BIO2: Unit 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1. covalent bonds
2. ionic bonds
3. hydrogen bond
4. hydrophobic interactions
5. van der waals interactions
1. cohesion/adhesion
2. moderation of temperature
3. lower density of ice
4. versatility as a solvent
* adhesion: water sticking to other polar substances
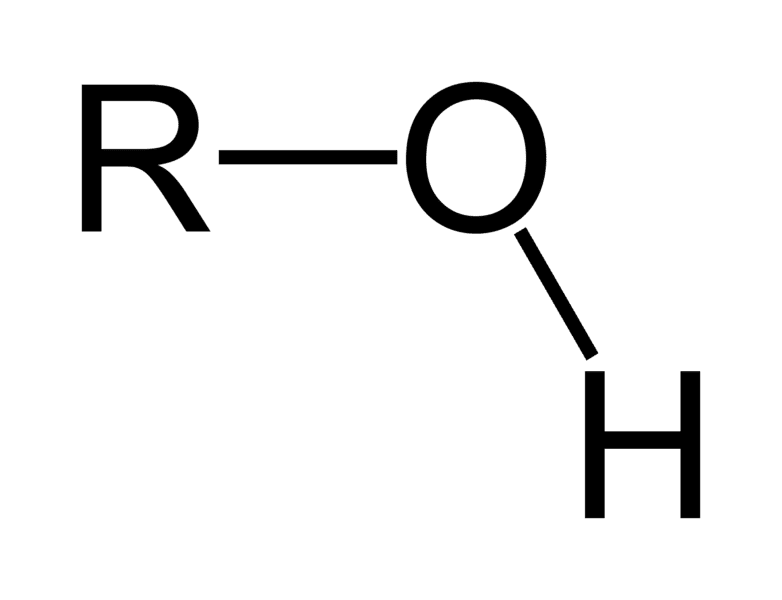
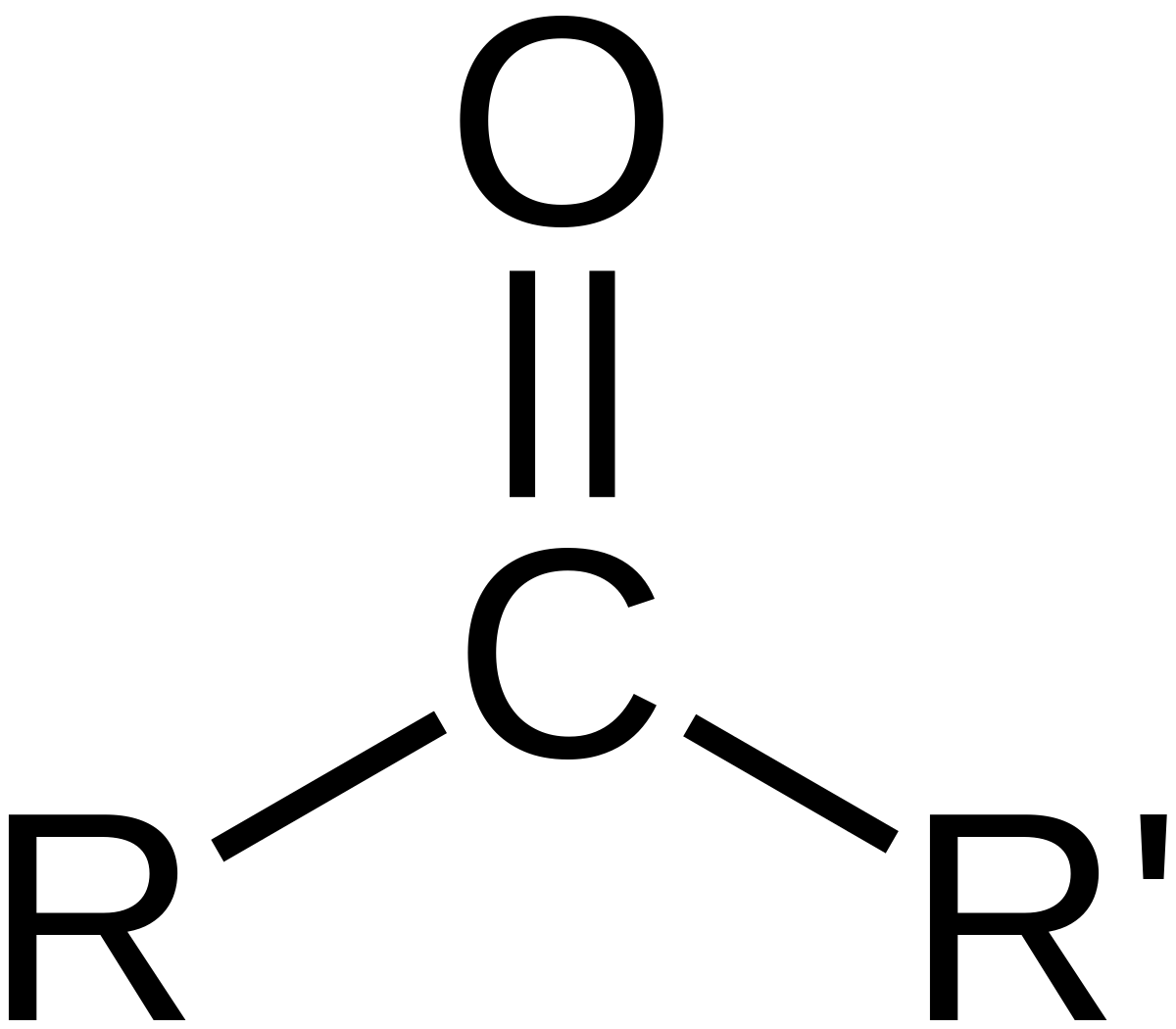
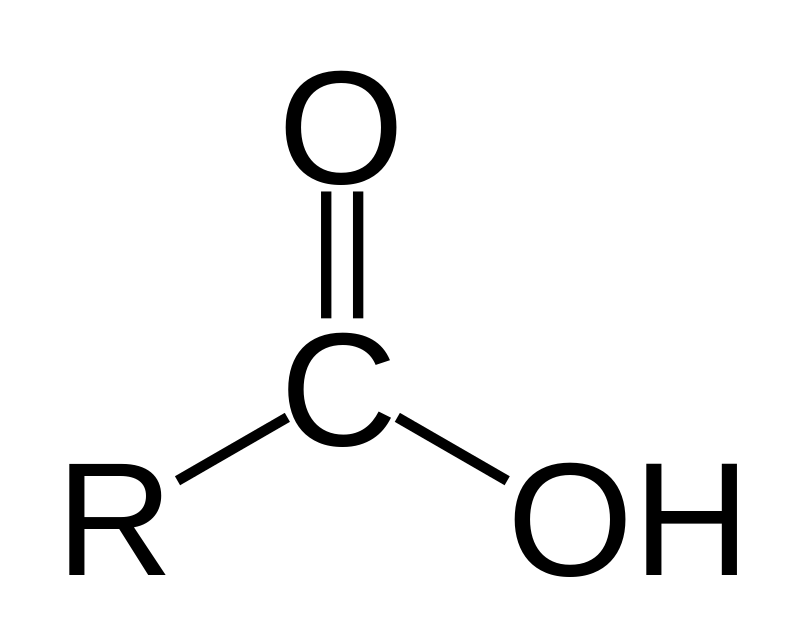
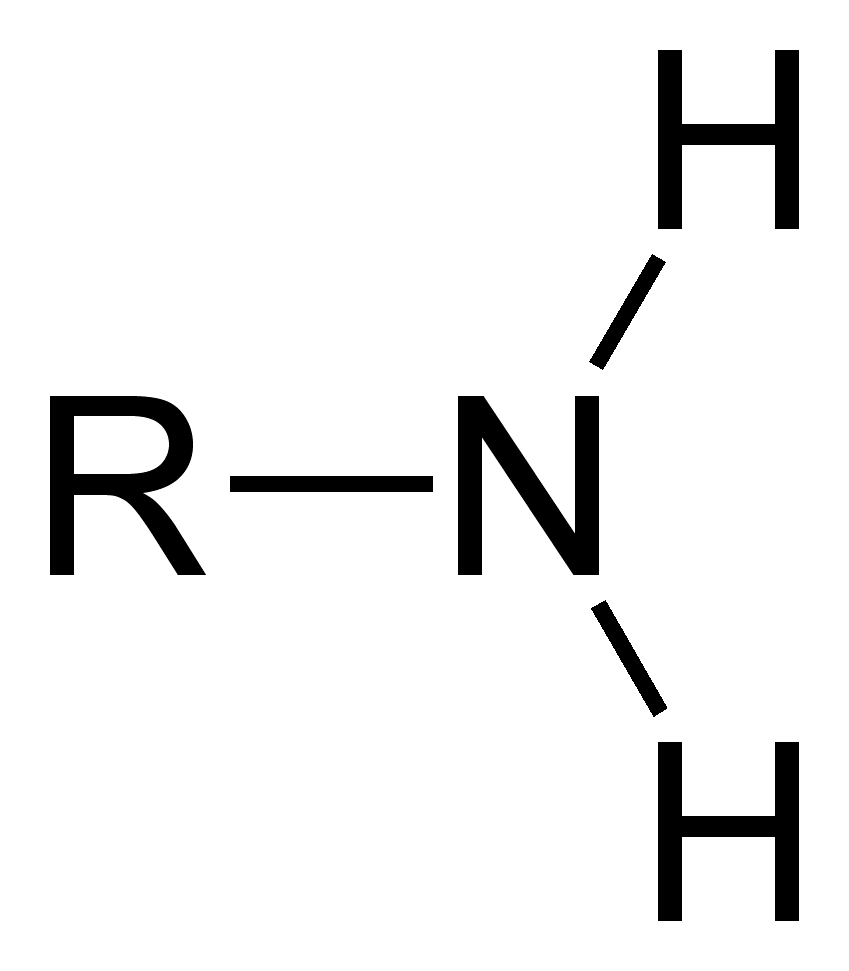
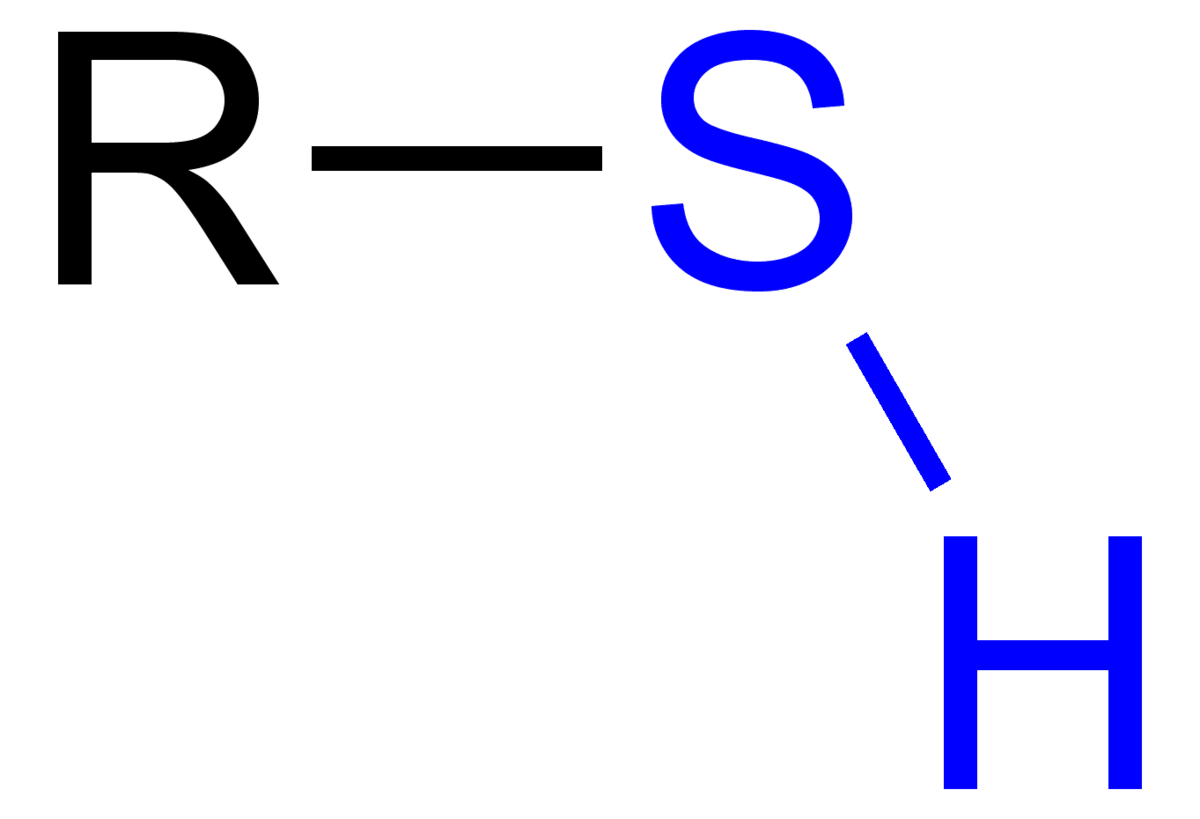
* deprotonated: doesn’t have H+
1. carbohydrates
2. proteins
3. nucleic acids
4. lipids
define: hydrolysis
a rxn in which a polymer is broken apart, consumes 1 water molecule
* monomer?
* polymer?
* link?
* atoms present?
* polysaccharide
* covalent glycosidic linkages
* C,H,O (1:2:1)
* monomer?
* polymer?
* link?
* atoms present?
* polypeptide
* peptide bond
* C,H,O,N,S
* monomer?
* polymer?
* link?
* atoms present?
* polynucleotide
* …
* C,H,O,N,P
what determines polysaccharide structure?
the sugar monomers + the position of the glycosidic linkages
1. amino group (+)
2. alpha carbon
3. carboxyl group (-)
1. 5 carbon sugar
2. phosphate group
3. nitrogenous base
* double stranded
* contains thymine
* has an H at C2
RNA
* single stranded
* contains uracil
* has an OH at C2
what are the 3 main types of lipids?
triglycerides (fats)
phospholipids
steroids
what makes lipids hydrophobic?
non-polar C-H bonds
what composes a triglyceride (fat)?
1 glycerol linked to 3 fatty acids by ester linkages
what composes a fatty acid?
a long hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group
which part of a phospholipid composes the hydrophobic core?
the hydrophobic tails form the core, the hydrophilic heads point outward
what are the steps of the Na/K pump?
3 Na binds to the protein intracellularly
1 phosphate from ATP binds to protein, rotating it to face outside the cell
the rotated protein releases Na outside of the cell
2 K binds with the protein
phosphate group is release and protein rotates back
2 K are released inside the cell
how does the Na/glucose co-transporter work?
2 Na bind and enter the cell, 1 glucose binds and enters the cell
what are the conditions inside and outside the cell that enable the Na/glucose co-transporter to work?
extracellularly: high [Na], low [glucose]
intracellularly: low [Na], high [glucose]
do Na and glucose go against or with their gradient with the Na/glucose co-transporter?
glucose goes against its gradient
Na moves with its gradient
what composes a steroid?
C-skeleton and 4 fused rings
what organelles are responsible for genetic control?
the nucleus and ribosomes
what organelles are responsible for manufacturing, distribution, and breakdown?
the endomembrane system (golgi, ER, etc.)
what organelles are responsible for energy processing?
mitochondria + chloroplast
what organelles are responsible for structural support, movement, and communication?
cytoskeleton
what are the 3 main components of the nucleus and their characteristics)?
nuclear envelope (bilayer with pores)
chromatin (includes DNA + associated proteins)
nucleolus (side of ribosome synthesis)
ribosome function?
protein synthesis
what are the 3 filaments of the cytoskeleton?
actin (microfilaments)
tubulin (microtubules)
fibrous (intermediate filaments)
actin (microfilament) function?
cell shape
cytokinesis
contractability
tubulin (microtubule) function?
intracellular transport (cell-to-cell)
cell motility (cilia + flagella)
fibrous (intermediate filament) function?
cell shape
anchoring of nucleus + organelles
why do the mitochondria + chloroplasts have its own DNA?
it is believed to be linked to a eukaryote’s phagocytosis origin
what energy centers to plants have?
mitochondria AND chloroplast
chloroplast function?
converts light energy to chemical energy
what part of the chloroplast collects light for photosynthesis?
thylakoids
peroxisome function?
breaks down fatty acids for energy
rough ER function?
makes proteins + membranes for ecport
Golgi apparatus function?
modifies proteins from rough ER
what is the path a protein travels during synthesis?
ribosomes → ER → cis Golgi → trans Golgi → final destination
lysosome function?
contain digestive enzymes that break down things
lysosomes fuse with vacuole to digest molecules
smooth ER function?
diverse functions inc manufacturing lipids, storing calcium, etc.
what types of molecules can cross membranes via simple diffusion?
small and nonpolar
what types of molecules can cross membranes via facilitated diffusion?
large, polar, or charged molecules
does facilitated diffusion require a protein?
yes, can be a carrier or channel protein
what types of molecules can cross membranes via primary active transport?
large, polar, or charged molecules
does primary active transport require a protein?
yes, a carrier protein
does primary active transport require energy?
yes, ATP is required
do molecules traveling via primary active transport move with or against the gradient?
both molecules move against the concentration gradient
what types of molecules can cross membranes via secondary active transport?
large, polar, or charged
does secondary active transport require a protein?
yes, a carrier protein
does seconadry active transport require energy?
yes, it requires indirect ATP from the Na gradient flowing from the outside of the cell in
do molecules traveling via secondary active transport move with or against their gradient?
Na moves with its concentration gradient
glucose moves against its concentration gradient
what is membrane potential?
a potential gradient that forces ions to passively move in one direction (+ attracted to - side and vice versa)
what is an electrochemical gradient?
a combination of concentration and electrical gradient (membrane potential)
what type of protein generates membrane potential?
carrier proteins
how does water act as a versatile solvent for ionic compounds?
the salt ionizes into its anion and cation which are then surrounded by the partial + and - end of the water molecules forming a hydration shell around them
how does water act as a versatile solvent for sucrose?
what can form hydrogen bonds with the sugar molecules (hydroxyl groups), dissolving it
what composes a phospholipid?
2 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol; phosphate group present
starch
monomer
function
structure/shape
where in nature?
glucose
storage in plants
helical, branched or unbranched
plants (chloroplasts)
glycogen
monomer
function
structure/shape
where in nature?
glucose
storage in animals
highly branched
animals
cellulose
monomer
function
structure/shape
where in nature?
glucose
structure/protection
unbranched, forms microfibrils
plant cell walls
chitin
monomer
function
structure/shape
where in nature?
glucose
structure/protection
unbranched, has N containing group
insect exoskeleton, cell walls of fungi
main function of triacylglycerides?
long-term energy source
what type of bonds hold the nucleotide bases together in DNA?
H-bonds
how many bonds are formed between the different nitrogenous base pairs?
3 H-bonds between G and C
2 H-bonds between A and T
how is DNA arranged in a prokaryote vs. eukaryote cell?
prokaryote: single circle of DNA
eukaryote: multiple strands of DNA (chromosomes)
do both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have cell walls?
prokaryotes: yes
eukaryotes: only in plants (cellulose) and some fungi (chitin)
what cells have peroxisomes, lysosomes, and centrosomes?
all eukaryotic cells