ONE FOR ALL ALL FOR ONE TYPE SHIT
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
as a result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, how is the oxidizing agent changed?
it gains electrons and gains potential energy
which of the following sequences represents the correct order in which metabolic reactions occur during the complete oxidation of glucose through aerobic respiration?
glucose → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
which of the following indicates a primary path by which electrons travel downhill energetically during aerobic respiration?
glucose → NADH→ electron transport chain→ oxygen
Why is glycolysis considered to be one of the first metabolic pathways to have evolved?
It does not involve organelles or specialized structures, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms. (like in archaea and bacteria too)
which chemical process generates the ATP produced in the citric acid cycle?
substrate-level phosphorylation
Which of the following molecules donates electrons directly to the electron transport chain at the highest?
NADH
What is the immediate source of the energy used to synthesize ATP by oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotic cells?
the proton-motive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane
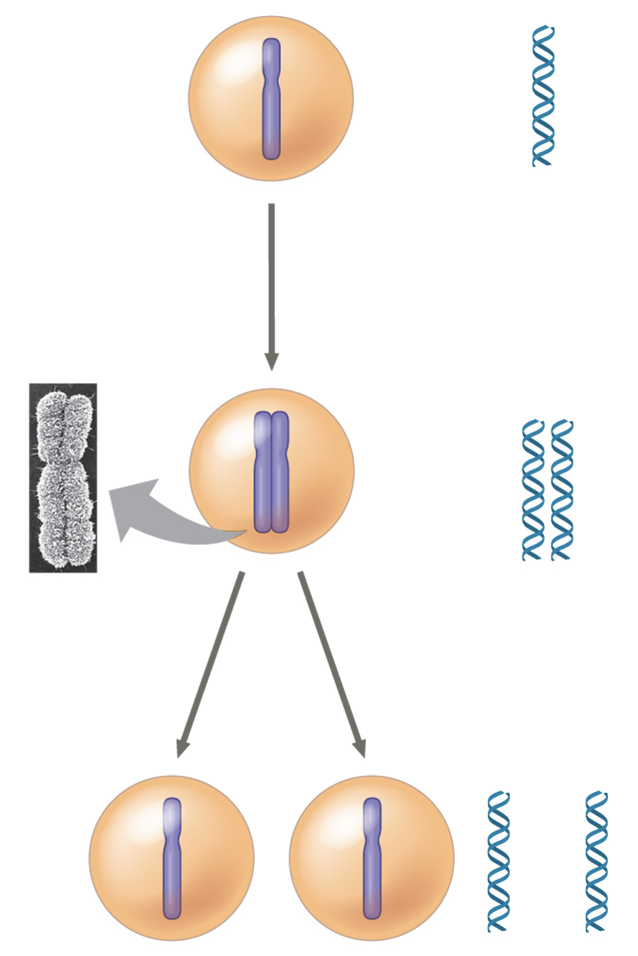
How many chromosomes are in the middle cell?
2
At what part of the cell cycle would you see a chromosome that looks like this?
M
At what time will the chromosome shown be split into two chromosomes, each the same as the other?
anaphase
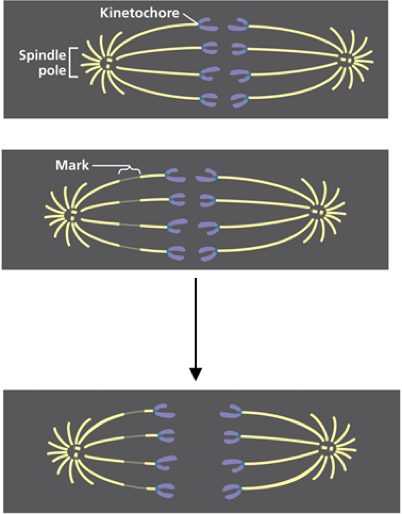
Stained microtubules are marked with a laser during mitosis. How would you explain the results shown?
microtubules shorten at the centrosome end
for what is cell division used?
growth and repair
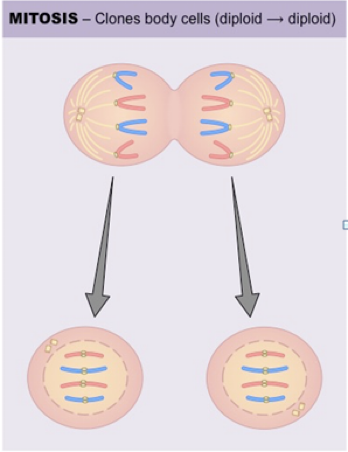
how does nuclear DNA enter daughter cells?
as identical copies of the same chromosomes
if you saw a cell with condensed chromosomes lined up in the center of the cell. you would know that the cell was in
metaphase
if you saw a cell with chromosomes condensing, you would know that the cell was in
prophase
if the nuclear envelope has disappeared but the condensed chromosomes are not yet lined up, the cell is in
prometaphase
if you saw a cell with chromosomes separating but not yet at the poles, you would know that the cell was in
anaphase
if asked what part of the cell cycle an adult’s eukaryotic was in, you would be most likely correct if you guessed
interphase
if you wanted to create a drug to stop chromosomes from lining up during mitosis, but otherwise not disturb the overall process, you would want to disrupt
kinetochores
what lines up chromosomes at the center of the cell in metaphase?
equal pulling from opposite poles
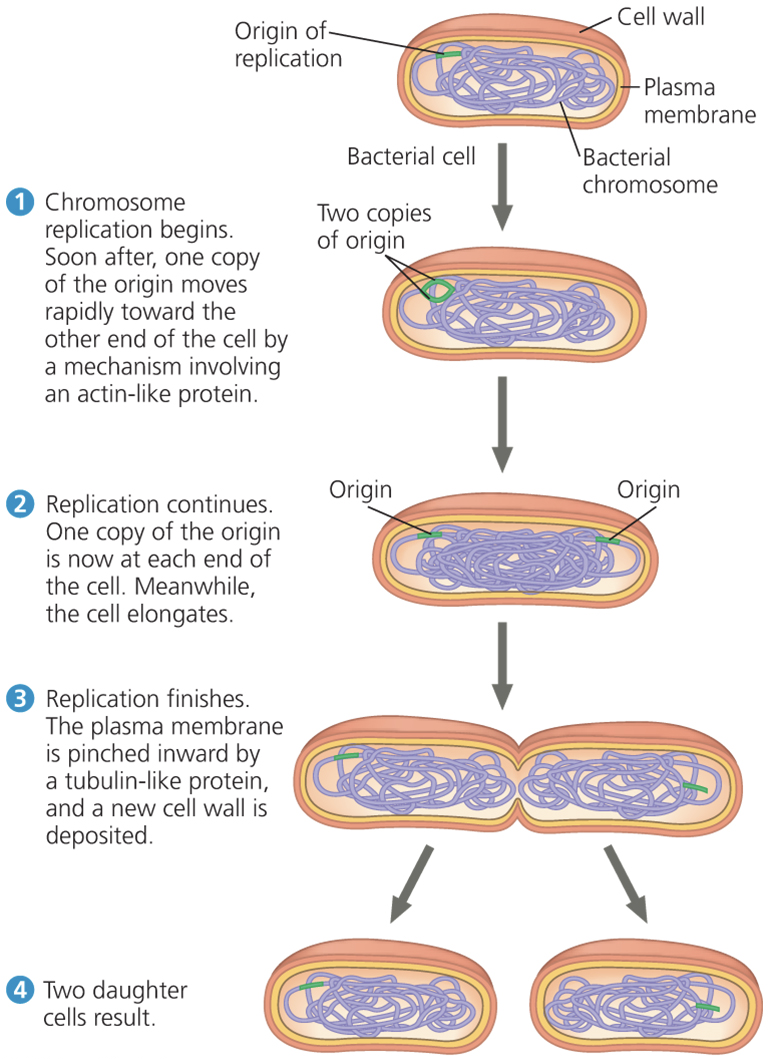
if studying a bacterial cell dividing, you would need to know about
binary fission
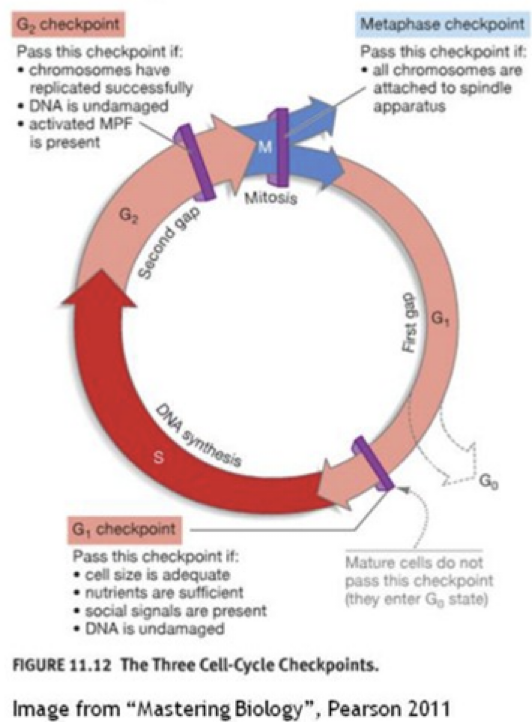
if you used a chemical to block ____ cells would stall during the cell cycle and have twice the normal amount of DNA
the G2 checkpoint
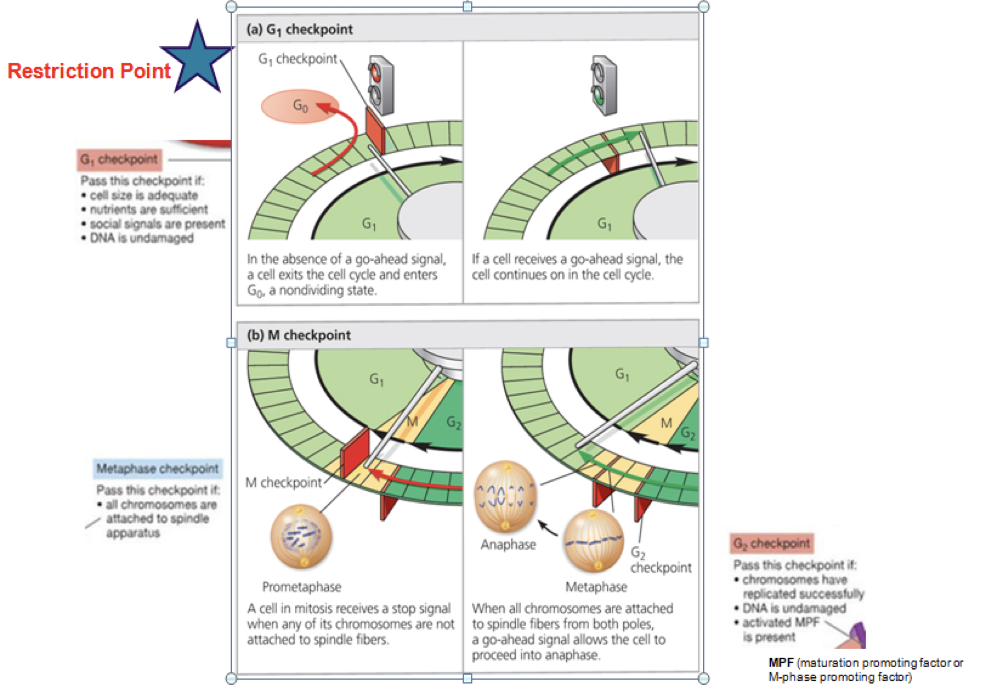
if you had a chemical to block ___ cells would stall during the cell and never synthesize DNA
the G1 checkpoint
When observing some cultured fibroblasts, you notice that cell division stops once there are 100 cells per square centimeter. You are observing ___
density-dependent inhibition.
A friend claims to have invented a way to cause wounds to heal more quickly. This might include manipulating
growth factors.
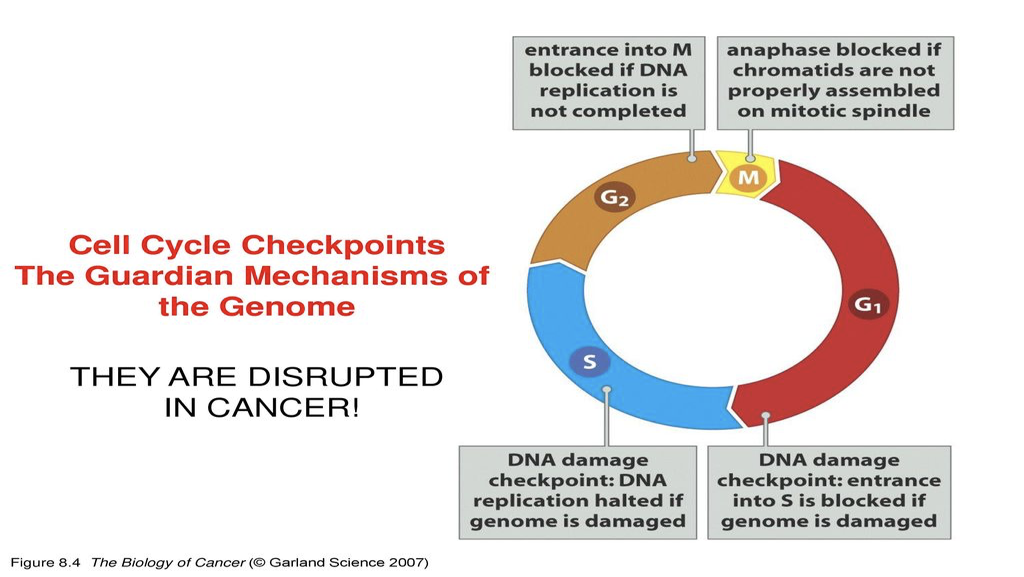
Without checkpoints during the cell cycle, what might happen?
mitosis before DNA synthesis is done, DNA synthesis without sufficient biochemical prep, insufficient cells in G0 for normal functioning, and daughter cells with the wrong number of chromosomes
the secretion of a signal molecule by a cell into the local environment, followed by a response by a number of cells in the immediate vicinity, is an example of
paracrine signaling
when a neuron responds to a particular neurotramsitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway
signal molecule
binding of the signaling molecule epinephrine to its receptor on the surface of the plasma membrane results in
increased concentrations of cyclic AMP in the cytoplasm
how are GPCR,s channel-linked receptors, and RTKs similar?
These are all transmembrane receptors
following activation of a receptor, which sequence below represents the correct order in which components will be involved in a signaling pathway that utilizes the second messenger cAMP?
G protein → adenyl cyclase → cAMP → protein kinase
which of the following is a second messenger
cAMP
which of the following enzymes adds a phosphate group to target proteins?
kinase
which of the following is the greatest advantage of having multiple steps in a transduction pathway?
having multiple steps provides for greater possible amplification of a signal
the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones is defined as
catabolism
which of the following statements about enzyme-catalyzed reactions is true?
the rate of reaction is greater than when the same reaction occurs in the absence of an enzyme
in most exergonic reactions, before products can be formed, the reactants must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the
activation energy of the reaction
the active site of an enzyme is the region that
binds substrates for the enzyme
a mutation results in an animo acid substitution at a site distant from the active site of an enzyme. how might this amino acid change alter the active site and substrate specificity of the enzyme?
by changing the conformation of the enzyme
an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is conducted in a test tube with a fixed amount of enzyme. increasing the enzyme concentration in the test tube may overcome the effect of which of the following conditions?
a saturated enzyme population
zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is required in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase in order for the enzyme to function properly. The zinc most likely functions as a(n)
cofactor necessary for the enzyme activity (remember coenzymes are the organic ones)
coopertivity is a form of allosteric activation in which
binding of a substrate molecule to one active site in a multisubunit enzyme stimulates the binding of substate molecules to the active sites of other subunits. (Cooperativity, feedback inhibition)
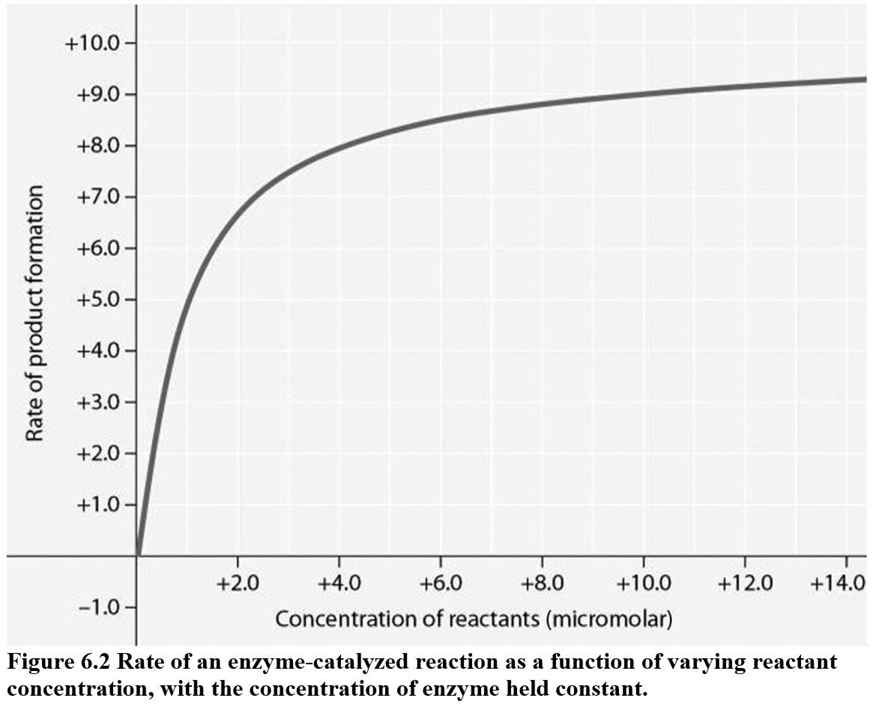
In Figure 6.2, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations
how can the rate of a chemical reaction be increased?
by adding a catalyst
Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. Which of the following statements regarding the molecules involved in this reaction is correct?
succinate is the substrate, and fumarate is the product
A series of enzymes catalyze the reactions illustrated in the following metabolic pathway:
X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding of A decreases the activity of the enzyme that converts X to Y. What is substance X?
a substrate
some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
their enzymes have high optimal temperatures
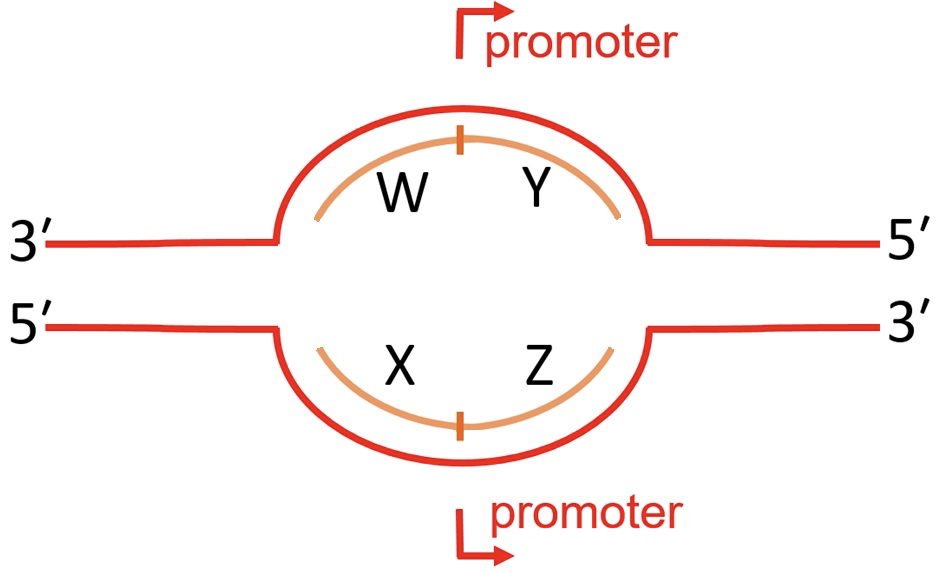
Consider the diagram below that depicts a transcription bubble, in which red strands are D N A and orange strands are potential R N A transcripts. Noting the location and orientation of the promoter, which letter(s) could represent proper transcripts?
Y, the promoter orientation, combined with 5’ to 3’ rules, specifies that strand Y is the only proper transcript.
The nontemplate strand of a portion of a gene reads
5’ ACTGGTTCA. What will be the sequence of the resulting transcript for this portion? (remember: contemplate strand is the same as the transcript, the only difference is replacing the T’s with U’s)
5’ ACUGGUUCA
Which of the following is a normal feature of eukaryotic mRNA
5’ cap, 5’ UTR, 3’ poly A-tail, and 3’ UTR
The function of the spliceosome is to
remove introns and splice together exons
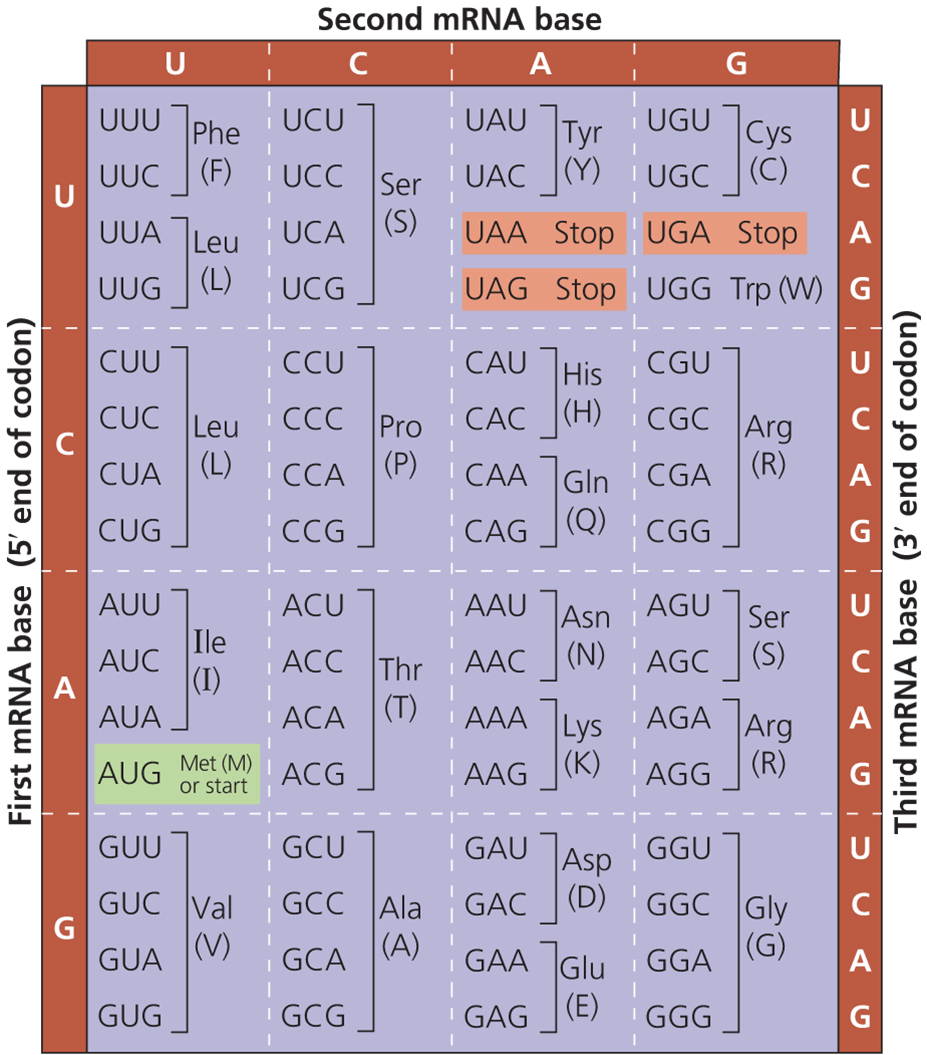
What is the minimum number of amino acyl tRNA synthetases there should be?
20
If the codon is 5’ UCG 3’ then what is the sequence of the anticodon?
5’ CGA 3’
In which group(s) of organisms would you expect to see coupled transcription and translation?
bacteria and archaea
during a normal translation cycle, where should you expect to find a polypeptide on a ribosome?
alterating between tRNAs attached to the P site and tRNAs attached to the A site
In which group(s) of organisms would you expect to see polyribosomes?
bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
a gene encoding a protein that normally contains and SRP is engineered to lack the SRP. What is expected to happen to the engineered protein?
it will be directed to the cytosol
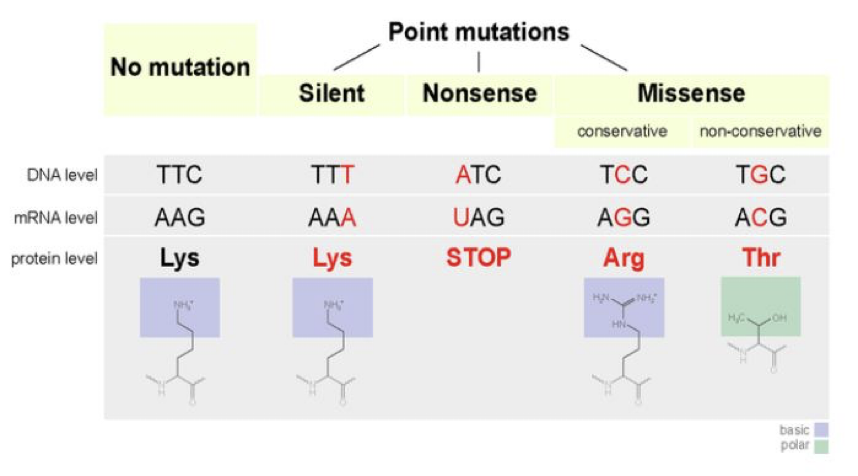
When a mutation caused by a nucleotide pair insertion occurs in a protein coding region, what is expected to occur?
frameshift
What does the operon model attempt to explain?
the coordinated control of gene expression in bacteria (only prokaryotes have operons)
Pair the following terms by their physical binding with each other":
promoter, operator, RNA polymerase, repressor protein.
RNA Polymerase with promoter; repressor protein with operator
which of the following is true of a normal E. coli cell with a normal trp operon?
it synthesizes tryptophan only when tryptophan is absent
imagine an E. coli cell with a mutation that renders its trp repressor protein completely inactive. which of the following would be true of that cell?
it always synthesizes tryptophan
imagine an E. coli cell with a mutation that renders its operator completely inactive. Which of the following would be true of that cell?
it always synthesizes tryptophan
imagine an E. coli cell with a mutation that renders its promoter completely inactive. Which of the following would be true of that cell?
It never synthesizes tryptophan
in normal E. coli cells, under which of the following conditions is the lac operon “ON”?
glucose absent, lactose present
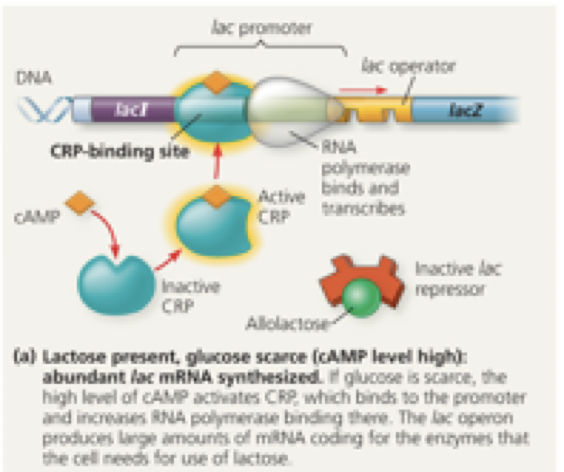
Glucose → Low
Lactose → High
cAMP level: high or low":
interaction of CAP with promoter: bound or unbound
interaction of Allolactose with repressor: bound or unbound
Interaction of lac I repressor with Operator: bound or unbound
Expression of lac operon structural genes: high or low
high
bound
bound
unbound
high
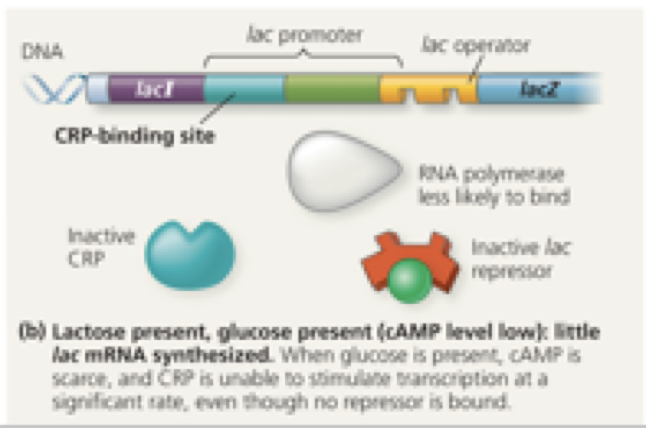
Glucose = positive or negative control
positive control
lactose = positive of negative control
negative control
in normal E. coli cells, in which the lac operon is “ON”, which combination of CRP and lac repressor proteins is bound to the lac operon
only CRP
imagine an E. coli cell in which the lac operator has a mutation that renders it unable to bind the lac repressor. When would its lac operon be “ON”?
when glucose levels are low
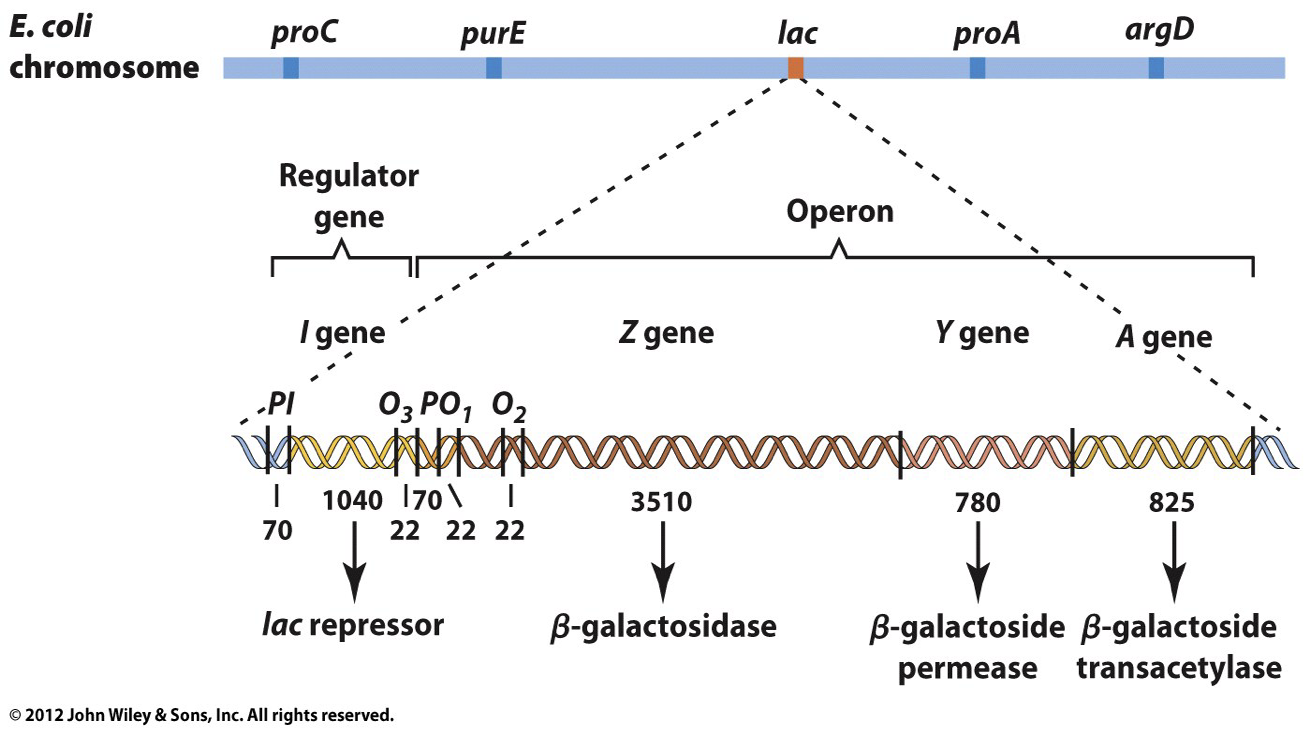
each of a group of E. coli bacterial cells has a mutation in its lac operon. Which of these will make it impossible for the cells to metabolize lactose?
mutation in lacZ (nonfunctional B-galactosidase gene)
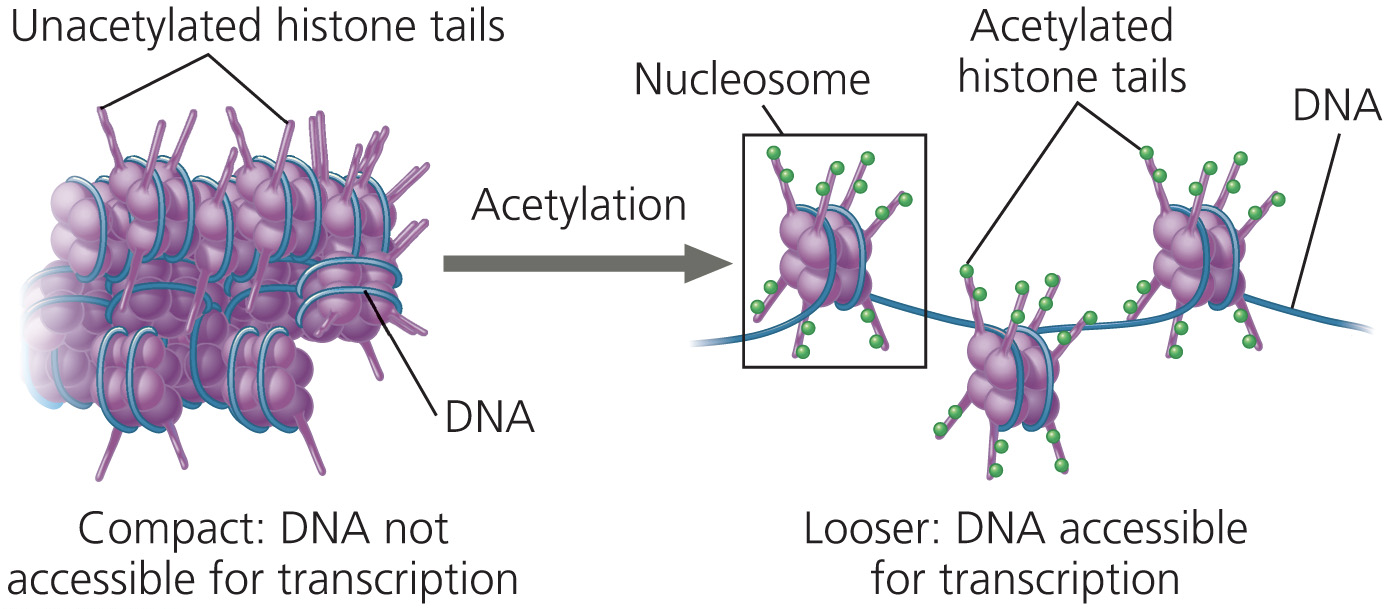
histone de-acetylases (HDACs) are enzymes that remove acetyl groups from histone proteins. With regard to their effects on transcription, HDACs should do which of the following?
repress transcription by condensing chromatin
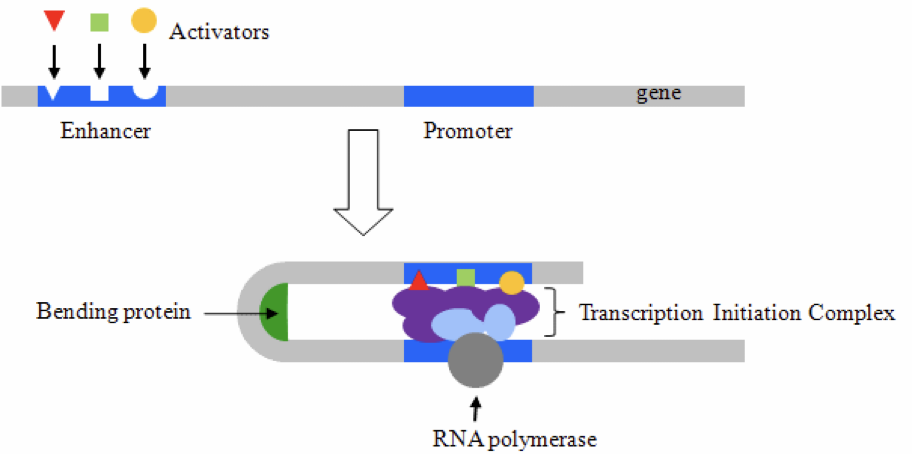
What type(s) of molecule(s) are enhancers?
DNA
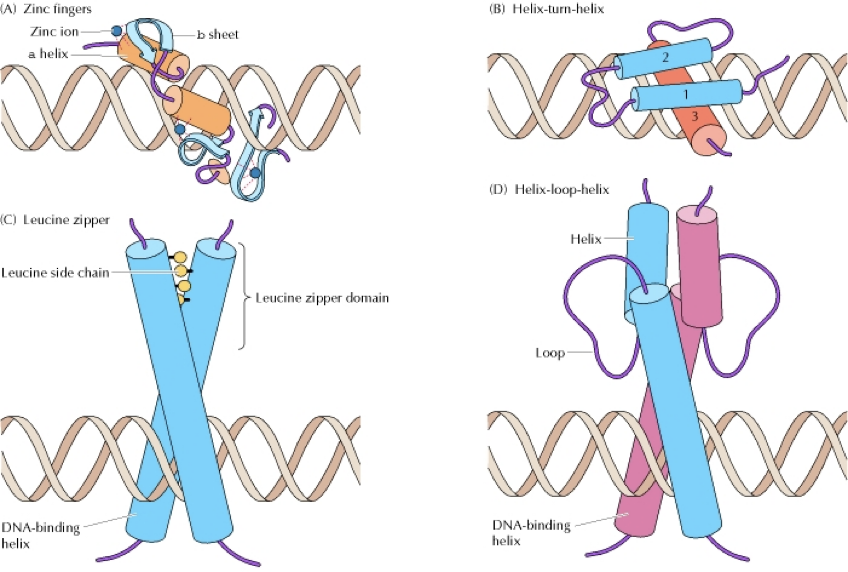
Which type(s) of molecule(s) are transcription factors?
protein
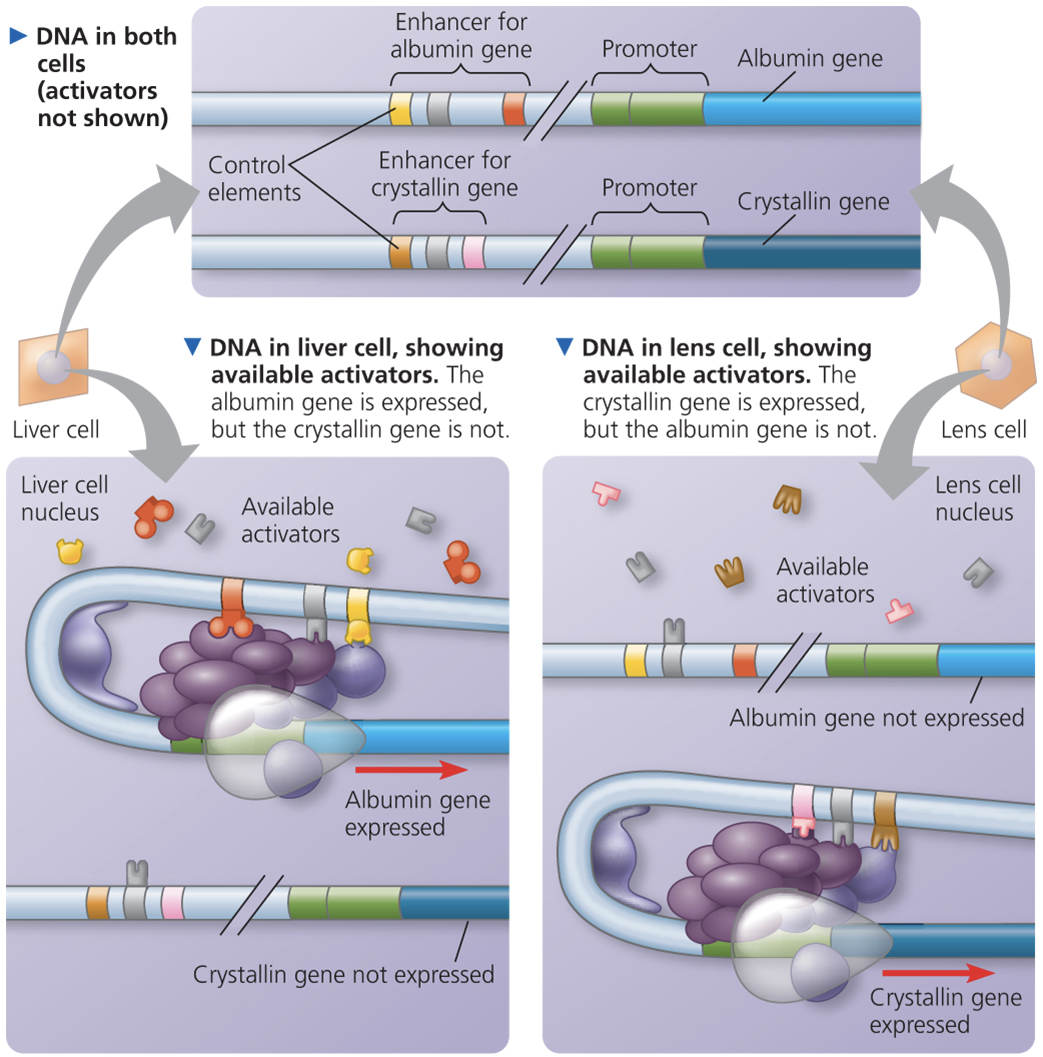
why is a myosin gene transcriptionally expressed in muscle cells but not in neurons?
Muscle cells express an activator protein that binds the myosin enhancer
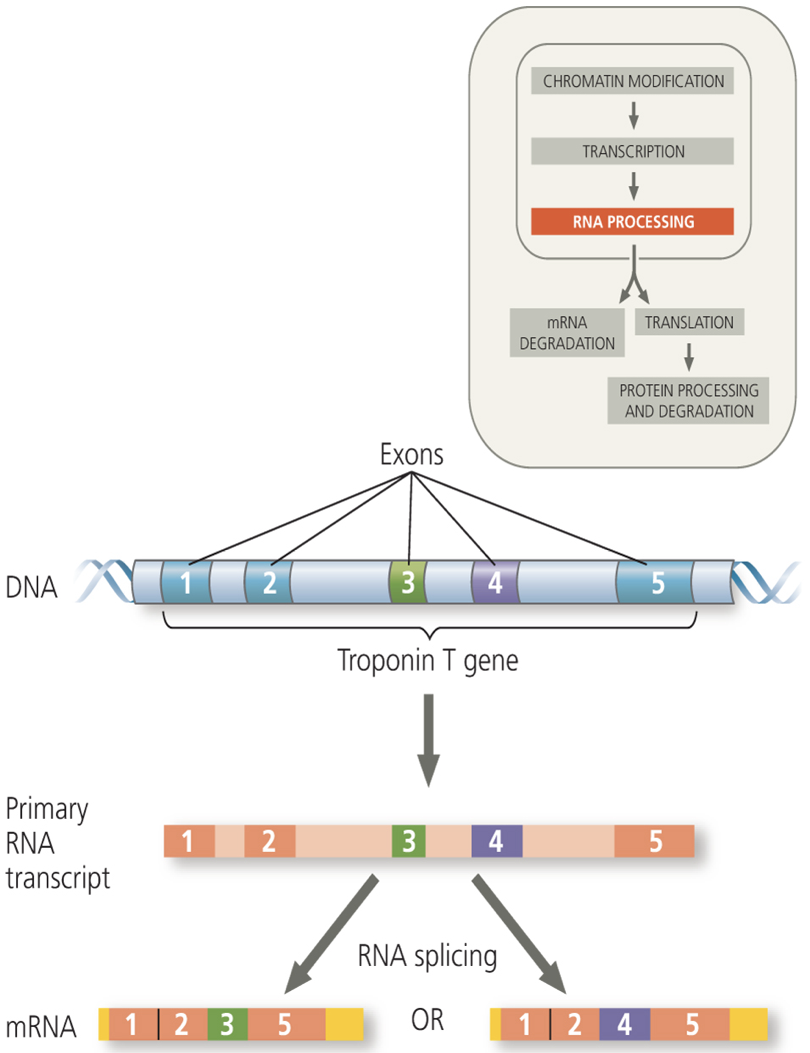
a specific gene is known to code for three different but related proteins. This could be due to which of the following?
alternative RNA splicing
A miRNA bins with perfect complementarity to a target mRNA of gene X. What is/are the outcome(s) for gene X in terms of gene regulation?
less mRNA of gene X and less protein of gene X
Which of the following methods would not determine if certain genes are turned on in a particular cell?
Use mi-RNA to inhibit mRNAs
an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is conducted in a test tube with a fixed amount of enzyme. Increasing the substrate concentration in the test tube may overcome the effect of which of the following conditions?
presence of a fixed amount of a competitive inhibitor
A drug designed to inhibit the response of cells to the steroid hormone aldosterone (a lipid-solube signaling molecule) would almost certainly result in which of the following?
a decrease in transcriptional activity of certain genes
signal transduction pathways that include phosphorylation cascade…
cause a structural change in each phosphorylated protein
phosphatase enzymes in signal transduction pathways function primarily to
inactivate protein kinases to turn off signal transduction pathways
the primary function of G proteins in signal transduction is
transmitting the signal from an activated receptor to the next protein in the pathway
True or false: The G protein can act as an intermediary between an effector (adeylyl clyclase) and protein kinases.
false
cancer results from uncontrolled cell growth resulting in formation of a tumor. the cell cycle is continually active and causes the cell to keep dividing even in the absence of the proper signal. theoretically, how might researchers disrupt signal transduction pathways as possible treatments for cancer?
disrupt the function of protein kinases involved in cell regulation
why are enzymes able to lower activation energy
they can bind to the reactants and put them into a favorable position, encouraging the formation fo the transition state
A series of enzymes catalyze the reaction illustrated in the following metabolic pathway: X→Y→Z→A. Product A binds to the enzymes that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding of A decreases the activity of the enzyme that converts X to Y.This product A functions as which of the following in terms of its effect on the enzyme that converts X to Y
allosteric inhibitor
signal transduction pathways that include a phosphorylation cascade…
cause a structural changei n each phosphorylated protein
what is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction: Pyruvate + NADH + H+ → Lactate + NAD+
Pyruvate
What is the primary function of beta oxidation in respiration?
breakdown of fatty acids
Which of the following molecules donates electrons directly to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
FADH2
Which statement best supports the hypothesis that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway that originated before the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth?
Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the evolution of mitosis?
Even in “primitive” mitosis in early eukaryotes, chromosomes were always attached to kinetchore microtubules in the spindle apparatus
which of the following signals is needed to allow cells to pass the M checkpoint and enter mitosis
All chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers
if there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase of mitosis, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis
10
what will happen if a cell in M phase is fused with a cell in G1 phase
The G1 nucleus will immediately begin to show signs of mitosis with a spindle formed and chromosomes condensed
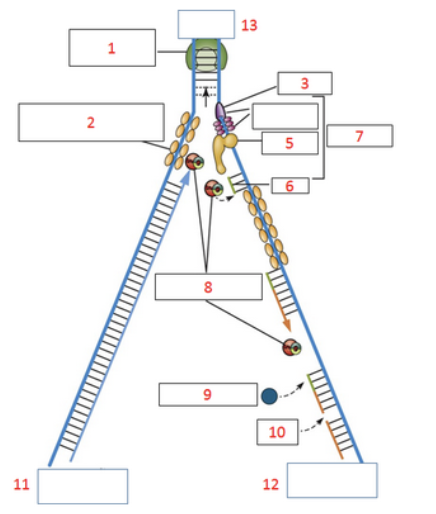
using the replication fork pictured below, what enzymatic activities are associated with the protein labeled #9 on the replication fork?
RNA polymerase I, 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity, 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity, and 5’ to 3’ polymerase activity
Suppose a 100-base-pair DNA molecule consists of 30% adenine bases. How many total hydrogen bonds are there holding the two strands together?
AT = 2 H bonds
CG = 3 H bounds
30% AT x 2 = 60 H bonds
70% CG x 3 = 210 bonds
60 + 210 = 270 H bonds