IaD Formative Review COMPLETE v2
1/537
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
538 Terms
What is the mechanism of action of Praziquantel (for Trematodes, Cestodes, Schistosomiasis)?
Increases membrane permeability to Ca²⁺ → contraction and paralysis of parasite
What is the mechanism of action of Albendazole?
Blocks microtubule assembly in parasite; Irreversibly inhibits glucose uptake
What is the mechanism of action of Niclosamide?
Inhibits mitochondrial phosphorylation of ADP; stimulates ATPase → lethal for scolex and segments
What is the mechanism of action of Mebendazole?
Inhibits microtubule synthesis (Blocks assembly and glucose uptake)
What are the treatments for Nematode (Roundworm) infections (where mechanism is not specified)?
Pyrantel pamoate; Ivermectin; Diethylcarbamazine
What is the topical treatment for Cutaneous Larva Migrans?
Thiabendazole
What are the drugs effective against Malaria liver stages?
Primaquine; Pyrimethamine
What is the mechanism of action of Chloroquine (Malaria)?
Blocks detoxification of heme into hemozoin → Heme accumulates and is toxic to plasmodia
What are the drugs effective against Malaria blood stages (excluding Chloroquine)?
Mefloquine; Atovaquone
What is the treatment for resistant Malaria cases?
Artemisinin (Coartem)
What are the prevention methods for Malaria?
Bed nets; Repellents; Screens (Protection from mosquito bites)
What are the treatments for Taeniasis?
Praziquantel (drug of choice); Albendazole; Niclosamide
What is the pharmacological treatment for Cysticercosis?
Praziquantel
What are the adjunctive therapies for Cysticercosis and their functions?
Steroids (relieve inflammation from dead larvae); Vitamin D & Calcium (help calcification)
What is the physical treatment for Cysticercosis?
Surgical treatment
What are the physical treatments for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
Surgical excision; Curettage; Heat; Freezing
What are the chemical treatments for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
2% Chlorpromazine & Clotrimazole; Paromomycin paste; Intralesional Sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam)
What is the function of Interferon gamma in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis treatment?
Injected intradermally to promote healing of the ulcer
What is the drug of choice for Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)?
Liposomal Amphotericin B
What are the alternative treatments for Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)?
Miltefosine; Sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam)
What is the treatment for Cryptosporidiosis?
Immunocompetent: Fluid/electrolyte replacement; Immunocompromised: Nitazoxanide
What is the mechanism of action of Nucleoside/nucleotide analogues (e.g., AZT/Zidovudine) for HIV?
Inhibits Reverse Transcriptase (RT) / Chain termination (Inhibits nucleic acid synthesis)
What is the mechanism of action of Fusion inhibitors for HIV?
Bind to gp41 preventing fusion of the viral envelope to lymphocytes
What is the mechanism of action of CCR5 antagonists for HIV?
Bind to co-receptors CCR5 on susceptible cells
What is the mechanism of action of Integrase inhibitors for HIV?
Prevent integration of proviral DNA into the host's genome
What is the mechanism of action of Protease inhibitors for HIV?
Interfere with cleavage of proviral polyproteins during budding
What is the mechanism of action of Acyclovir (HSV/VZV)?
Inhibition of viral DNA polymerase / Chain termination
What is the mechanism of action of Ganciclovir (CMV)?
Inhibits viral DNA polymerase (Nucleoside analogue)
What is the mechanism of action of Amantadine (Influenza A)?
Inhibits viral uncoating
What is the mechanism of action of Oseltamivir and Zanamivir (Influenza A & B)?
Neuraminidase inhibitors (Sialic acid analogues)
What is the mechanism of action of Pegylated interferon (IFN) for HCV?
Cytokines which render cells refractory to viral infections
What is the mechanism of action of Sofosbuvir (HCV)?
Nucleos(t)ide analogue that inhibits RNA elongation (NS5B Polymerase inhibitor)
What is the mechanism of action of Dasabuvir (HCV)?
Non-Nucleos(t)ide analogue; binds allosterically and inhibits NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
What is the mechanism of action of Simeprevir, Boceprevir, and Telaprevir (HCV)?
NS3/4A protease inhibitors (Inhibition of HCV Polyprotein processing)
What is the mechanism of action of Daclatasvir (HCV)?
NS5A inhibitor (Inhibition of viral assembly and release)
What is the treatment for Streptococcal Pharyngitis?
Penicillin
What are the treatments for Pityriasis Versicolor?
Topical: Miconazole or Clotrimazole; Systemic: Fluconazole or Itraconazole
What is the mechanism of action of Corticosteroids for Allergy?
Suppress transcription of proinflammatory genes
What is the mechanism of action of Sodium chromoglycate for Allergy?
Blocks mediator release from mast cells
What is the mechanism of action of Montelukast for Allergy?
Leukotriene receptor antagonist
What is the mechanism of action of Omalizumab for Allergy?
Anti-IgE mAb (↓ IgE & ↓ FcεRI)
What is the mechanism of resistance to Penicillins and Cephalosporins?
Inactivation by β-lactamases (Hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring) or Target PBP alteration
What is the mechanism of resistance to Macrolides?
Target 50S ribosomal subunit alteration
What is the mechanism of resistance to Aminoglycosides?
Target 30S ribosomal subunit alteration
What is the mechanism of resistance to Flucloxacillin?
Target PBP2a alteration
What is the mechanism of resistance to Rifampicin?
Target Rpob alteration
What is the mechanism of resistance to Trimethoprim?
Folate biosynthesis bypass
What is the treatment for Motion Sickness?
H1 antihistamines (First-generation)
What is the vector for Malaria (Plasmodium species)?
Female Anopheles mosquito
Which Plasmodium species causes Malignant Tertian malaria and is the most fatal?
P. falciparum
What is the "Red Flag" complication known as Blackwater Fever associated with?
Massive hemolysis leading to hemoglobinuria (P. falciparum)
Which Plasmodium species is associated with Cerebral Malaria?
P. falciparum
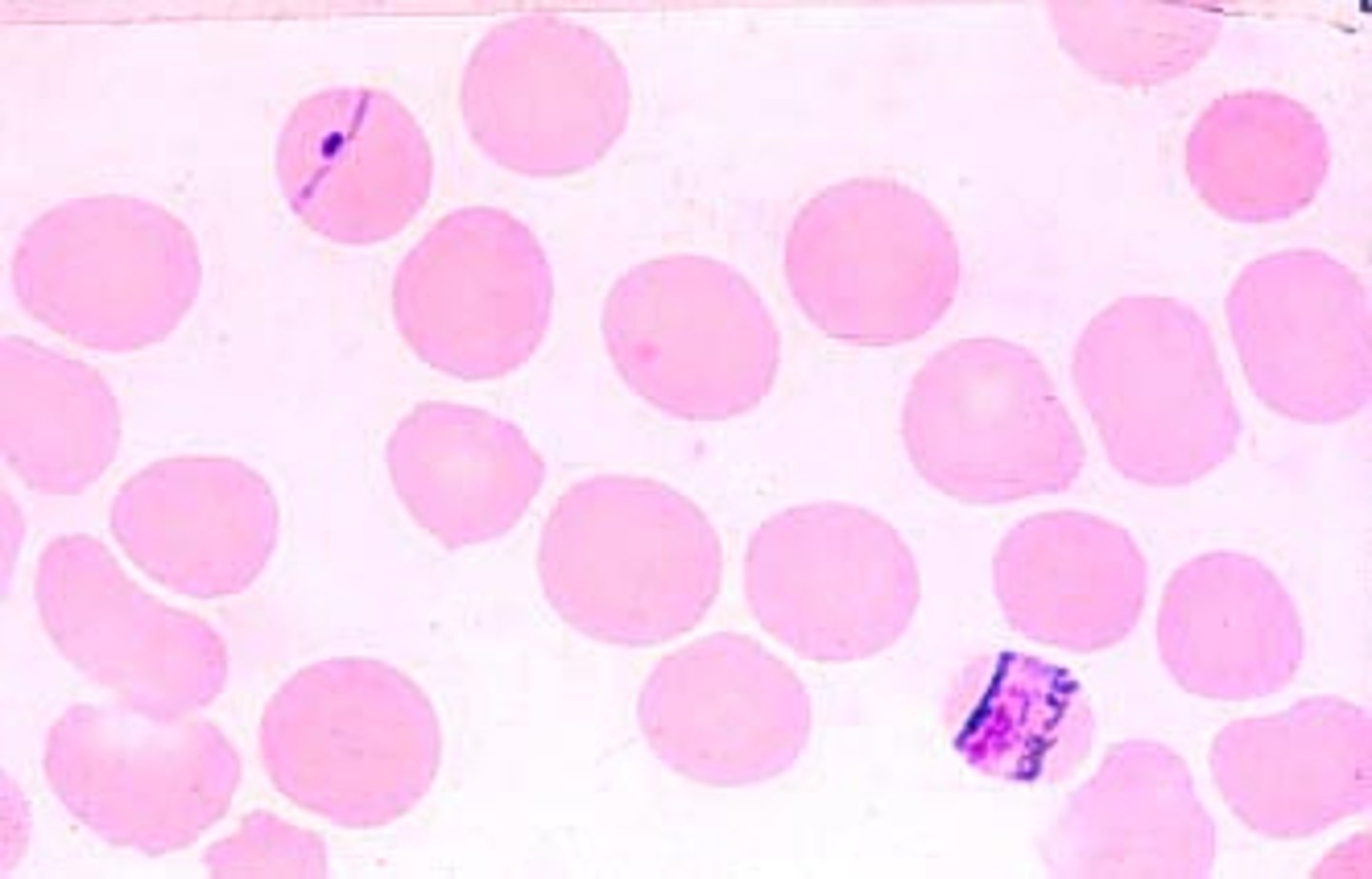
What is the microscopic appearance of P. falciparum gametocytes?
Sausage or Banana-shaped
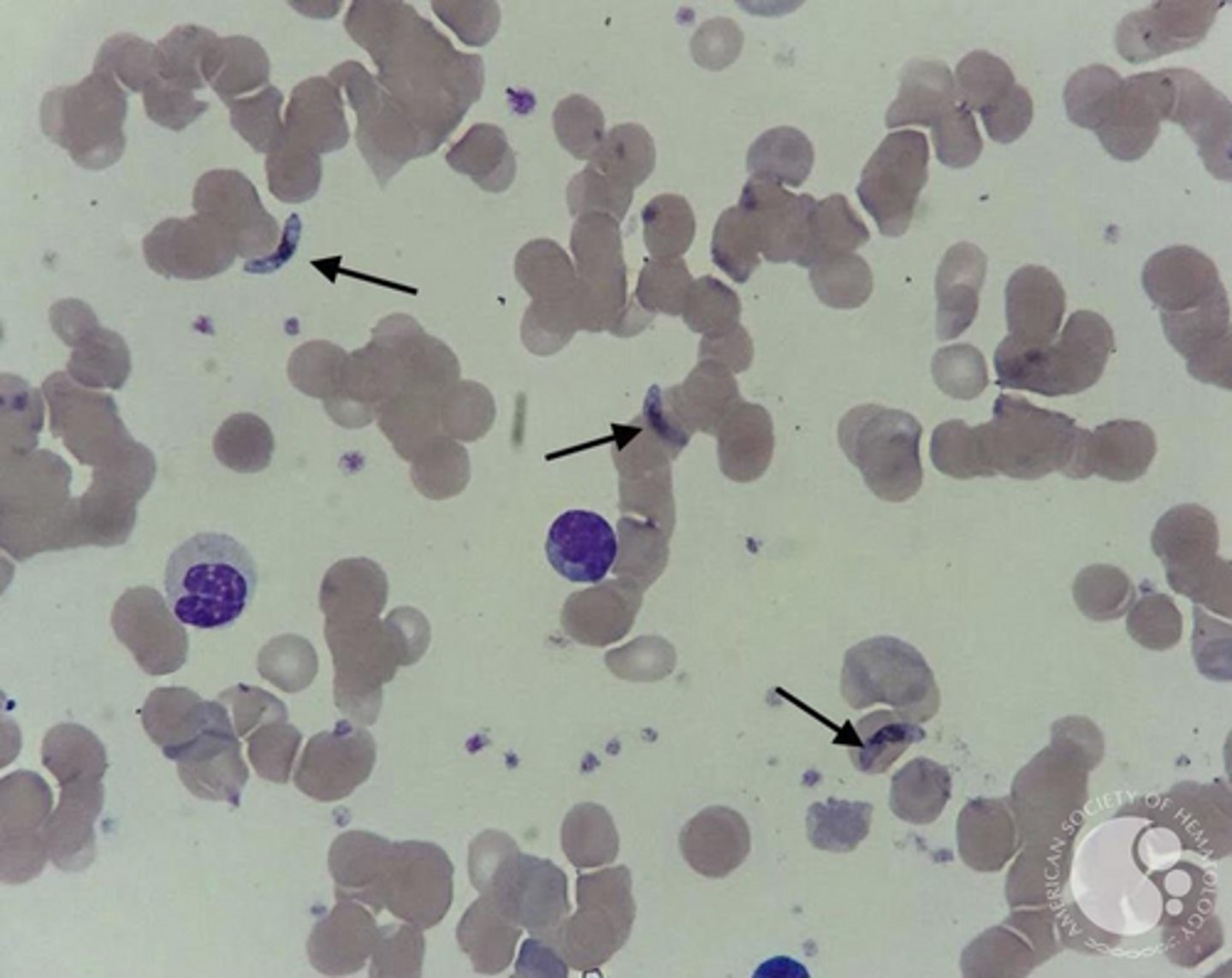
What is the "Red Flag" microscopic feature of P. falciparum ring stages?
Multiple Ring stages in one RBC
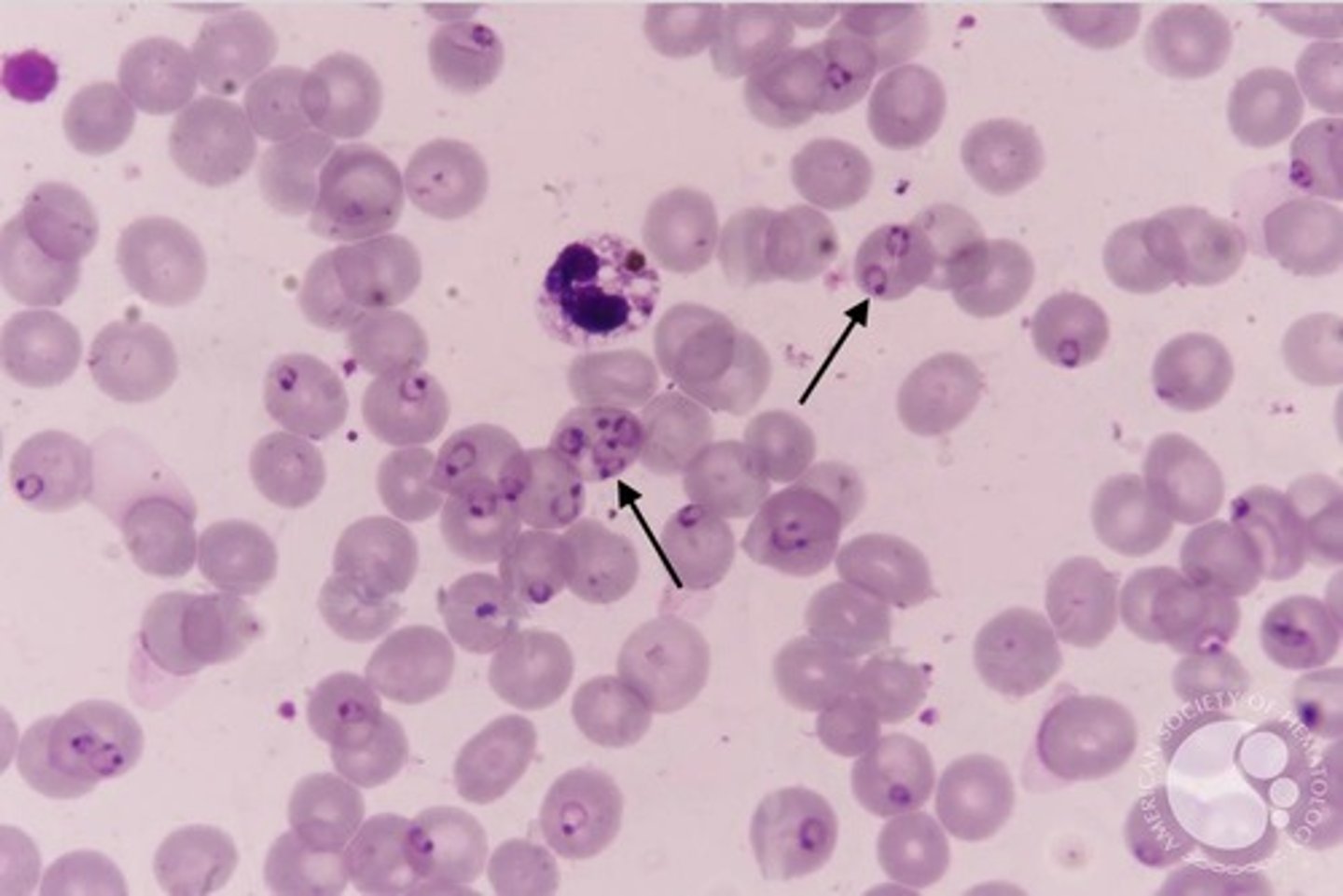
Which Plasmodium species cause Benign Tertian malaria?
P. vivax & P. ovale
What is the specific cause of relapse in P. vivax and P. ovale infections?
Dormant Hypnozoites in the liver
What is the microscopic appearance of RBCs infected with P. vivax?
Enlarged RBCs with "Schüffner's dots" (red granules)
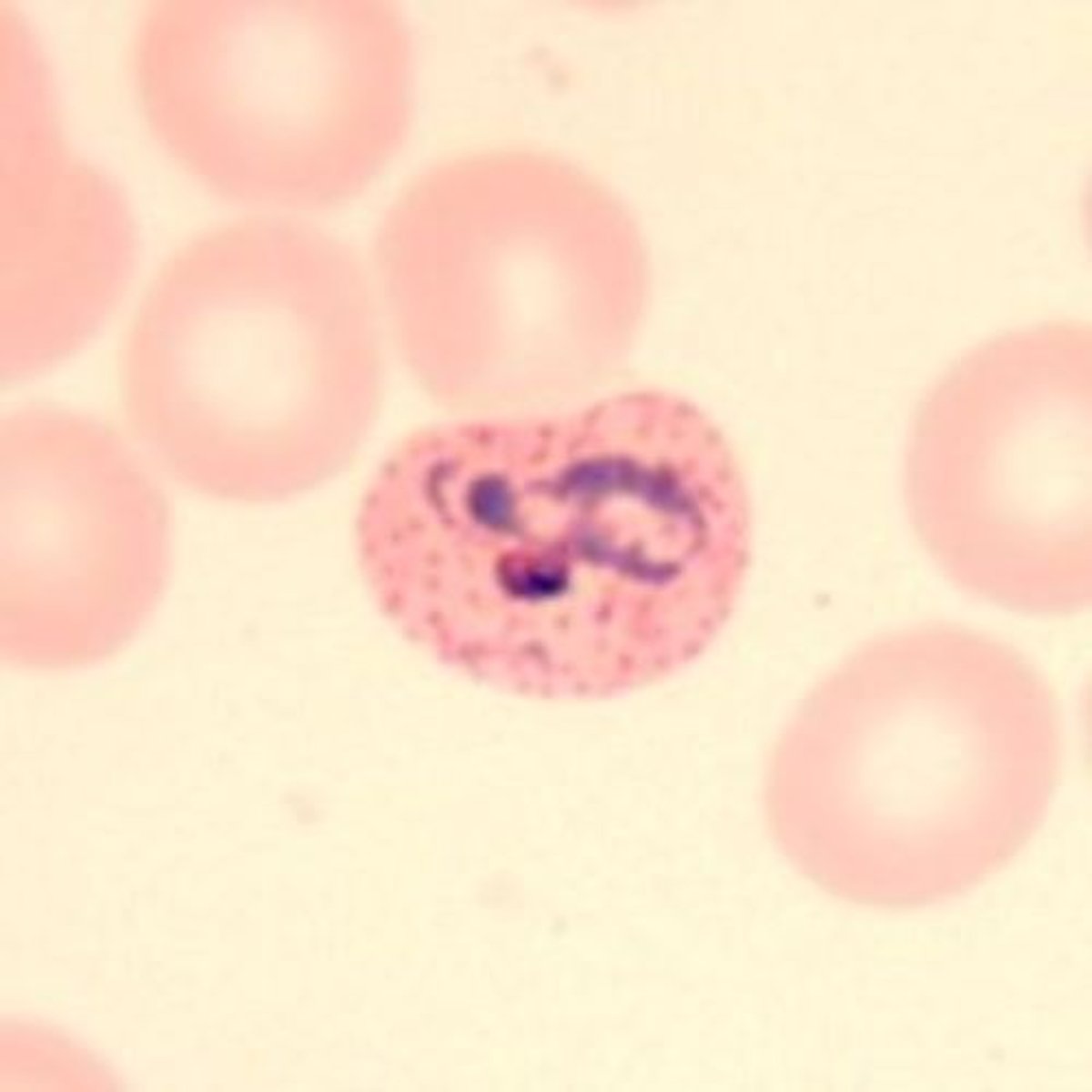
Which Plasmodium species is associated with Nephrotic Syndrome (Quartan malaria)?
P. malariae
What is the microscopic appearance of P. malariae trophozoites?
"Band form" trophozoites
What is the Infective Stage of Plasmodium for humans?
Sporozoites (injected by mosquito)
What is the Diagnostic Stage of Plasmodium in humans?
Trophozoites, Schizonts, or Gametocytes (in blood)
What is the Gold Standard for diagnosing Malaria?
Thick & Thin Blood Smear (Giemsa stain)
What is the specific purpose of the Thick Blood Smear in malaria diagnosis?
Detection of parasitemia
What is the specific purpose of the Thin Blood Smear in malaria diagnosis?
Species identification
What is the standard treatment for P. falciparum malaria?
Artemisinin-based Combination Therapy (ACT)
What drug is required to kill liver Hypnozoites in P. vivax/ovale to prevent relapse?
Primaquine
What is the major contraindication for Primaquine?
G6PD deficiency
What is the vector for Leishmaniasis?
Female Sand fly (Phlebotomus)

What is the Infective Stage of Leishmania (found in the sand fly)?
Promastigote (Flagellated)

What is the Diagnostic Stage of Leishmania (found in human macrophages)?
Amastigote (LD Body, Non-flagellated)
Which Leishmania species cause Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
L. tropica / L. major
What is the classic clinical sign of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
"Oriental Sore" (painless ulcer with raised edges)
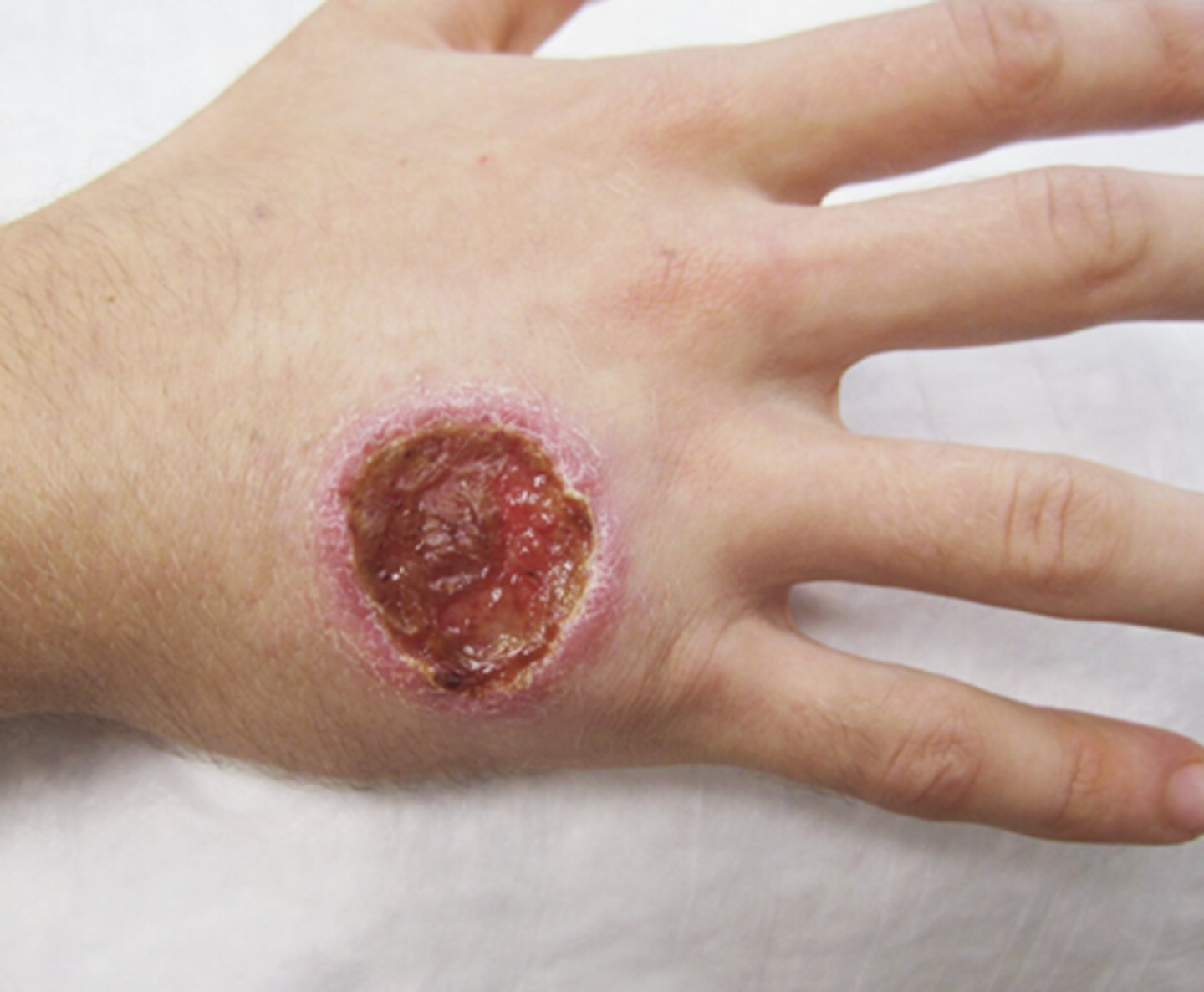
How is Cutaneous Leishmaniasis diagnosed?
Skin smear from ulcer edge showing Amastigotes inside macrophages
Which Leishmania species cause Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)?
L. donovani / L. infantum
What are the "Red Flag" signs of Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)?
Hepatosplenomegaly (massive spleen), irregular "double rise" fever, pancytopenia, hyperpigmentation
What is the Gold Standard diagnosis for Visceral Leishmaniasis?
Bone Marrow Aspirate showing Amastigotes
What is the treatment for Leishmaniasis?
Sodium Stibogluconate (Pentostam) or Liposomal Amphotericin B
Which opportunistic protozoan causes severe diarrhea in HIV/AIDS patients (CD4 < 200)?
Cryptosporidium parvum
What is the clinical presentation of Cryptosporidium in AIDS patients?
Chronic, profuse, watery diarrhea (cholera-like)
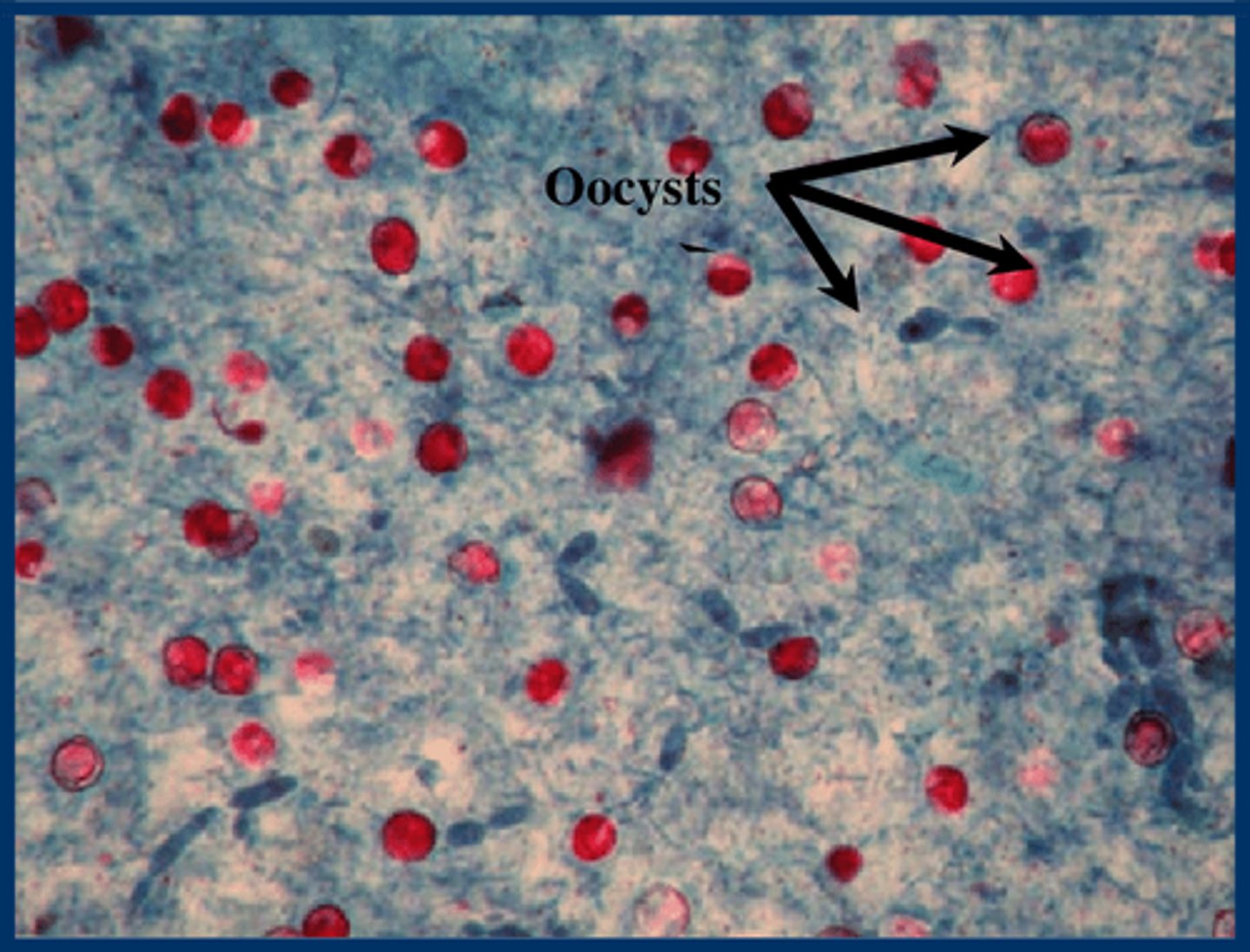
What specific stain is used to diagnose Cryptosporidium?
Modified Ziehl-Neelsen (Acid-Fast) Stain
What is the microscopic appearance of Cryptosporidium with Acid-Fast stain?
Red/Pink Oocysts against a blue background
Why is Cryptosporidium difficult to eliminate from water supplies?
It is resistant to chlorine
What is the intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni?
Biomphalaria snail
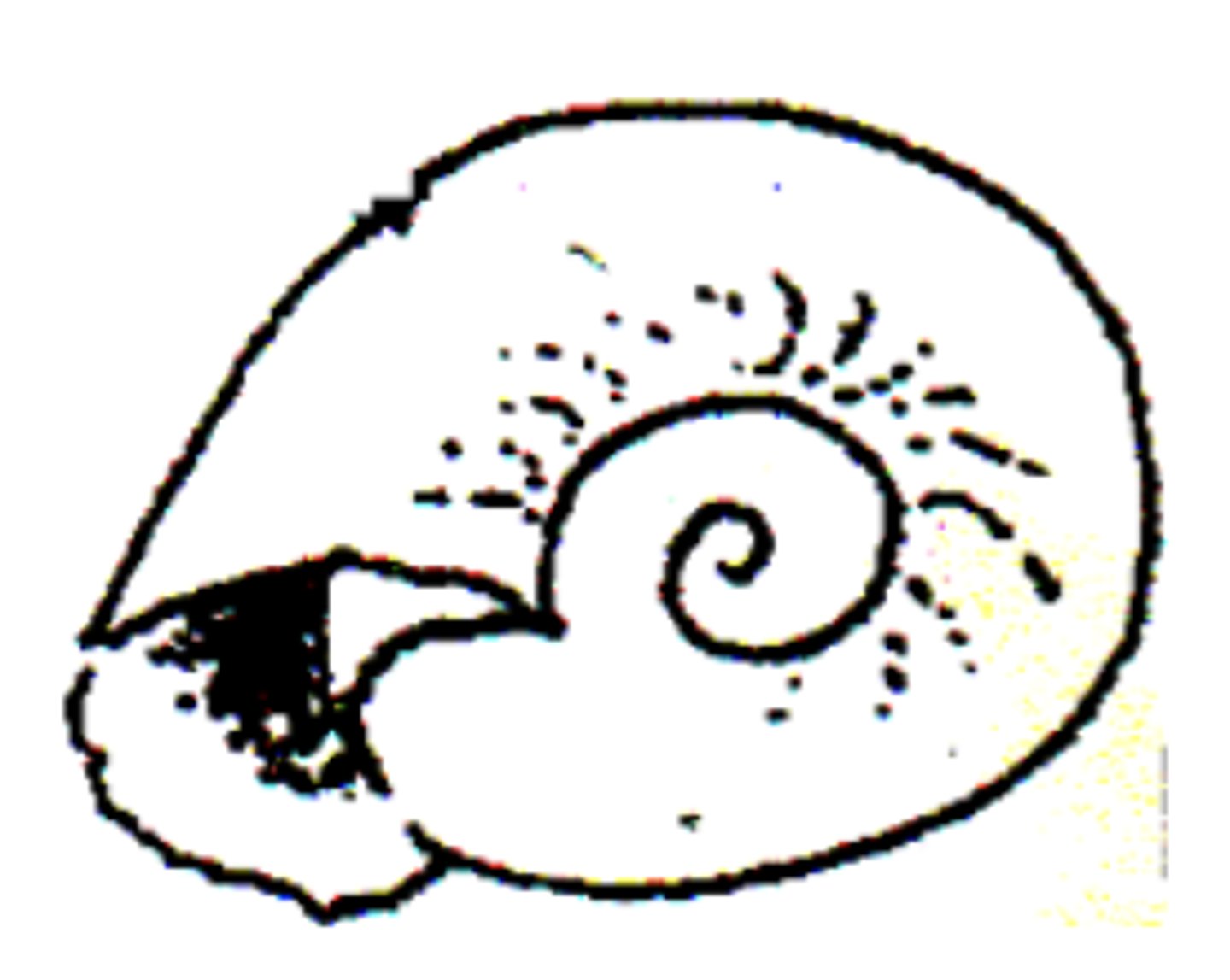

What is the intermediate host for Schistosoma haematobium?
Bulinus snail
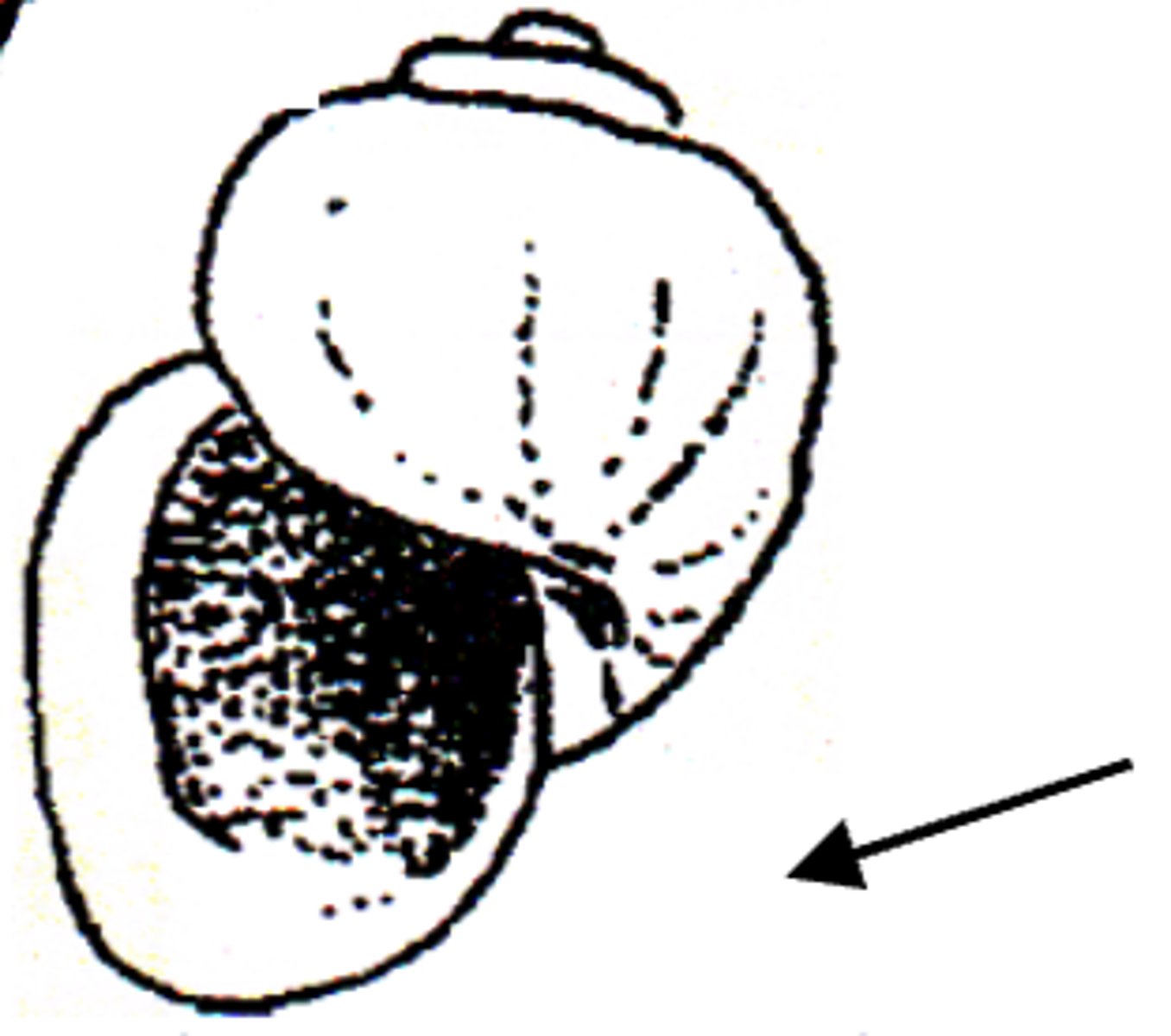
What is the Infective Stage of Schistosoma?
Cercaria (penetrates skin)
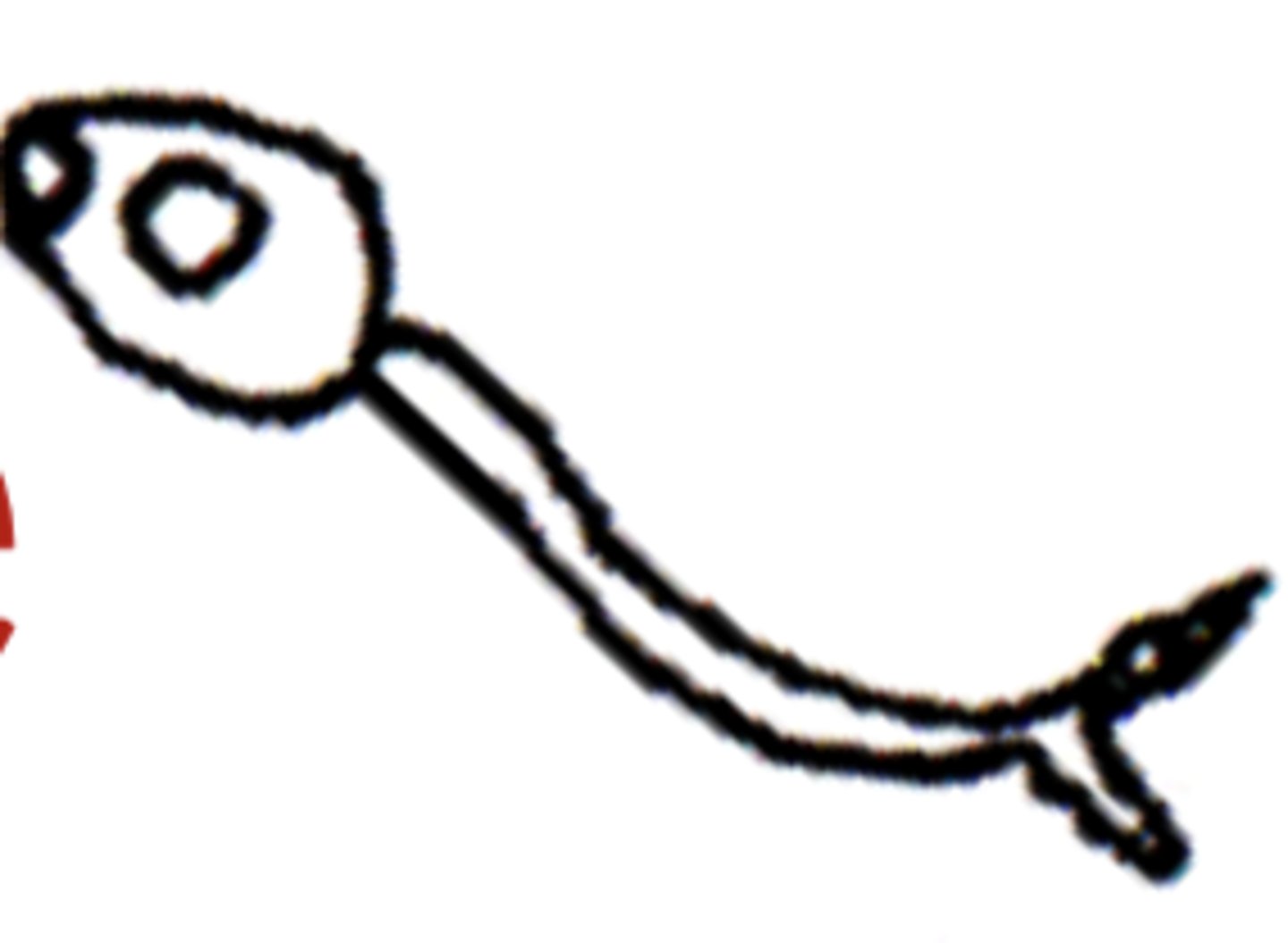
What causes the pathogenesis (granuloma and fibrosis) in Schistosomiasis?
The EGGS trapped in tissues (Type IV Hypersensitivity)
What is the microscopic appearance of Schistosoma haematobium eggs?
Terminal Spine
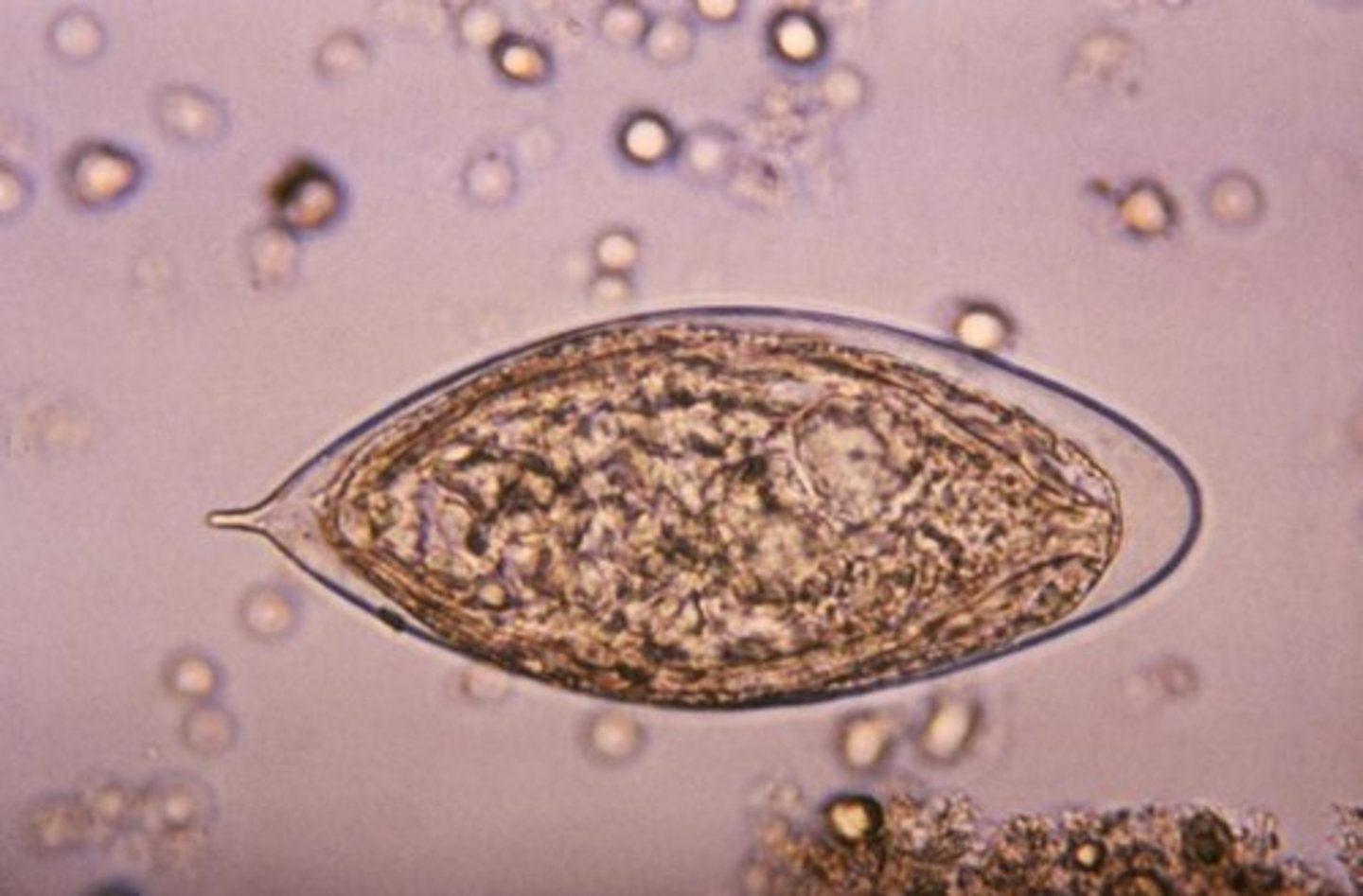
What clinical sample is used to diagnose Schistosoma haematobium?
Urine
What are the "Red Flag" complications of Schistosoma haematobium?
Terminal Hematuria and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
What is the microscopic appearance of Schistosoma mansoni eggs?
Lateral Spine

What clinical sample is used to diagnose Schistosoma mansoni?
Stool
What are the clinical complications of Schistosoma mansoni?
Portal Hypertension, Esophageal Varices, Hepatosplenomegaly
What is the treatment for all Schistosoma species?
Praziquantel
What is the intermediate host for Taenia saginata (Beef Tapeworm)?
Cattle
What is the intermediate host for Taenia solium (Pork Tapeworm)?
Pig
How do humans acquire intestinal Taeniasis (adult worm)?
Eating undercooked Beef (T. saginata) or Pork (T. solium) containing cysticerci
How do humans acquire Cysticercosis/Neurocysticercosis?
Ingesting Taenia solium EGGS (fecal-oral or autoinfection)
Which Taenia species causes Neurocysticercosis?
Taenia solium
What is the "Red Flag" clinical presentation of Neurocysticercosis?
Seizures/Epilepsy ("Swiss cheese" brain on CT)
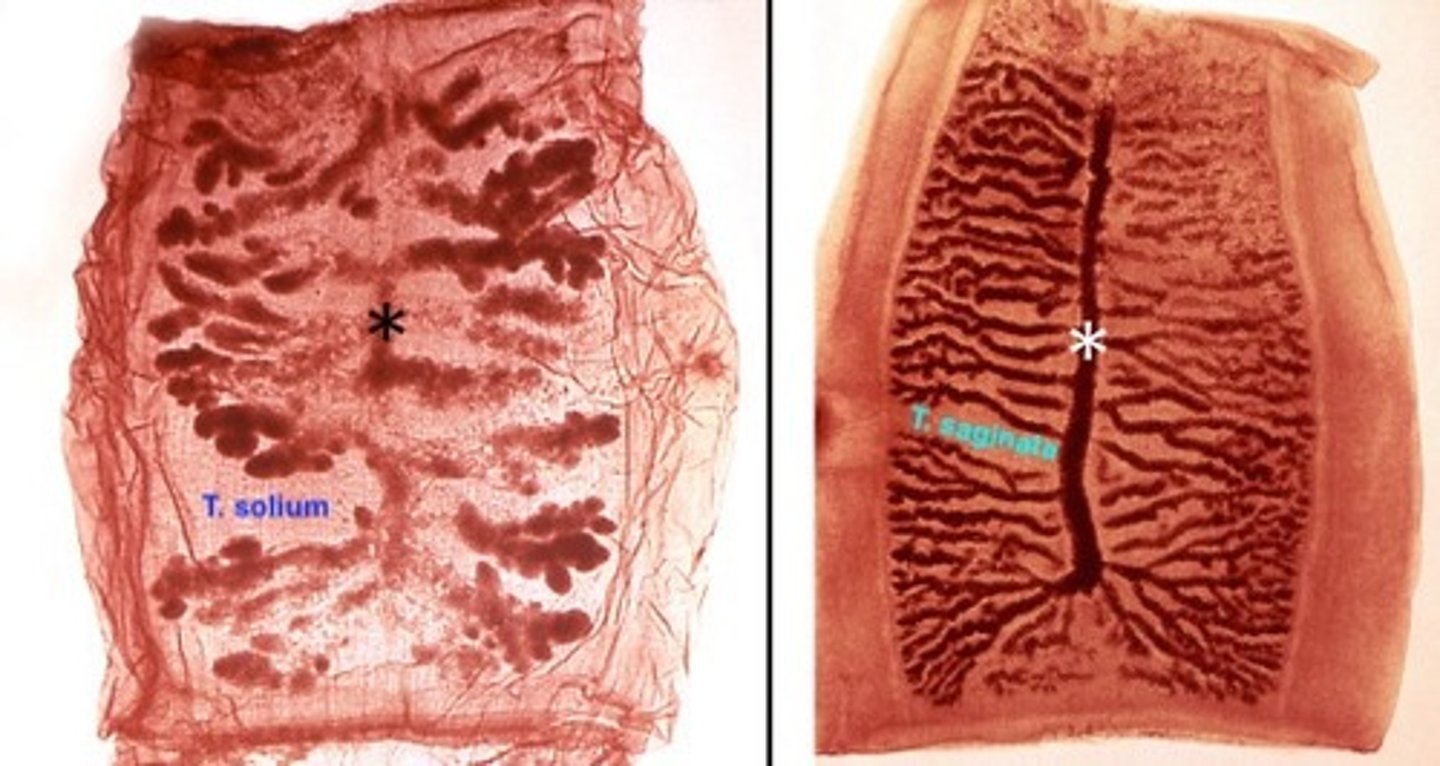
How do you distinguish T. saginata from T. solium based on gravid segments?
T. saginata has >15 uterine branches; T. solium has <13 uterine branches