9. Lysosomes
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Christian de Duve
differential centrifugation
developed in 1934
won the 1974 Nobel prize for discovering lysosomes (in 1955)

Lysosomes
a. 50+ hydrolytic enzymes (ex: proteins, nucleases)
b. enzymatic activity is optimum @ pH 5
c. "marker enzymes" --> acid phosphatase
Why have an optimum activity pH of 5 for lysosomes?
The wayward lysosomal enzymes that are transported out of the cell via the constitutive pathway are at a pH of 5, so their activity is compromised by up to 100%
categories of lysosomes
heterophagy
autophagy
sepcialized
Heterophagy
Discovered by Rudolph Virchow
white blood cells were giving birth to red blood cells

Ellie Metchnikoff
1884 - "phagocyrosis"
phagoon - eat
kytos - cavity
suggested "probiotics"
Gerontology
Optimization
enhancing the delivery of bacteria or therapeutic agents to the lysosome and modulating the lysosomal environment and activity
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
Autoimmune Disease
patients are very sensitive to curare, but symptoms can be ameliorated with Eserine (Physostigmine)
patients improved but some had too little ACH release, while others had few ACH-R
1960s - minute edd plate, potentials = one vesicle
Dan Drachman
3H α-bungarotoxin - binds to the ACH-R
used electroplax (that specialized in electric organs of the Torpedo Ray) to count ACH-R
mAb agents ACH-R
a. injected into mouse --> MG-like symptoms
b. blood from MG patients --> injected into normal mice - MG again - therefore heterophogy of the ACH-R --> decrease number of ACH-R
Vyvgart
is the FC fragment of an IgG antibodies
Capillary endothelial cells bind all IgG molecules and help them to recycle increasing their half life in the blood
competes for these FcRns receptors with all IgGs thus causing all circulating IgG molecules, including the anti-Ach IgGs, to have a much shorter half life
FDA approved in 2021 to treat myasthenia gravis
Autophagy
discovered by Yoshinori Ohsumi (nobel prize - 2016)
self-eating cell to break down and recycle old or damaged parts
ex: mitochondria 5 to 6 days
peroxisomes 1 to 2 days
starts when the membrane structure (phagophore) forms from the RER
encloses the material to be degraded, forming an autophagosome, which is tagged by the protein LC3
lysosomes binds to the autophagosome, breaking down its contents
Certain drugs, such as bafilomycin A1 and chloroquine, can interfere with this essential recycling process
Chloroquine
a lysosomotropic agent and accumulates preferentially in lysosomes
May sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapy agents, but harm normal cells too
non-inherited Lysosomal diseases
caused by environment
ex: silicosis (aka miner’s diseases)
chloroquinie
silica particles inhaled into the lungs are taken up by cells, but can't be properly broken down by the lysosomes
An outside agent enters a cell, which can then cause the lysosome inside to become leaky
releasing its destructive contents into the cell and leading to inflammation and cell death
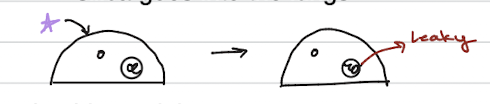
inherited Lysosomal diseases
illnesses related to problems with the cell's recycling centers, the lysosomes
known as lysosomal storage diseases, which means they are hereditary—passed down through families
involve the lysosomes failing to break down certain substances, causing them to build up and be "stored" inside the cell
leads to damage and disease
Tay-Sachs Diseases
causes by a defeat in the Hexosaminidase A (HEXA) gene
leads to the body being unable to properly break down a fatty substance called gangliosides
causes a toxic accumulation of gangliosides particularly in the brain, leading to progressive neurological damage
no Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) available to treat this disease
occurs in approximately 1 out of every 5,000 births
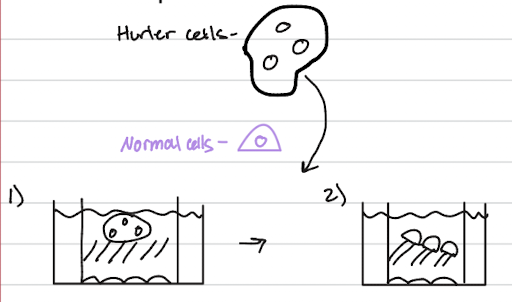
Hurler Syndrome - MPS 1:
caused by a defect in the alpha-L-iduronidase enzyme, leading to the accumulation of waste inside cells
using a co-cell culture experiment:
when defective Hurler cells are grown in the same dish as normal cells
the normal cells release the missing functional enzyme into the surrounding fluid
then taken up by the Hurler cells, thereby "correcting the Hurler cell" and clearing the accumulated waste
relates to the existence of treatments like Aldurazyme, a form of enzyme replacement therapy
I(inclusion)-cell Disease
inherited condition and type of lysosomal storage disorder
the cell's waste disposal units (lysosomes) are empty because they lack the necessary lysosomal enzymes
the missing enzymes are found in large amounts outside the cell
key to this problem lies in a defect that occurs in the cis-Golgi apparatus
the cell fails to add a crucial shipping label, the M6P (Mannose-6-Phosphate) "zip code," to the enzymes
Without this M6P tag, the enzymes are incorrectly shipped out of the cell instead of being delivered to the lysosomes
can import normal, correctly-tagged enzymes from outside
but normal cells cannot import the mis-tagged I-cell enzymes proving the M6P tag is essential for proper enzyme delivery and uptake.
Gaucher Disease
Deficiency in Glucocerebrosidase
Leads to enlargement of the Spleen
Erosion of the Long Bones due to
accumulations of GlucocerebrosideCerezyme was the first ERT for Lysosomal Diseases - 1991
Pompe Disease
a lysosomal storage disease that can be treated with a medication called Myozyme
caused by a deficiency in the essential enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA)
the lysosomes need to break down a type of sugar molecule
Myozyme is a form of Enzyme Replacement Therapy that is given to patients to replace the missing GAA enzyme
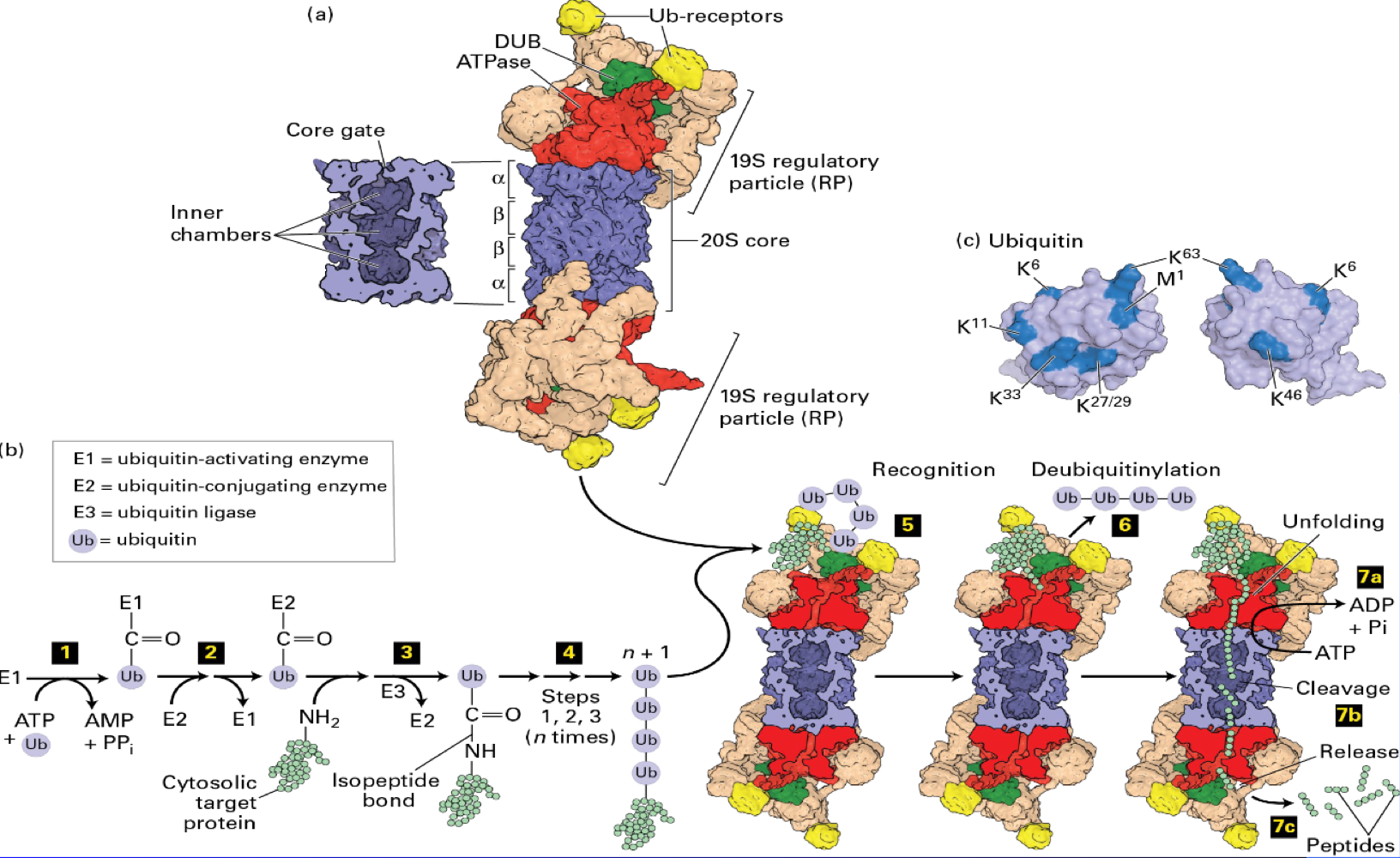
Proteasome
are large protein complexes responsible for hydrolyzing (breaking down) proteins only, acting as the cell's main protein shredders
vital for the cell, evidenced by the fact that yeast mutants with defective ___ died
are massive structures (750,000 Daltons), are involved in managing cellular stress through the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)
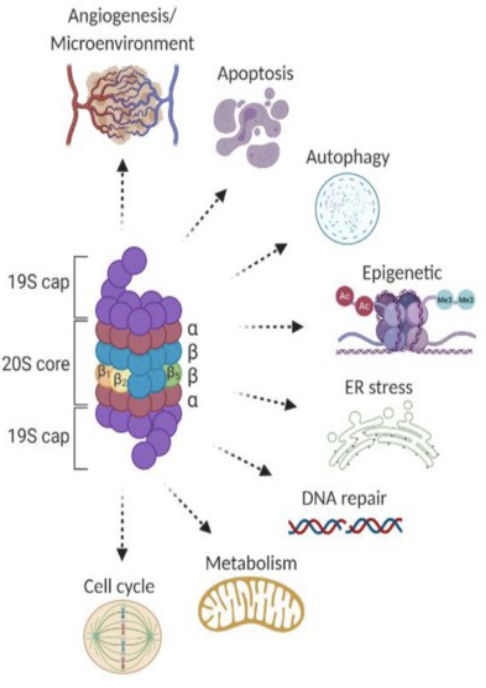
Effects of proteasome inhibitors
Increase ER Stress
Trigger Apoptosis
Turn off cell survival pathways
Affect mitochondrial function
Influence epigenetic changes
Influence DNA Repair
Proteasome Inhibitors and Cancer
important class of drugs used in cancer treatment
receiving regulatory approval:
bortezomib (Velcade)
carfilzomib
ixazomib
drugs work by entering a cancer cell and blocking the action of the proteasome (the cell's protein shredder)
Specifically, bortezomib inhibits the proteasome's protein-cleaving sites,
leading to the accumulation of damaged and regulatory proteins inside the cancer cell
This buildup of proteins triggers cell stress and ultimately causes the cancer cell to die, making it an effective targeted therapy
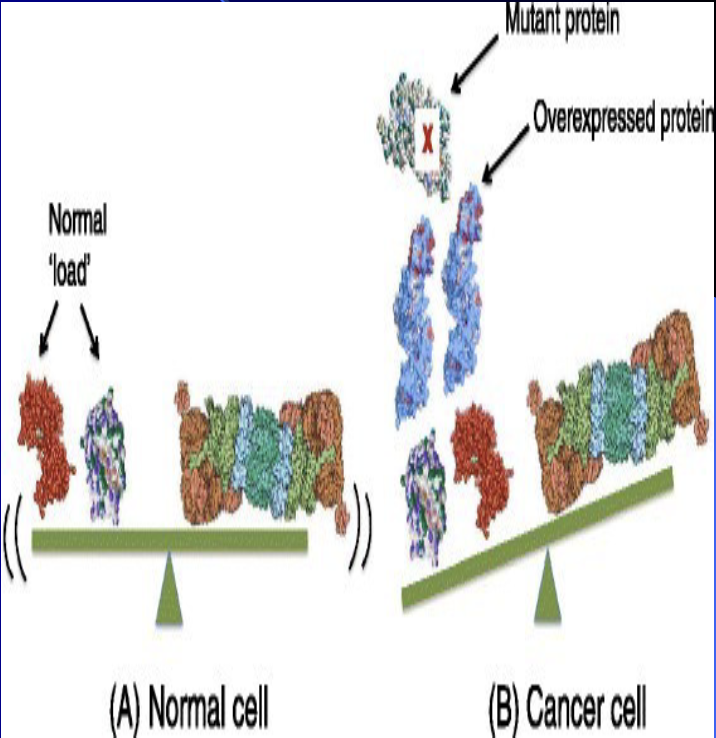
But why are cancer cells more sensitive to proteasome inhibitors than normal cells
Cancer cells overproduce normal proteins and generate mutated proteins as well, so cancer cells rely heavily on proteasomes to protect them from proteotoxicity – the failure to clear these proteins from the cell. This imbalance triggers apoptosis in cancer cells