5: Allostery in Hemoglobin
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
the binding of a negative allosteric effector to an allosteric enzyme (K-system) that shows positive cooperativity in substrate binding:
causes a shift to the right in the sigmoidal curve of v v. [S]
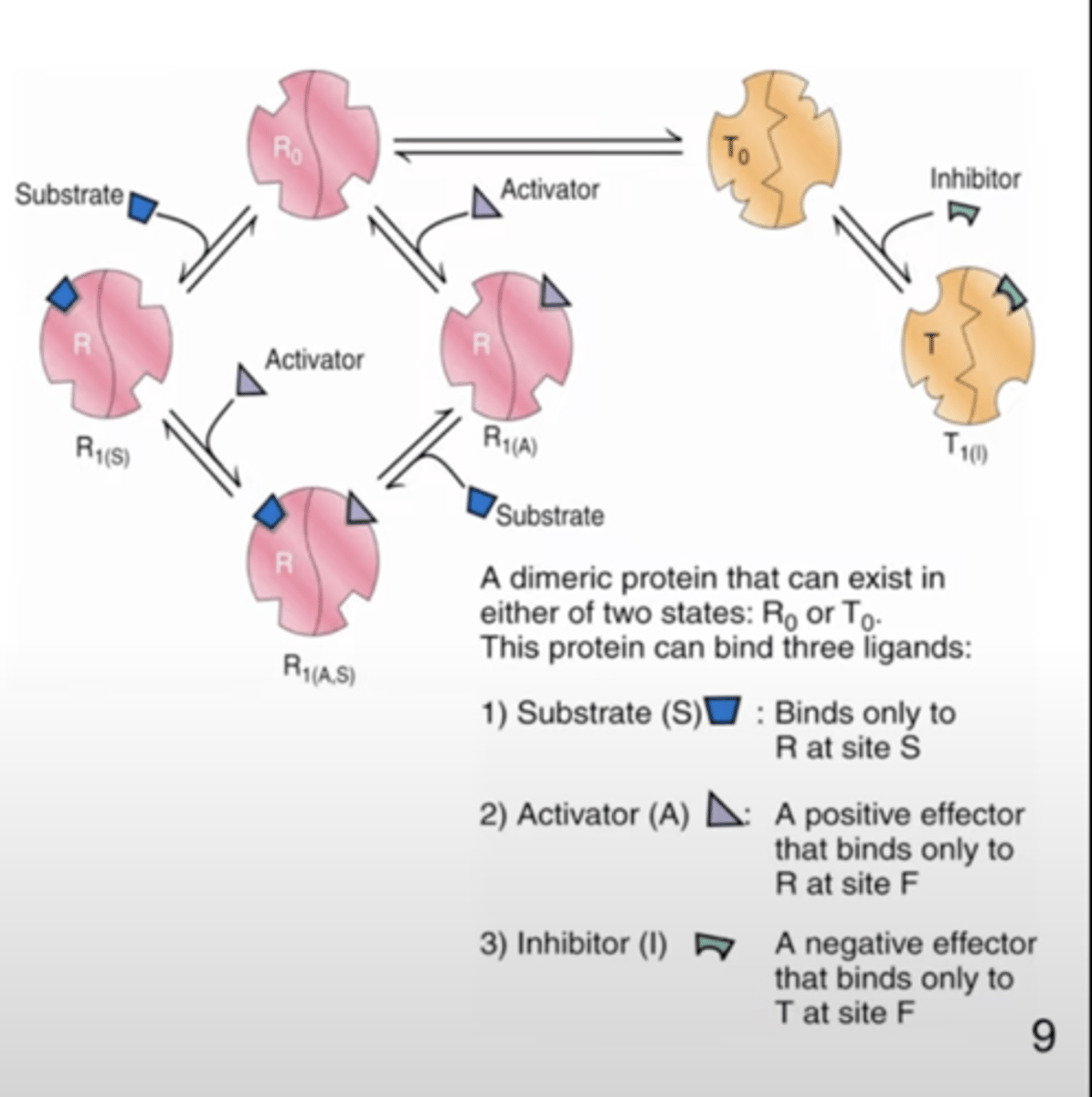
Monod-Wyman-Changeux (MWC) model
- inhibitor : negative effector
- inhibitor binds preferential to the T form
- T0/R0 equilibrium is shifted towards T0
- # of S binding sits decreases -> T0/R0 is increased
- decrease the affinity of S binding and increase cooperativity
the addition of a negative allosteric effector to an enzyme that acts as a V-system causes the half-maximum velocity (Km) to ________ and Vmax to _______
remain constant
decrease
K systems
- Vmax does not change
- Km changes in the the presence of A and I
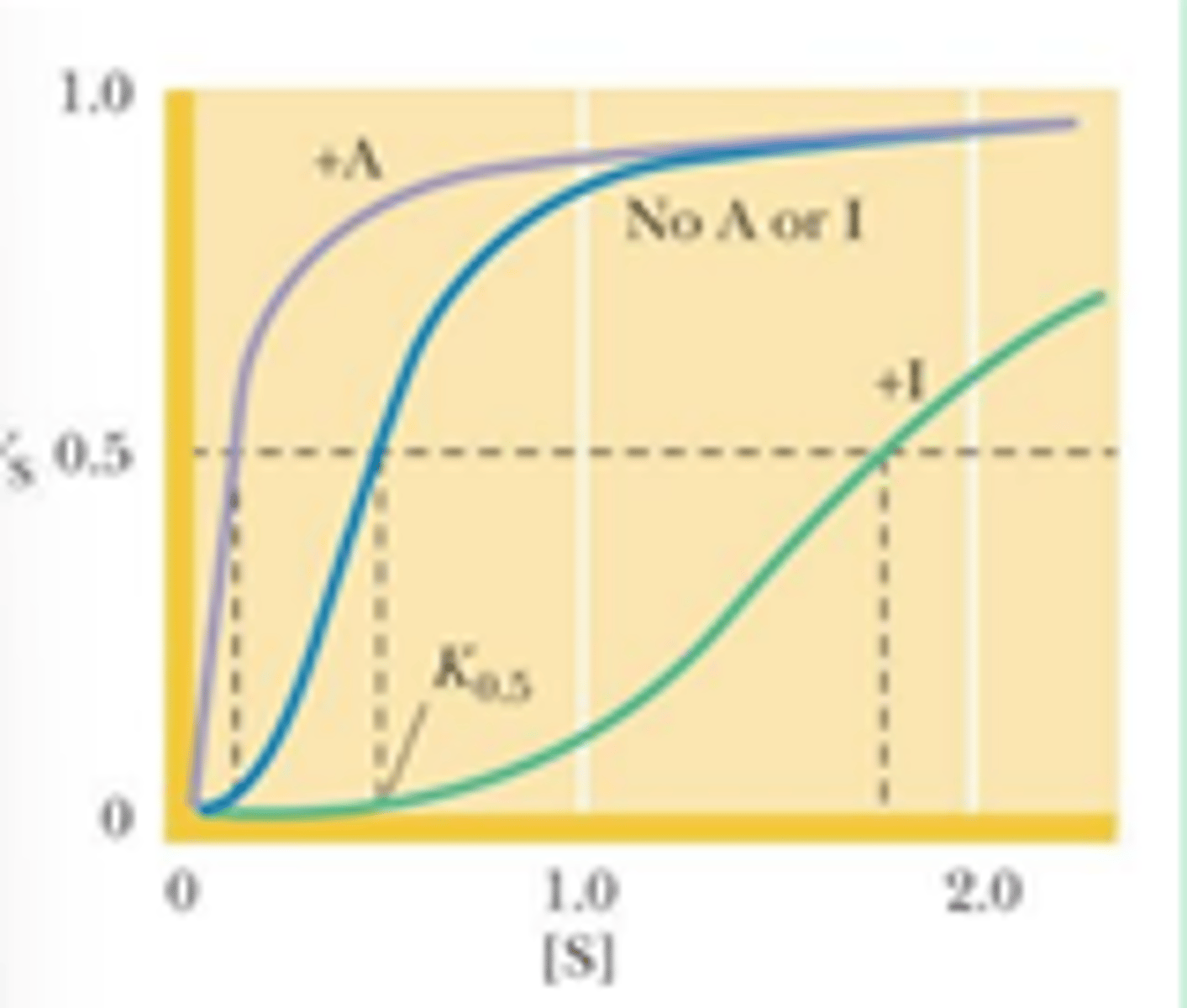
V systems
- Km does not change
- Vmax changes in the presence of allosteric effectors
- R and T forms of the enzyme have the same affinities for S, but differ in their affinity for A and I and their catalytic properties
- when [S] > Km
Hemoglobin (Hb)
- blood
- oxygen transport proteins
- tetrameric
- 2 alpha chains of 141 residues and 2 beta chains of 146 residues
myoglobin (Mb)
- muscle
- oxygen-storage proteins
- 153 residues
- contains heme
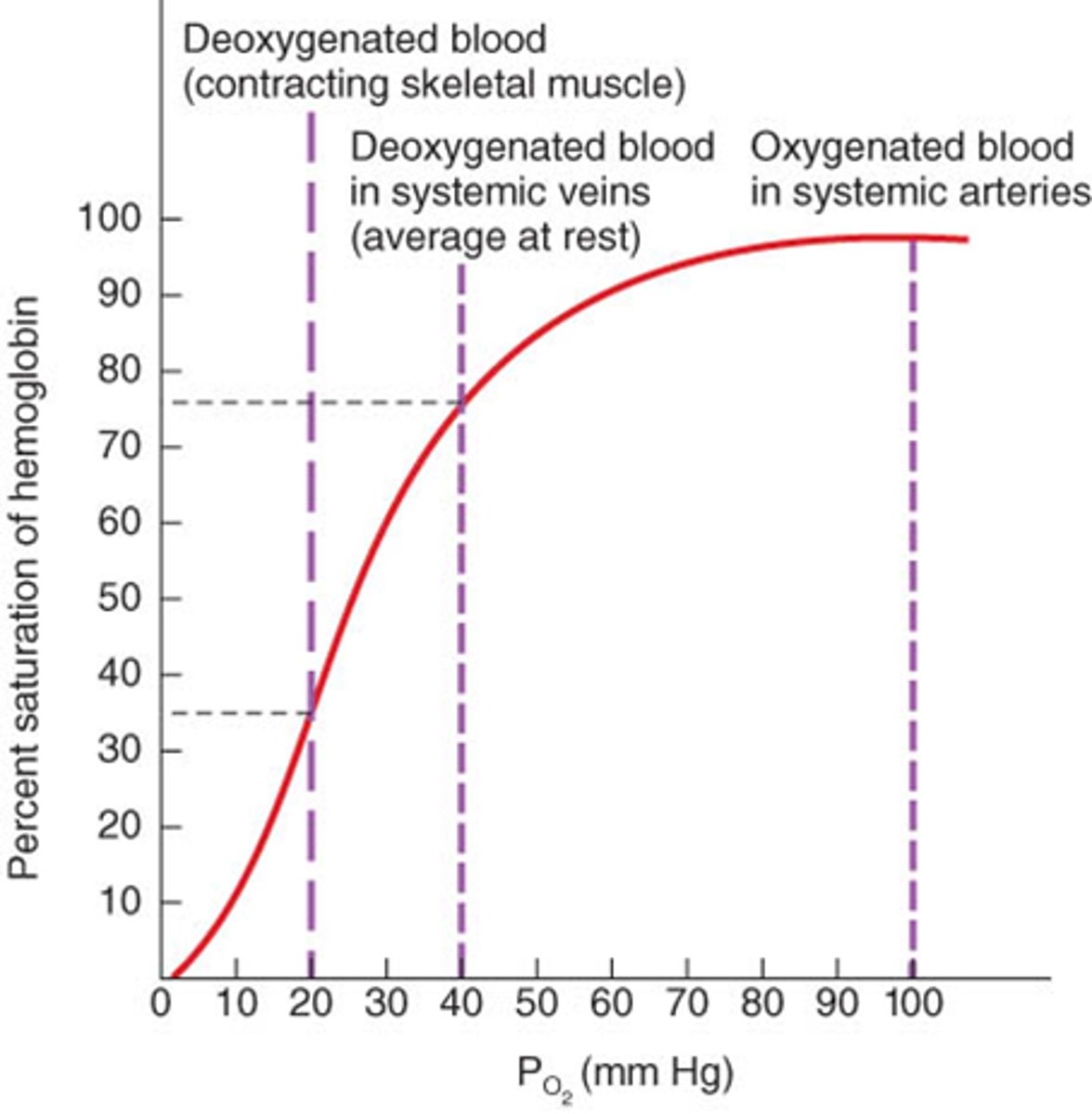
what binding curves of Hb and Mb show?
- Hb -> SIGMOID shaped O2 binding curves
- Mb -> MICHAELIS-MENTEN type substrate binding curves
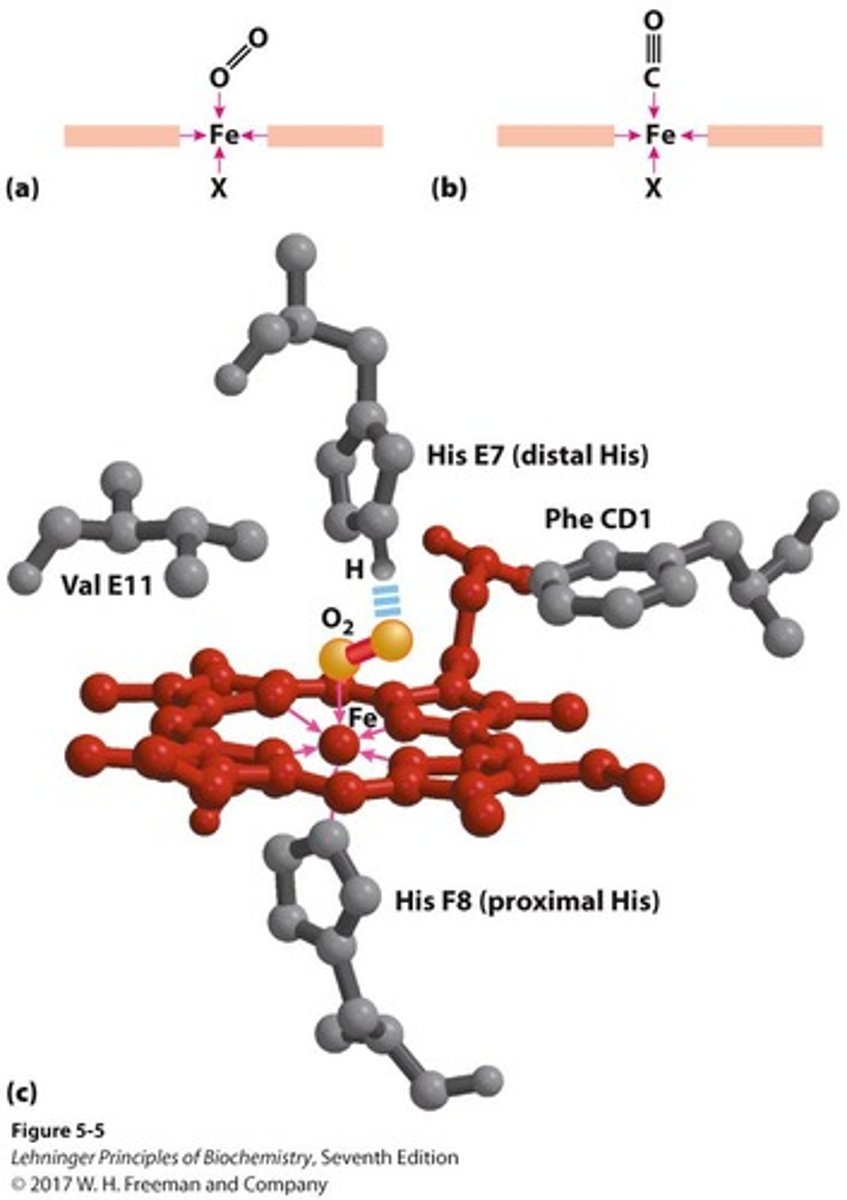
how does Mb and Hb bind to Fe2+
- both uses heme (a ring shaped iron containing molecule that is a prosthetic group for various proteins)
- heme -> binds to oxygemn reversibly

how does oxygen bind to Mb and Hb
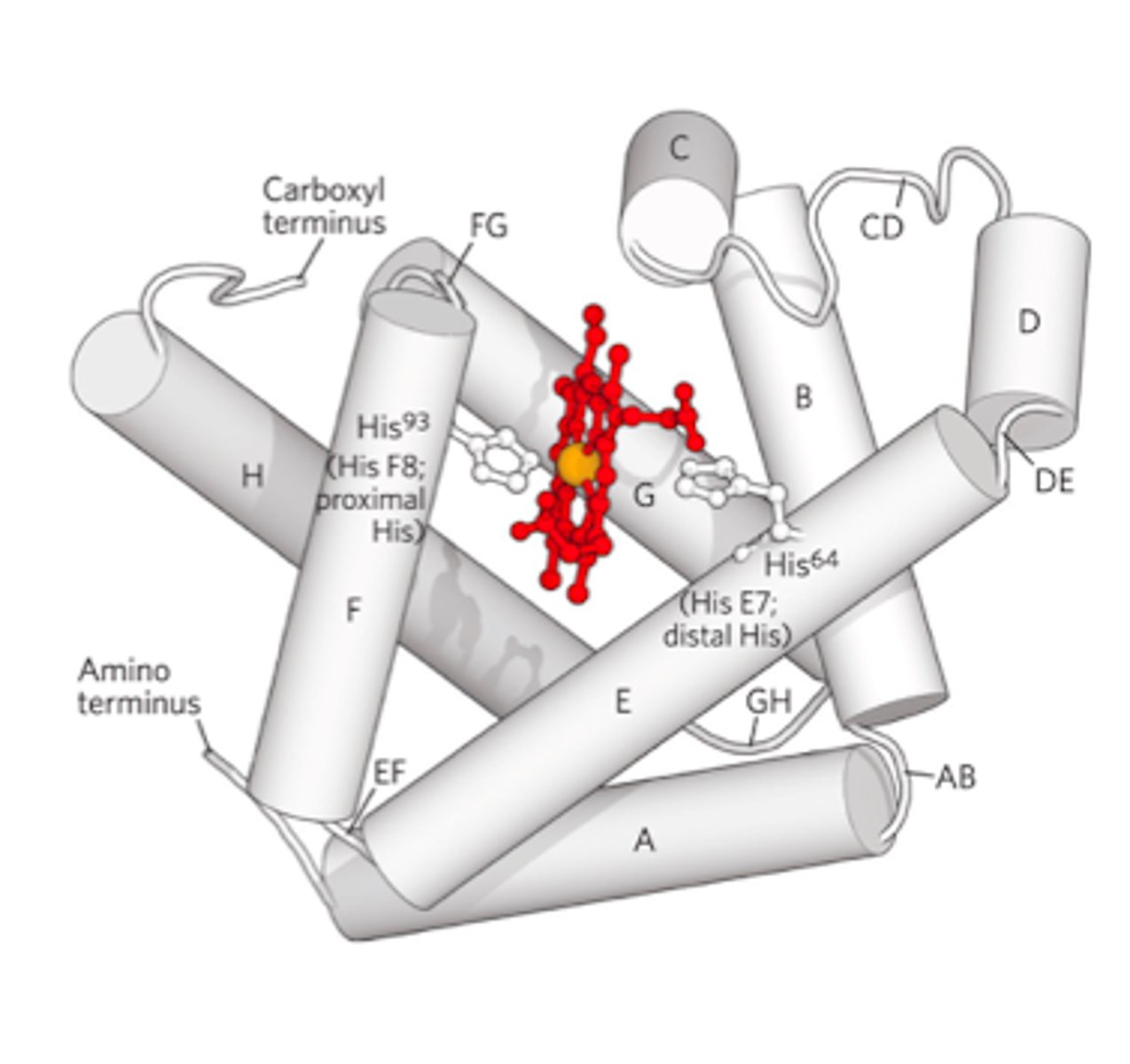
- iron interacts w/5-6 ligands -> 4 are the N atoms of the porphyrin and the 5th ligand is donated by the imidazole sides chain (His F8)
- His F8 -> on the 6th or "F" helix and the 8th residue in the helix
- when Mb or Hb bind to O2 -> O2 molecules adds to the heme iron as the 6th ligand -> O2 is tilted relative to a perpendicular to the heme plane
O2 binding ______ Mb conformation
ALTERS
- Fe2+ lies slightly above the the plane of heme
- when O2 binds to Fe in heme of Mb, the heme Fe is drawn toward the plane of the porphyrin ring
- O2 brings the Fe2+ more in line with the plane of heme
- Mb -> this small Fe2+ adjustment is minimal consequences
- Hb -> similar change of Fe2+ -> initiates a series of conformational changes that are transmitted to adjacent subunits -> cooperativity

Mb structure
- MONOMERIC heme protein
- polypeptide "cradles" the heme group
- Fe2+ (ferrous iron) binds to O2
- oxidation of Fe2+ -> Fe3+ (ferric iron)
Metmyglobin
- Mb with Fe3+
- DOES NOT BIND TO O2
- Fe3+ is due to oxidation of Fe2+
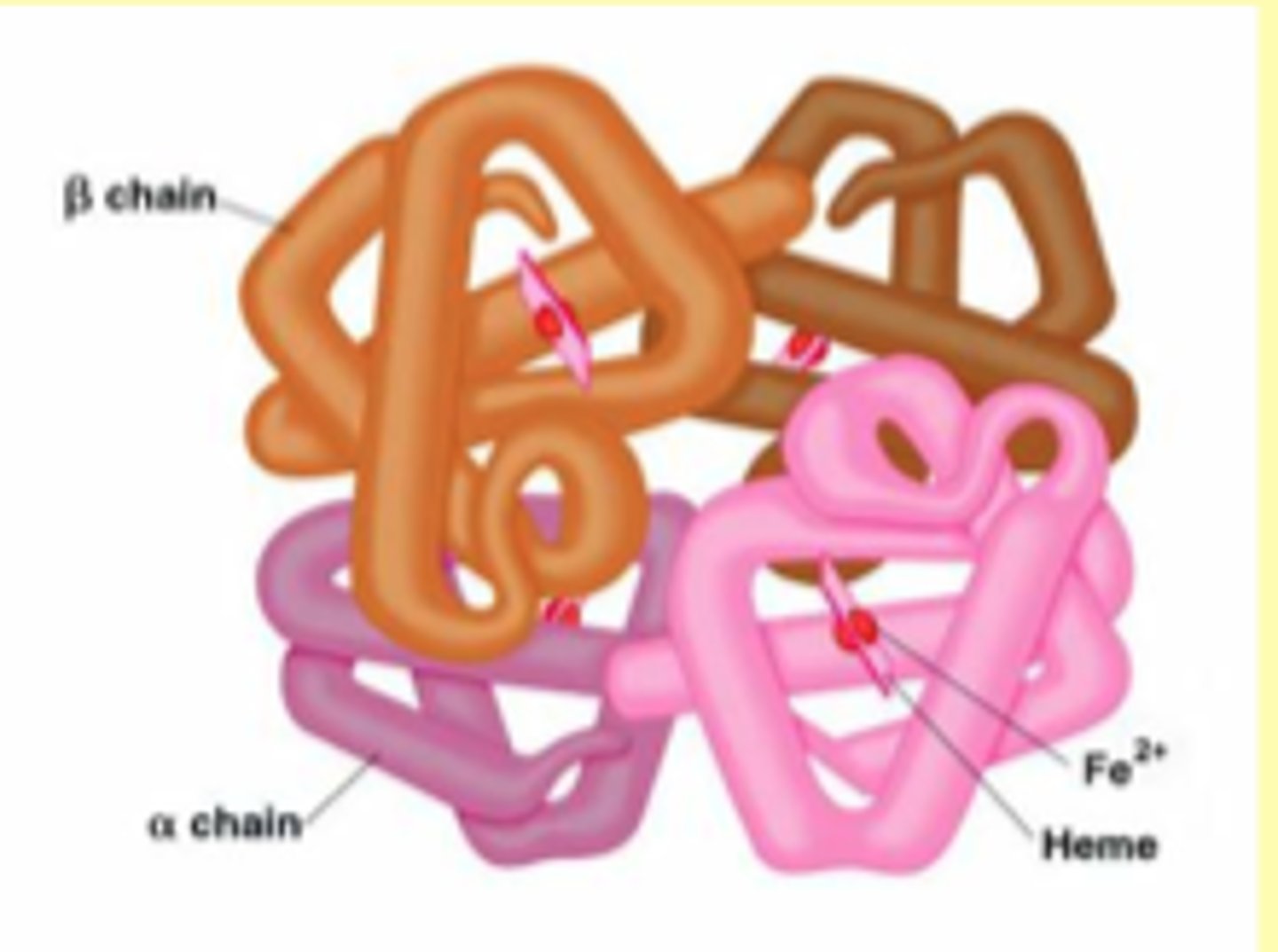
Hb structure
- α2β2 TETRAMERIC structure
- αβ dimer of Hb w/packing contacts -> α1β1 and α2β2 contacts are important for subunit packing -> helices B, G, H, and GH corner
- sliding contacts α1β2 and α2β1 are made with the other dimer
α1β1 and α2β2 of Hb are _______. they are _________ during oxygenation.
packing contacts
unchanged
does Hb show cooperativity in O2 binding?
- hemoglobin has sigmoid shaped O2 binding curves -> positive cooperativity
- the 4 heme groups are a long way apart -> cooperativity in oxygen binding is not due to direct heme-heme interactions
how does changes in Fe2+ movement due to O2 binding affect Mb and Hb
- Mb -> little consequences
- Hb -> conformational changes in the hemoglobin molecule
conformational changes of Hb due to O2 binding
- in deoxy-Hb the iron atom lies out of the heme plane
- as O2 binds -> Fe2+ moves closer to the plane of the heme
- as Fe2+ moves, it drags HisF8 and F helix with it
- the change is transmitted to the subunit interfaces -> conformational changes leads to rupture of salt bridges
O2 binding to Hb rotates one αβ pair by _____ degrees
15
salt bridges in Hb
- salt bridges stabilize deoxy-Hb (T state)
- salt bridges are present between diff subunits -> 8 salt bridges
- for oxy-Hb (R state) -> salt bridges are broken
- salt bridges and Hbonds involving interactions bt N and C terminal residues in the α chains
- salt and Hbond involving interactions with C terminal residues of β chains
cooperativity of Hb is MWC or KNF model
- BOTH
- O2 binds first to the 2 α subunits
- large conformational change occurs when 2 O2 are bound to Hb -> increases the affinity of the β subunits for oxygen
- deoxy-Hb has low affinity for O2
- heme group of the β subunits are inaccessible to O2
- 1st O2 binds to α subunit
- small changes in tertiary structure of the other α subunit increases its affinity for O2 3 fold (KNF model)
- Hb with 2 O2 bound is in equilibrium w/a form of the protein in which all four subunits are in the R state -> equivalent to T/R transition in MWC model
- large change in quaternary structure
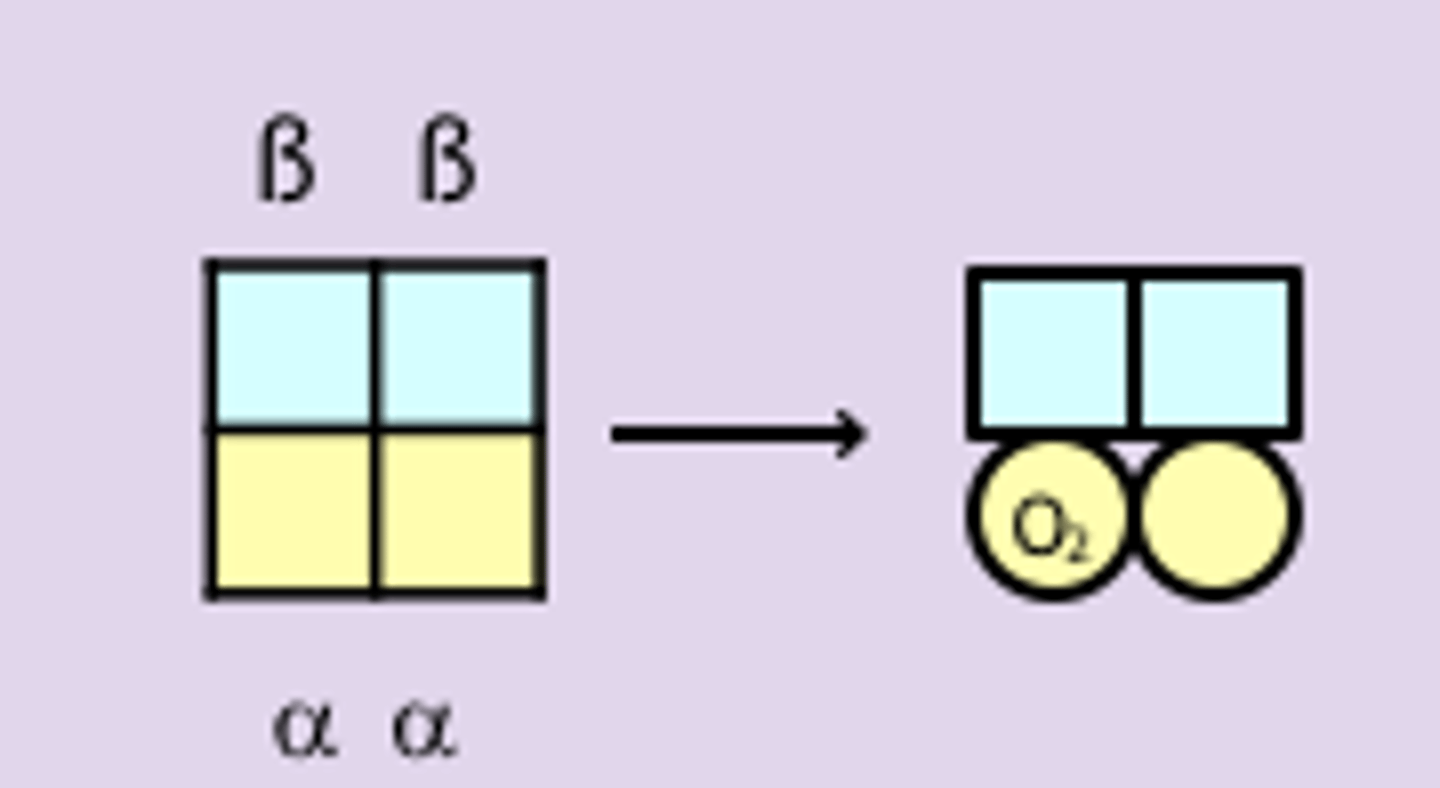
how does cooperative binding of O2 influences Hb function
- Hb must bind O2 in lungs and release it in capillaries
- Hb becomes saturated with O2 in the lungs -> partial pressure is ~ 100 torr
- in capillaries, pO2, is about 40 torr and O2 is released from Hb
- the binding of O2 to Hb is cooperative -> perfect for function
Mb has a ______ affinity for O2 than Hb at all O2 pressures
greater
- since Mb is an oxygen storage protein
Bohr effect in Hb
- the antagonism of O2 binding by H+ is termed the Bohr effect
- binding of H+ diminishes O2 binding and vice versa
- protonation of His146 induces R-to-T transition of Hb -> decreasing affinity for O2
- in deoxy-Hb -> 3 amino acids residues form two salt bridges -> stabilize the T quaternary structure
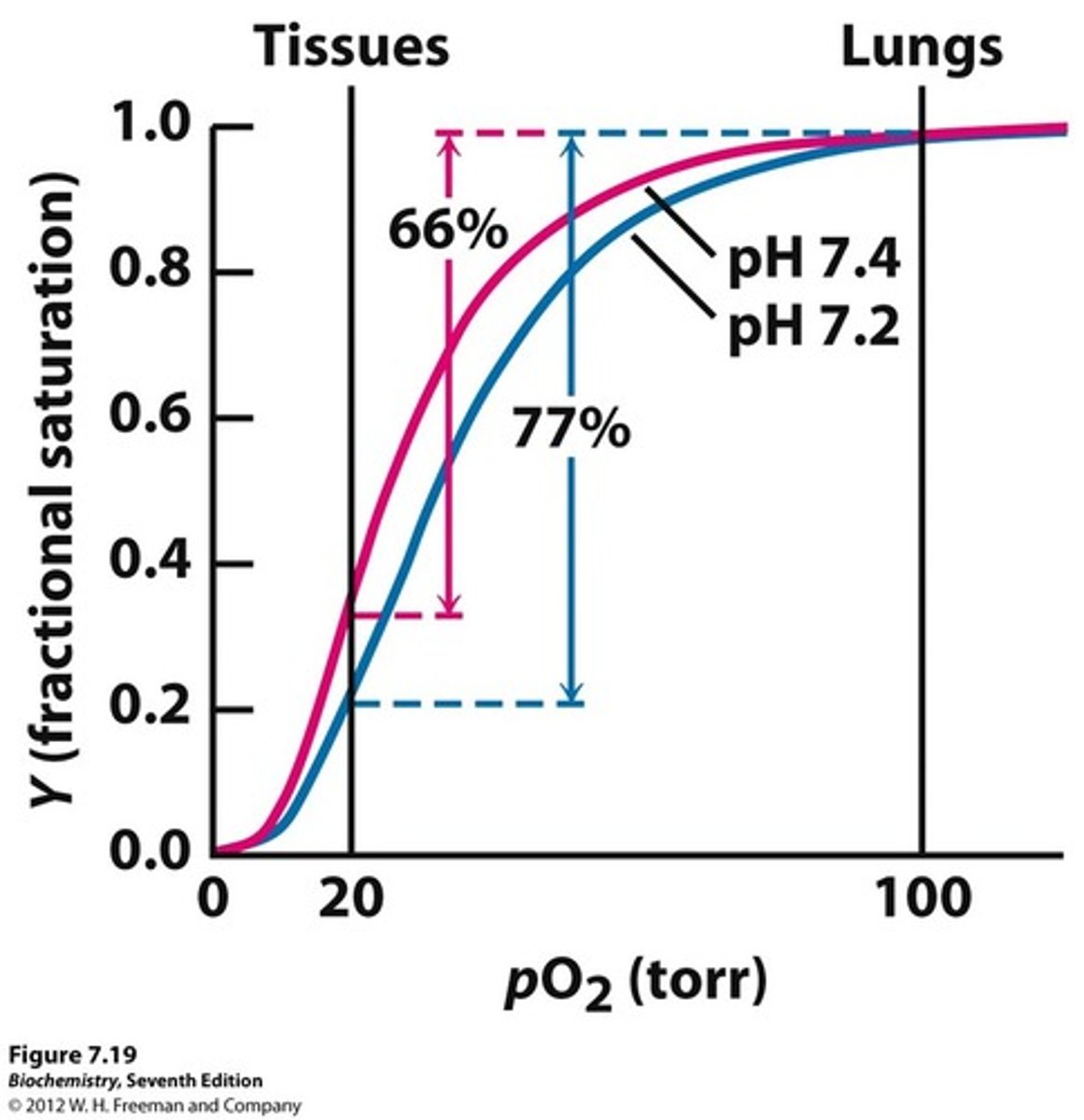
in condition of alkalosis, the affinity of O2 for hemoglobin is _______. and the curves shifts _______.
higher
left
CO2 affect in O2 binding of Hb
- Hydration of CO2 in tissues and extremities leads to proton production -> O2 binding decrease
- CO2 + H2O <-> H+ + HCO3-
- these protons are taken up by Hb as O2 dissociates
- reverse occurs in the lungs
- CO2 DECREASES O2 BINDING
bicarbonate dehydration in Hb
- at lung-artery interface
- bicarbonate dehydration (required for CO2 exhalation) consumes extra H+
- promotes CO2 release and O2 binding
CO2 ______ deoxy-Hb
STABILIZES
- stabilizes deoxy-Hb from reacting w/terminal amino groups -> forms a carbamate group (neg charges) and participates in salt bridges
- deoxy-Hb (T state) is stabilizes
2,3 biphosphoglycerate is an _______ effector of Hb
NEGATIVE ALLOSTERIC
- in absences of 2,3 BPG, O2 binding to Hb follows a rectangular hyperbola -> Michealis-menten
- sigmoid binding curve is only observes in presence of of 2,3BPG
- 2,3 BPG binds at a site distant from the Fe where oxygen binds
- 2,3BPG is in the center of a cavity bt two β subunits
- 2,3BPG binding stabilizes the deoxy form (T state) -> reduce affinity for O2
what are the 3 positive changes that the negative charges interact with in the cavity where 2,3BPG is
2 Lys, 4 His, 2 N- termini
fetal Hb
- fetal Hb has a higher affinity for O2
- circulatory system is entirely independent form its mothers when in the womb
- gas exchange is across the placenta
- fetal Hb -> γ chains in place of β-chains -> α2γ2 structure
- lower affinitiy for 2,3BPG -> higher affinity for O2
- γ-chains have a Ser instead of His at position 143 -> lacks two of the positive charges in BPG-binding cavity -> BPG binds less tightly -> fetal Hb thus looks more like Mb in its O2 binding behavior
Hb is a _______ with ______ substrate binding and ______ effectors.
tetramer
cooperative
allosteric
SHOWS FEATURES OF BOTH MODEL