways
Small-size gamtes
do not have enough resources to develop into a zygote by themselves, but they can be produced in large numbers and they move rapidly (highly mobile)
Large-size gametes
can't move much and can't be produced in such large numbers, but they have enough resources for a successful zygote
Medium-size gametes
at a disadvantage compared to large & small gametes because they are too big to be very mobile or very abundant (not making many of them) but not big enough to have enough nutrients for a successful zygote
Intrasexual selection
within a single sex, they are competing with each other
males compete with each other for opportunities to mate with female
think intrasexual; a for alpha; male wants to be alpha (idk it helped me memorize it)

Intersexual selection
individuals of one sex are choosy in selecting their mates from the other sex (usually female choosy about male)

Sex-role reversal
a change in the typical behavior patterns of males and females; i.e. females compete for access to males or when males choose selectively among potential mates
happens when males invest so much and females so little
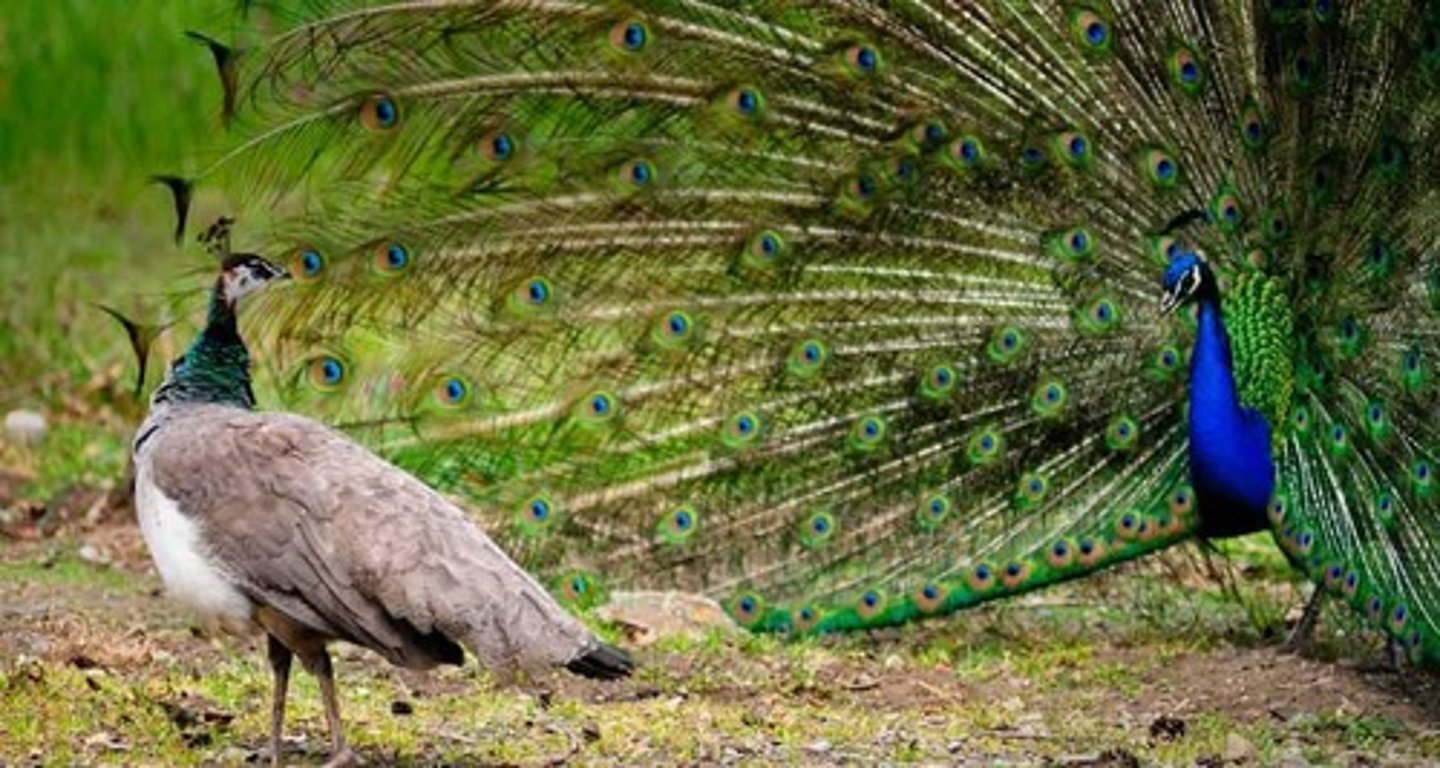
Jacana bird
males build nests, defend nests, and are picky in choosing a female; females are the showy ones that show off their qualities and look for male partners
likely because the rate of predation on jacana nests was so high that strong selection pressures were put onto women to make a lot of eggs
example of

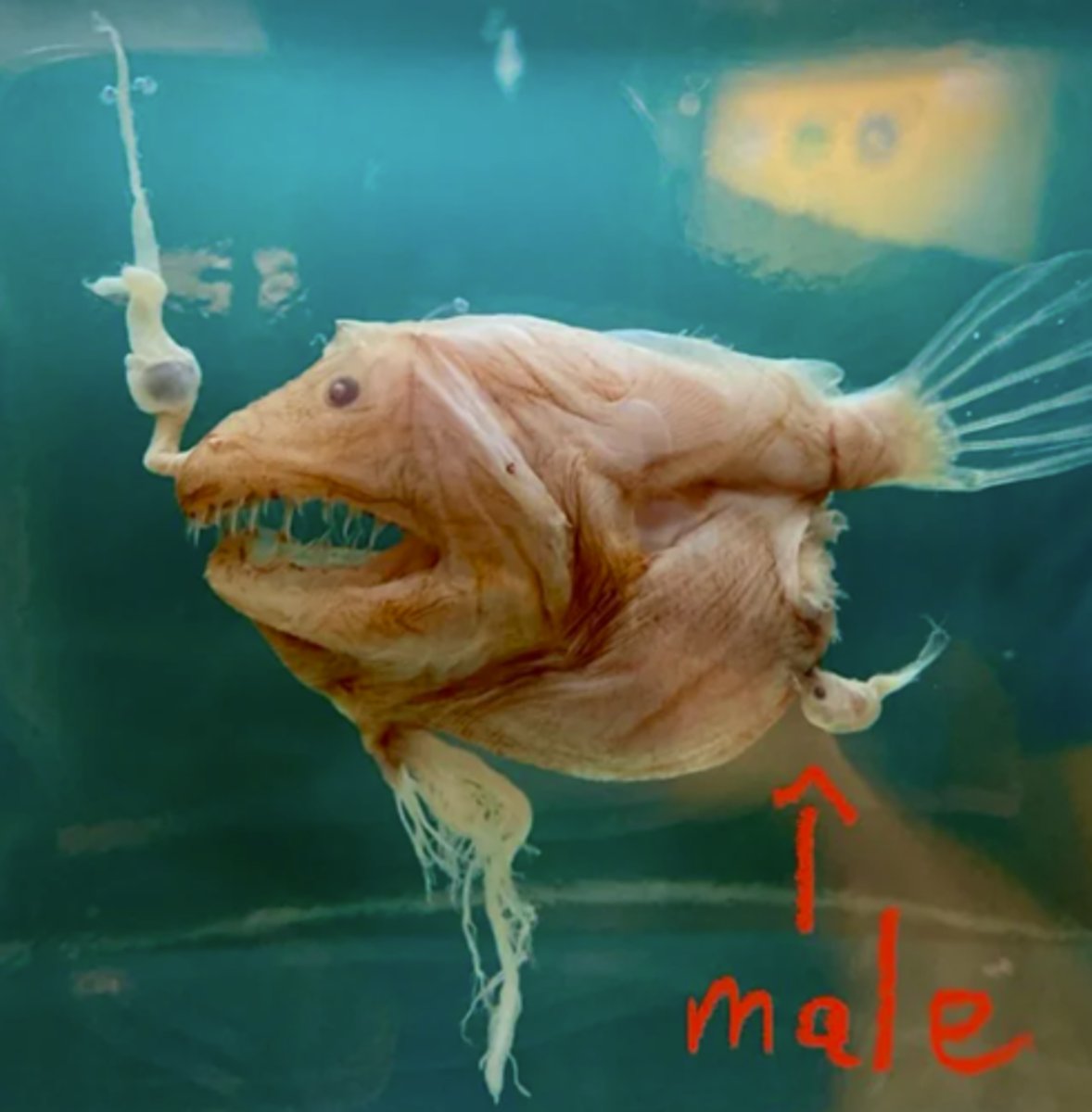
Anglerfish
high sexual dimorphism; once a male finds a female they stick to her and parasitize her because this will likely be the only female they will ever see; sometimes multiple males will latch onto one female; when she releases eggs they fertilize them
The male is very small, female is a normal looking sized fish

Black widow
high sexual dimorphism; females are much larger; eat the males
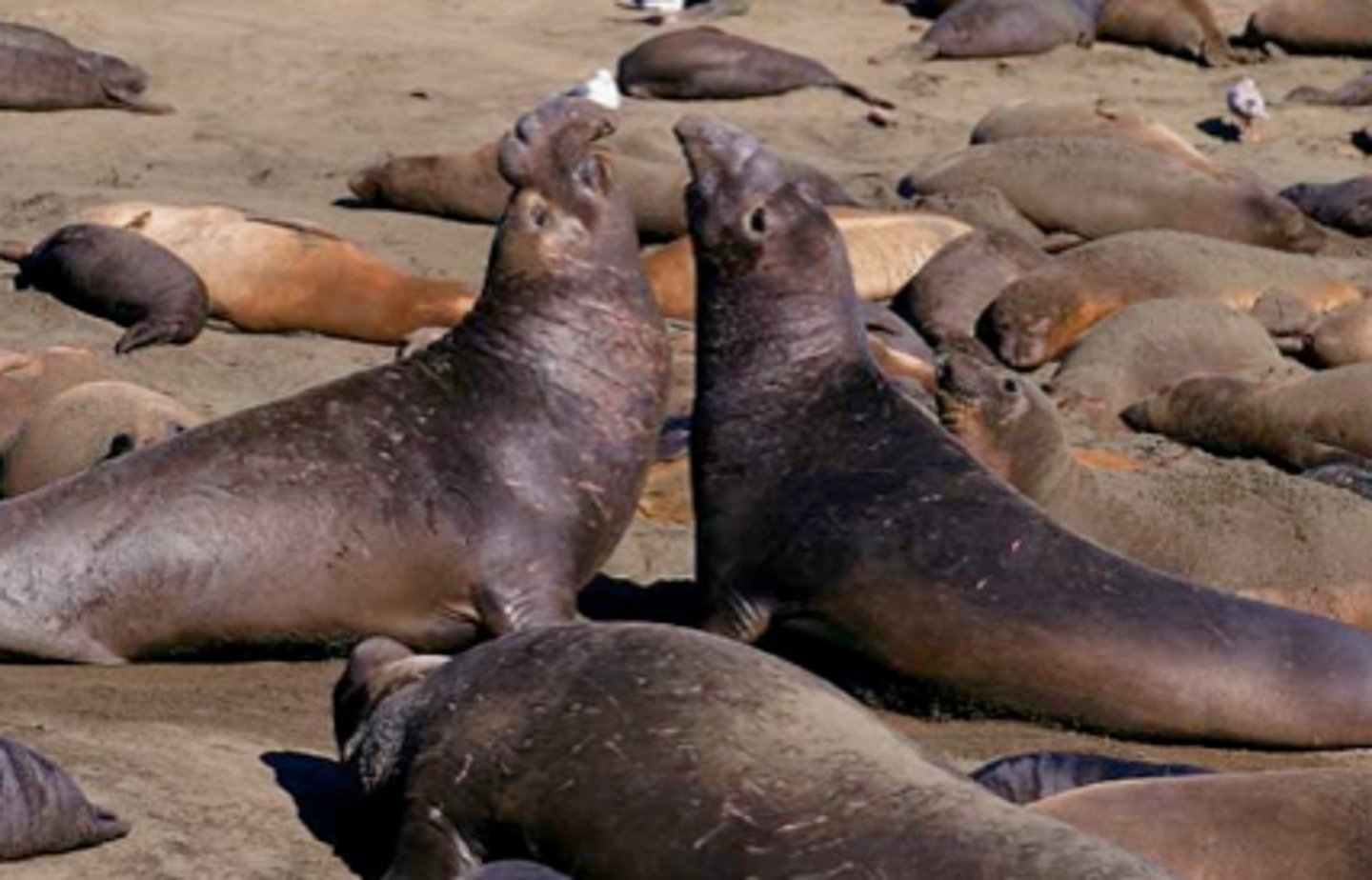
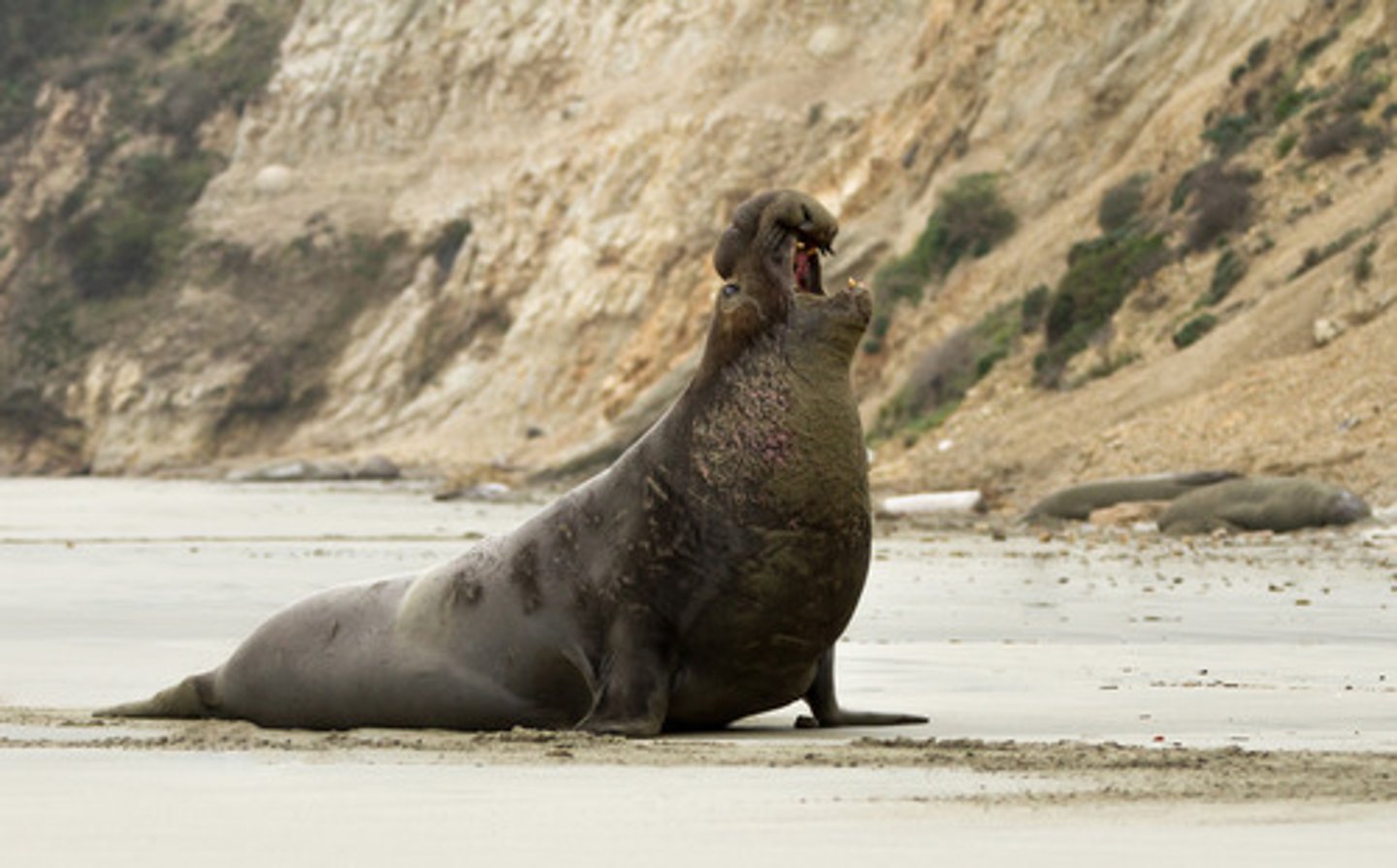
Elephant seal
males are huge and fight violent battles for control of the beach; winning male mates with resident females (females have no choice); the result of that is pups
(intrasexual)

Peafowl
peahen prefer peacocks with large and symmetrical eyes on their tails (intersexual)

Paternity uncertainty
the fact that a man cannot be sure that the children born to his female partner are his; but maternity is always known
Monogamy
single mate/spouse

Polygyny
multiple female mates/wives
uncommon in humans as a marriage system

Polygamy
multiple mates/spouses; ambiguous because sex of mates/spouses is not specified

Obligate
cannot change it; stuck with it
i.e. humans are obligate air breathers, we cannot suddenly breath underwater
Facultative
there are options; can switch around
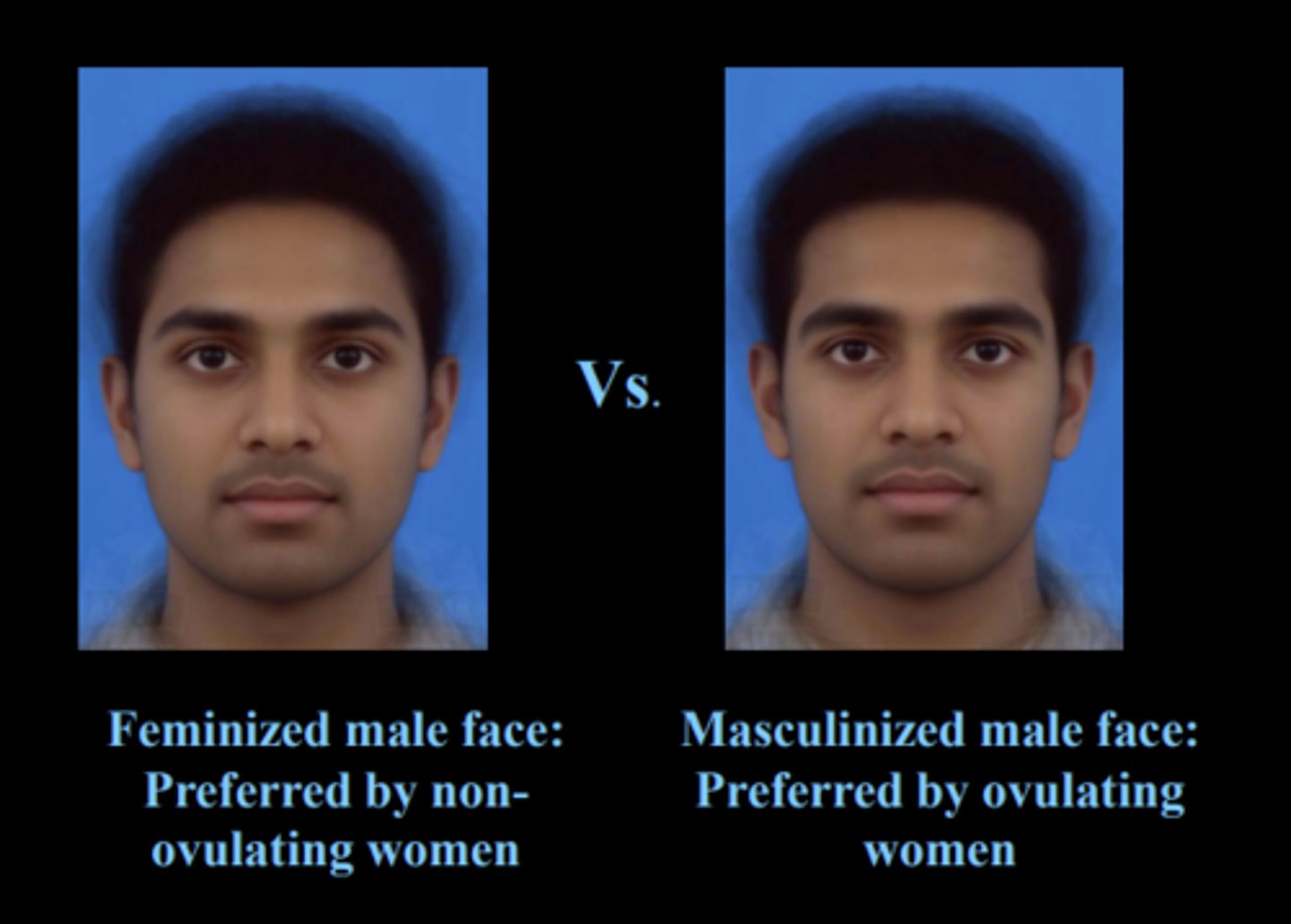
Do ovulating women prefer feminized male faces or masculinized male faces?
masculinized male face, because it increases the likelihood of good genetics
Do non-ovulating women prefer feminized male faces or masculinized male faces?
feminized male face
Testosterone
- correlates with things that might benefit offspring (like male dominance)
- testosterone reduces immune function
- masculinized faces reflect higher testosterone levels
evidence of testosterone combined with overall good health might serve as a signal of high genetic quality
Male facial morphology
feminine faces - preferred by babies and non-ovulating women
masculinized faces - preferred by ovulating women

Immunocompetence
the ability of the immune system to recognize and respond effectively to pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances
testosterone reduces immune function
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
part of immune system; important for self/non-self recognition
It is better to be heterozygous (different genes on matching chromosomes) than homozygous (same genes on matching chromosomes) for MHC genes
women rate men who are heterozygous for 3 MHC loci as more attractive and healthy than men with homozygous at even just 1 of the 3 loci
Burger King study
wanted to see how each sex views the other sex's attractiveness
Burger King uniform was used to depict lower income; moderate economic success was normally dressed (normal shirt and pants); highly economically success was depicted with a suit
Then they got some people in their circle (3 M, 3 F) and labeled each one attractive, moderately attractive, and unattractive (ignoring their clothes) and had them put on each of the outfits and asked scenario questions (would you get coffee/one-night-stand, would you marry, etc.)
The Burger King study found...
males tend to be less choosy & more accepting of short-term mating opportunities; more affected by actual attractiveness than outfits
females tend to care more about a potential partner's resource control, they cared more about the outfit/economic success depicted by the outfit (still looked at attractiveness but cared more about outfits/jobs)
Lonely Hearts advertisement
males are consistently more likely, across all societies studied, to express a preference for a younger mate
Facultative polyandry
having a single main mate who invests in offspring, but occasionally engaging in mating with someone else who offers better genes; optional
among many nonhuman species, males do not invest anything in offspring, so selection favors females who prefer to mate w males that are likely to have the best genes for the environments in which they live; in a species like ours in which male parental investment is common, females may face a tradeoff between males who (1) will be good investors but not have the best genes and (2) males who have good genes but who may not be willing to invest in offspring
Cues to female fertility
Faces - fuller lips, shorter & narrower jaws = fertile
WHR - low WHR = fertile
Voice - high voice = fertile
Waist to hip ratio
waist circumference divided by hip circumference; reflects fat distribution, not underlying pelvic anatomy
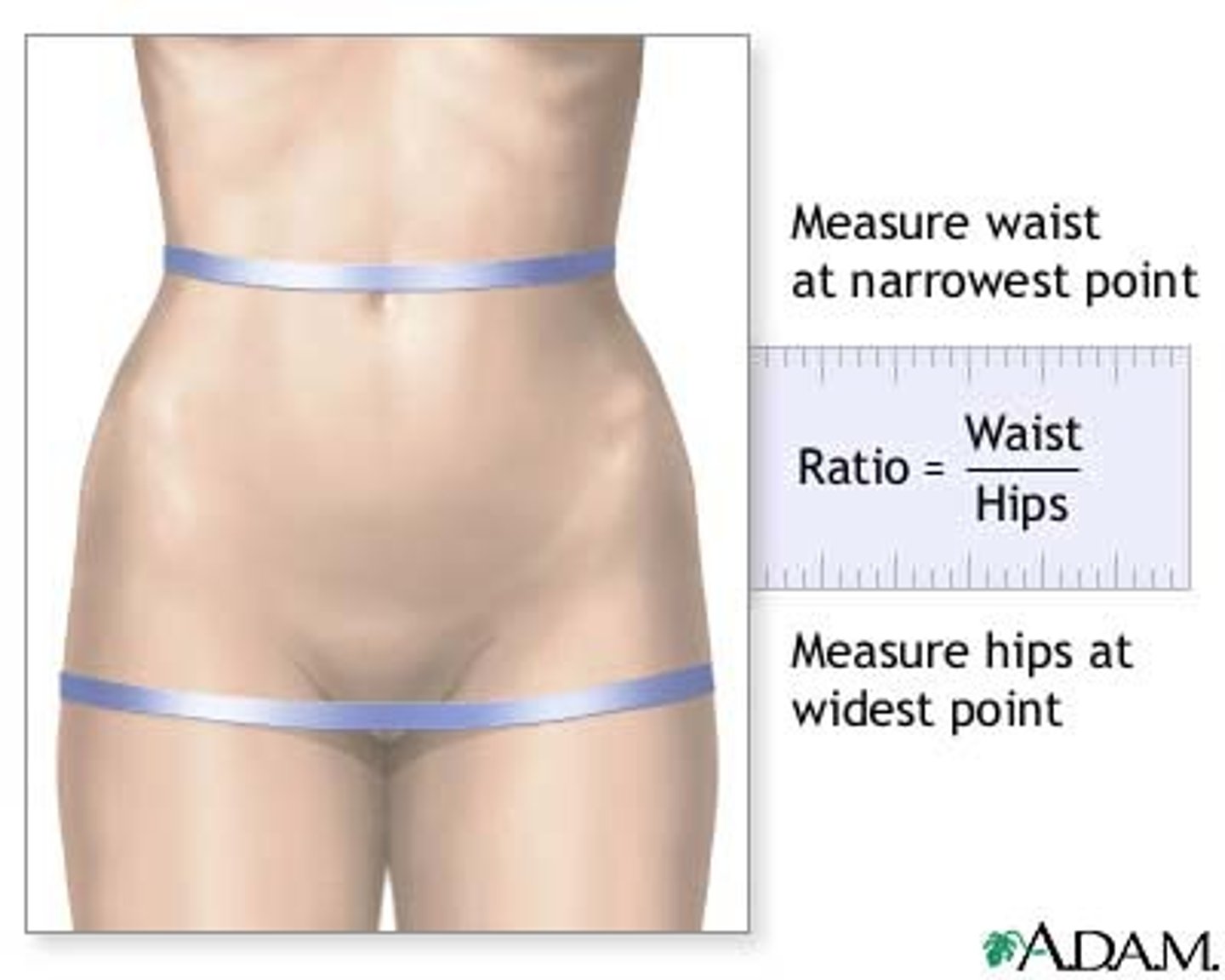
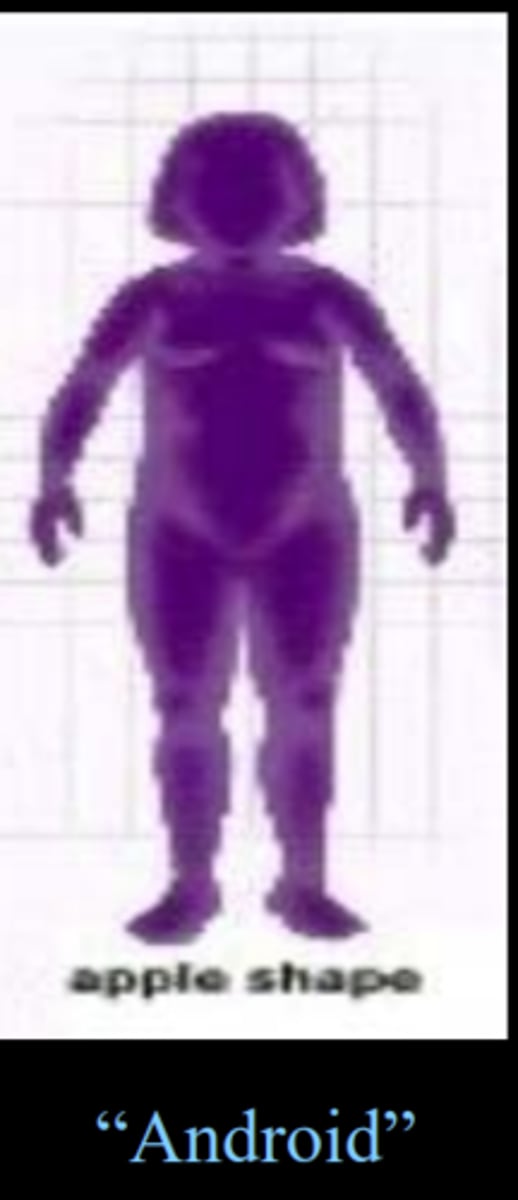
Android
apple shape
high WHR
tip for remembering: think of android and apple both starting with an a

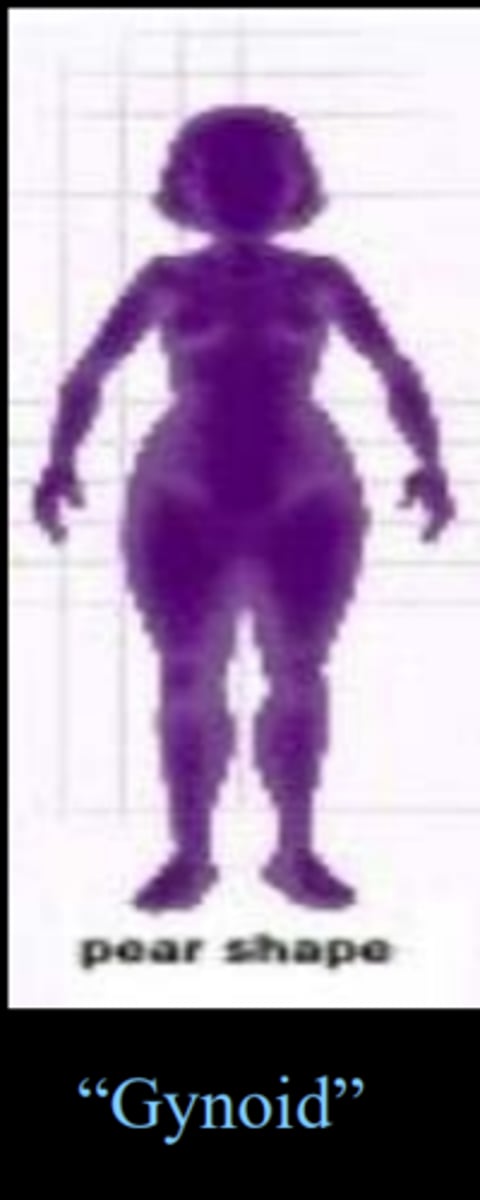
Gynoid
pear shape
low WHR
higher fertility, better health, less masculine hormonal profiles

Greater upper body strength
among our ancestors, evidence of physical strength may have been a cue of male formidability (if they got into a fight would they win)
i.e. a male's ability to fight & maintain control of resources
Ovulating women...
report more interest in extra-pair copulation;
may engage in more extra-pair copulations;
wear tighter & more revealing clothing;
rate other women as uglier;
report more interest in sex, feel more attractive, and think their clothes are sexier, but only if they have a mate (might be due to mate's behavior);
prefer odors of more dominant men, but only if mated (in a pair bond)
- i.e. stinky t-shirt study
Sperm competition
if you have sperm from more than one male that have access to ova at the same time, the sperm will compete with each other to fertilize the ova
i.e. cat fish
Sperm longevity
sperm lifespan inside female body; after ejaculation, sperm can live inside the female body for around 5 days
tells you how long the matings have to be to create conditions for sperm competition
the longer the longevity, the more sperm competition
Cross-cultural studies of sexual behavior
Mothers - a lot of direct care is common
Fathers - indirect care is more common than lots of direct care, most do not direct care much at all but depends on the society
AND lots of cross cultural variation in both types of care
Female sexual behavior
A couple things about female sexual behavior:
- engage in facultative polyandry
- think less about sex in a day than men
- more likely to go to a date/have sex/etc. with a man if he has a good job & money
Paternity discrepancy
disagreement or uncertainty regarding the biological father of a child
Physiology
the study of how the body and its parts work or function
Extra-pair copulations
intercourse by an individual involved in a mating pair-bond with someone outside that pair-bond; a mating by a male or female with someone other than his or her primary partner in a seemingly monogamous species
Double matings
in humans, copulations as much as 5 days apart (maybe longer) can result in sperm competition
matings within such a time period are called double matings
Internal fertilization
fertilization of an egg by sperm that occurs inside the body of a female
creates another complication and asymmetry; maternity is always known while paternity can be uncertain, males can end up wasting investment on females producing offspring with other males and on offspring that are not theirs
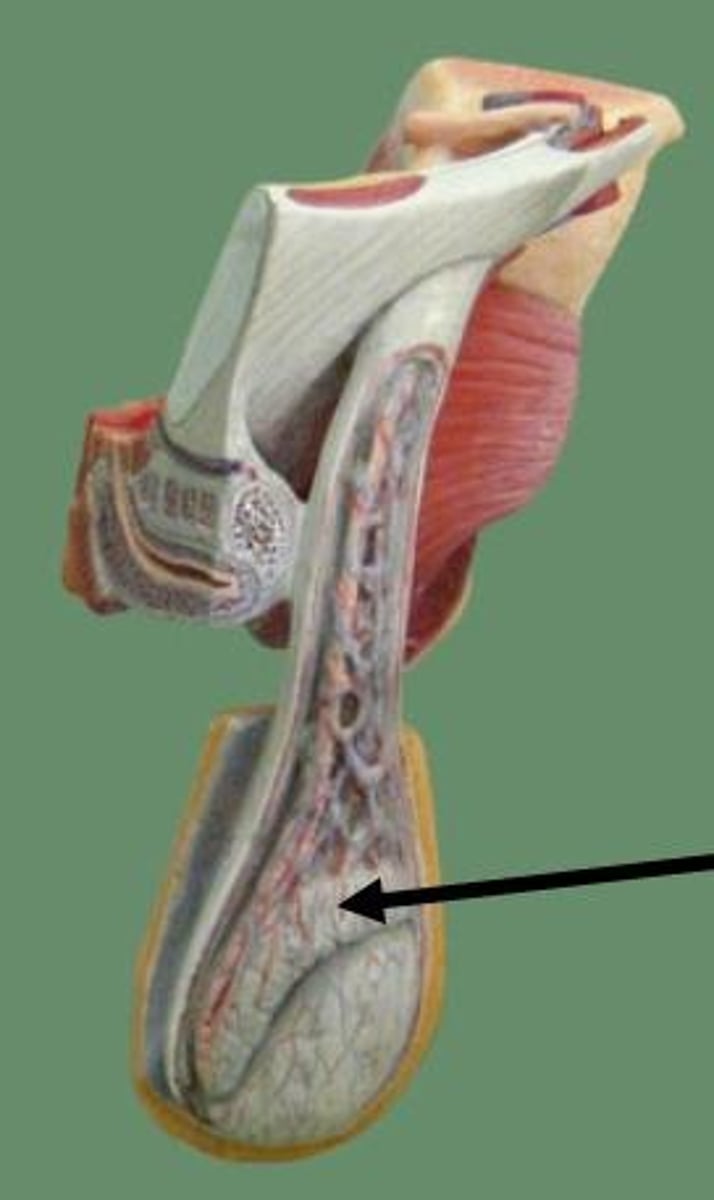
Why external testes?
because it was important to get the epididymis to get it to a cooler place to make sperm last longer; thought to be because of sperm competition
Epididymis
sperm storage area
Inbreeding avoidance
individuals avoid sexual contact with people who could be sexual partners were it not for their relatedness
Inbreeding depression
reduction in offspring quality because they receive copies of deleterious
i.e. If your grandpa has a bad gene that there has to be two copies of that gene, and you carry a copy, your offspring will be okay if you do not mate with someone with that gene. But if you mate with your cousin with whom you share a grandpa, and they also get that gene, your offspring will be born with that gene
i.e. Habsburg jaw

The Westermarck effect
individuals raised close together early in life (as if they were siblings) are unlikely to be sexually attractive to each other as adults
Kibbutzim
unrelated children raised together do not find each other attractive as mates as adults, despite encouragement from community to marry
Romantic love as a commitment device
romantic love may serve as a commitment device that helps solve these problems; when you are in love, you feel so devoted to your partner that you are willing to forgo other possible mating opportunities
don't need to know analogy but may help: When you rent an apartment, you usually sign a lease. The lease commits you to paying rent for a fixed amount of time even if a better apartment comes along, and it commits the landlord to allowing you to stay in the apartment during that time even if a renter willing to pay more comes alone; the lease is your and your landlords credible commitment
Credible commitment
how can you know that your mate is truly committed to the relationship and won't leave if someone more attractive comes along
Evidence of romantic love as a commitment device
people who are in relationships rate people as less attractive than people who are not in relationship; participants rated magazine advertisements, including the attractiveness of people shown in them
Parental behavior
everything parents do as parents, even if it harms their offspring
Parental care
the things parents do as parents that benefit their offspring
Parental investment
parental care that, once it consumed by any one offspring, it is no longer available to any other offspring (i.e. food)
the nature of the good, if it is consumed by one offspring, can another offspring benefit from it
all parental investment is parental care
Hoopoes
bird that produces more offspring to kill them and feed it to their other kids
parental behavior because they are killing their offspring
parental care because they are doing so to feed their offspring
Direct care
hands on stuff; holding, feeding, cradling, helping with homework, etc.
Cross-cultural patterns
Mothers - a lot of direct care is common
Fathers - indirect care is more common than lots of direct care (most do not direct care much at all, but depends on the society)
Aka
small scale society with highest direct care from fathers
Baby schema
large head relative to body, high and protruding forehead, large eyes, chubby cheek, small nose and mouth, short and thick extremities, plump body shape
**we have evolved to respond to these to trigger the need to nurture
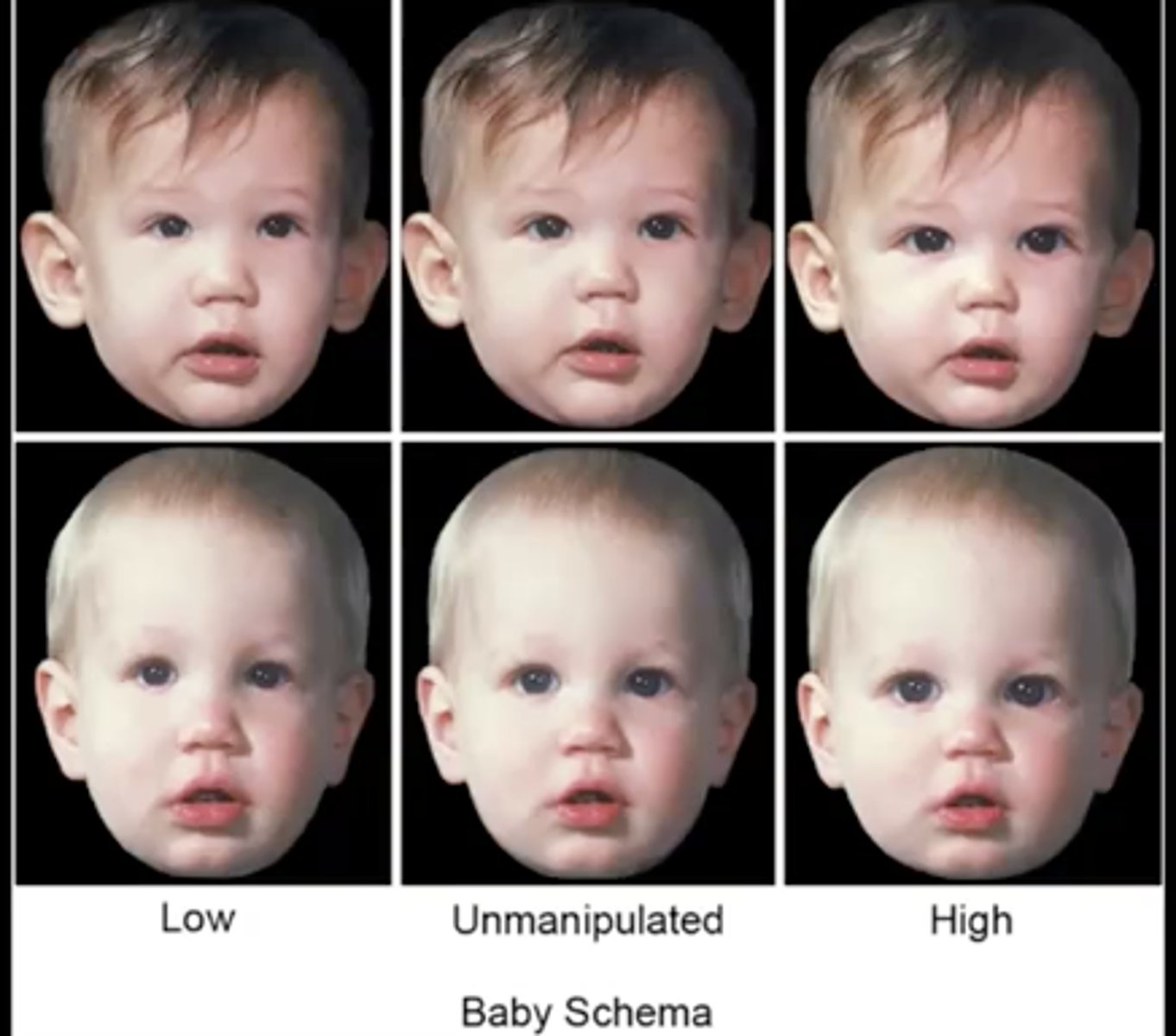
Austrian baby schema study
Austrian study found:
- the higher the baby schema, the cuter the babie
- the higher the baby schema, the more motivated they are to take care of them
!Kung women and birth spacing
don't give birth very often (~every 4 years) to try not to overrun the food supply and/or because of the Lack effect
Lactational amenorrhea
the mothers constantly are holding their babies, so the babies nurse at will and are constantly nursing (as opposed to American traditions where babies have schedules for feeding);
**the stimulation of the nipple releases hormones that postpone menstruation
Postpartum taboos
a taboo on sex; a rule that you cannot have sex after giving birth for a certain amount of time (for !Kung it's years)
Lack effect
idea to have less children so that the population can be supported better
the !Kung are constrained by their circumstances, so to have more kids would not = more survivors
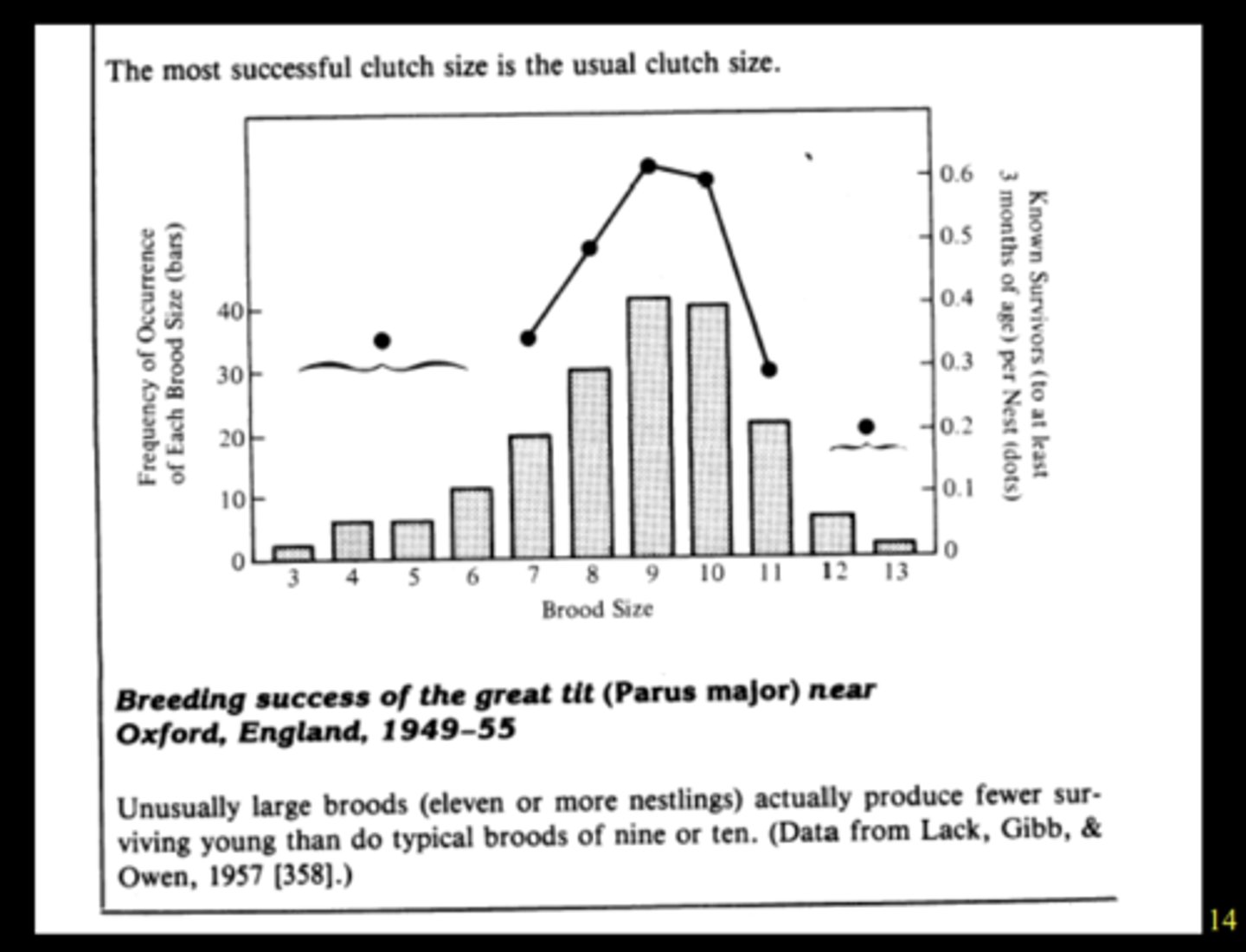
Great tit bird
Larger broods (11+ eggs) produce less surviving young than typical broods (9-10 eggs)
(brood size = how many eggs are being laid)

The backload model
shows the amount of weight a female has to carry on her back; the weight of food and the weight of offspring are shown on the model; when carrying an infant the load is the largest
women in societies that give birth more often (every 1-4 years) have to backload more in terms of weight
infant mortality goes up sharply when birth spacing is tighter than four years
!Kung women and backload
their work can be measured in terms of backload because they are carrying their kids on the front and the food on their back; carry their kids until they are 6 yrs old
when the !Kung stopped hunting and gathering in the 1970s, this pattern ended; backload was no longer a constraint, and they started having children every 2-3 years
Sex-biased parental investment
when a parent invests in a certain sex more than another
the Mukogodo take better care of their girls (take them to clinics, breastfeed longer, stay closer to them); favoritism shown to daughters when they have better reproductive prospects than sons
Mukogodo
cave-dwelling, hunting & gathering, beekeeping Yaaku-speakers until the 20th century
since about 1936, due to intermarriage and receipt of livestock bride wealth payments, they have become house dwelling, livestock-keeping Maa-speakers
Maasai
a seminomadic ethnic group in Kenya; high status
Trivers-Willard hypothesis
mothers can adjust offspring sex ratio according to their own body condition
If conditions are good, mother will be biased to invest in favor of male (competitive offspring)
If conditions conditions are poor, mother will be biased to invest in favor of female (non-competitive offspring)
Paternity confidence and male parental investment
low paternity confidence = low paternity investment; investing into offspring that isn't yours defeats the point of growing your line
Albuquerque Men's Study
- 1,325 men interviewed at the Bernalillo County Motor Vehicle Division in 1990-93
- the men recalled 2,582 for which they were the putative (one recognized by society as the father) father
- most were confident about their paternity (that they were the father):
- 2,516 births with high confidence
- 32 births with low confidence
- 34 births in which the men did not answer
Coefficient of relatedness (r)
a measure of genetic similarity; the average proportion of genes shared by related individuals; for each generation link there is a 0.5 probability that a copy of a gene will be passed on.
r = Σ (0.5)^L
Matrilineal vs. patrilineal descent
tracing family line through the female descents (matrilineal) rather than through male lineage (patrilineal)
Human Relations Area Files
a large cross-cultural database, with each society coded for many characteristics
Codes needed for HRAF
1. Source of altruism
2. Paternity certainty