FAM Final Exam
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
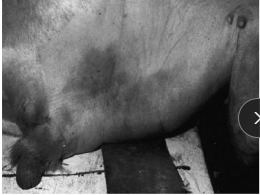
Preputial Prolapse in ruminants
Et: Pendulous sheath, Lg preputial orifice, Absence of retractor prepuce muscles, Brahman, Brahman-cross, Angus, Polled Hereford
Cs: edema, cellulitis, necrosis
Tx: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Hydrotherapy, Bandaging/sling, Reefing Sx (GA, resection)
Penile Hematoma in ruminants
Et: Trauma during breeding
tunica albuginea rupture at distal sigmoid flexure
Cs: Swelling cranial to scrotum, bruising, preputial prolapse, pain, reluctance to breed
Tx: 60d sexual rest, NSAIDs + antibiotics, hydrotherapy, Sx to remove clot (suture tunica albuginea)
<15 cm: good prognosis (medical)
>15 cm: poor prognosis (surgical)
Retropreputial Abscess / Intra-preputial Adhesions in ruminants
Et: Preputial trauma w/ 2ndary infection
Tx: Lance + drain
Poor repo prognosis <30%
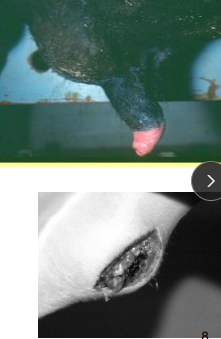
Sheath Rot (Pizzle Rot) / Enzootic Balanoposthitis in ruminants
Et: Corynebacterium renale
Wethers on high-protein diets
Cs: Swollen, inflam, ulcers, pus, foul odor, reluctance to urinate/breed
Tx: Antibiotics (Penicillins or cephalosporins), NSAIDs, Topical antiseptics, clean bedding
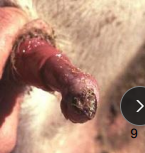
Penile Ulcerative Dermatosis in ruminants
Et: Parapoxvirus (Contagious Ecthyma / Orf)
Cs: Swelling, ulcers, scabs, pain, reluctance to breed, secondary infections(abscesses)
Tx: Antibiotics (oxytetracycline), Topical antiseptics, NSAIDs, Isolate, Vax, Disinfect equipment
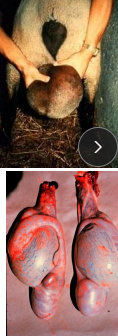
Orchitis and Epididymitis in ruminants
Number one ram infertility problem
Et: Brucella ovis (contagious venereal dx)
direct contact
Cs: Enlarged, firm epididymis, testicular atrophy, pain, poor semen quality
Dt: Serology (ELISA, CFT), PCR (semen/urine)
Tx: Cull, virgin/disease-free rams, male vax, biosecurity
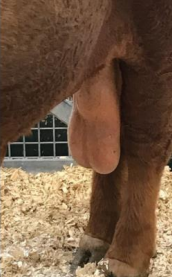
Inguinal Hernias in ruminants
Et: Congenital, Acquired
Inguinal hernia (#1): contents within inguinal canal
Scrotal hernia: contents into scrotum
Indirect hernia (#1): loop remains within tunica vaginalis
Direct hernia: intestine protrudes through rent in vaginal tunic
Dt: Rectal palpation, US
Tx: 60d sexual rest + Sx
Flank Laparotomy: indirect hernias, standing, poor visibility, close inguinal (vertical mattress non-absorbable)
Inguinal Herniorrhaphy: better visibility, right lateral, Close tunic then skin Close skin
Fertility Outcome: Good

Castrations in ruminants
Why: Prevent unwanted breeding, Improve temperament, Better feed efficiency, Higher-quality meat, Market preference, Flexible herding
When: younger preferred, avoid hot/flys
Rx: Local anesthesia, NSAIDs, Vax for tetnus
Sx:
Open (Bloody): Scrotal incision(most common) → distal 1/3 to 1/2 of scrotum, Newbury knife,
Calves <2m : twist and pull
Calves >2m : emasculator
Best choice for Goats & Llamas
Closed (Bloodless): elastrator bands (<3w) → dairy cattle 1-3w, Burdizzo (>2m), Crush not cut
Teaser Maless in ruminants
Why: Detect estrus
How: Use infertile males w/ libido
Penile Translocation: Ventral Midline incision near prepuce, Free penis tunnel to it SQ, fix with sutures, close SQ + skin
Epididymectomy(Infertile, Can Copulate): scrotal incision, remove caudal epididymis, suture tunica vaginalis + skin, can still transmit dx
Vasectomy: cut over ductus deferens, ligate ends, close skin, can still transmit dx
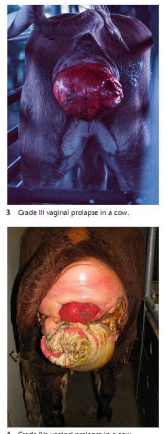
Vaginal Prolapses in ruminants
Et: Late gestation, pluriparous females, high estrogen, high abdominal pressure
Cs: Prolapsed vaginal tissue, tenesmus, edema, contamination
Tx: Epidural, clean, hypertonic sugar/glycerin wrap, lubricate, replace (Last out = first in), retention sutures (Bootlace/Buhner), Cull post-calving
High Recurrence Rate
Remove sutures before calving
Prognosis:
• Grade 1: Minor, easily reduced.
• Grade 3: Severe necrosis with poor prognosis
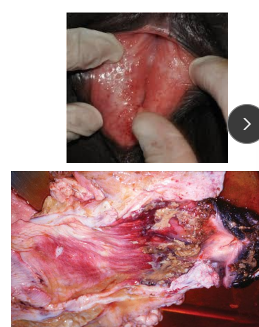
Necrotic Vaginitiss in ruminants
Et: Post-dystocia complication
Cs: Anorexia, fever, toxemia, arched back, elevated tail, dysuria, straining, vulvar swelling, purulent vaginal discharge
Tx: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Vaginal douches, IV fluids, epidural
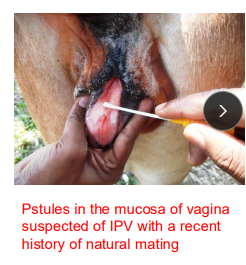
Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitiss (IPV) in ruminants
Et: BHV-1, Natural breeding, flies, equip
Cs: Fever, raised tail, frequent urination, mucopurulent discharge, white ulcers, infertility/abortion
Tx: NSAIDs, antiseptics, Antibiotics, Vax, Isolation, fly control
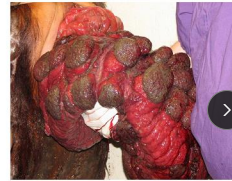
Uterine Prolapses in ruminants
Occurs within 0-6 hours postpartum
Et: <6hrs post partum, Dystocia, Hypocalcemia, Excessive straining
Cs: Fully everted horns, exposed caruncles (“raw hamburger”)
Tx: calcium + oxytocin, Epidural, Warm saline + dilute antiseptic wash, Hypertonic sugar/glycerin wrap, lubricate, frog-leg position and palm back in starting cervical, Buhner suture
Emergency: moist towels ASAP
Good survival and repo prognosis
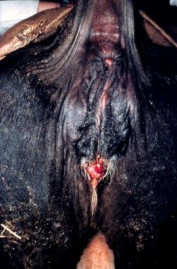
Uterine Torsion in ruminants
90% occur at/near term (>7 months gestation)
Et: left-sided, late term
Dt: PE
Vag: Twisted vaginal lumen
Rectal: Crossed broad ligaments (“X” pattern)
Tx:
Manual Correction (fully dilated): epidural, rotate counterclockwise if left torsion
Plank-in-Flank / Schaffer Method (partially dilated): roll cow around fetus, left torsion = roll left

Uterine Tears and Ruptures in ruminants
Et: excessive traction during dystocia, Dorsal wall near cervix: most common
Cs:
Immediate: Bleeding, visible uterine defect
3–5 days later: Fever, depression, ileus
Dt: Vag palpation, Abdominal tap (cloudy fluid = peritonitis), US, explore Sx
Tx:
Sm Tears (<5 cm): Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Oxytocin
Lg Tears (>5cm): laparotomy + Sx repair, Cull
Retained Fetal Membranes in ruminants
Et: Failure to expel placenta >24hrs postpartum: most resolve in 10d spontaneously
Dystocia, twins, stillbirth, hypocalcemia, heat stress, premature birth, Se / Vit E deficiency
Seq: Metritis, Displaced abomasum, Ketosis, Reduced fertility
Tx: resolve spontaneously <10d, Trim hanging tissue, Ceftiofur, Flunixin, Oxytocin, PGF2α, Vit E/Se/Ca supplements
Never manually remove!!!
Toxic/Acute Puerperal Metritis in ruminants
Et: E. coli (primary), Trueperella pyogenes (secondary)
Dystocia, Retained fetal membranes, Poor hygiene : pre-expose
Cs: Fever, depression, anorexia, dehydration, copious fetid uterine discharge, uterine atony, decreased milk yield, laminitis, extended calving interval, poor conception rates
Tx: Intrauterine antibiotics (Ceftiofur), NSAIDs (Flunixin), uterine lavage
Pyometra in ruminants
Et: Chronic uterine inflam w/ pus accumulation
Open: Cervix open → discharge visible
Closed: Cervix closed → risk of rupture
Cs: Mucopurulent discharge (open), No discharge (closed),Anestrus, Persistent CL
Dt: Rectal (fluid-filled uterus), US (echogenic fluid, thick endometrium)
Tx: PGF2α, Estrogen + Oxytocin, Antibiotics, NSAIDs
<120d: Good prognosis- can conceive
120d: Poor prognosis- fibrosis, infertility
Pseudopregnancy (Hydrometra/Mucometra) in small ruminants
Et: Luteal persistence, uterine fluid buildup
Older, multiparous does
Cs: Anestrus (no heat cycles), Enlarged, fluid-filled uterus, No fetus
Dt: US, low PAGs
Tx: PGF2α (dinoprost)
Luteolysis, fluid expelled in 2–3d, breeding possible next cycle
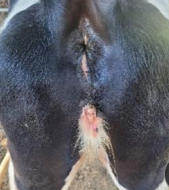
Freemartinism in ruminants
Et: Mixed-sex twins
Cs: Aplastic uterus/cervix, Short vagina, Enlarged clitoris
Bull: normal
Heifer: sterile
Dt: Rectal w/ no uterus/cervix, Vag probe w/ short canal, XX/XY chimerism chromosome test
Tx: Cull, Breeding Soundness Exam
Cesarean Section in ruminants
Why: Preserve dam and calf survival, Maintain fertility
Inadequate space, crushes finger, excessive force, vag tears, fetal distress, exhaustion
2 Feet visible >2 hrs, if in doubt- C section
How:
Left flank: standing, live calf, dead w/o smell
Paramedian: down, dad calf w/ smell
Steps: Exteriorize uterus by holding fetus limb, long incision, remove placenta, flush
Sut: Utrecht suture or double layer inverting for uterus, internal/external oblique, skin w/ ford interlocking
Rx: Caudal epidural, locals, Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Oxytocin, Estradiol
Prognosis:
Live fetus: Excellent
Dead fetus: Guarded
Comp: Peritonitis, Metritis, Retained fetal membranes
Prevent: calving-ease sires for heifers
Normal Urine Characteristics
Alkaline urine: normally
Viscosity: Watery
Colour: light yellow = normal
Transparency: Clear = normal
Odor: ammonia or ketones = abnormal
USG: 1.020–1.040
pH: 7.0–8.0
Bacti, Bld, Glucose, Ketones, Protein: None
Abnormal Urine Differentials
Red urine
Hematuria: Pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, enzootic hematuria
Hemoglobinuria: Leptospirosis, bacillary hemoglobinuria, copper toxicity, postparturient hemoglobinuria
Myoglobinuria: Capture myopathy, recumbency
Glucosuria: stress, IV glucose, steroids, xylazine, enterotoxemia
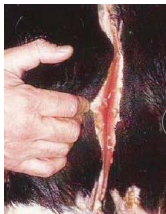
Congenital Urinary Diseases in ruminants
Hypospadias: Dermatitis, recurrent UTI
Can live with
Polycystic kidneys: Diagnosed at necropsy
Bilateral renal hypoplasia: Diagnosed at necropsy
Ectopic ureter: Diagnosed at necropsy
Persistent/Patent Urachus in ruminants
Rare, males
Et: Urachus fails to close post-birth
Cs: Intermittent urine dribbling from umbilicus, wet umbilicus, omphalitis
Dt: US
Tx: Cauterization, Sx removal of umbilical remnants, Antibiotics, NSAIDs, IV fluids
UTIs: Cystitis, Urethritis, Pyelonephritis in ruminants
Pyelonephritis → #1 issue in females
Et: Corynebacterium renale, E. coli
Ascends uterus to kidneys
Common post-parturition(dairy), Multiparous cows
Cs: Polyuria, hematuria, pyuria, anorexia, weight loss, hypoproteinemia, anemia, ↑ BUN + creatinine, proteinuria, hematuria, bottle jaw
Dt: Rectal palpation of Lg left kidney, UA, culture
Tx: Antibiotics for 3w, hygeinene
Poor Prognosis
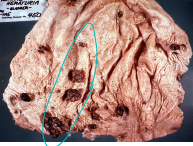
Enzootic Hematuria in ruminants
Et: Chronic bracken fern ingestion
Cs: hemorrhagic cystitis and bladder tumors & GI
Zoonotic in milk
Acute Renal Failure in ruminants
Et:
Acute tubular necrosis
Renal ischemia: severe dehydration, toxemia, sepsis
Pigment nephropathy: hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria
Drug-induced nephrosis: aminoglycosides, tetracycline, sulfas, NSAIDs
Toxic plants: oak (#1), oxalates, pigweed
Ethylene glycol toxicity: calcium oxalate crystals
Dt: Isosthenuria despite dehydration, Abnormal UA, Azotemia, electrolyte imbalances, Renal biopsy(blindly), US
Tx: Treat primary cause, IV fluids (saline), Furosemide, dopamine
No urination = grave prognosis
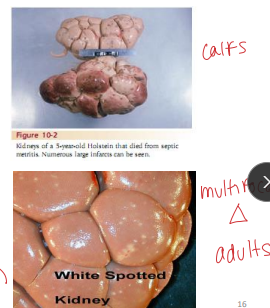
Embolic Nephritis / White Spotted Kidney in ruminants
Et: Adult cattle w/ septicemia
Neonatal calves w/ navel ill
Cs: Toxemia, proteinuria, pyuria
Dt: Rectal palpation w/ Lg kidney, Necropsy
Tx: Antibiotics, IV fluids
Urolith Types in ruminants
Phosphate Calculi: Struvite/magnesium ammonium phosphate (#1)
sandy appearance, Crystals visible on preputial orifice
Calcium Carbonate: Lush legume/clover or alfalfa hay
Smooth, dark appearance
Silicate Calculi: Dry, arid climates, Grass/cereal hays
Single, rough, hard stones
Oxalate Calculi: Oxalate-rich grasses

Obstructive Urolithiasis in ruminants
Et: Formation of urinary tract calculi in urethral process or sigmoid flexure
castrated males, grain, Ca:P imbalance, Estrogenic or high-silica/oxalate pastures, reduced water intake, sorghum-based rations
Phosphate Calculi: Struvite/magnesium ammonium phosphate (#1)
Cs: Dysuria, stranguria, hematuria, pulsation of urethra, abdominal pain and distention, mineral deposits on preputial hair, rectal prolapse, Ruptured urethra/Water belly (urine in subcut tissue of ventral abdomen), Ruptured bladder (uroperitoneum, fluid wave), Pyelonephritis / Hydronephrosis
Dt: US, rads, Abdominocentesis
Tx
Rx: before rupture, w/ diet changes
Decompression (temp), Diazepam/Xylazine (relax, not for complete obstruction) dissolution (acid/Ammonium chloride)
Sx: Urethral amputation (temp), retrograde catheterization and flushing (tricky), Cystotomy, Urethrotomy, Perineal Urethrostomy, Penile Amputation, Bladder Marsupialization
Perineal urethrostomy and marsupialization #1
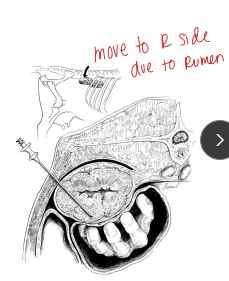
Cystotomy + Urethrotomy in ruminants
Indication: Obstructive Urolithiasis
Valuable w/ intact bladder and urethra
How:
Cystotomy: first
GA w/ Paramedian laparotomy
Incise bladder and remove all stones
Perform normograde catheterization & flushing
Close bladder w/ 2-layer inverting absorbable sutures
Urethrotomy: second
Palpate and incise urethra proximal/distal to stone and remove
Close w/ simple interrupted sutures
Comp: Stricture formation
Perineal Urethrostomy in ruminants
Indication: Obstructive Urolithiasis
Salvage procedure for feedlot calves w/ intact bladder
Not suitable for breeding males
Does not address bladder stones
How:
Standing w/ caudal epidural
Skin incision of upper perineal
Comp: Stricture formation
Penile Amputation in ruminants
Indication: Obstructive Urolithiasis
Salvage procedure for feedlot calves w/ intact bladder
Not suitable for breeding males
How:
Standing w/ caudal epidural
Penis exteriorized and amputated
Fix stump to perineal region
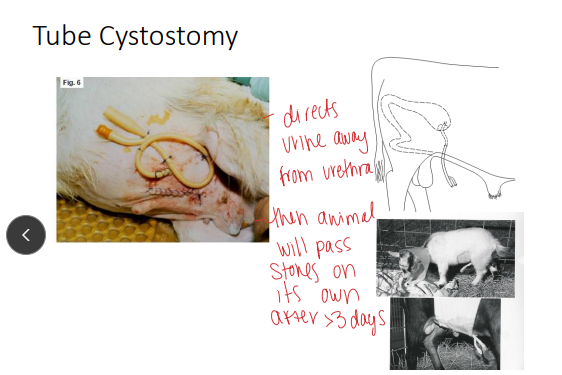
Tube Cystostomy in ruminants
Indication: Obstructive Urolithiasis
Valuable w/ intact urethra!!, bladder can be ruptured
Preserves breeding ability
How:
GA Laparocystotomy
French Foley catheter through bladder and abdominal wall for >7–10d
Occlude intermittently to ensure patency
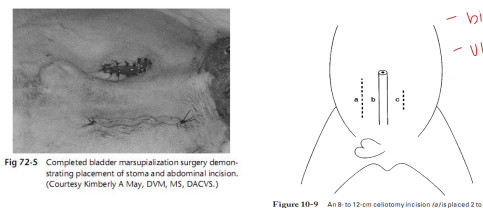
Urinary Bladder Marsupialization in ruminants
Indication: Obstructive Urolithiasis
Salvage for pets urethral/bladder rupture or stricture formation
How:
Permanent stoma from bladder mucosa to ventral skin
Hole is 1–2 cm
Comp: Frequent cystitis, urine scalding, stoma stenosis, urine dribbling
Pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) in pigs
Et: Herpes virus
all ages, feral swine (not commercial)
Cs: CNS signs, death, weak piglets, Foaming at mouth, hemorrhage, liver necrosis
Dt: Serology on tonsillar tissues
Tx: Vax
Swine influenza
All ages
Et: H1N1, H1N2, H3N2
Endemic in most herds
Cs: Fever, coughing, pneumonia, Intermittent resp and infertility Dx
Dt: nasal swab Serology
Tx: rapid return to normality in 7-10d, Vax
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PPRS) in pigs
Et: all ages, economic loss
Endemic in most herds
Cs: Pneumonia in Weaners, Repro Failure in Sows,
Duroc’s: Red ears, lung edema/hemorrhage, hemorrhagic spots in heart
Wild boar: Pulmonary hyperplasia, cardiac edema/hemmorage
Dt: VI, Serology
Tx: Vax
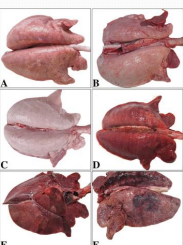
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (Enzootic Pneumonia) in pigs
Et: Swine
Endemic in most herds
Cs: Acute Pneumonia, prolonged cough, breathing difficulty (thumps); Consolidation of lungs- anterior, cardiac, intermediate, and anterior diaphragmatic lobes
Dt: PCR, Serology
Tx: Medicated feed, Vax, disease-free herd
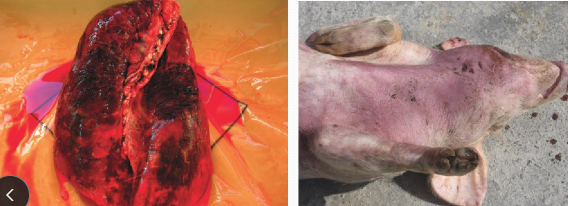
Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia in pigs
Et: Pigs 8-16w
Cs: Resp distress, cyanosis of the ears, sudden death w/ hemorrhage from nose
Dt: Culture, PCR, Serology (ELISA)
Ddx: bacillus anthracis
Tx: Antibiotics, Medicated feed/water, Vax

Atrophic Rhinitis in pigs
Et: B. bronchiseptica (mild), Tox P. multocida (severe)
Cs: Sneezing, snuffling, nasal discharge, severe turbinate damage, nose malformation, nose bleeds
Dt: Nasal Culture
Tx: Antibiotics, Medicated feed/water, Vax
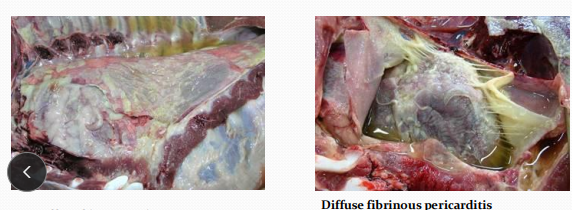
Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in pigs
Et: Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma, pigs
Cs: Coughing, fever, anorexia, dyspnea, thumping, cyanosis (especially in extremities), diffuse fibrinous pleuritis and pericarditis
Dt: culture of lung tissue
Tx: Antibiotic, Medicated feed/water, Vax
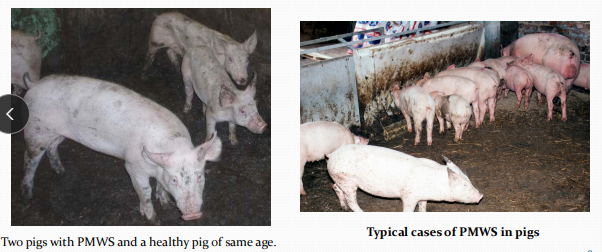
Porcine Circovirus Disease in pigs
Et: Porcine Circovirus Type 2-3
Cs:
Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome: Poor growth in weaners and growers, Repro failure, Death in sows
Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome: Widespread hemorrhages, multifocal erythematous in grower and finisher pigs
Porcine circovirus type 2 enteritis: Grower-Finisher Pigs w/ Mild Diarrhea, enlarged Mesenteric Lymph Node, thickening of intestinal mucosa
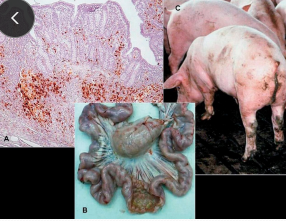
Dt: IMH
Tx: Vax
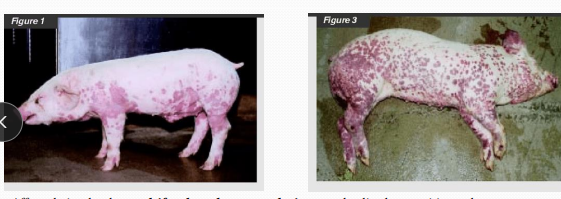
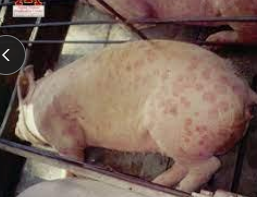
Erysipelas (diamond skin disease, rhomboid urticaria) in pigs
Et: Endemic in most herds
immunocompromised and non-vaccinated pigs
Cs: Septicemia, acute death, diamond skin lesions, arthritis, lameness, endocarditis, abortion, infertility
Dt: isolation, serology
Tx: Antibiotic, Medicated Feed/Water, Vax

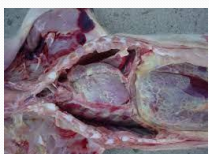
Greasy pig disease (Exudative epidermitis) in pigs
Et: Staphylococcus hyicus
Affects all ages
Cs: Dark patches of flaky greasy skin lesions, toxemia, death
Dt: culture
Tx: Antibiotic, spray w/ bleach/chlorhexidine, auto vax
Glässer’s disease in pigs
Et: Haemophilus parasuis
Cs: sudden death in sows and suckling pigs, meningitis, middle ear infection, pleuropneumonia, pericarditis, peritonitis
Dt: culture
Ddx: Anthrax-like
Tx: Antibiotic, Medicated Feed/Water, Vax

Colibacillosis in pigs
Et: Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Piglets 2-4d old, older pigs are not affected
Cs: watery yellow diarrhea, dehydration, SI inflam
Dt: Fecal culture, necropsy w/ milk filled stomach
Tx: Antibiotic, Medicated Feed/Water, Vax, Electrolytes, All-in-all-out
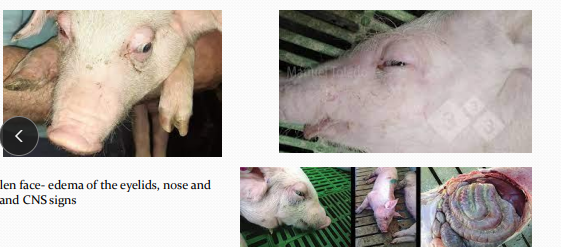
Edema disease in pigs
Et: hemolytic E. coli → Shiga toxin 2e
Weaner pigs, dietary changes, overfeeding, poor hygiene
Cs: Swollen face, dullness, blindness, head pressing, lateral recumbency, paddling leg movement, coma, death
Dt: ELISA of toxin
Tx: Antibiotic, Medicated Feed/Water, Vax
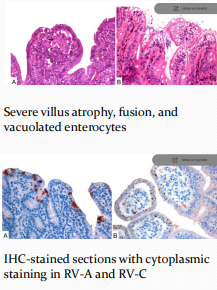
Rotaviral Diarrhea in pigs
Et: Group A (#1)
Endemic in lg swine herds, fecal-oral exposure, asymptomatic adults
Cs: mild osmotic diarrhea, dehydration
Villous atrophy
Dt: fecal pH <7, ELISA, IHC, FA, EM, PCR, cytoplasmic staining
Ddx: E. coli, TGE, coccidia, Cl. perfringens
Tx: supportive, vax (sows/nursing/preg)
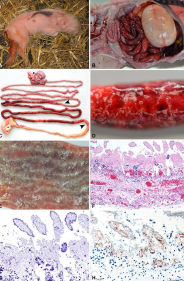
Enterotoxemia in pigs
Et: C. perfringens Type A + C
Very young piglets
Cs: bloody pink pasty feces, acute necrotic enteritis in piglets, sudden death; intestinal gas bubbles and white, necrotic villi
Dt: culture, ELISA, beta-toxin presence
Tx: Medicated feed/water, electrolytes, vax, antitoxin
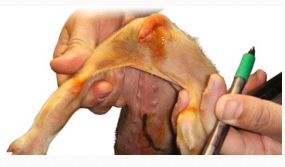
Clostridium difficile enteritis (Neonatal typhlocolitis) in pigs
Et: piglets <7d of age
Cs: Yellow pasty/watery diarrhea, colon edema
Dt: Toxin w/ PCR or ELISA
Tx: Medicated feed/water, electrolytes, vax, antitoxin
Salmonella in pigs
S. choleraesuis
Et: All ages
Septicemia/endotoxemia
Cs: Necrotizing enterocolitis w/ rectal strictures, cyanosis, fever, bloody diarrhea with necrotic debris, sudden death
Dt: culture, PCR
Tx: Isolation, antibiotics, electrolytes, medicated feed/water, vax
S. typhimurium
Et: Zoonotic
Cs: yellowish diarrhea, necrotic mucosa, blood, dehydration, proctitis and tenesmus
Dt: Red-yellow w/ blank center colonies on culture
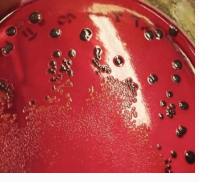
Tx: Isolation, antibiotics, electrolytes, medicated feed/water, vax
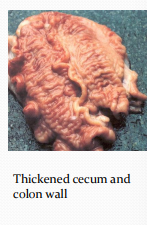
Porcine Intestinal Spirochetosis in pigs
Et: Brachyspira pilosicoli
Fecal-oral route, grower-finisher pigs
Cs: self-limiting diarrhea <14d
Dt: Culture or PCR of intestinal content
DDx: Swine dysentery, Salmonella typhimurium, Trichuriasis, PPE
Tx: Antibiotics, segregated early weaning, all-in-all-out pig movement, isolate

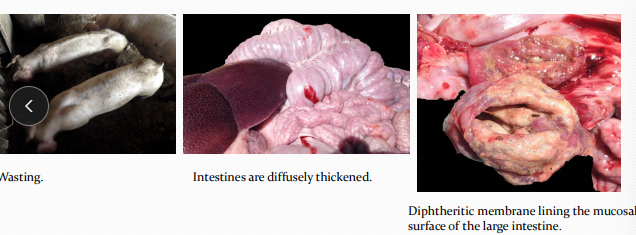
Swine dysentery in pigs
Et: Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
growers and finishers
Cs: Colitis with watery bloody diarrhea, black and tarry feces, death
Dt: fecal culture or PCR
Tx: Antibiotics, medicated feed/water
No vax
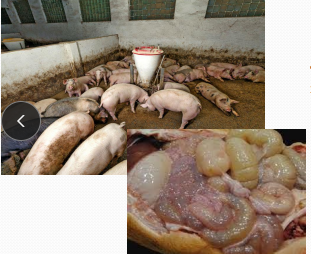
Lawsonia intracellularis in pigs
Et: Growers, finishers >6w-20w old
Porcine intestinal adenopathy (PIA): Chronic diarrhea, weight loss, pot-bellied
Regional ileitis (RI): SI inflam, chronic diarrhea, weight loss, pot-bellied
Necrotic enteritis (NE): Hosepipe gut, thickened sm intestine, pale pigs, black tarry feces
Proliferative hemorrhagic enteropathy: Bloody gut, massive bleeding into sm intestine, pale pigs, black tarry feces, sudden death
Cs: hose like Thickening of mucosa of terminal ileum, Cerebriform pattern visible from serosal surface
Dt: Serology, PCR, histopath
Tx: antibiotics, medicated feed/water, vax
Transmissible gastroenteritis (TGE) in pigs
Et: Coronavirus, all ages
Cs: Diarrhea, vomiting, thin/transparent intestinal wall, SI distension; GIT w/ foamy, yellow, odoriferous fluid + milk curds
Dt: PCR, FAT, IHC, serology
Tx: electrolytes, all-in-all-out, vax, feed sows dead piglet GIT
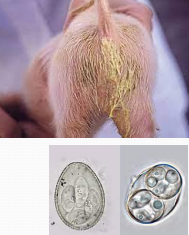
Isospora suis in pigs
Et: Coccidiosis, piglets 5-15d
Continuous farrowing houses
Cs: watery or pasty yellow to white diarrhea, weakness, dehydration, poor weight gain
no blood
Dt: Intestinal/fecal smears
Tx: Sulfas in water, coccidiostats-medicated feed
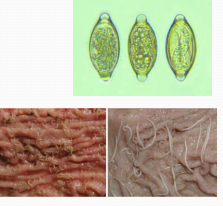
Worms in pigs
Et:
Trichuris suis (whipworms): Bloody diarrhea in pigs 3w- 6mold
Strongyloides ransomi (threadworms): Infects baby pigs through colostrum
Ascaris suum (white worms): finishing pigs 2-3m old on concrete floors w/ straw bedding
liver milk spots
Metastrongyles (earthworm parasite): pigs in pasture

Dt: fecal, Postmortum, ELISA, PCR
Tx: Ivermectin, Fenbendazole, Levamisole, Pyrantel, Dichlorvos, Piperazine, pasture rotation, age based grouping
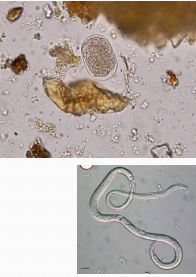
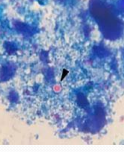
Cryptosporidium suis in pigs
Et: pigs 8–21d old
contaminated water, poor hygiene
Cs: Diarrhea, dehydration, weight loss
Dt: Acid-fast stain fecal
Tx: electrolytes, hygiene, none specific
Campylobacter coli in pigs
Et: colostrum-deprived piglets
Poor farrowing house hygiene
Cs: creamy diarrhea, dehydration, loss of condition
Dt: fecal culture
Tx: antibiotics, all-in-all-out
Streptococcus in pigs
S. suis
Et: suckling and recently weaned pigs
Cs: Meningitis (#1), bronchopneumonia, polyarthritis, polyserositis, endocarditis, abortion
Multisystem dx
Dt: culture
Tx: Antibiotic, all-in-all-out, vax
S. porcinus (pig strangles)
Et: weaners and finishers
Cs: Jowl abscesses, purulent lymphadenitis of head/ neck
Dt: culture
Tx: Antibiotic
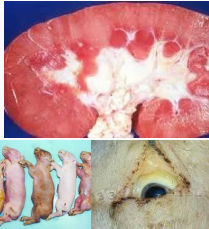
Leptospirosis in pigs
Et: wildlife, rodents, zoonotic
liver and kidneys
Cs: Abortions, jaundice, renal damage
Sows and gilts: Abortions, stillbirths, infertility
Weaners and growers: Jaundice, acute death
Dt: Micro-agg serum test, FAT, IHC, PCR
Tx: Medicated feed, vax, rodent control
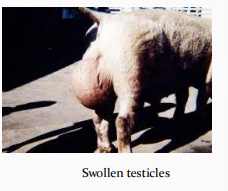
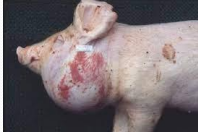
Brucellosis in pigs
Et: breeding pigs
Cs:
Females: Infertility, return to heat 30–45d after breeding, late-term abortions, stillbirths, weak piglets, vulval discharges
Boars: Swollen testicles, infertility
Life long carriers
Dt: culture, BAPA test, SCT, STT, PCFIA
Tx: Cull, no Tx, No vax
Postpartum dysgalactia syndrome in pigs
Et: udder and uterus infection
12hrs-3d after farrowing
Cs: Mastitis, Metritis, Agalactia
Sows: Depression, constipation, fever, anorexia, restlessness during suckling
Piglets: Diarrhea, reduced weaning weights, starvation, death
Dt: Based on CS
Ddx: PRRS, influenza, metritis, cystitis
Tx: Antibiotics, anti-inflam, oxytocin, adopt out sm piglets, avoid overfeeding before farrowing, secure footing
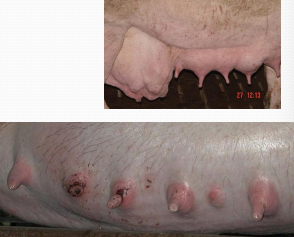
Mastitis in pigs
Acute
Et: E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas
around farrowing, solid floors, wood shavings, needle teeth
Cs: Depressed, inappetent, reluctant to rise, fever, hard, hot, painful udder, altered milk
Tx: Antibiotics, Anti-inflam, Oxytocin, Hygiene, foster out baby’s
Chronic:
Et: after weaning, early preg, injury
Cs: Hardened udder lumps in the udder
Tx: None; cull
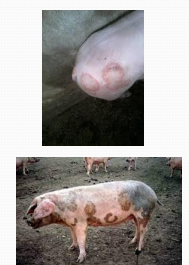
Ringworm in pigs
Et: Dermatophyte fungal infection
All ages
Cs: Circular skin lesions behind the ears, back, and flanks
Dt: skin scrapings
Tx: Self-limiting

Iron Values in pigs
Iron deficiency anemia
Cs: Pale piglets, poor growth, tachypnea, sudden death, thin-walled heart, edema of lungs/CT
Dt: Bld smear w/ microcytic hypochromic bld
Tx: Iron dextran @ 3 -5d old, supplementation
Iron toxicity
Et: pigs deficient in vit E/Se injected w/ iron dextran
Cs: Lameness in 2rs after iron injection, dark/ swollen injection site, heavy breathing, pale, death in 24hrs
Dt: History of iron dextran injection
Tx: Vit E/Se injection/supplement in last 2m of preg or 2d before iron injections
Vitamin E deficiency in pigs
Et and Cs:
Mulberry heart disease: Cardiomyopathy
sudden death in healthy-looking pigs <4m old
Hepatosis dietetica: Hepatic necrosis and hemorrhage
sudden death in apparently healthy pigs
White muscle disease: Pale skeletal muscle
rare
Dt: Bld selenium level
Tx: Supplement Vit E/Se last 2m of preg
Salt poisoning in pigs
Et: water deprivation or excess consumption
Cs: Dehydration, incoordination, blindness, head pressing, nose twitching, convulsions, dog-sitting, falling, paddling legs, death
Dt: Serum or CSF Na level
Tx: Slow fluids, mannitol, diazepam/midazolam
Poor prognosis even w/ Tx
Malignant hyperthermia (porcine stress syndrome) in pigs
Et: Inherited, calcium dysregulation
Pietrain, Poland China, Landrace
Triggered by stress or halothane GA
Cs: Hyperthermia, muscle fasciculation, rigidity, tachypnea, tachycardia, arrhythmia, myoglobinuria, metabolic acidosis, renal failure, death
Tx: Cooling, dantrolene, Ace, use local analgesia instead of halothane
Orthopedic issues in pigs
Neonatal Polyarthritis
Et: Strep suis, Staphylococci, Trueperella pyogenes, E. coli, Actinobacillus suis
Common cause of death/culling in suckling pigs
Cs: Lethargy, pain, poor suckling, swollen/painful/warm joints, lameness
Dt: Clinical exam, pus in joints, swelling of umbilical stalk
Tx: Antimicrobials, all-in/all-out, hygiene
Foot disorders
Et: Heel erosions, hoof wall cracks, necrotic ulcers
Trueperella pyogenes, Fusobacterium necrophorum, Borrelia suilla
Slippery floors, heavily preg
Cs: Lameness, swelling, progression to three-legged lameness
Tx: antibiotics, wound care, NSAIDs, ensure safe flooring, biotin diet support
early is key
Gastric Issues in Potbellied pigs
Gastritis & Gastric FB
Cs: Vomiting, colic, infection
Dt: X-rays
Tx: Sx, fuids, nutritional support, antibiotics, tetanus vax
Constipation
Et: FB, low water intake, low fiber diet
Tx: Increase water intake, mineral oil, mild laxatives, stool softeners, enemas, Sx, exercise, dietary fiber
Skin Disorders in Potbellied pigs
Dry, Flaky Skin: Manage with moisturizers
Sarcoptic Mange: Intense itching; treat with ivermectin injections
Skin Tumors: May be malignant; surgical removal, pathology
Sunburn: Common in light-skinned pigs
Aggression in Potbellied pigs
Et: Onset ~1–1.5 years, social dominance behavior
Cs: Lunging, snapping, biting
Tx: training
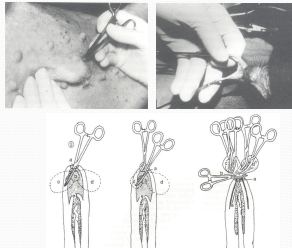
Castration in pigs
Commercial
When: <1w old
How: Open castration w/ scrotal incision, remove all tunics
Potbelly Pigs
When: <3m old
Rx: TKX or gas
How: Prescrotal incision and closed castration w/ ligation
Cryptorchids
AKA: one nutters or rigs
Et: Retained testicles, show pigs, mounting behavior
How: Incise over retained side, ligate spermatic cord, close abdomen
Never perform unilateral castration on cryptorchid
Teaser Males
Use: Heat detection/stimulation
Methods:
Vasectomy: cranial to scrotum, Isolate and excise vas deferens
Epididymectomy: Remove tail of epididymis
In very young boars
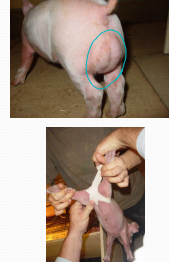
Scrotal Hernias in pigs
Et: Hereditary
Dt: detected @ castration
DDx: Hydrocele, scirrhous cord, hematoma
Tx:
Taping: Elasticon fig 8 around legs post-castration. Revolve in 5d
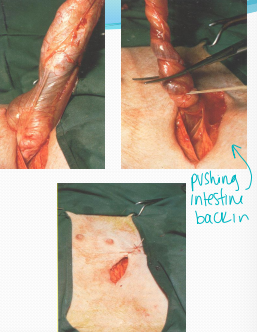
Sx: Pre-castration, incise over inguinal ring, reduce hernia by twisting, ligate spermatic cord, close ring, remove other testicle

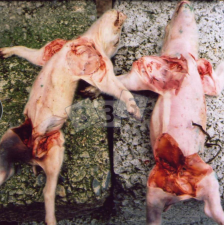
Rectal Prolapse in pigs
Et: Crowding, cold stress, coughing, short tail docking, enteritis, constipation, mycotoxins
Tx: Sx (Epidural, Amputation/replace, purse-string suture), Rectal prolapse tube
Umbilical Hernias / Infected Navels in pigs
Et: Origin from umbilical abscess
Tx: Elliptical skin incision, stab through body wall, excise hernia sac and flush, close
Repair only in valuable animals
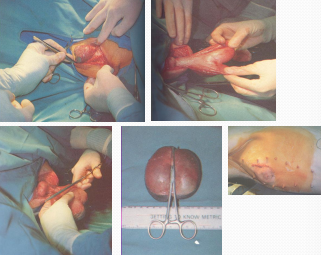
Preputial Diverticulum in pigs
Why: Penis entrapment, contamination, diverticulitis
How:
Open: Incise over lateral aspect, exteriorize diverticulum, ligate, close incision
Closed: through preputial orifice to evert diverticulum
Sutures optional in young boars

Female Reproductive Management in pigs
Dystocia
PE: Age, vaginal exam, general status
Tx:
Stable Gilt: Time and oxytocin
Open cervix, stable sow: Manual extraction, oxytocin
Closed cervix, unstable sow: C-section
Ovariohysterectomy in Potbelly Pigs
Why: Prevent breeding, treat infection/tumors
When: Age: 6–8 weeks optimal
How: Linea alba incision, 3-clamp technique, SQ skin closure
Cesarean Section
Rx: Epidural + line block, TKX or inhalant
Sut: Inverting uterine closure
How:
Op: Lateral flank incision, remove ALL piglets
Post Op: Hand-rear piglets
Routine Trimming in pigs
Needle Teeth Removal
When: <24–48 hrs of birth
How: Clip sharp tips of 8 needle teeth (deciduous canines/incisors)
Use sterile tools; avoid gum trauma
Disinfect between litters
Tail Docking
Why: prevent tail-biting/infection
When: 3–7 days of age
How: cutters/scissors/cauterizer, leave 1–2 cm tail
Too short = risk of rectal prolapse
Tusk Trimming
Why: Prevent injury
When: every 6–12m
How: wire saw, bolt cutters, or grinder, sedate, Trim just above gum line
Foot Trimming
Why: Lameness, overgrowth, infection
When: Every 6–12m
How:
Restraint: Chute, sling, or sedation
Tools: Hoof shears, rasp, or grinder