Earth Systems and Resources Quiz 2 ( soil, watersheds, seasons, geology)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Crust
solid matter
Mantle
Lower part is solid matter, upper part is liquid [ convection currents ]
Upper liquid part = asthenosphere
outer core
liquid matter
convection currents…
drive movement of plants based on density differences and magma
Describe movement of convection currents
Magma in asthenosphere rises as heated up, cools down and expands and falls. Cycle Between hot and cold and warm and cool is what drives movement of convection currents.
soil horizon
O - Humus
most susceptible to weathering
surface litter like leaves and other decaying matter
A - top soil
phosphorus and nitrogen are examples of some of the limiting nutrients that are found
unrenewable
mineral soil with most organic material accumulation and soil life(worms)
E - eluviation layer
sand and silt
infiltration
mostly containing of silicates
zone of leaching ( nutrients from upper horizons seep into lower horizons)
minerals are washed away by leaching so lack of minerals like clay or iron
B - subsoil
zone of accumulation = minerals like iron, clay, aluminum and organic material and other nutrients accumulate a process referred to as eluviation
little to no organic matter
C - parent material
gives soil rest of its characteristics
large layer of unbroken rocks
materials that is broken down to give soil
least weathered
R - Bed rock
Solid rock
not weathered at all
Weathering
Breakdown of rock to form soil
ex: lichen and moss can breakdown / primary successores
ex: wind and water, ice, animals , growing plants
Erosion
Movement of soil someplace else
ex: wind, agriculture, ice, gravity , water
Deposition
The dropping of sediment in a new place
ex: sand dunes , formation of an island
Particle sizes +characteristics
Sand - largest
highest permeability and porosity
Silt - medium
Clay - smallest
Lowest permeability and porosity
Highest fertility / nutrient level
negative charge and nutrients are positive so clay attracts nutrients
high water holding capacity
characteristics of particles
permeability = ability of air/liquid to go through
Porosity = pores / spaces between particles
fertility = how much nutrients ( fertile ) the soil has
Farmers want soil to be
loam because its a mixture of sand silt and clay so has the best of each component
soils with smaller particles have a ___ water holding capacity
higher
Chemical weathering
acid rain, rust on rocks
Biological weathering
plants growing in rocks, human activity , animal burrowing
Watershed Characteristics, these characteristics influence what
Area
Length
Slope
soil
vegetation
divides ( boundary with other watershed )
Watershed characteristics influence rainwater flow through the watershed
runoff often causes what
erosion and picks up and carries elsewhere
watershed characteristics and classifications are influenced by
runoff and infiltration
Water table
the ground below which the ground is saturated with water, usually below infiltration
Aquifer
a body of porous rock and sediment saturated with groundwater, usually below water table
Recharge process
water infiltrates into soil and then percolates deeper into ground to replenish underground aquifers
Watershed classification differ based on runoff and infiltration rates, provide examples
urban - high runoff , low infiltration
forested = high infiltration and low runoff
Riparian Zones
important component of watersheds with vegetation. Can trap and filter certain types of pollutants
Pollution enters watersheds from
Agricultural runoff
industrial dumping
urban runoff
erosion
solid waste
Due to runoff and infiltration some of these pollutants can enter into groundwater
Factors affecting the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth
rotation ( 1×24 hrs )
revolution ( 1 per 365 days )
tilt of axis(23,5 degrees )
atmospheric conditions
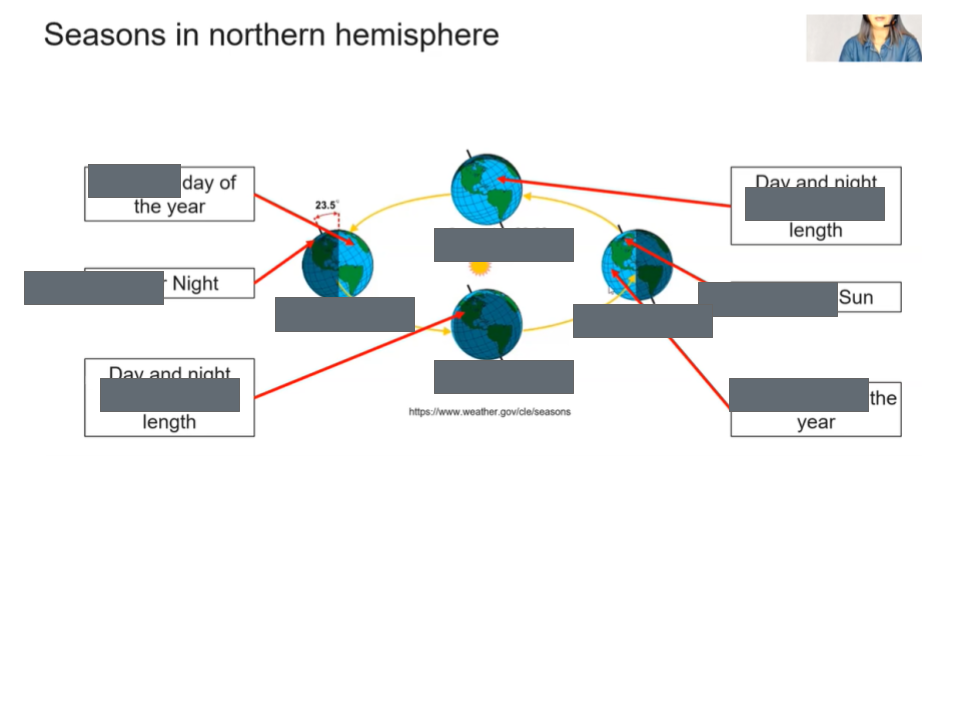
What causes seasons
summer happens in the northern hemisphere when it is tilted towards the sun so that it gets the most direct rays. Sun rises higher and stays above the horizon longer and its rays strike the ground most directly.
Albedo
Proportion of light that is reflected by a surface, mostly determined by a color
surfaces with a high albedo reflect more light and thus gain less heat
like ice snow
surfaces with low albedo absorb light and heat
pavement
Weather
short term atmospheric conditions for the area
Climate
An area’s general pattern of weather or atmospheric conditions over a long period of time
front
boundary between two air masses
Cold front ___ warm fronts by creating a ___, how does this work
displaces, wedge, cold air is denser than warm air so the warm air is pushed upwards