Cell Life Cycle, Mitosis, and Skin Structure: A Comprehensive Biology Review
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
Mitosis
Cell division of the somatic (body) cells resulting in two identical daughter cells.
Cell division
Replacing cells and generating new cells, important for growth and repair.
Growth
The process where a single cell develops into a multicellular organism.
Repair
The process of replacing old or damaged cells with the same type of cell.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm in a cell.
Chromatin
Unwound DNA in non-dividing cells.
Chromatids
Two identical chromatin threads held together at a centromere.
Chromosomes
Tightly coiled DNA strands visible during mitosis.
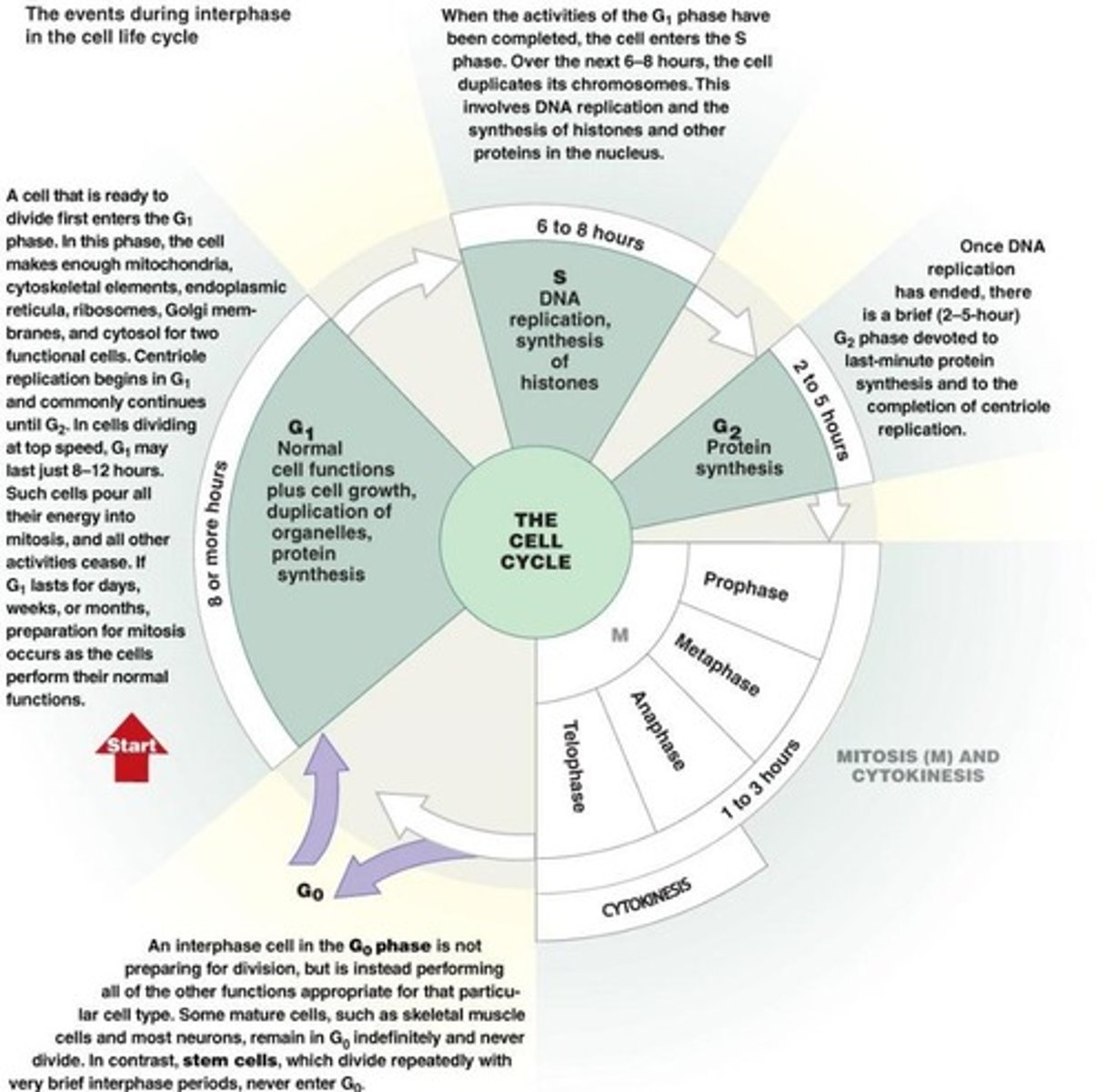
Interphase
The longest phase of cell division where the cell grows and prepares for division.
G1 (growth 1)
Initial growth stage of interphase.
S (synthesis)
Stage of interphase where DNA is duplicated.
G2 (growth 2)
Second growth period of interphase, checking growth and environmental conditions.
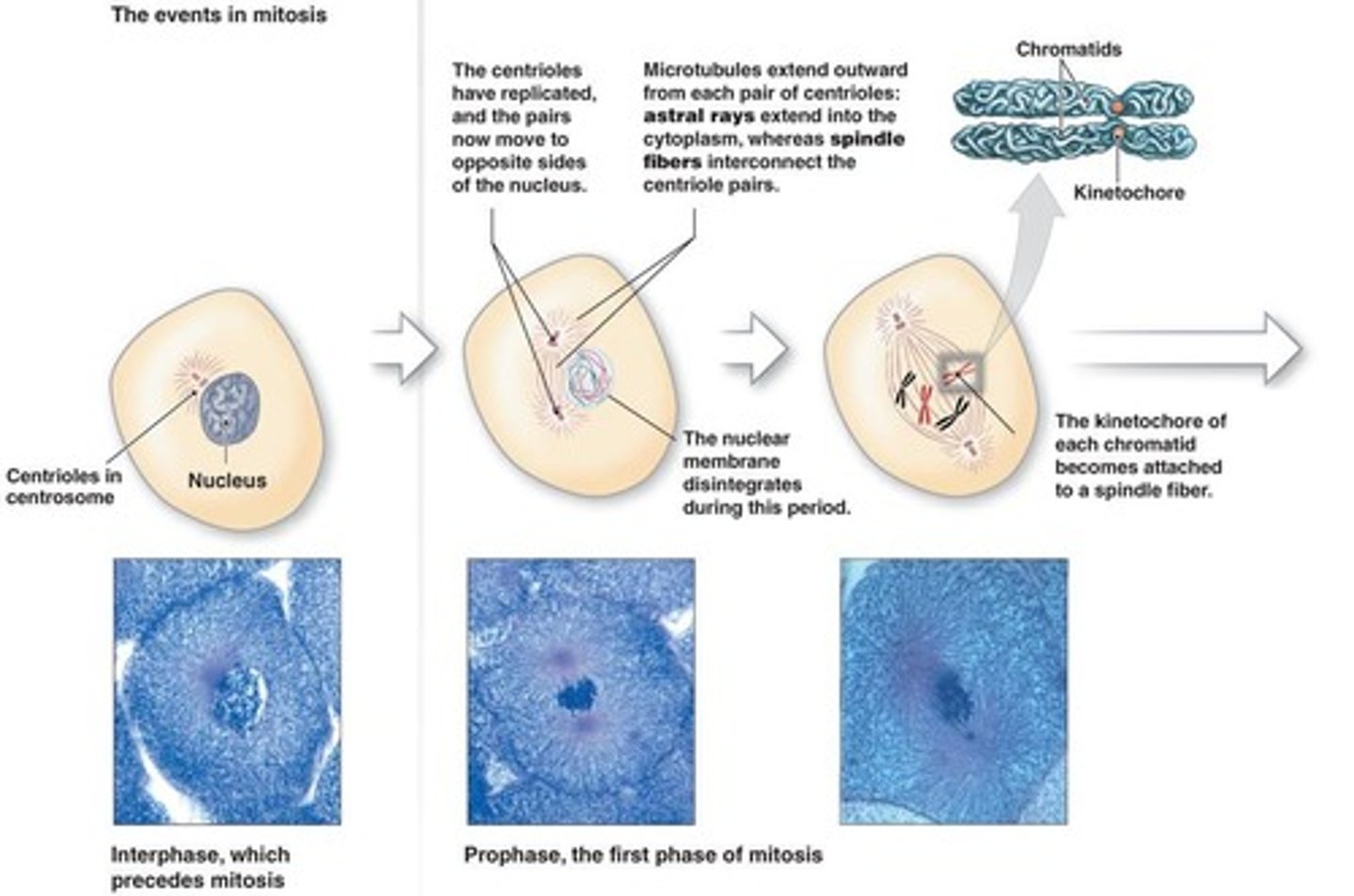
Prophase
1st phase of mitosis where chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
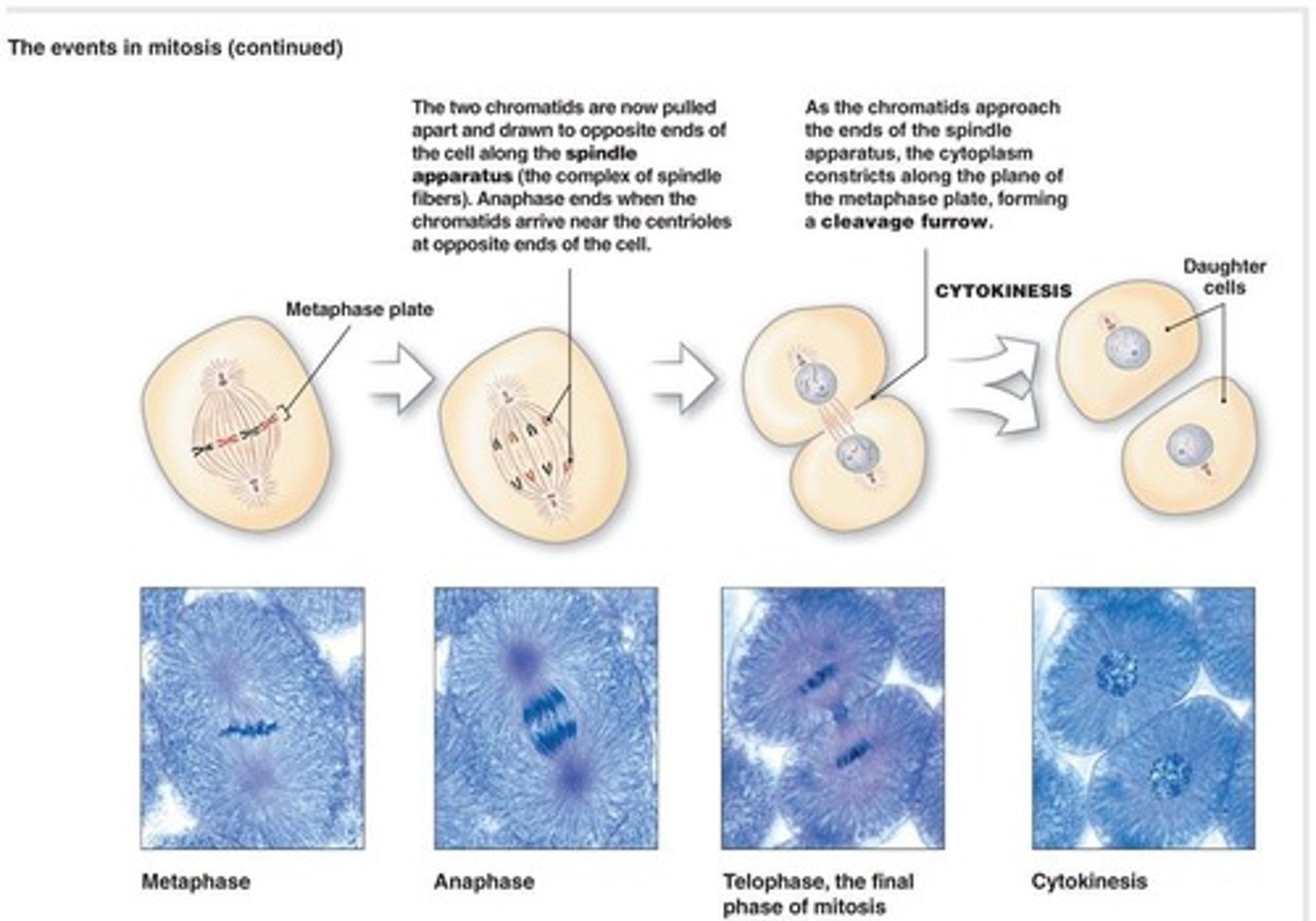
Metaphase
2nd phase of mitosis where chromosomes align at the equatorial plate.
Anaphase
3rd phase of mitosis where centromeres split and chromosomes move to opposite poles.
Telophase
4th phase of mitosis where chromosomes reach poles and begin to uncoil.
Cleavage furrow
The indentation that begins to form in the cytoplasm during anaphase.
Daughter cells
Two identical cells formed from the division of a parent cell.
Mitosis duration
Usually completed in about twenty-four hours, with one to two hours spent in mitosis.
Somatic cells
Body type cells that undergo mitosis, such as skin, hair, and liver cells.
Gametes
Sex cells that are not somatic, including sperm and oocyte cells.
Mitosis consistency
During mitosis, chromosomes are duplicated and divided between daughter cells with great consistency.
Mutation
An alteration in the information within the DNA molecule that occurs occasionally (about once in every one million cell divisions).
Random mutations
Copying mistakes that occur during DNA replication; even DNA is not perfect.
Induced mutations
Mutations that are changed due to environmental factors, such as radiation, pollution, or cigarette smoke.
Missense mutation
A type of mutation that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into a protein.
Nonsense mutation
A mutation that creates a premature stop codon in the protein sequence.
Silent mutation
A mutation that does not change the amino acid sequence of a protein.
Insertion/deletion mutation
Mutations that involve the addition or loss of nucleotides in the DNA sequence.
Duplication mutation
A mutation that results in the duplication of a segment of DNA.
Frameshift mutation
A mutation caused by insertions or deletions that shift the reading frame of the genetic code.
Mutagenic factors
Factors that increase the mutation rate.
Common mutagens
Substances that may cause cancer, such as chemical agents (e.g., tobacco tar), radiation (e.g., UV and X-ray), and viruses.
Benign tumor characteristics
1) Usually localized (easily removed), 2) Grows slowly, 3) Encapsulated (sealed/doesn't spread quickly).
Malignant tumor characteristics
1) May not be localized, 2) Grows rapidly, 3) May not be encapsulated (may spread quickly).
Metastasis
The spreading of a primary tumor by blood vessels or lymph vessels to new areas to become secondary cancer masses.
Oncogene theory
Theories that describe how proto-oncogenes can become oncogenes, leading to rapid cell division and greater potential to cause cancer.
p53 gene
A gene that acts as an off switch, stopping cells with damaged DNA from dividing; if mutated, cells continue to divide.
Neoplasm
A term that means tumor.
Why is cancer so deadly?
1) Tumor cells are mostly immature and nonfunctional, 2) Tumor cells interfere with proper function of nearby systems, 3) Tumors may crowd organs and rob tissues of vital nutrients.
Stages of cancer
1 - 4, where stage 1 has the best probability of cure and stage 4 has the worst probability.
Cancer treatments
1) Surgery (best for localized, nonmetastasizing cancers), 2) Radiation (used to shrink tumor size), 3) Chemotherapy (chemicals toxic to rapidly dividing tumor cells).
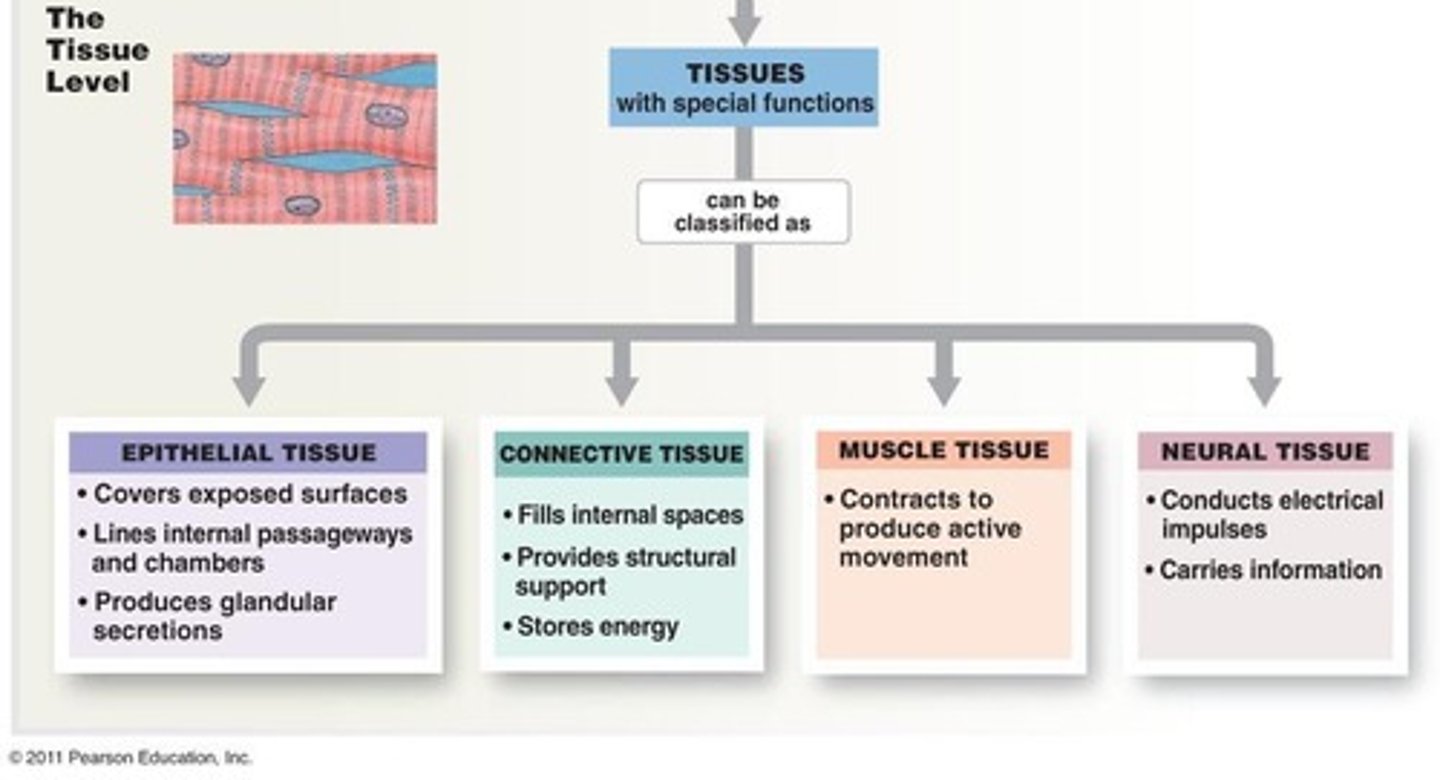
Tissues
Groups of individual cells working together to perform a specific function.
Histology
The study of tissue structure.
Four distinct types of human tissue
1) Epithelial, 2) Connective, 3) Muscle, 4) Nervous.
Epithelial tissue
Covers surfaces, lines cavities and hollow organs, and forms glands.
Connective tissue
Fills, supports, covers body parts, stores fat, and transports (e.g., blood).
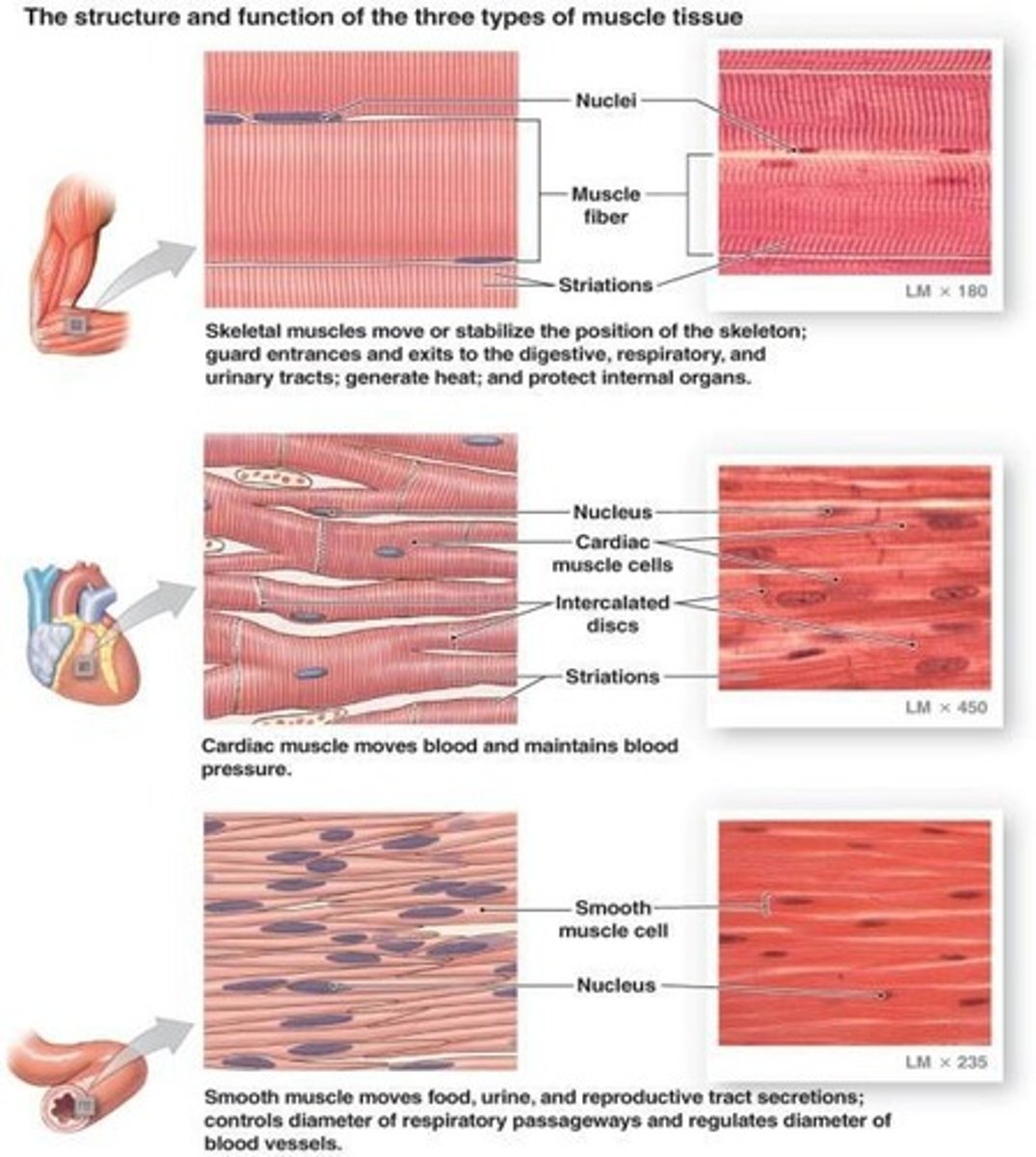
Muscle tissue
Contracts to provide movement of the body and organs.
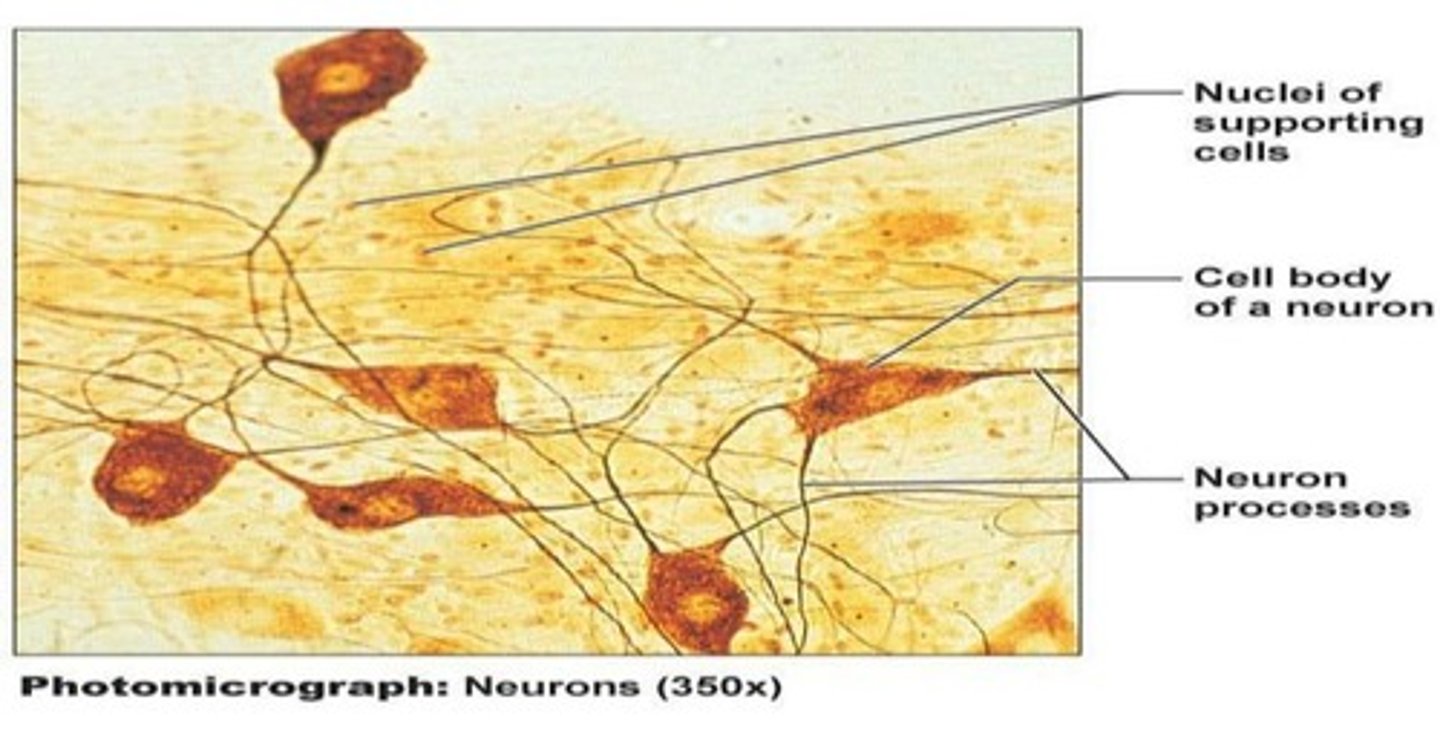
Nervous tissue
Conducts impulses from organ to organ; used for communication.
blastocyst
a zygote (egg sperm combo) that has developed after about three weeks into development.
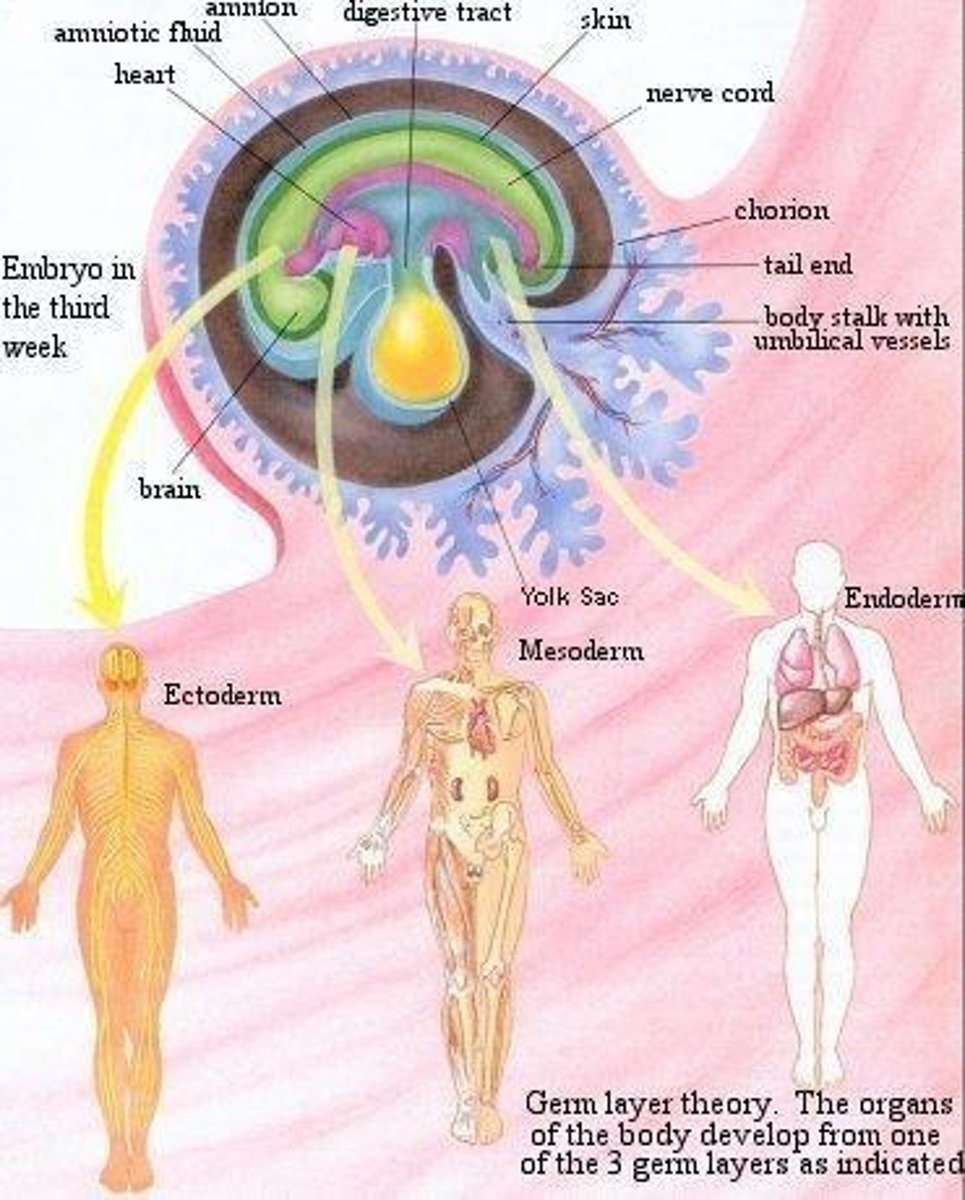
primary germ layers
several layers of tissue that develop from a blastocyst.
ectoderm
the primary germ layer that forms the nervous system, skin, sense organs, and some glands.
mesoderm
the primary germ layer that forms the skeleton, muscles, blood, kidneys, and most sex organs.
endoderm
the primary germ layer that forms the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory organs, and urinary bladder.
femur
the bone that is formed by the mesoderm.
ovaries
the reproductive organs that are formed by the mesoderm.
fingernails
the structures that are formed by the ectoderm.
trachea
the airway that is formed by the endoderm.
gall bladder
the organ that is formed by the endoderm.
epithelial tissues
tissues that cover body surfaces, line cavities and tubes, and comprise glands.
avascular
a characteristic of epithelial tissues indicating they have no blood supply and receive nutrients by diffusion.
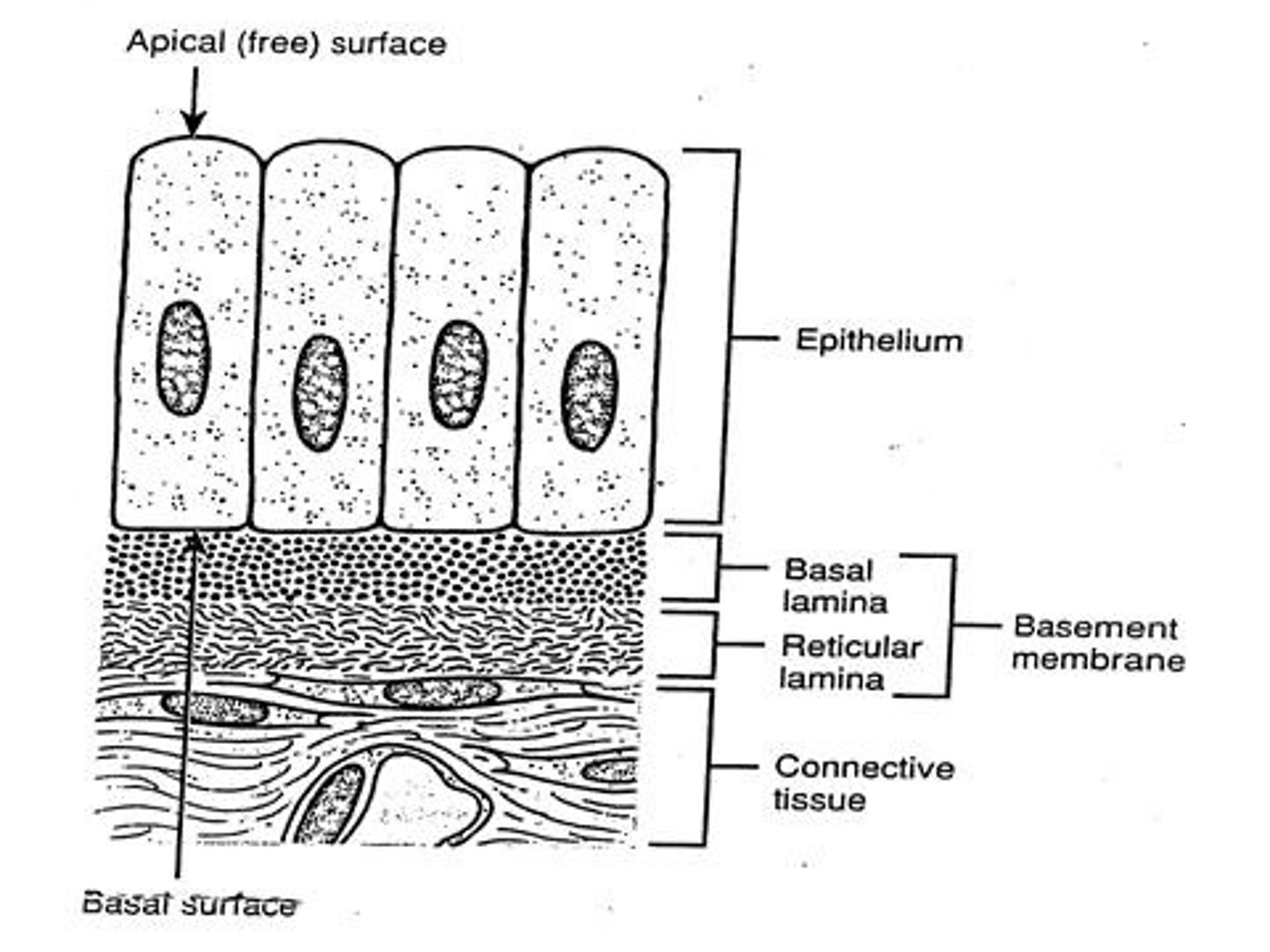
basement membrane
the structure that anchors epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue.
basal lamina
the layer secreted by the epithelium that is part of the basement membrane.
reticular lamina
the layer secreted by the connective tissue that is part of the basement membrane.
squamous epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue where cells are flat and scale-like, specialized for diffusion or protection.
cuboidal epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue where cells are cube-shaped with a centrally located nucleus, specialized for secretion.
columnar epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue where cells are column-shaped with the nucleus in the lower third, specialized for absorption and some secretion.
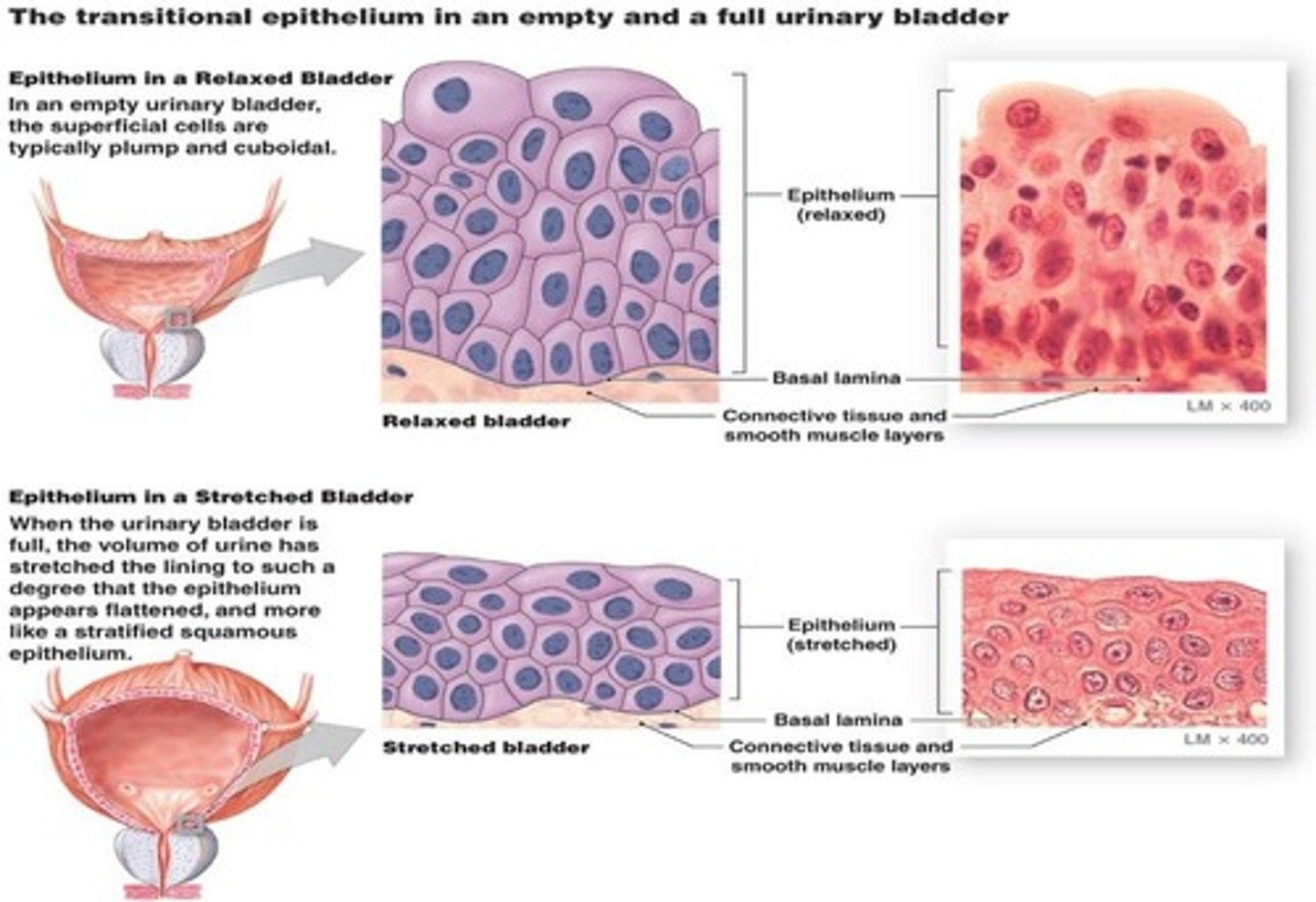
transitional epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue that can change shape when stretched, found only in the urinary system.
simple epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue consisting of one layer of cells, good for diffusion.
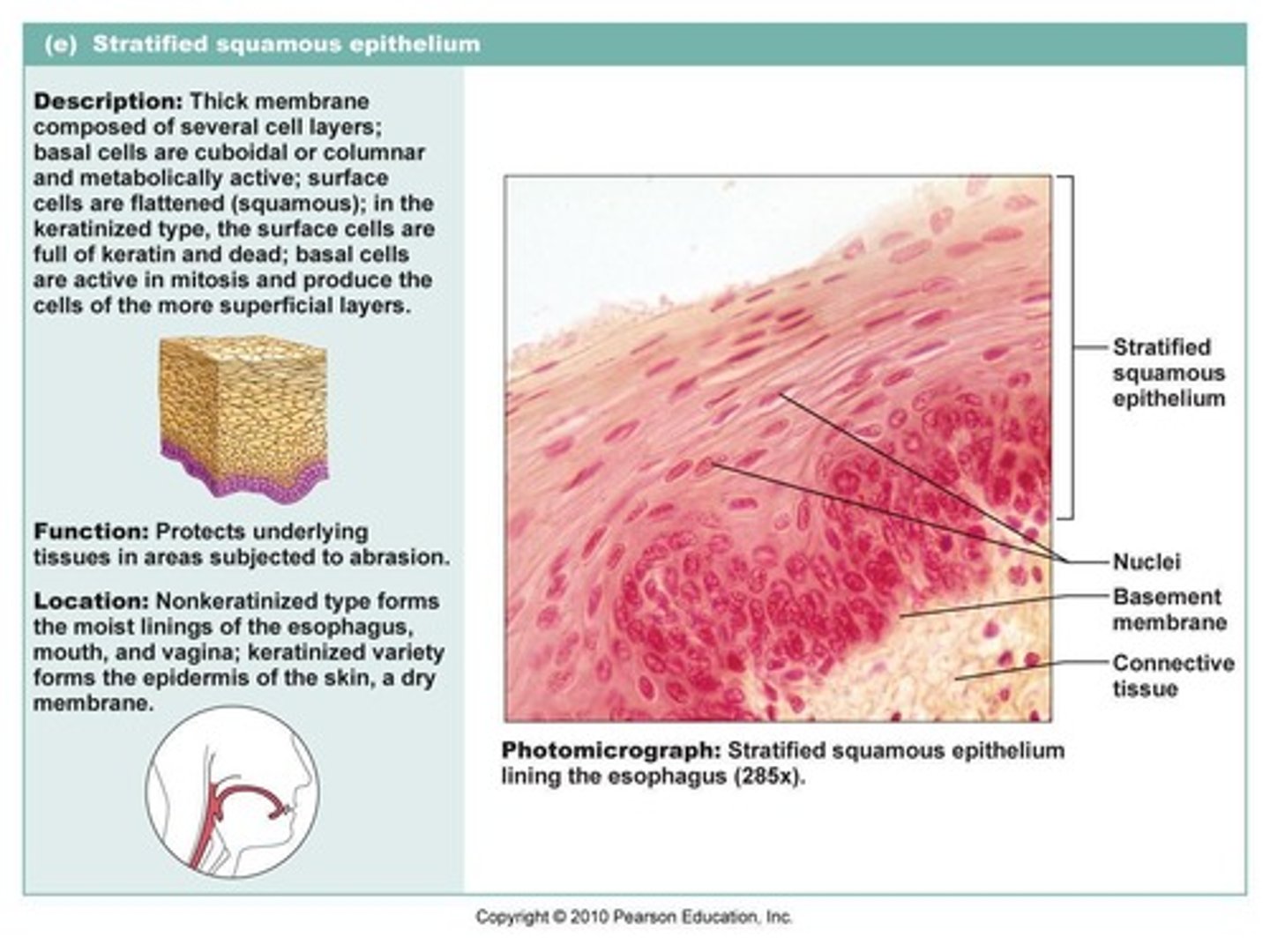
stratified epithelium
a type of epithelial tissue consisting of two or more layers of cells, good for protection.
simple squamous epithelium
a single layer of thin flattened cells through which substances freely pass by secretion or diffusion, found in the lungs and blood vessels.
stratified squamous epithelium
composed of many layers of mostly flattened cells, may be up to sixty layers thick in some areas, providing protection against abrasion.
simple cuboidal epithelium
composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells, primarily involved in secretion and some absorption.
Simple columnar epithelium
Composed of elongated cells whose nuclei are located near the basal portion of the cell.
Function of simple columnar epithelium
Functions in mostly absorption and some secretion in the digestive tract (and also in the female reproductive tract).
Cilia
Small, hair-like structures that move substances.
Goblet cells
Look like a cup and secrete mucus; they have no nuclei.
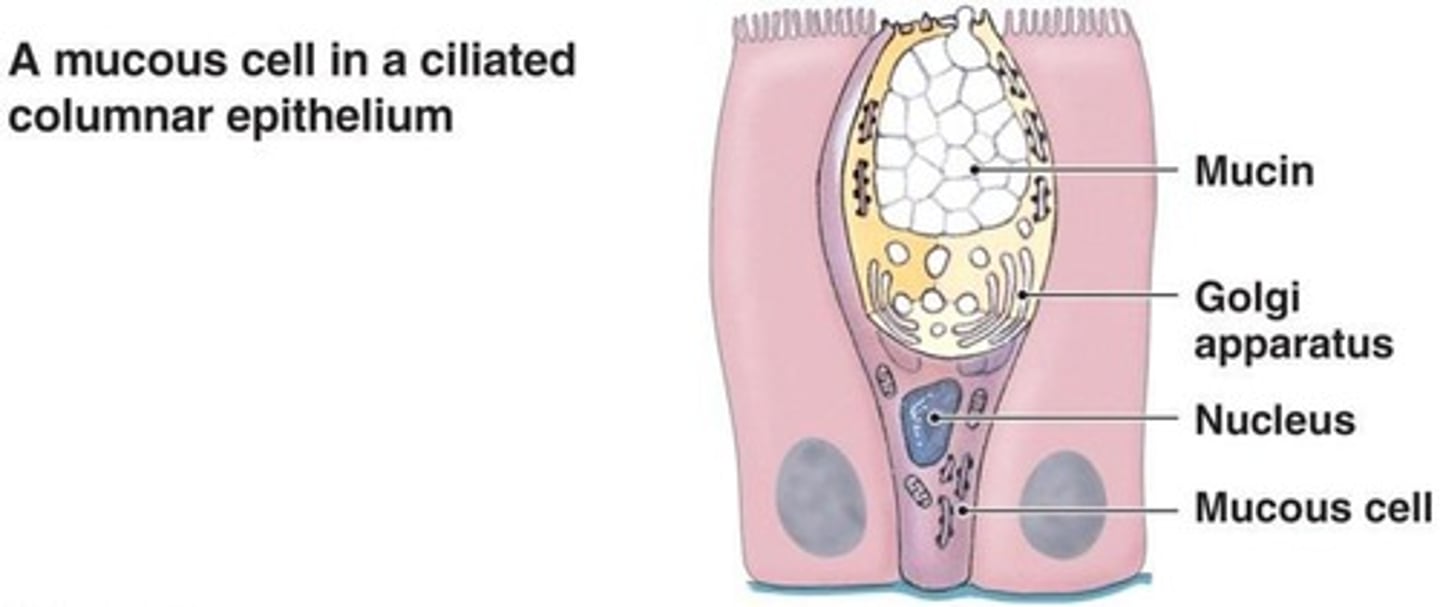
Pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar epithelium
Appears 'falsely' stratified because the nuclei are located at several levels within a single layer of cells that all touch the basement membrane.
Location of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Lines the glottis (opening) of the upper respiratory tract among other locations.
Glandular epithelium
All glands are composed of epithelial cells that are specialized for secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters, breast milk, digestive enzymes, skin oils, tears, sweat, etc.
Classification of glands
Glands are classified by arrangement of cells, secretion location, and method of secretion.
Tubular glands
Secretory portion of the gland is tubular.
Alveolar glands
Secretory portion of the gland is alveolar.
Exocrine glands
Include a duct that opens onto a body surface.
Endocrine glands
Are 'ductless' glands that secrete contents into blood or lymph vessels.
Merocrine glands
Secretion of just a 'liquid' substance.
Serous type of secretion
'Watery' fluids, for example, salivary glands.
Mucous type of secretion
'Thick' fluids, for example, goblet cells.
Apocrine glands
Secretion is 'liquid' and top portion of the cell.
Holocrine glands
Secretion is liquid and the entire cell.
Classification of goblet cell
Goblet cells are classified as merocrine.
General characteristics of connective tissues
Acts to connect, support, bind, store fat, transport substances (blood).
Vascularity of connective tissues
Fat tissue and bone are very vascular; cartilage, ligaments, and tendons are avascular.
Extracellular matrix
Connective tissue is mostly extracellular matrix, which acts to separate the relatively few cells from each other.
Components of connective tissue
Connective tissue always has two components: cells (of several sorts) and extracellular matrix (nonliving).
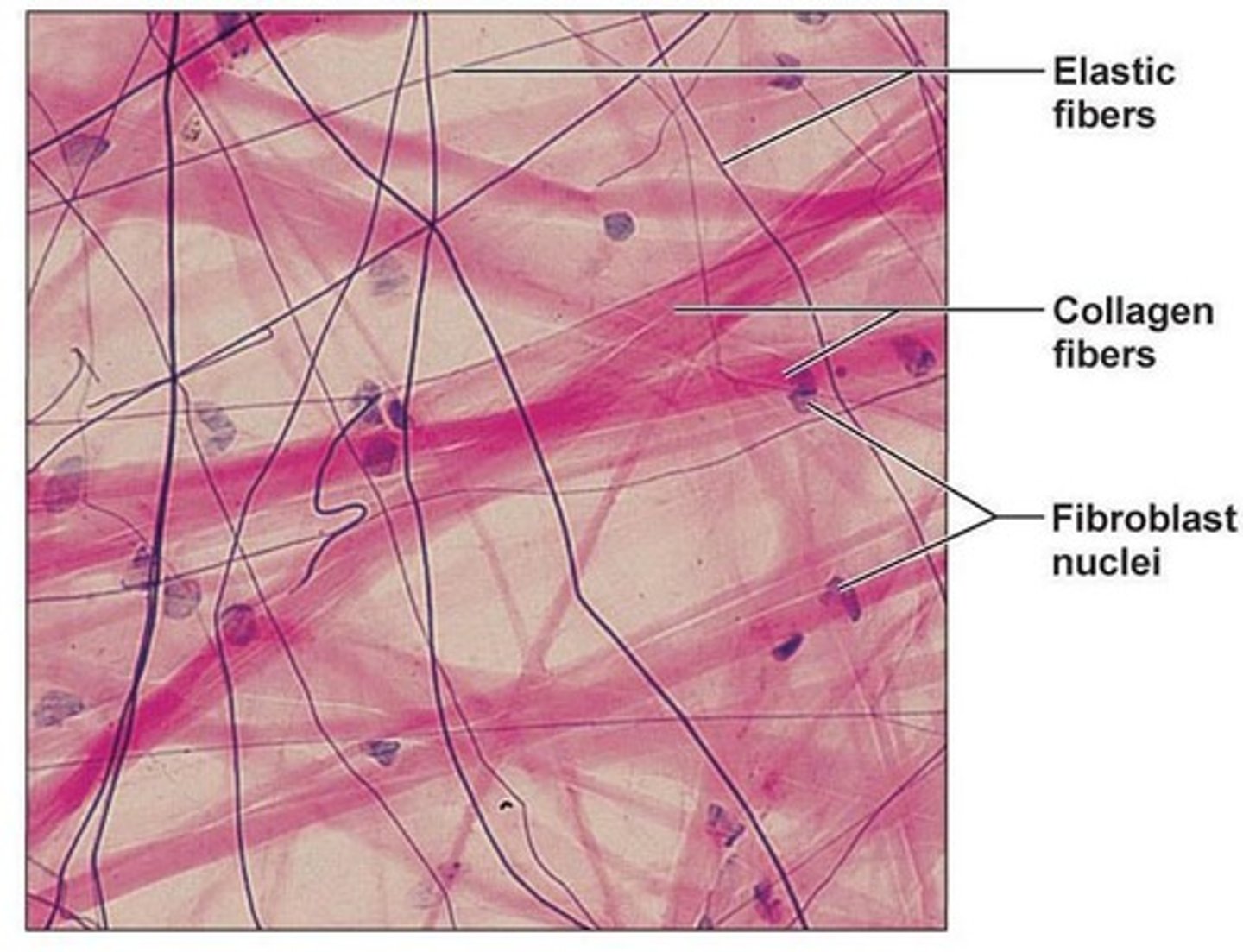
Types of cells in connective tissue
Different cell types include fibroblast, chondrocytes, osteocytes, mast cells.
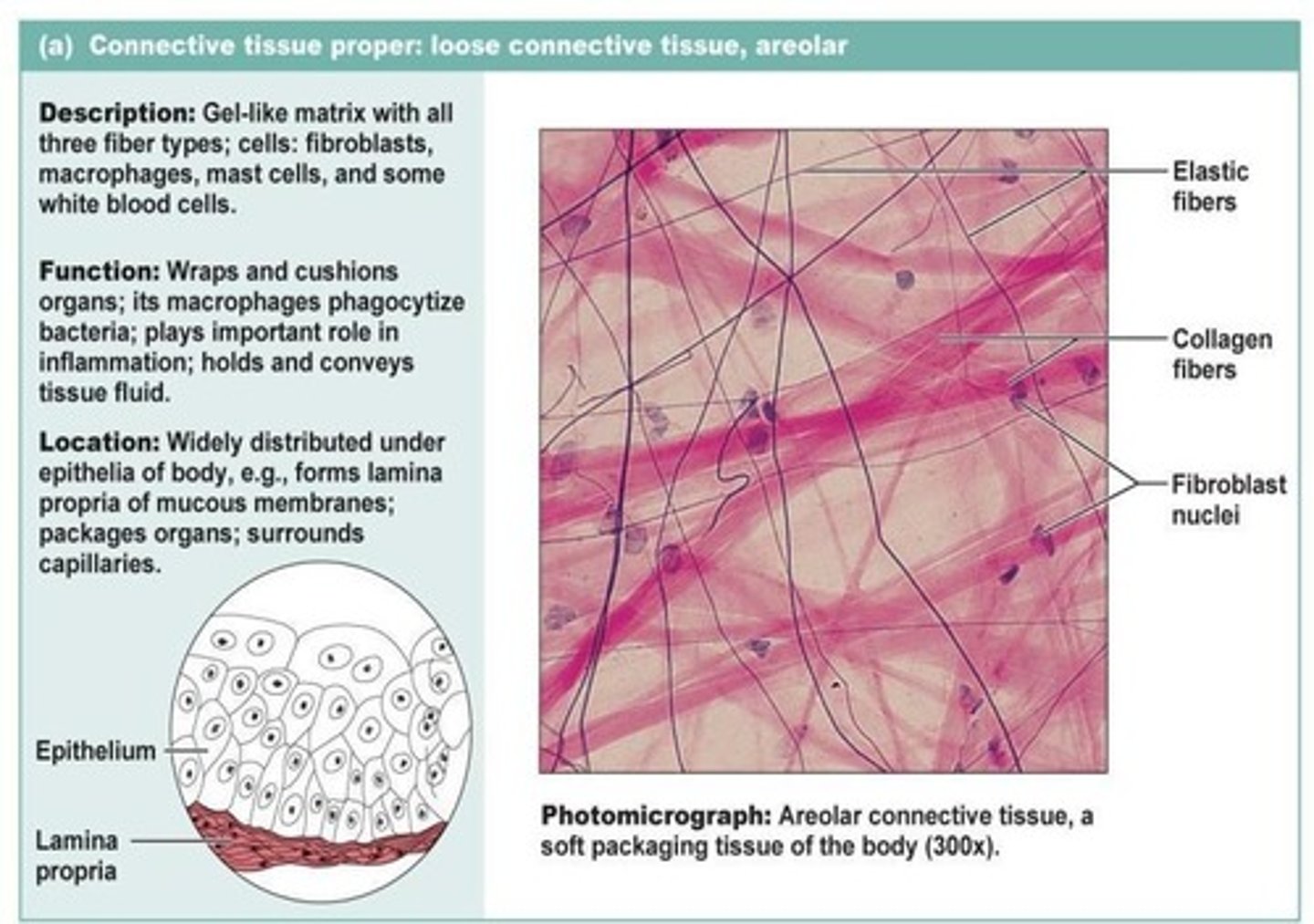
Areolar (loose) connective tissue
Cells are fibroblasts; fibers include elastic and collagen; functions to wrap and cushion.
Adipose tissue
Composed of specialized cells called adipocytes that have a large fat vacuole.
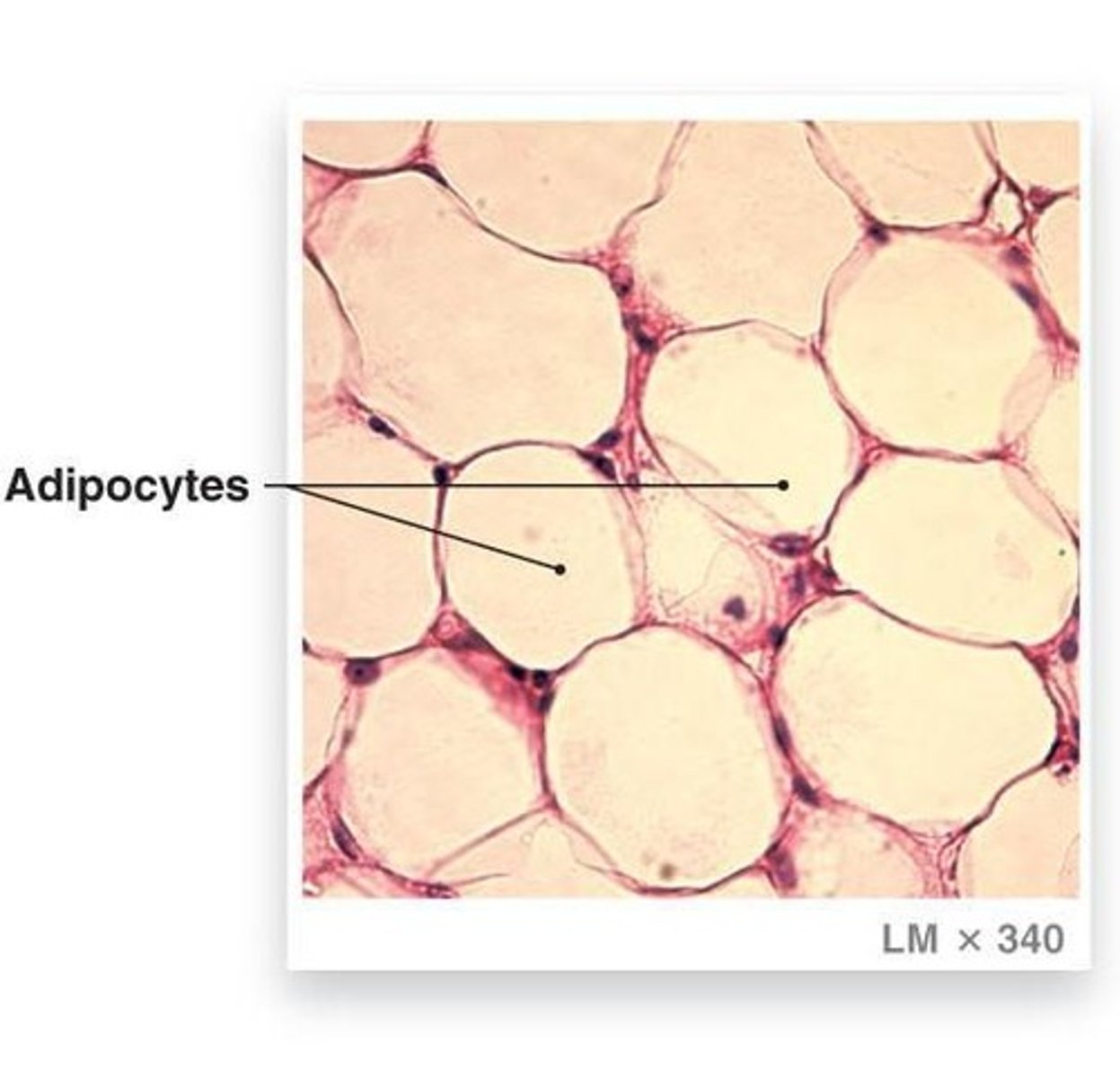
Locations of adipose tissue
Found in the hypodermis around blood vessels, abdomen, breasts, around eyes, and kidneys.
Functions of adipose tissue
Insulates, cushions, and stores energy.