AST101
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Midterm 1 material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
The order of the solar system
Sun → Mercury → Venus → Earth → Mars → Jupiter → Saturn → Uranus → Neptune
Explain planets’ orbit movement
the planets all orbit in the same plane - ecliptic plane
the planets all orbit the same direction
the sun rotates in the same direction that planets orbit
the planets all have elliptic orbits
the closer the planet is to the sun, the faster it orbits
Describe characteristics of Mercury
closest planet to the Sun
no atmosphere
highly cratered surface
rocky exterior with a huge iron core
temperature fluctuates between -170C and 425C
no moons
Describe characteristics of Venus
about the same size as Earth
has lots of volcanoes
thick CO2 atmosphere
runaway greenhouse effect makes it even hotter than Mercury
temperature is constant at 460C
it rains acid
no moons
rotates very slowly and backwards
Describe characteristics of Earth
about the same size as Venus
lots of volcanoes
O2+N2 atmosphere
large oceans regulate CO2
surface heavily effected by life
has 1 large moon
23.4 degree orbital tilt produces significant seasons
Describe characteristics of Mars
lots of extinct volcanoes
very thin CO2 atmosphere
oceans have evaporated
no evidence for life
has 2 small moons
polar ice/dry-ice caps
planet wide dust storms
25.2 degree orbital tilt produces significant
What are terrestrial planets?
These are Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars. They are
small
rocky
relatively thin or no atmosphere
have few moons
made from heavy elements
Describe characteristics of Jupiter
largest planet in the solar system
thick gaseous atmosphere surrounds a giant ball of liquid hydrogen
has very faint rings
many moons - more than 60 known to date
Describe characteristics of Saturn
second largest planet in the solar system
structure is similar to Jupiter
has spectacular rings
has more than 60 moons
Describe characteristics of Uranus
coldest planet
small rocky core
thick water + ammonia + methane mantle
thick H2/He atmosphere
rotation axis tilted 98 degrees
thin rings and lots of moons
Describe characteristics of Neptune
furthest planet from the Sun
structure very similar to Uranus
rotation axis tilted 28 degree
more surface features than Uranus
strongest winds in the solar system: up to 2,100 km/h
What are Jovian planets?
These are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. They are
large
contain gas + liquid
have many moons
mostly light elements
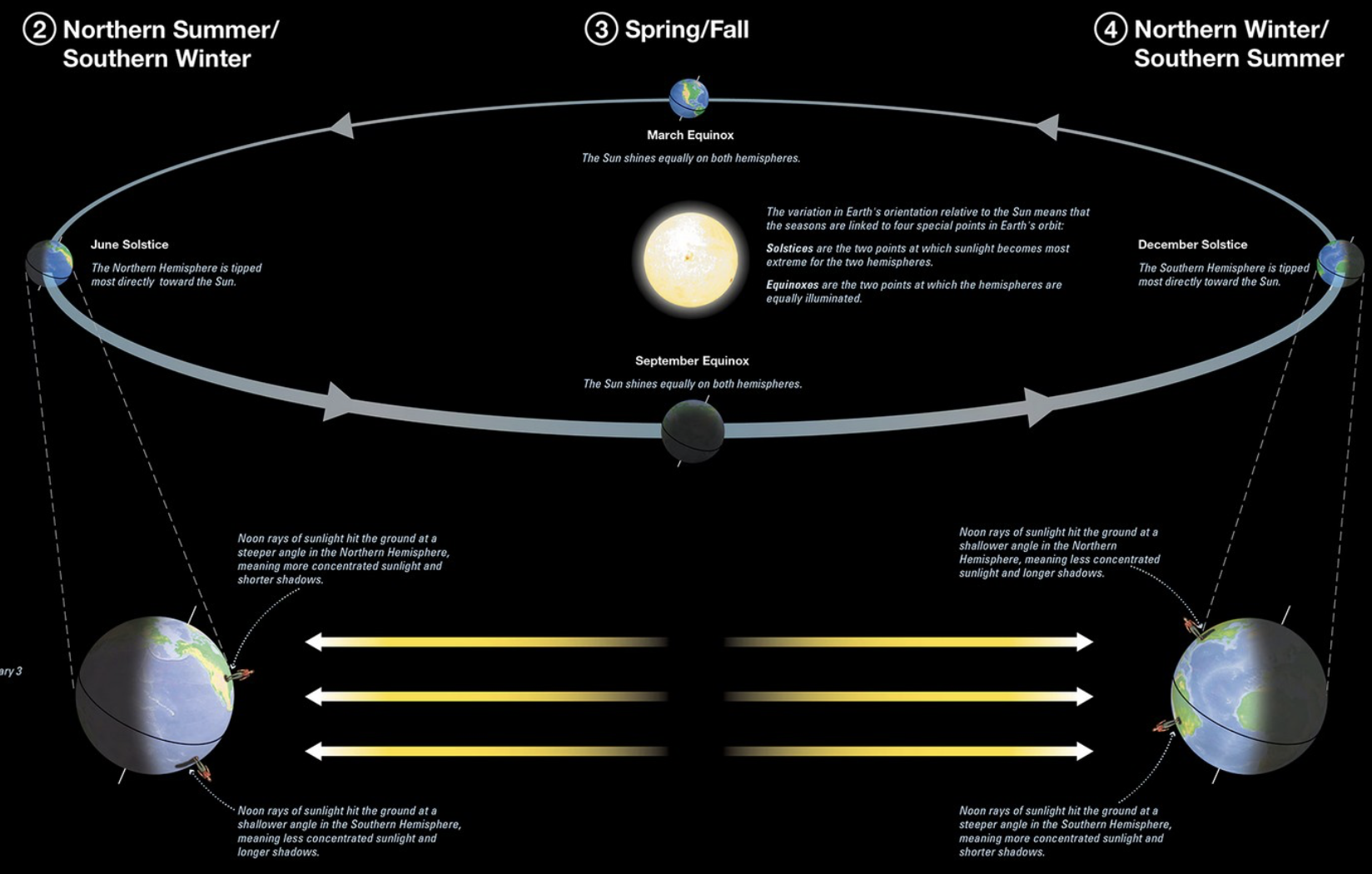
Describe season of summer in terms of Sun & rotation
during Summer,
daylight is longer & darkness is shorter
Sun gets ‘higher’ in the sky so sunlight is more direct & Earth is hotter
Describe season of winter in terms of Sun & rotation
In winter,
daylight is shorter and darkness is longer
sun does not get as ‘high’ in the sky, so sunlight is at an angle & Earth is colder
Describe how Sun shines on Northern and Southern hemispheres throughout different times of the year.
What does the phase of the moon depend on?
It depends on where the Moon is compared to the Sun

Describe this moon phase
New Moon
when the moon is in the direction of the sun
the only time a Solar eclipse can happen (when the Moon blocks the Sun)
Unlit side faces the Earth
rises with the Sun and sets with the Sun
not generally visible on Earth

Describe this moon phase.
Waxing Crescent
happens 3-4 days after the new moon
rises around 3h after the Sun (9am)
sets around 3h after the Sun (evening-early night)
easiest to see right after sunset

Describe this moon phase.
Waxing Quarter
1 week after the new moon
moon is lit from the side
rises around 6h after the sun (12pm)
sets around 6 hours after the sun (midnight or later)
easiest to see at night before midnight

Describe this moon phase.
Waxing Gibbous
10-11 days after the new moon.
rises around 9h after the Sun (3pm)
sets around 9h after the Sun (night)
easiest to see at night - but may set before sunrise

Describe this moon phase.
Full Moon
two weeks after the new moon
the only time a Lunar eclipse can happen (moon enters Earth’s shadow)
rises around 12h after the sun rises (5pm)
sets around 12h after the sun sets (closer to sunrise)
visible most of the night
Describe this moon phase.
Waning Gibbous
10-11 days before the next new moon
rises around 3h after the sun sets (9pmish)
sets around 3h after the sun rises (in the morning)
rises before midnight, and is up the rest of the night and morning

Describe this moon phase.
Waning Quarter
around a week before the next new moon
rises around 6h before the sun rises (midnight)
sets around 6 hours before the sun sets (afternoon)
rises around midnight, and is up the rest of the night and morning

Describe this moon phase.
Waning Crescent.
2-4 days before the next new moon
rises around 3h before the sun rises (late night)
sets around 3h before the sun sets(early evening)
easiest to see before sunrise.
Describe process of Solar Eclipse
It’s when the Moon blocks light from the Sun to Earth. Happens when the New Moon crosses the ecliptic plane.
It only casts a shadow on a small part of the Earth

Why does Solar Eclipse happen rarely?
Since the Moon’s orbit is tipped relative to the ecliptic plane.
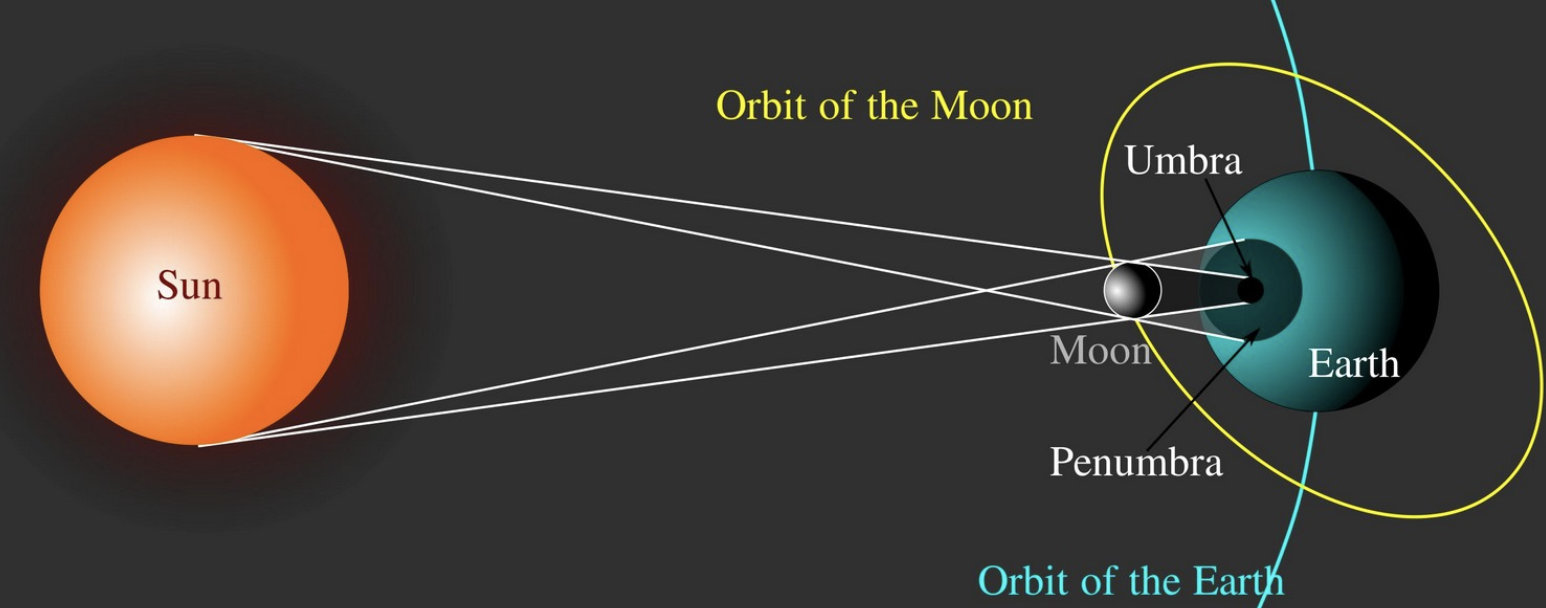
Describe the process of Lunar Eclipse
It happens when the Moon enters the Earth’s shadow. It’s when a full moon crosses the ecliptic plane. It’s more common than a Solar Eclipse since Earth has a bigger shadow.
What is Geocentric Universe?
In Geocentric model of the Universe, the Earth is the centre of it. All celestial objects revolve around the Earth
What is Retrograde Motion?
Retrograde motion is planets turning around relative to the stars.
What is Nicolaus Copernicus’ idea of the Universe? (1473-1543)
Copernicus suggested that Sun is the center of the Universe and planets orbit in circles around it. He also suggested that moon orbits the Earth.
He also explain Retrograde motion - he observed that Earth orbits faster than Mars; as Earth passes Mars, the position of Mars on the sky, compared to background stars, changes. This can explain the motion of the planets
What are Tycho Brahe’s (1546-1601) contributions to astronomy?
He made extremely precise measurements of the motion of Mars
Observed a SuperNova
Used parallax to constrain distances
From his data, current models clearly had problems
Kepler’s First Law
The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
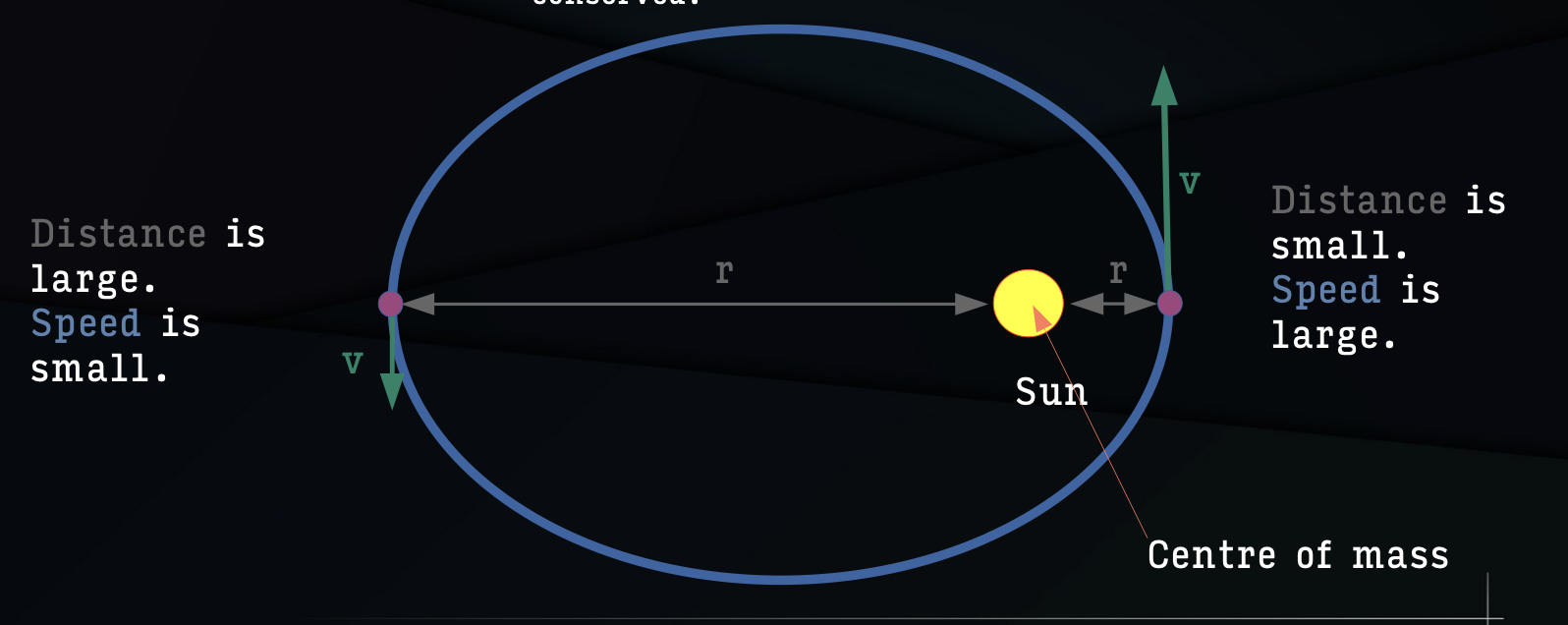
Kepler’s Second Law
A planet moves faster in the part of its orbit nearer the Sun and slower when farther from the Sun, sweeping out equal areas in equal times
Kepler’s Third Law
More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower average speeds, obeying a precise mathematical relationship.
T=365.24 sqrt root r3. T - orbital period in days; r - orbital radius in AU; 1 AU is the radius of the earth’s orbit
What did Galileo Galilei discover?
He developed and used telescopes; experimented with laws of motion & gravity. Using telescopes, he discovered that:
the moon has craters
Jupiter has moons that orbit it so not everything revolves the Earth
Venus has phases
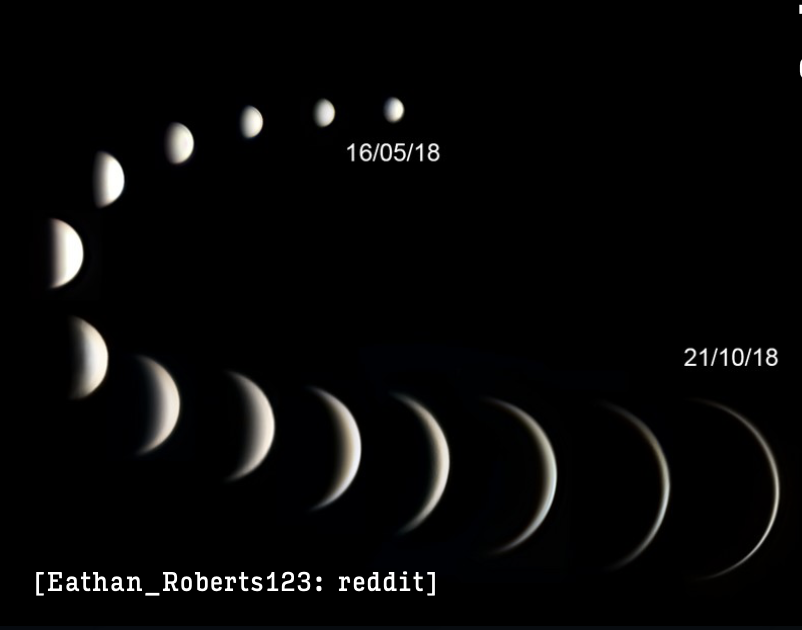
What are phases of Venus?
Galileo discovered that the apparent size of Venus changes throughout the year. The ‘new’ phase happens when Venus appears largest. the ‘full’ phase’ happens when Venus is in line with the Sun and when it appears the smallest.

Newton’s First Law
An object in motion remains in motions unless acted upon by an outside force
Newton’s Second Law
Acceleration is proportional to Force and inversely proportional to mass/
A=F/m
F=mA
More Force → more acceleration
More Mass → less acceleration
Newton’s Third Law
For every force, there is always an equal and opposite reaction force.
What is momentum? what about angular momentum?
p=mV. Mass times Velocty
Angular momentum is mass times velocity times distance (w=mVr).
Momentum is always conserved
Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
F = (G M1M2) / d²
There is a force between any two objects in the Universe. It’s proportional to the product of the masses of each object & inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Escape velocity
Escape velocity is the minimum speed an object must attain to overcome the gravitational pull of a celestial body, such as a planet, and move away indefinitely without additional propulsion.
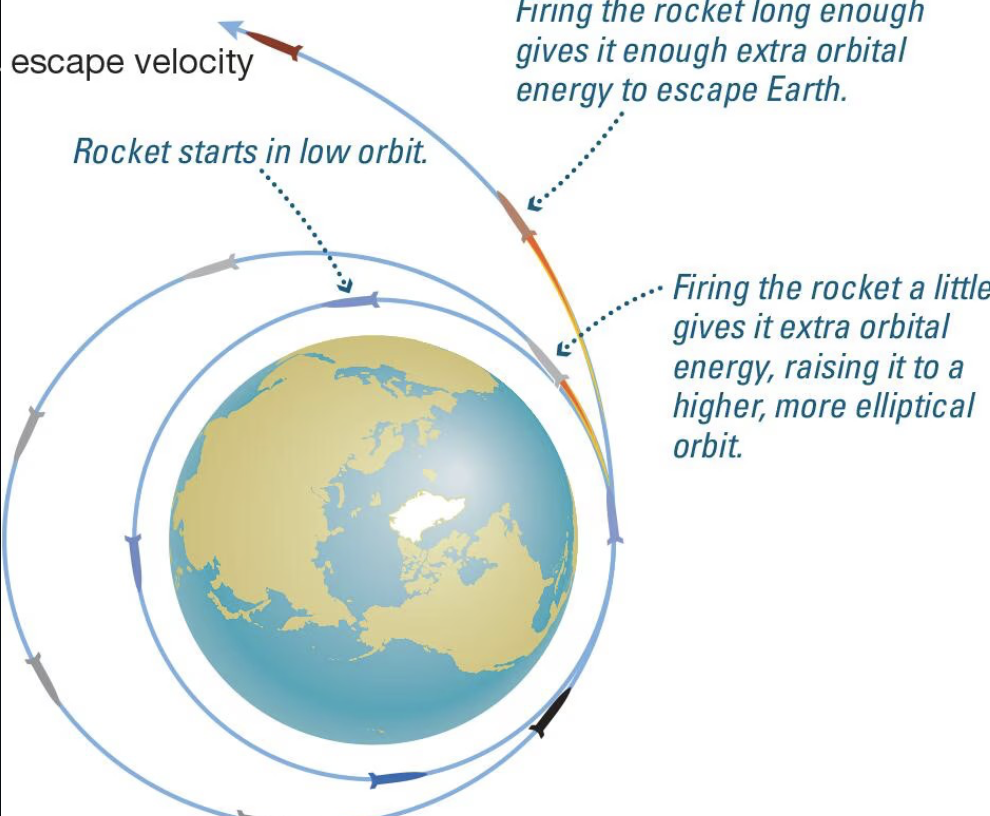
Freefall
State of object when the only force acting on it is gravity
How do tides happen?
Tides happen due to varying gravitational force squeezing both the Earth and the Moon.
Friction with the rotating earth causes the tidal bulge to lag behind. This lag applies a force on the Earth, causing its rotation to slow down.
What is Spring tide?
In a full moon or new moon, the tidal forces from the Moon and the Earth add. It happens when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are lined up - Moon can be on either side.
These are the largest tides and happen twice per month - at new moon and full moon.

What is Neap Tide?
In a quarter moon, the tidal forces from the Sun partially cancel the tidal forces from the moon. It happens when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are minimally lined up. These are the smallest tides and happen at the quarter moons.
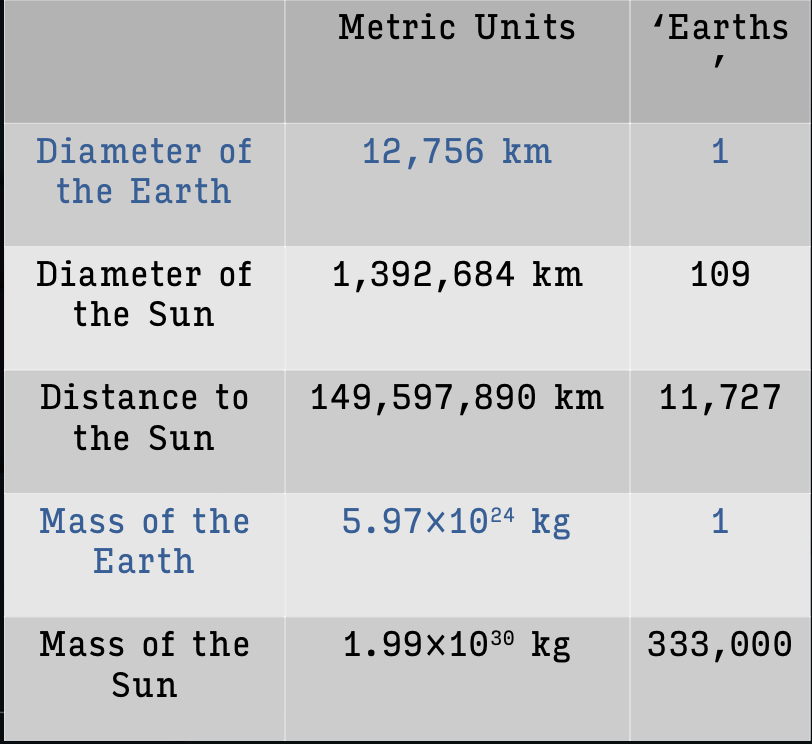
What are metrics of the Earth and the Sun?
Why is the sunset red?
Sun is actually white and radiates all colors. We see red Sun because atmosphere scatters blue light and red light makes it through the atmosphere unscattered.
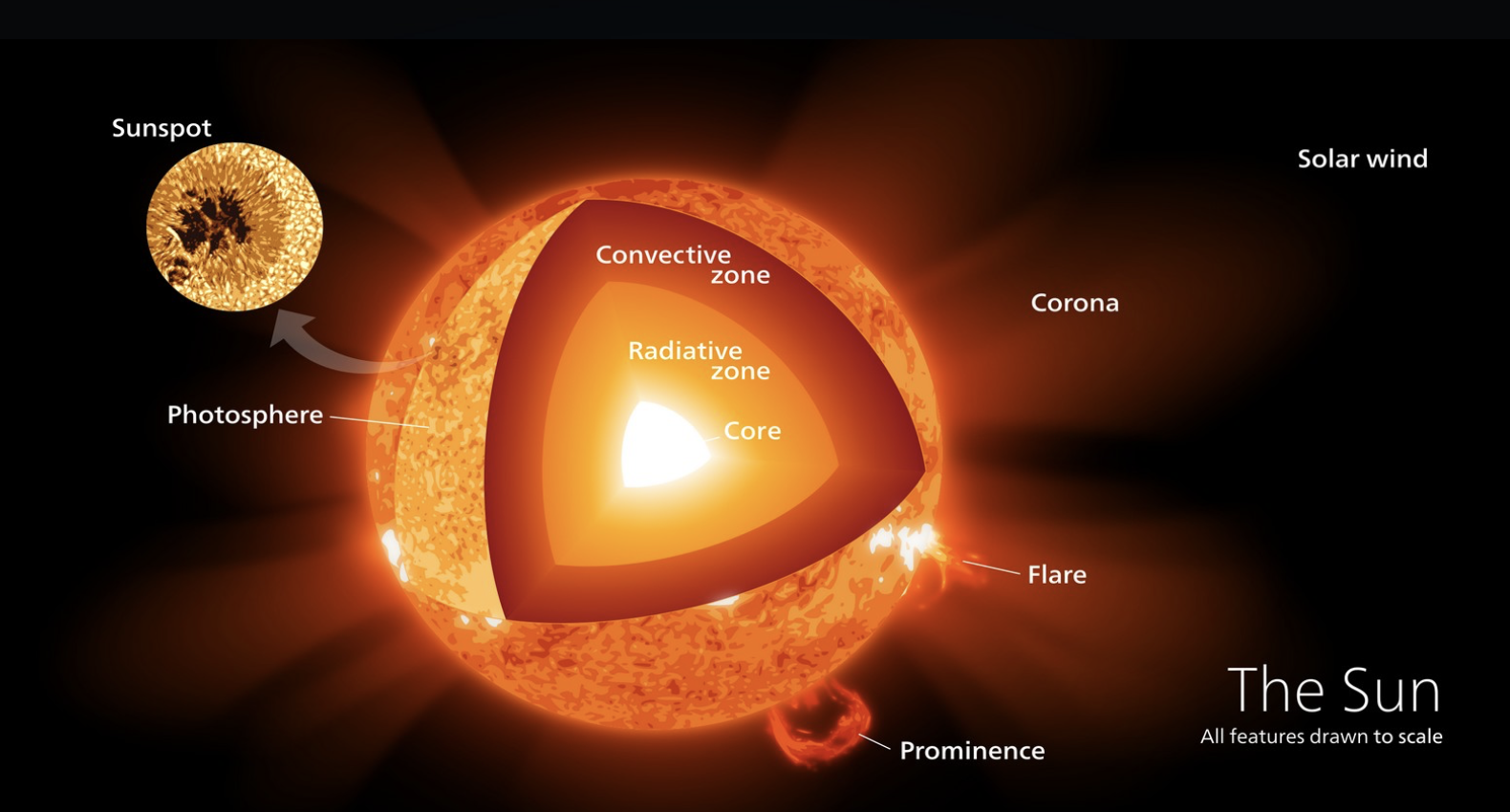
Describe structure of the Sun
What is fusion?
Fusion is process of combining 4 protons. By doing this you can get
2 positrons
2 neutrinos
2 gamma rays
1 helium nucleus.
This has lower mass then what you started with. The remaining mass becomes energy - so fusion releases a lot of energy
Why is fusion hard?
Fusion is hard because protons have positive charge - so they repel each other. Unless the speeds are really high, the protons push apart when they get close and don’t collide.
What makes fusion possible?
High temperature → high speed. It needs to be millions of degrees for fusion to happen, as well as very high density.
Describe the processes of reaching hydrostatic equilibrium in the Sun
Density above equilibrium → rate of fusion increases → temperature increases → pressure increases → core expands → density drops → equilibrium restored.
Density below equilibrium → rate of fusion decreases → temperature decreases → pressure decreases → core contracts → density increases → equilibrium restored
How does fission happen?
If a slow neutron hits a molecule, it forms a new element which is unstable. The strong force can no longer hold it together - so it breaks up into smaller pieces. The total mass of these smaller pieces is less than before so remaining mass is converted to energy.
Where are Nuclear fission and Nuclear fusion used in?
Nuclear Fission: nuclear power plants, small nuclear bombs
Nuclear Fusion: thermonuclear bombs (hydrogen bombs)
Describe core of the Sun
In core of the Sun, fusion takes place.
It’s around 10 Million C.
It’s over 100 times density of water.
Describe Radiative Zone of the Sun
It’s hot but calm.
A few million C so now fusion takes place here.
Around the density of water
Describe Convection Zone of the Sun
Hot plasma rises, bring heat to surface. It also has bright and dark regions because of plasma rising and sinking when cooling. This creates Sunspots - cooler spots on the Sun
Hundreds of thousands of C
Density of styrofoam