Nursing Foundations Final Exam
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Common demographics of nurses
Mostly women, men more likely to further education-nurses largest group of health care workers in the world
Nurse’s role in each practice site-most common
Hospitals, medical centers, community based hospitals
Advanced nursing roles
NP-often in medical offices; diagnose and exam patients
CNM (certified nurse midwife)-help deliver babies; in hospitals
CRNA (certified registered nurse anesthetist)-administer meds while watching patients; high responsibility
CNS (clinical nurse specialist)-can only work in hospitals
Florence Nightingale
Created foundation of modern nursing-implemented hand washing, first nursing researcher, soldiers in Crimean war
Mary Seacole
Brought attention to need of nurses-understood effects of Chlorea; health of soldiers during Crimean war
Clara Barton
Founded RedCross
Linda Richards
FIRST licensed RN nurse
Mary Eliza Mahoney
FIRST trained black RN nurse in US
Isabel Hampton Robb
Attention to unity of nursing schools; led to creation of National League of Nursing and ANA
Lillian Wald
Founded Henry Street Settlement for people of poverty and immigrants; helped found NAACP
First nursing schools and licensure laws
1872-FIRST general training school for nurses —> New England Hospital
1873-FIRST 3 American training schools - Belleuve Training School for Nurses (NYC), Connecticut Training School for Nurses (New Haven), Boston Training School for Nurses (Massachusetts General Hospital)
New York-first state to require licensure to work
Key characteristics of profession
Services vital to humanity, special knowledge, indv. responsibility, independence, motivated by services, code of ethics, organization that encourages high practice standards
Names and purposes of 3 ANA docs
1) Nursing’s Social Policy Statement: Essence of the profession
Defines nursing-states nursing is a profession
2) Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice
Outlines expectations of professional role
3) The Code of Ethics for Nurses w/ Interpretative Statements
9 provisions
Guides nurses when faced w/ ethical dilemmas
Purpose of Accreditation
Ensure all programs teach all topics necessary to become a nurse
2 Accrediting agencies
ACE - for 2 years/smaller programs
CCNE - acredits BSN/higher - FSC
Diploma programs vs. ASN vs. BSN
Diploma programs - least common, typically 3 or 2 years
ASN programs - 2 years
BSN programs - 4 years
6 QSEN Competencies
Patient-centered care
Teamwork and collaboration
Evidence-based practice
Quality Improvement
Safety
Informatics
Essentials align w/ AACN
Purpose of Nurse Practice Act
Defines standards & scopes of prof. nursing, sets min. edu requirements, protects legal titles, disciplinary action of licenses
Negligence
Failure to act as a reasonably prudent person would have
Malpractice
Negligence applied to the acts of the profession by commission or omission
Informed consent
Full knowing authorization for care, treatment, or procedure by patient themselves
HIPPA
First comprehensive protection for disclosure of health info
Info can only be given to those who need to know to complete their job
Info may be shared w/o consent if safety is questioned
Autonomy
Respect for people’s rights
Beneficence
Do good
Nonmaleficence
Do no harm
Justice
Be fair
Fidelity
Loyalty
Veracity
Truth telling
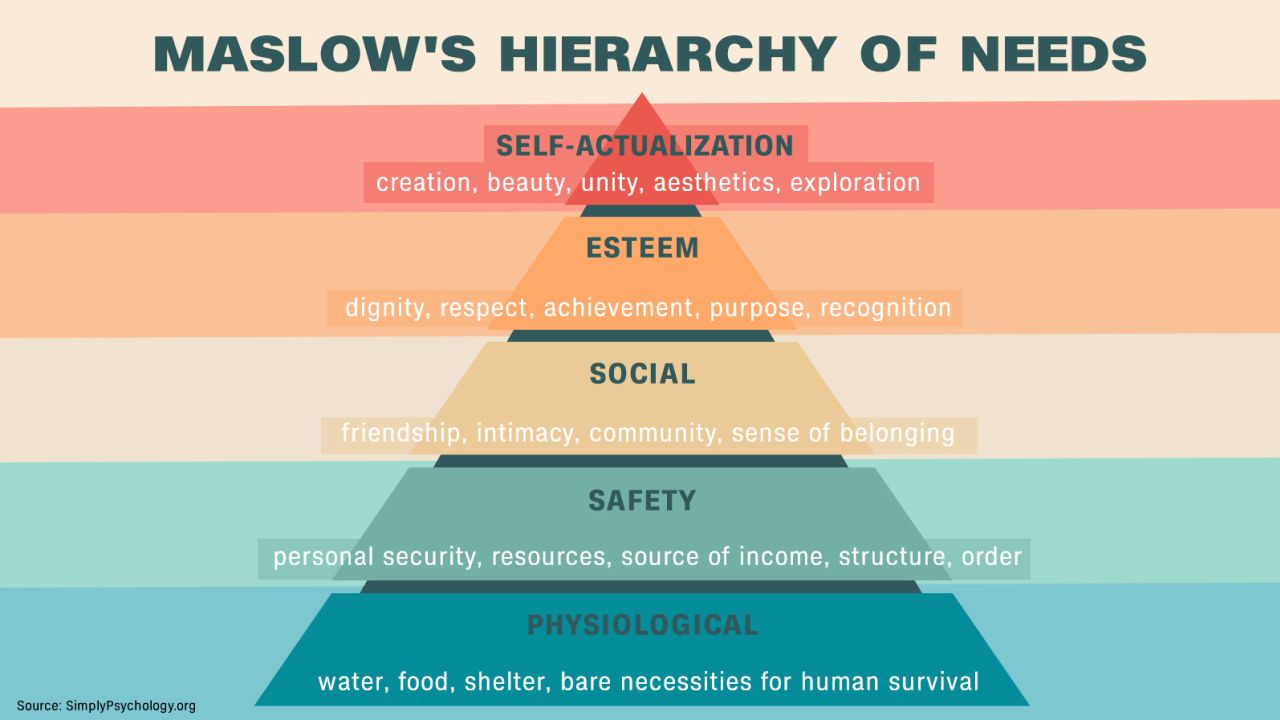
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs
Physiology, Safety, Social, Self esteem, Self-actualization
3 Foundational Concepts
Person-mind/body
Health-state of wholeness
Environment-external/internal stressors
Feedback Loop
Input-info, energy, matter
Throughput-processes to convert input
Output-end result
Evaluation-measuring success/failure
Feedback-communicating findings
Theory terminology
Phenomena-event perceived through our senses
Theories-laws that explain phenomena, how they’re predicted & controlled; what we know vs. what we don’t
Philosophy-set of beliefs abt how the world works
Conceptual models-more specific set of concepts, organized phenomena
Middle-range theory-narrow focused theory; connects grand theories to nursing practice
6 C’s of nursing w/ definitions
Compassion-be w/ another in their suffering
Competence-using evidence-based knowledge in application of interventions
Conscience-directs moral, ethical & legal decision-making
Confidence-trust in one’s ability to care for others
Commitment-maintaing and elevating standards and obligations of nursing
Comportment-professional presentation of nurses; behavior, attitude, apperance
Critical thinking
A mode of thinking in which the thinker improves the quality of his/her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structure of thinking-thinker raises questions, gathers information, reasons well, is open-minded and communicates effectively
Nursing Process AAPIE
Assessment, analysis, planning, implementation, evaluation
Subjective vs Objective data
Subjective-anything patient says
Objective-nurses observations, numerical
Nursing diagnosis vs Medical diagnosis
Nursing-”at risk for …”
Medical-actual diagnosis
Clinical reasoning
Focuses on the client’s reponses to a health problem, should include the client’s perceived needs, health problems, related experiences, health practices, and lifestyles.
Solid oral meds
Tablet, enteric-coated tablet, troche, caplet, capsule
5 Rights of med admin
Right client
Right med
Right route
Right time
Right dose
Right documentation
Abbreviations
STAT = immediately
PRN = as needed
PO = by mouth
ID = intradermal
IV = intravenous
QID = 4 times a day
SL = sublingually
IM = intramuscular
TID = 3 times a day
BID = 2 times a day