Anatomy Block 1 Lecture
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
anterior (ventral)
frontal view of the body
posterior (dorsal)
view of the back of the body
superior
towards the head, above smth
inferior
towards the feet, below or bottom of smth
proximal
closest to the trunk of the body
distal
furthest from the trunk of the body
rostral
toward/closer to the front/nose
caudal
toward or closer to the tail/back
how does blood flow through a capillary bed?
blood enters via the arterial side(has lots of smooth muscle) and leaves via the venous end
arterioles along w/ precapillary sphincters constrict/dilate to control blood flow of capillary beds
involves hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures
hydrostatic pressure
blood flows into capillary beds from arteriole end →push pressure that pushes OUT blood plasms along w/ dissolved nutrients and oxygen gases into the interstitial space, delivering it to tissue away from the brain supply (15-20 mg of Hg)
interstitial space
fluid filled gap between cells and tissue involved in capillary beds
colloid osmotic pressure
lower pull pressure that pulls water and proteins back in bc of positvely charged proteins creating an opposite charge
HOWEVER, not all fluid gets pulled back in
importance of lymphatic vessels
take left over fluid in the interstitium and bring it over to lymph nodes for them to filter, clean, and put it back into blood circulation via the venous system →preventing edema
edema
results when lymphatic vessels are blocked causing effected body area to swell bc of buildup of excess tissue fluid
neuron
nerve cell that receives, collects, and transmits info
basic building block of the nervous system
structural neurons
multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, and pseudounipolar
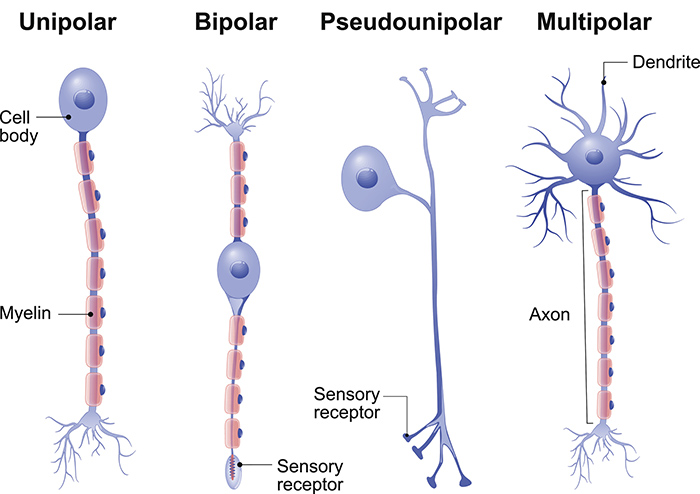
multipolar
2+ processes; has many dendrites and 1 axon
mostly found in the CNS: motor and intraneurons
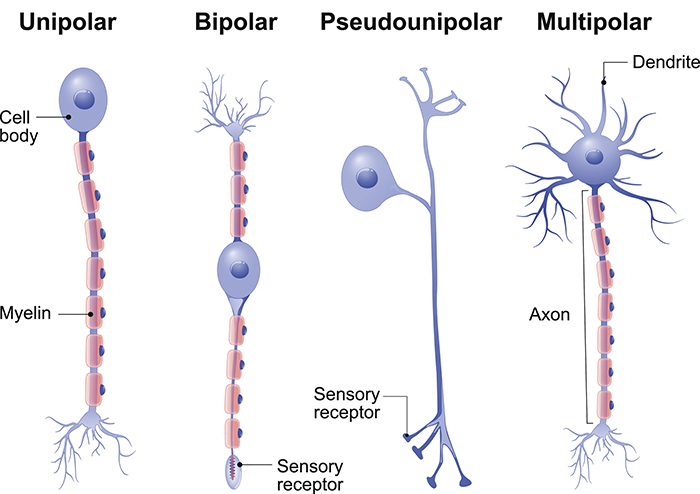
bipolar
2 process; has 1 dendrite/sensory receptor and 1 axon
rare: found in special sensory organs
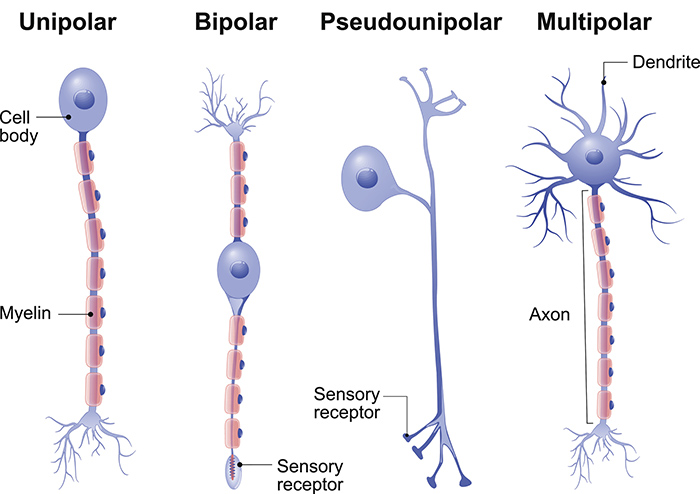
unipolar
1 short/single process; no dendrites and one axon
develops as a bipolar neuron first
found in the PNS
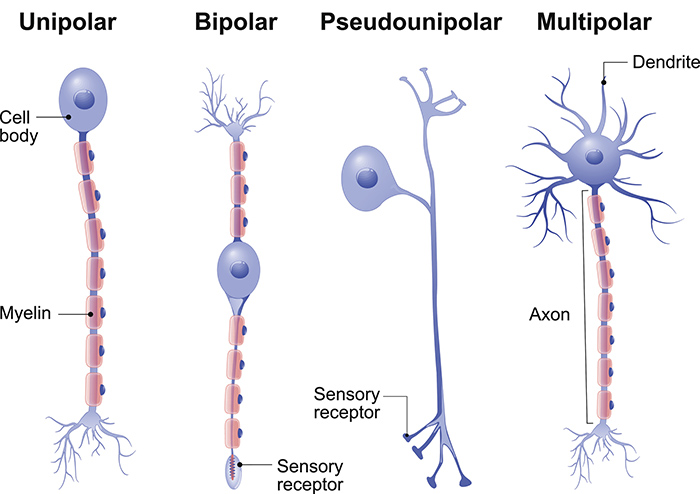
pseudounipolar
axon branches into two
one branch connected to dendrites (PNS) which recieve sensory info and the other is connected to the CNS
sensory neurons
functional neurons
sensory (afferent) neurons, intraneurons, motor (efferent) neurons
sensory (afferent) neurons
transmit impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors in PNS
bring in info via spinal chord or brain and then relay that info to an intraneuron
activated by physical modalities or chem signals like visible light, sound, hear, physical contact, smell and taste
most are pseudounipolar
intraneuron
forms connection between sensory and motor (efferent) neurons
located in the CNS
operates locally as their axons connect w/ nearby sensory and motor neurons
once they decide if info is critical, they talk to motor neurons and tell them to go out into the PNS and talk to an effector to get them to start movement
can save time and prevent injury by not sending messages all the way to the brain or not past the spinal chord
multipolar
motor (efferent) neurons
conducts impulses from integration center (CNS) to an effector
body stays in the CNS but its axon goes into larger nerves in the PNS to talk to an effector to tell them to make muscle contraction happen
most common functional neuron
multipolar
effector
skeletal gland/muscle
glia (glial cells/neuroglia)
non-neuronal cells in the CNS and PNS that dont make electrical impulses but instead function as helper cells that aid in functioning
CNS neuroglia/glial cells
astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
protect and support neurons through feeding, regulation of ions, formation of synapses, growth and memory signaling
sense when neurons release glutamate
give energy by getting blood sugar from capillaries
control environment around neurons by taking and releasing ions
help form synapses in developing neural tissue
produce molecules for neuronal growth
send calcium signals involved w/ memory
most abundant glial cell in CNS
microglia
are phagocytes (cells that engulf/digest random particles, debris, and dead cells)
act as macrophages of CNS therefore are defensive cells that come from blood cells (monocytes)
they move to the CNS during embryonic and fetal period
smallest/least abundant glial cells in CNS
ependymal cells
line central cavity of spinal chord and brain
have cillia which help circulate CSF
oligodendrocytes
produce myelin sheaths that wrap around axons in the CNS
have few branches
PNS neuroglia
satellite cells and schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
satellite cells
surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia to help w/ nutrient exchange
schwann cells (neurolemocytes)
surround parts of the axons to make myelin sheats in the PNS
skeletal muscle
act as pumps that press against veins (making them push blood toward the heart) since valves prevent backflow of blood (mostly in the lower limbs)
40% of body weight
has striated cells
controlled by voluntary division of the nervous system
all are considered organs bc they have 2/4 tissue types: nervous, muscle, and connective-blood vessel
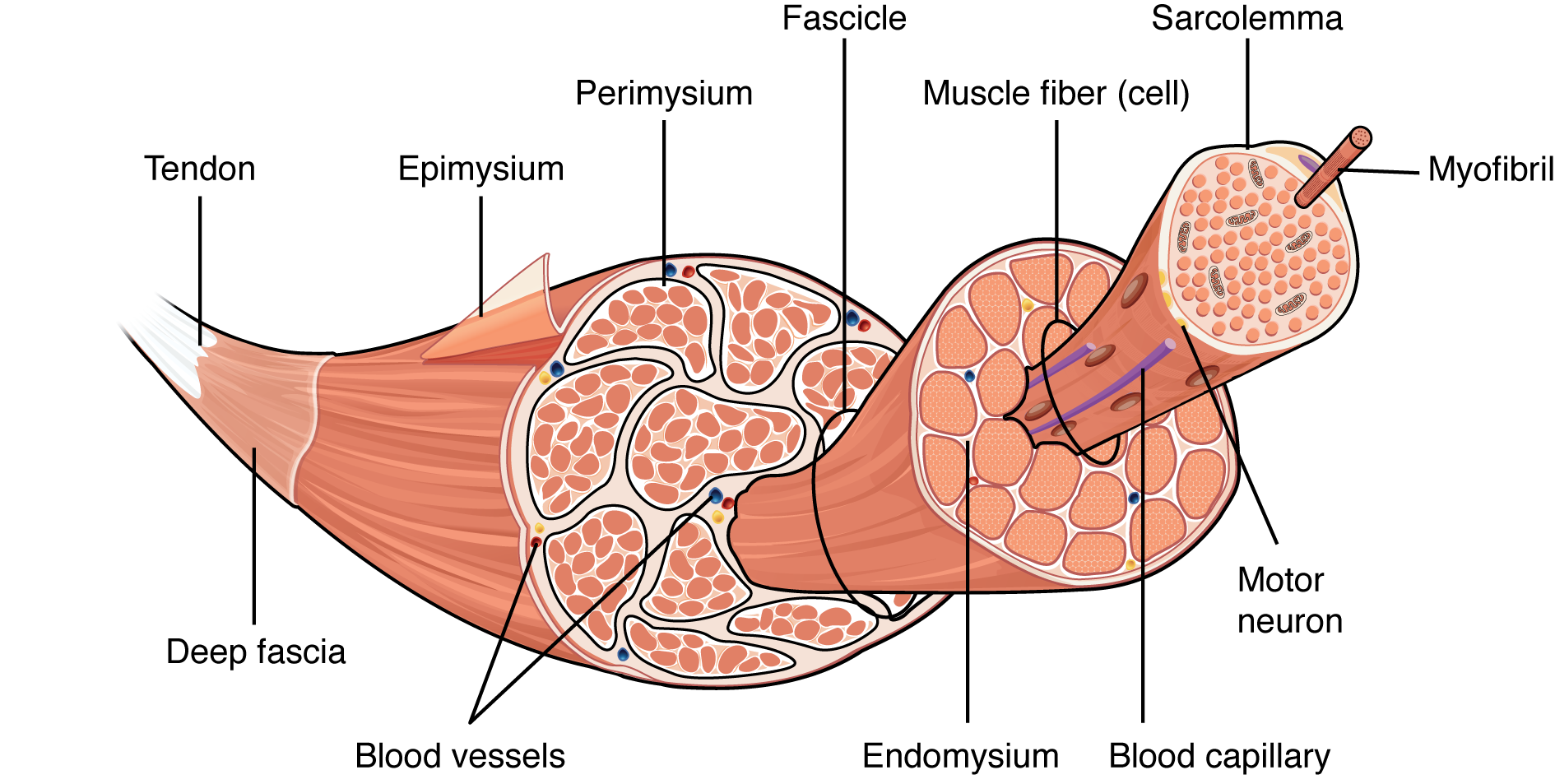
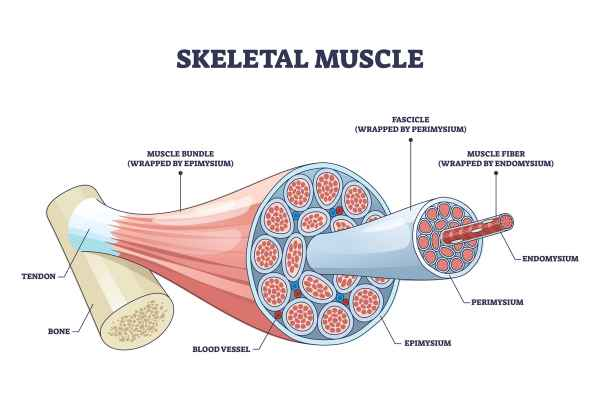
skeletal muscle structure
epimysium
fascicles
endomysium
muscle fiber
sacromere
myrofibrils
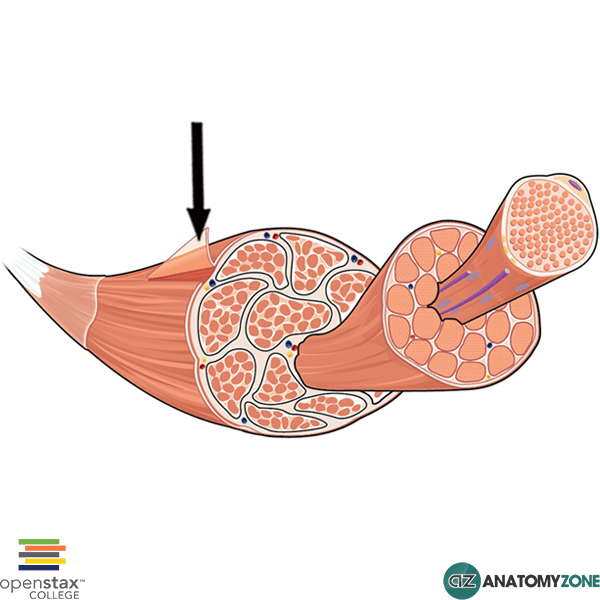
epimysium
thin/dense connective tissue membrane on the outside of the musce body
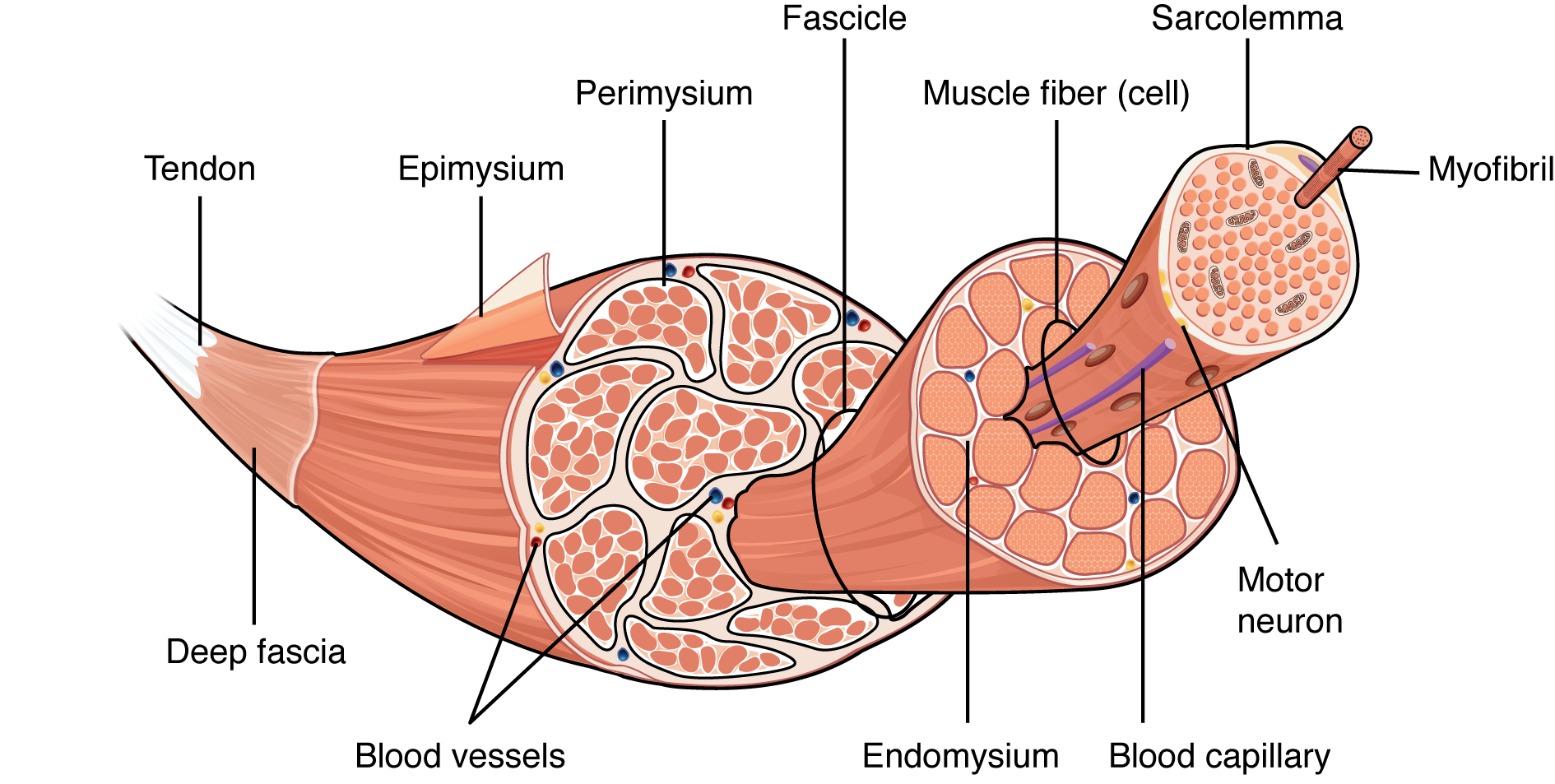
fascicle of muscle
bundle of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium
endomysium
connective tissue membrane that covers muscle fibers(cells)
muscle fiber
individual muscle fibers/cells that are covered in endomysium
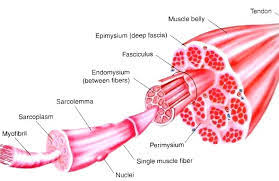
sacrolemma
plasma cell membrane of muscle fibers
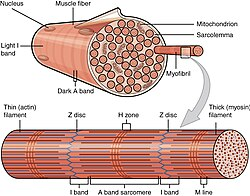
myrofibrils
rod-like organelles in muscle cells in charge of contracting units
contraction and connective tissue of muscles
connective tissue sheaths are connected to tendons and provide elasticity as well as carry blood vessels and nerves
when muscle fibers contracts, force pulls on the connective tissues and pass onto the tendonds which then pulls on the bone itself
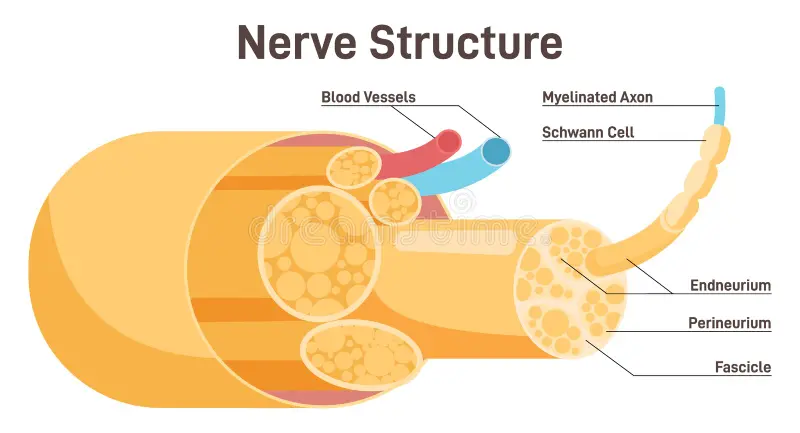
nerve structure
epineurium - outer membrane of the nerve body
fascicles - bundles of axons covered w/ perineurium membrane
axons covered w/ endoneurium membrane w/ blood vessels inside
intramembranous ossification
bone formation directly from mesenchymal (no cartilage) at around 8 week of embryonic development (contiues during embryonic and fetal development)
flat bones of the skull (except some base parts of it), mandible, along w/ the clavicles are formed
endochondral ossification
begins during embryonic developement and CONTINUES during childhood and adolescence
responsible for bone lenthening until epiphyseal plates close
most bones of the skeleton including long bones (femure, humerus, tibia, etc.) along w/ short, irregular bones, vertebrae, pelvis, base of skull are formed by replacing a hyaline cartilage model
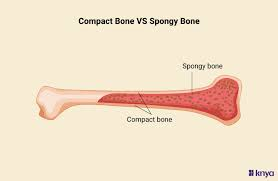
compact bone
smooth, solid, and dense outer layer of bone
made of osteons
makes up most of the diaphysis or shaft of long bones
provides strength, protection, and weight-bearing
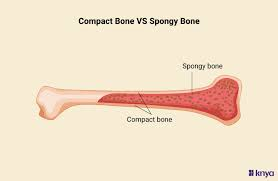
spongy bone (trabecular/cancellous bone)
honeycomb of small needle-like or flat pieces called trabeculae where red/yellow bone marrow is found
found inside flat bones and inside the ends or epiphyses of long bones!
helps reduce bone weight and resist stress
osteoporosis
low bone mass bc of bone reabsorption(breaking down) OUTPACING bone deposition(bone building)
most common in women a4 menopause bc of the secretion of estrogens help maintain bone density
osteosarcoma
form of bone cancer
normally originates in a long bone often near the knee
common in 10-25 year old
cancer cells come from osteoblasts-LIKE cells and secrets osteoid which alters affected bone by eroding medullary cavity internally and the compact bone externally
often metastasizes to the lungs
symptoms: bone pain and swelling, diagnosed X-RAY or imaging
treatment: surgical removale (bone graft/prosthesis or amputation, chemotherapy, removal of lung metastases
if detected early 60-70% chance of survival
osteoarthritis
common degenerative joint disease where there is detoriation of the articular cartilage; seen a lot in aging
no synovial membrane(connective tissue that lines inside of synovial joints→ make synovial fluid to lubricate joint and fee cartilage) involvement but inflammation, pain and decrease in the use of the joint or present
gouty arthritis
metabolic disease where the waste product, uric acid (made by the cells and excreted through urine) is too much in quantity → builds up in the blood and makes salt crystals that stay in the joints causing pain and decreases motion
atherosclerosis
when the arterial wall has plaque (lipid) buildup
macrophages are transformed into foam cells as they try to get rid of the stuff
plaque gets BEHIND the endothelium cells and builds WITHIN the wall →pushing int the lumen causing: localized inflammation, cellular necrosis, and increased shear pressure causing the wal to rupture leading to possible formation of thrombosis (clotting of blood)
risk factors include life factors and predisposition
lymph nodes
nodes that filter and clean excess fluids (esp from capillary beds)
has immune cells (lymphocytes, macrophages) that detect and fight infections/cancer
sentinel nodes
nodes that are the frist to get lymphatic fluid from a speciifc area
important bc often the first place cancer spread
efficient for checking of matastasis
paired bones of cranium
symmetic on both sides; one on each side
temporal bones
parietal bones
unpaired bones of cranium
single bone; fall on the midsagittal line; not seprated by sutures
frontal bone
occipital bone
sphenoid bone (looks like a bat, middle)
ethmoid bone (between eyes, part of nasal cavity)
has perpendicular plate that drops inferiorly and forms the upper region of the septum of the upper nostrils
paired bones of the face
maxillae
zygomatic bones
nasal bones
lacrimal bones
palatine bones
inferior nasal conchae
unpaired bones of the face
mandible - rare to see any abnormalities
vomer - makes the inferior portion of the nasal septum and fuses w/ the perpendicular plate
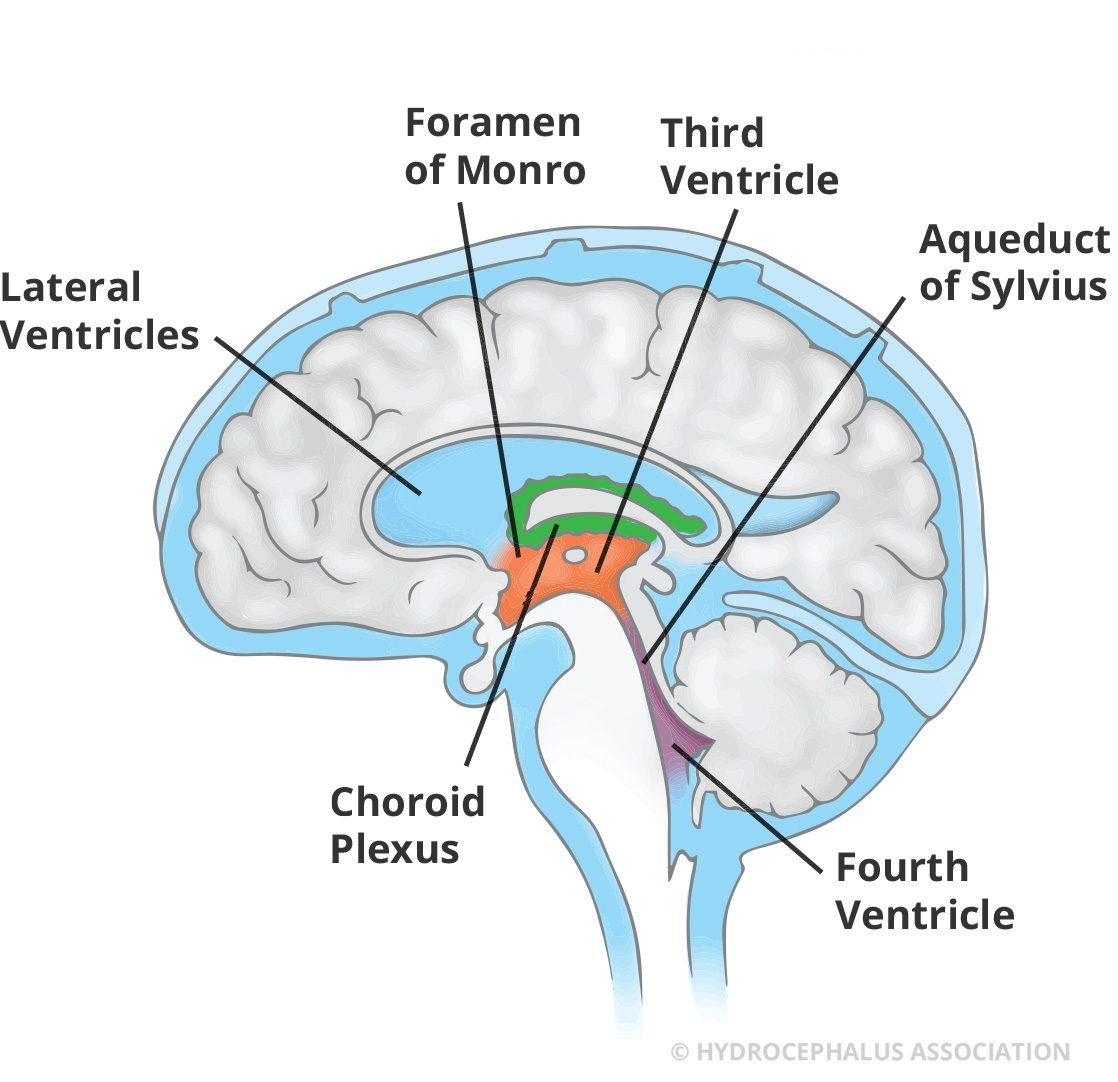
CSF
cushions and nourishes the brain and spinal cord, removes waste made by neurons, and carries chm signals
location: ventricles of the brain, subarachnoid space (between arachnoid mater and pia mater), central canal of spinal cord (little amt)
flows to the subarachnoid space via lateral and median apertures of the 4th ventricle
production: made in the choroid plexus (roof of the ventricles), where modified ependymal cells covered by capillary rich pia mater filter blood plasma and make CSF
reabsorption: goes into dural venous sinuses (i.e superior sagittal sinus) via arachnoid granulations → into bloodstream
abt 500mL/day is produced and recycled
hydrocephalus (water on the brain)
excessive accumulation of CSF →increase intracranial pressure
cause of excess production of CSF or inadequate recycling of CSF (idiopathic and or congenital)
also can be caused bc of tumor/ swelling →blocking cerebral aqueduct/4th ventricle, blocking of arachnoid granulations (post meningitis bc of scarring), or bc of overdeveloepd choroid plexus in infants causing excess secretion
infants have enlarged skull/ventricles bc cranial bones aren’t fused yet and adults are susceptible to quick damage bc bones are rigid
treatment: surgical shunt to drain CSF from ventricles into the abdominal cavity
diagnosed via CT or MRI scan
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges due to bacterial or viral infection whcih can spread to nervous tissue and cause brian inflammation (encephalitis)
diagnosis: CSF sampling via lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
needle inserted below L1-L2 (common: L3-L4 or L4-L5)
look for microbes, chemicals, or pressure
bacterial infection cause - releases metabolic waste/proteins into CSF
antibiotic treatment
viral infection cause → non living, need a host cell to reproduce (viral rna takes over nucleus and makes more viruses.) once cell is full →becomes dead and leaves cellular debris(cell membrane fragments) are left in CSF
antiviral treatment
4 regions of the brain
cerebrum
diencephalon/thalamus
brainstem
cerebellum
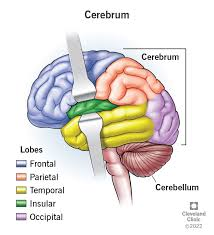
cerebrum
consists of the cerebrum hemispheres (83% of brain mass), and the olfactory and optic nerves
has lots of fissures (deep grooves that seperate major parts of the brain) including the transverse fissure which seperates the cerebrum from the cerebellum (top/bottom division) and the longitudinal fissure which separates the cerebral hemispheres (left and right division)
also has sulci(grooves on the surface of hemispheres or the valleys between) and gyri (twisted ridges between sulci (top of the mountain)
has 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, and a hidden lobe - the insula (deep lobe underneath the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes
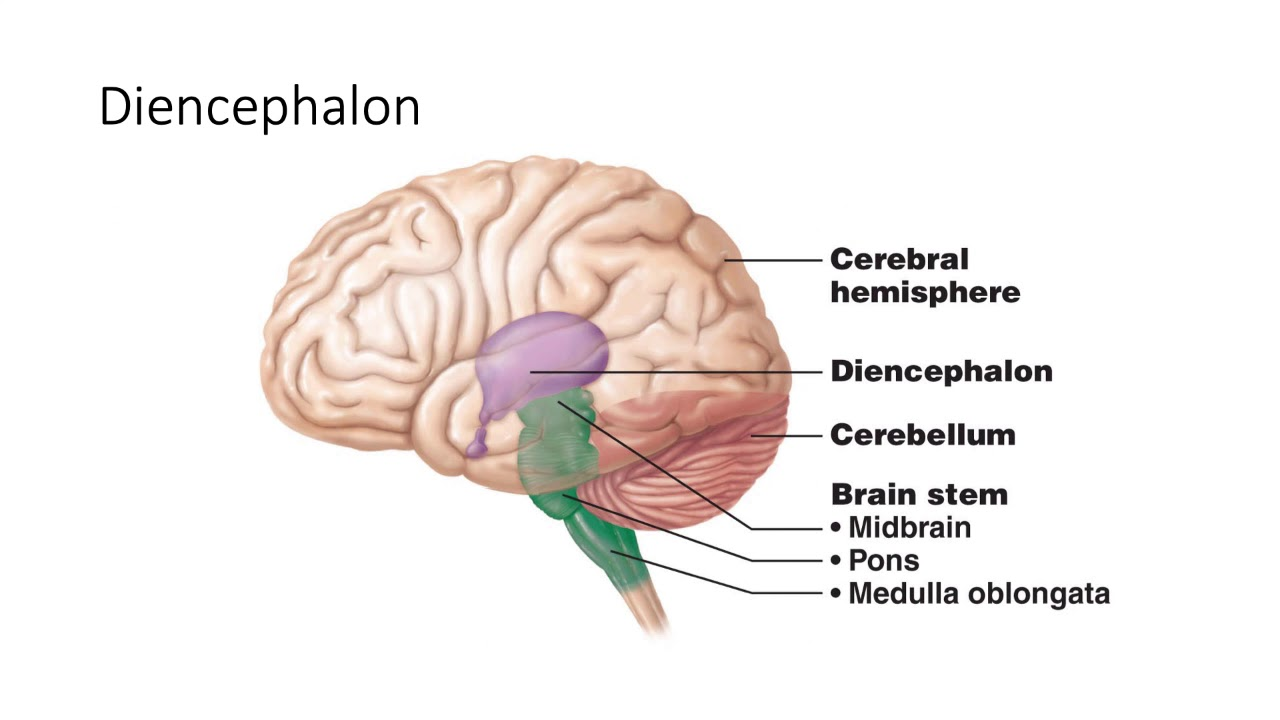
diencephalon
made of the hypothalmus, thalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus, penial, and pituitary glands; center of the brain
mostly made up gray matter and intraneurons that recieve messages and relay them
relay area of the brain: 90% of everything that goes into the brain is processed here
the thalamus acts as a receptionist as thats where messages come through and get “transferred”
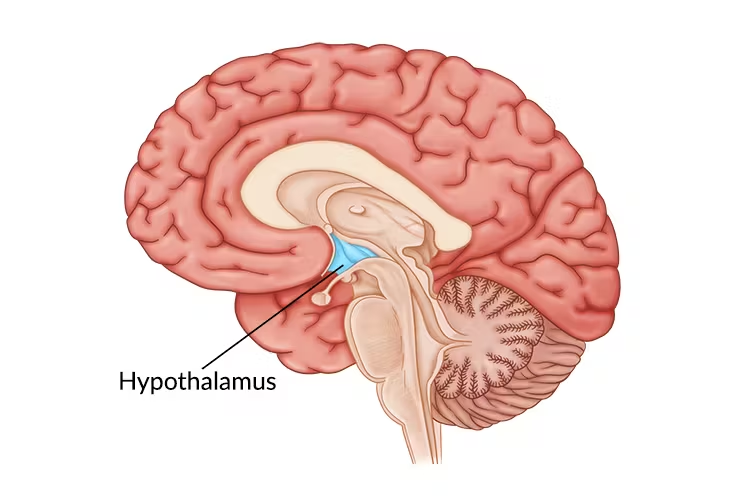
hypothalamus
located below the thalamus in the diencephalon and between optic chiasma and mamillary bodies
helps form walls of 3rd ventricle
connected to the pituitary gland
regulates homeostatic functions like sweating (body temp reuglation), eating (hunger/thirst), reproductive, growth, emotional responses, control of behavior, regulation of sleep-wake cycles, formation of memory
recieves info from the thalamus
generates messages
controls the endorcrine system
controls ANS (parasympthatic and sympathetic)
if damaged → severe weight loss/obesity, sleep disturbances, dehydration, and emotional disorders
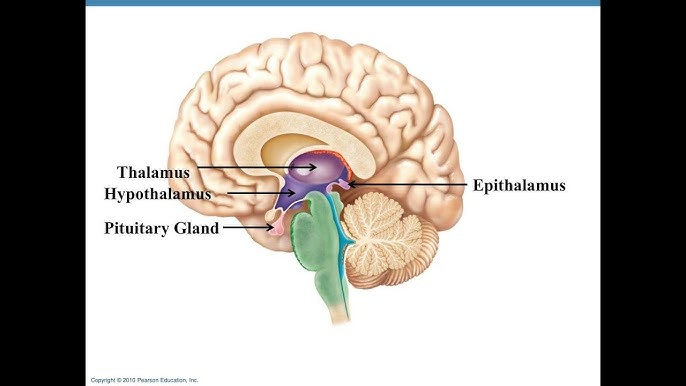
epithalamus
dorsal part of the diencephalon
forms part of the top of third ventricle
made up of a tiny group of nuclei and the pineal gland which comes from ependymal glial cells and secretes melatonin hormone for night time under the influence/control of the hypothalamus
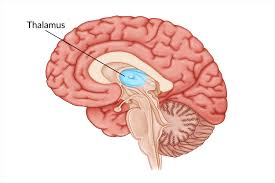
thalamus (inner room)
80% of diencephalon and walls of the third ventricle
dozen major nuclei that send axons to regions of the cerbral cortex and either amplify or tone down signals
relay station for incoming sensory messages
every part of the brain that communicated w/ cerebral cortex relays signals through the thalamic nuclei
receives afferent impulses (signals from the PNS)
gateway to the cerebral cortex
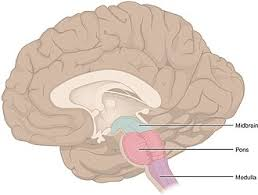
brain stem
made of the the midbrain, pons, and medulla - connected to the spinal cord
10/12 pair of cranial nerves are found here - involved w/ innervation of face and head
production of autonomic behavior important for survival i.e parasympathetic (rest and digest) and sympathetic (fight or flight)
has auditory and visual reflexes
all nerve fibers (axons) that branch off the spinal cord reach the cerebrum via the brain stem
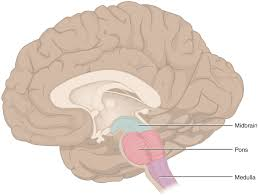
medula oblongata
most caudal part of brain stem
decussation of pyramids - cross over of motor tracks (left side of the brain controls the right side of the body and vice versa)
4 CN :
VIII vestibulococlear
IX glossopharyngeal
X vagus
XII hypoglossal
symmetrical and has lots of nuclei or visceral centers that each control different process: cardiac center, vasomotor center, respiratory center, hiccuping, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing center (inhibiting and stimulation)
important for autonomic function
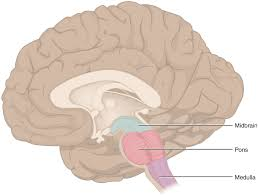
pons
bridge betwee medulla and midbrain
has 3 CN:
V trigeminal
VI abducens
VII facial
has motor tracts coming from the cerebral cortex
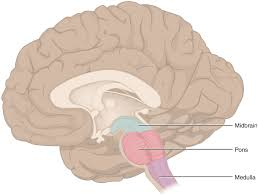
midbrain
between the diencephalon and the pons
cerebral aqueduct
has big red/brown pigmented nuclei that work to together regarding specific processes
red nuclei - control limb
brown nuclei (substantia nigra) - neuronal cells bodies that make dopamine and have lots of melanin which is important for coordinated body movements and limb control
if uncontrolled → Parkinson’s disease (cell death in substantia nigra)
posteriorly has two little bumps called corpora quadigemina (4 bodies organized in a square pattern) which are important for visual via superior colliculi, which jerk head in response to flashing lights and sound via inferior colliculi which jerk head in response to a loud sound
cerebellum
“little brain on top of the big brain” that helps maintain equillibrium and smoothly coordinate body movements through communication w/ dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra
dorsal to pons and medulla
arbor vitae - lots of white/light brown matter
2 cerebellar hemispheres w/ surface folded into folia (ridges)
3 total regions: cortex - gray matter, arbor vitate, internal white matter
3 lobes: anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular lobes
brain tumors
can grow in many different parts of the brain
symptoms vary depending on size and location
frontal lobe tumor → behavior changes
thalamus tumor → disruptions in hormonal secretions
cerebellum tumor → difficulty in movement coordination
most dont metastasize bc of blood brain barrier
cancer cells from body can enter the brain via bloodstream → secondary brain tumors
not common for cells from the brain to go outside of CNS
facial artery and cavernous sinus’ role in encephalitis and meningitis development
facial vein is connected w/ the angular vein which is connected to (has anastomoses) with w/ the superior ophalmic vein
superior ophalmic vein drains intro the cavernous sinus(important for blood drainage) and allow bidirectional blood flow further allowing infections to spread from the face throughout the veins
bacteria that enters sinus can lead to cavernous sinus thrombosis and potentially lead to meningitis/encephalitis
CN locations and characteristics
pairs found in ventral aspect
CN I olfactory and CN II optic come from middle/optic chiasm
10 other pairs come from brain stem
CN X vagus is the largest nerve
pass through foramina
CN 1 olfactory
location - nasal cavity
function - smell
type - visceral sensory
anosmia: loss of smell sense bc of ethmoid bone fracture or olfactory fibers lesions
CN II optic
location - eye retina
function - vision
type - special somatic sensory
CN III oculomotor
location - eye muscles (ventral midbrain)
function - eye movement inside of eye, iris constricting, lens shape (4/6 intrinsic and 2/6 extrinsic muscles)
type - somatic and visceral motor
CN IV trochlear
location - superior oblique
funciton - eye movment
type - somatic motor
CN V trigeminal
location: jaw/face
function: facial sensation; chewing
three branches: 1. ophalmic 2. maxillary 3. mandibular
type: both
sensory nerve of the face regarding touch, temperature, and pain
mandibular branch has somatic motor control of chewing muscles
innervated muscle of maastication
CN VI abducens
location: lateral rectus muscle
function: eye movement outward
type: somatic motor
CN VII facial
location: muscles of facial expression
function: facial movements and taste
three branches: temporal, zygomatic, buccal
type: both
CN VIII vestibulocochlear
location: inner ear(cochleal semicircular canals and vestible)
function: hearing and balance
type: sensory
CN IX glossopharyngeal
location: tongue/throat
function: taste, swallowing, saliva
type: both
CN X vagus
location: thoracic/abominal organs
function: parasympathetic control, voice, swallowing
type: both
CN XI accessory
location: neck, shoulder
function: head rotation, shoulder elevation
type - motor
CN II hypoglossal
location: tongue
function: tongue movement
type: motor
mimetic muscles
scalp, eyelids, nasal, mouth
control expression
all motor innverated by CN VII facial nerve
all sensory innervated by CN V trigeminal
scalp: epicranius (occipitofrontalis)
eyelids: orbicularis oculi (orbital palpebral/lacrimal), corrugator supercilli
nasal: nasalis
mouth: orbicularis oris, zygomaticus minor
zygomatic major, risorius w/ sygomaticus major, levator labii superioris, depressor labii inferioris, levator anguli oris, depressor anguli oris, buccinator, mentalis, platsyma
scalp mimetic muscles
epicranius - wrinkles in the forehead. astonishment
eyelid mimetic muscle
corrugator supercilli - vertical folks, protects against light, thinker’s brow
orbicularis oculi (orbital, palpebral/lacrimal) - lateral folds, concern
nasal mimetic bone
nasalis
mouth mimetic muscles (zygomatic)
zygomaticus minor
originates from zygomatic bone
zygomaticus major - lifts corners of mouth upwards, laughter/pleasure
comes from zygomatic bone, corner of mouth
mouth zygomatic bones (levator/depressor)
levator labbi superioris - pulls on upper lip
comes from infraorbital margin/skin of upper lip
depressor labii inferioris - pulls lower lip down, perseverance
levator anguli oris - lifts corners of mouth, self confidence expression
depressor anguli oris - pulls corners of mouth down, sadness
mouth mimetic muscles
risorius w/ zygomatic major - make nasolabial folds , laughing muscle
buccinator - blows air out mouth, keeps mucous membrane free from folds
quadrilaterl shape
originates from mandible (molar/cheek area)
forms pterygomandibular raph, extends to angle of mouth, forms lateral wall of vestibule
mentalis - chin lip furrow, doubt/indecision
platysma - tenses anterior neck skin
clinical significance of TMJ
temporal mandiublar joint which is important for mastication, speech, swallowing, and facial movements (condyle and temporal bone)
TMJ syndrome
acute/chronic pain in the TMJ or mastication joint process (where condylar process and temporal bone meet)
also can be inflammation masstication muscles which are innervated by CN V
constant pain → joint
pain while chewing → lateral pterygoid muscle
radiating pain across jaw → masseter
issues radiating into temporal region → temporalis
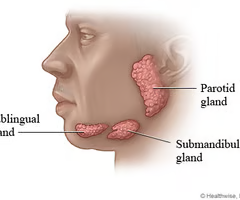
salivary glands
produce and release saliva into oral cavirt via stensens duct (parotid gland) includes parotid, submandibular, and sublingual
chemical part of digestion
all are innervated by CN VII facial and CN IX glossopharyngeal which controll parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation
parotid gland
largest gland - infeiror to or underneath the zygomatic bone
aka stensen’s duct
mumps
mumps
inflammation of parotid gland caused by myxovirus