Algorithms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
abstraction
ignoring unnecessary information and focusing on the main problem
decomposition
when you break a problem into smaller tasks to make it easier to solve
algorithm thinking
using both abstraction and decomposition to solve a problem
algorithm
set of instructions for solving a problem
binary search
find midpoint. compare to target. If not equal determine if > or < . discard the other half of the list. find new midpoints and repeat
what is the prerequisite for binary search
list must be ordered
linear search
compare first item in list with item you want to find. If item not found, keep going down the list.
does data need to be ordered in linear search
no
Bubble sort
compares each item with the next one and swaps them if out of order. When it goes through the data - that is a pass. Algorithm finishes when no more swaps are made
merge sort
divides list into half until each item is seperate. It merges sets and sorts them. Eventually ordered whole data set.
insertion sort
inserts the first item into sorted list. inserts another item. sorts the items
what is the first item in insertion sort called
the anchor

start / end
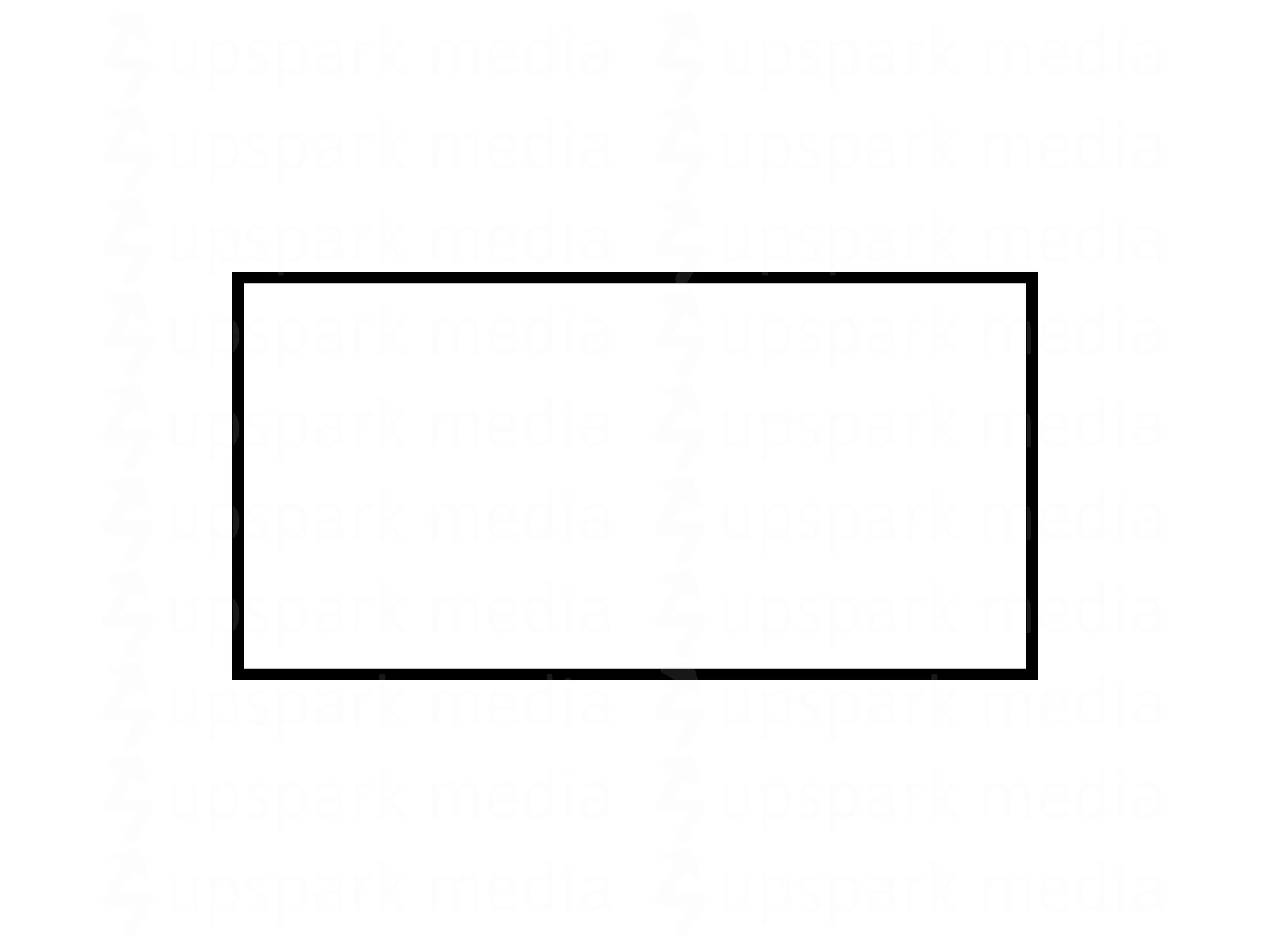
calculation / assignment
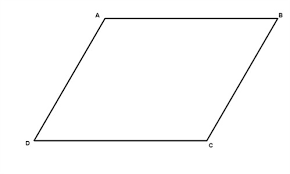
input / output

decision. For and while loops
what is the sign for finding the remainder of a division
%
what is the symbol for integer division
//
what do variables and constants both do ?
temporarily store data in a location in the memory
how is a variable different to a constant
users can change variables whilst the program is running
what can be used to display decomposition of a complex problem
structure diagrams
what are trace tables
tables used to track the value of variables as a program runs
name 2 searching algorithms
linear search , binary search
what is the midpoint in binary search if there’s an even
the truncated value of (lowest value + highest value)/2
advantages of merge sort compared to other sorting algorithms
faster for larger lists