3.1 Principles Of Biomedical Science
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:22 AM on 3/22/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
epidemiologists
Someone who investigates health related matters such as disease outbreaks and chronic illnesses by gathering information, examing data, and looking for patterns
2
New cards
Genetic Diseases
Disease that is inherited.
3
New cards
What kind of disease is Sickle-Cell Anemia (Genetic or Infectious)
Genetic
4
New cards
Infectious Disease
Disorders caused by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. They are contracted or caught
5
New cards
What kind of disease is Influenza(Flu) (Genetic or Infectious)
Infectious
6
New cards
How might the condition of a host affect how successful a pathogen is at causing disease.
Vaccination or diseases that they already had, diet, sleep, hydration, age, and immunity system play a part on how successful the pathogen is at causing the disease
7
New cards
Bacteria
Living, microscopic, unicellular, prokaryotic, organisms
8
New cards
What infectious agent is this? Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (TB). The symptoms of TB depend on where in the body the bacteria are growing. Usually, TB bacteria grow in the lungs where they cause a bad cough that lasts three weeks or longer, pain in the chest, and coughing up blood or the phlegm from deep inside the lungs. Other symptoms include weakness, fatigue, weight loss, no appetite, chills, and fever.
Bacteria
9
New cards
Viruses
Non-living, microscopic, agent that make up of an outer protein shell called a capsid and either DNA or RNA
10
New cards
What infectious agent is this? The influenza virus, the flu, affects the respiratory system. Symptoms include runny or stuffy nose, itchy or sore throat, cough, congestion, slight body aches or a mild headache, sneezing, watery eyes, a low-grade fever, and fatigue.
Virus
11
New cards
Fungi
Living, multicellular eukaryotic organism
12
New cards
What infectious agent is this? Tinea pedis causes athlete's foot. Symptoms include dryness, itching, stinging, burning, cracking and peeling skin and blisters between the toes or on the soles of the feet. Toenails may be thick, crumbly, ragged, discolored, or pulling away from the nail bed. Athlete's foot thrives in thick, tight shoes that squeeze the toes together and create warm, moist areas between them. Damp socks and shoes and warm, humid conditions also favor the organisms' growth.
Fungi
13
New cards
Prions
Non-living submicroscopic proteins
14
New cards
What infectious agent is this? Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) results in dementia, walking difficulties, hallucinations, confusion, and death.
Prions
15
New cards
Protists
Living, microscopic single-celled eukaryotic animal-like organisms
16
New cards
What infectious agent is this? Giardia lamblia causes giardiasis. Giardia parasites live in the intestines of people and animals. Before the parasites are passed in the stool, they become encased within hard shells called cysts, which allows them to survive outside the intestines for months. Once inside a host, the cysts dissolve and the parasites are released.
Protists
17
New cards
Helminths
Living, multicellular eukaryotic worms. Both microscopic and macroscopic varieties exist
18
New cards
What infectious agent is this? Taenia, a tapeworm infection, results in nausea, loss of weight, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea, weight loss, and malnutrition. Invasive infections result in fever, cystic masses or lumps, allergic reactions to the larvae, bacterial infections, and neurological symptoms including seizures
Helminths
19
New cards
Portal of Entry
Skin, Respiratory Tract, Gastrointestinal Tract, Urogenital, & Conjunctiva
20
New cards
Portal Of Exit
Skin, Respiratory Tract, Gastrointestinal Tract, Urogenital & Conjunctiva
21
New cards
Direct Contact
Disease transmission that occurs when a susceptible host touches an infected individual or is exposed to their body fluids.
22
New cards
What kind of contact is it when you infect someone by directly sneezing on them
Direct
23
New cards
Indirect Contact
Disease transmission that occurs when a susceptible host inhales infected particles, touches an infected object, or is bitten by an infected insect.
24
New cards
Influenza(Flu) Etiology
(Being around other people who have the flue) Most people get the flu when they breathe in tiny airborne droplets from the coughs or sneezes of someone who has the flu. You can also catch the flu if you touch something with the virus on it, and then touch your mouth, nose, or eyes.
25
New cards
Athletes Foot Etiology
having damp (wet) socks/shoes and not replacing them
26
New cards
Familial Hypercholesterolemia Etiology
Genetics
27
New cards
Example of a disease with risk factors associated with lifestyle
smoking leads to lung cancer
28
New cards
What is used to identify bacteria
lab tests are conducted that look at specific characteristics of the organisms. The way in which the organisms grow, their morphology, or shape of their cells, and their ability to metabolize, or digest, certain compounds all provide clues as to the organisms' identity. To identify the specific bacterium infecting the hospital patients, the first step is to culture, or grow, it from patient samples and make observations about how the bacteria grow and their gross morphology
29
New cards
How are bacteria named
By their genus and species
30
New cards
When identifying the agents responsible for causing a disease, why is evaluation of colony morphology not enough?
Some of the colonies could end up looking the same to the naked eye. Doesn't say what specific bacteria it is, so we have to do gram staining.
31
New cards

What kind of Spirilla is this
They’re all Individual Spirillas
32
New cards

What kind of Cocci is this?
Diplococci
33
New cards

What kind of Cocci is this?
Individual Cocci
34
New cards

What kind of Cocci is this?
Chain of Cocci
35
New cards

What kind of Cocci is this?
Staphylococci
36
New cards

What kind of Bacilli is this?
Individual Bacilli
37
New cards
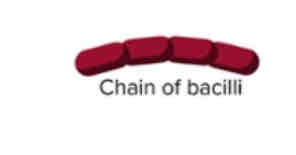
What kind of Bacilli is this?
Chain of Bacilli
38
New cards
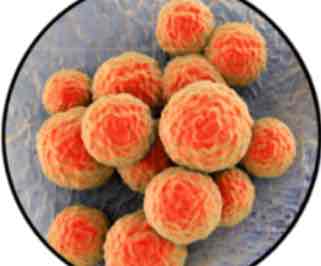
What kind of a shape is a coccus
sphere
39
New cards
What kind of a shape is a Bacilli
Rod
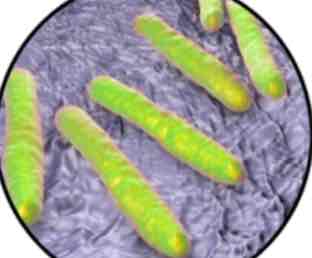
40
New cards
What kind of a shape is a spirilla
spiral
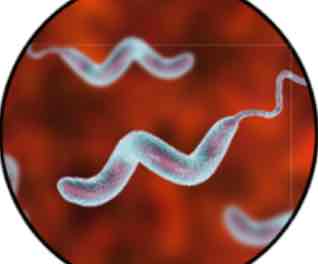
41
New cards
What color is Gram Positive
Purple

42
New cards
What color is Gram Negative
Pink
