Lecture 6: Nervous regulation of the circulation, and rapid control of arterial pressure Dominant Role of Kidney
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1. Baroreceptor reflexes
2. Chemoreceptor reflexes
3. CNS ischemic reflexes
4. Atrial regulation
What are short term regulations of arterial blood pressure? (4)
1. Hormonal; Kidney
What are Long term regulations of arterial blood pressure? (1)
1. Capillaries (capillary fluid shift)
What are Intermediate term regulations of arterial blood pressure? (1)
bring oxygen and nutrients into body tissues
What is the major purpose of the circulatory system?
in the smallest blood vessels called the capillaries
When does capillary exchange happen?
lipid vesicles and transport through endothelial cells by endocytosis and exocytosis.
How does substances move between the blood and surrounding tissues?
The hydrostatic forces dives fluids and blood solutes OUT of the capillaries
Since capillaries have a higher fluid and blood solutes where does the hydrostatic forces drive fluids into?
the differences in (protein) between the blood and interstitial tissues.
What is osmotic (onconic) pressure (Po) generated by?
The hydrostatic pressure inside and outside the capillaries (PH).
What is hydrostatic force generated by the difference in?
higher than from the outside
Since tissues contain much less fluid than blood, PH (hydrostatic pressure of capillaries) from inside capillaries is
the blood vessels
Blood has a much higher protein content due to Albumin which draws water into
The arterial end is higher BP because the arterial end of a capillary bed is relatively closer to the heart than the venous end.
What end (venous or arterial) where is capillary blood pressure higher?
Net inward flow
With the osmotic pressure remaining the same throughout, the balance shifts from net outflow at the arterial end to what at the venous end?
This means more fluid is filtered out than reabsorbed back in.
The net outward filtration pressure is greater than the net inward filtration pressure which means what?
15%; Lymphatic system
How much fluid is left in the tissues after capillary exchange? What is the left over fluid picked up by?
external swelling or enlarged
internal organs from abdnormal accumulation of excess fluid in tissues.
Swelling: face, hands, arms, ankles, legs,
What is Edema?
1. Increased filtration
- either from increased BP or increased capillary permeability
2. Decreased reabsorption due to reduced blood albumin
3. Obstruction of lymphatic drainage
What are the three principle groups of causes of Edemas?
1. Sympathetic
- important in control of circulation
2. Parasympathetic
- important in regulating heart function
What are the two branches of the Autonomic nervous system? What do they control?
1. Sympathetic stimulation markedly increases the activity of the heart
2. Increases the heart rate and enhances its strength and volume of pumping.
What does sympathetic nerve fibers to the heart do? (2)
1. Parasympathetic plays a minor role in regulating of the circulation
2. Its most important circulatory effect is to control heart rate by way of parasympathetic nerve fibers to the heart (Vagus nerve)
What does Parasympathetic control of the heart do? (2)
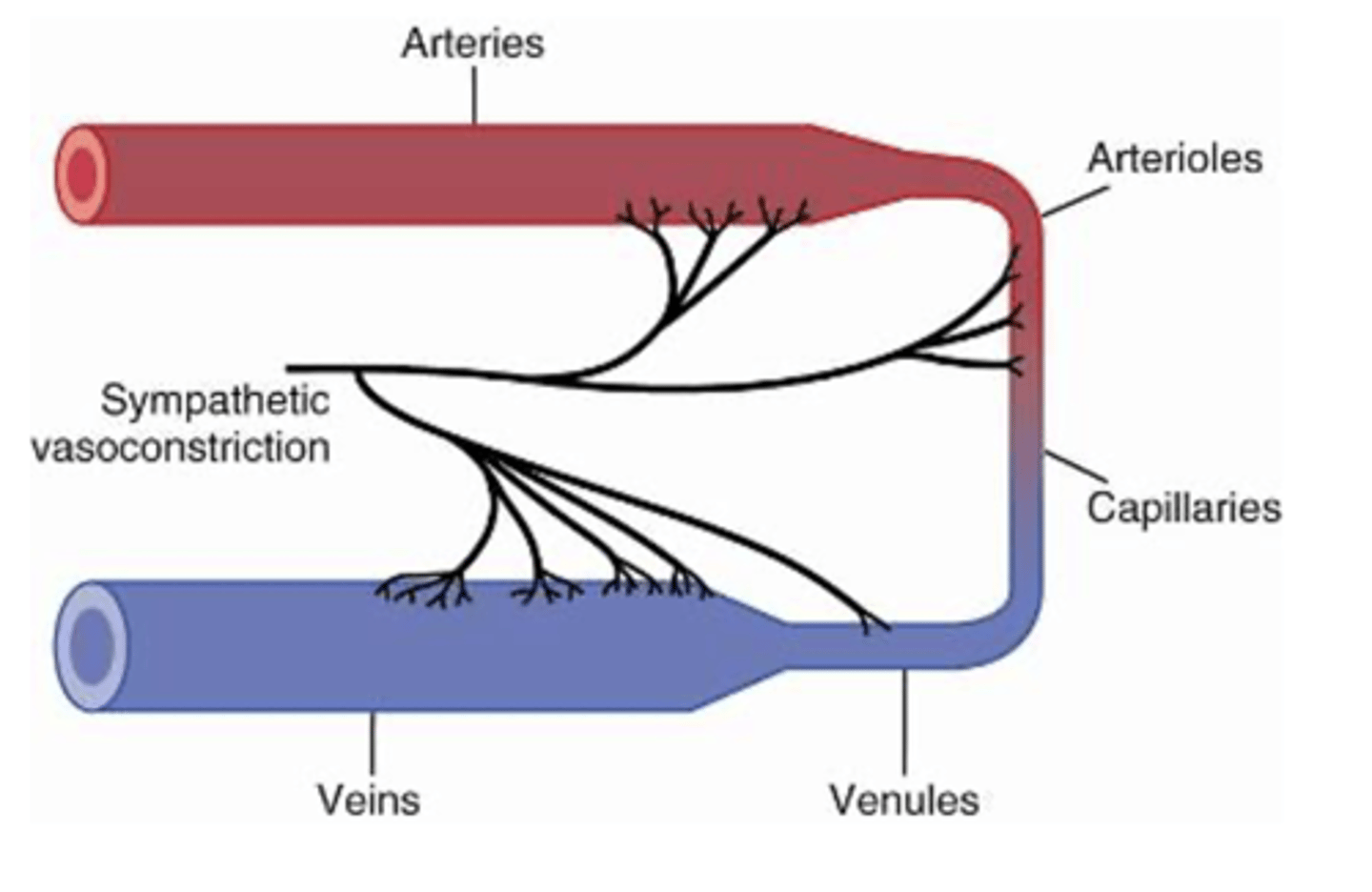
Sympathetic nerve fibers
innervate all vessels and the Large veins and the heart
except capillaries and precapillary
sphincters and some metarterioles
What do sympathetic nerve fibers innervate? What do they not innvervate?
allow sympathetic nerves to increase vascular resistance
What does the sympathetic innervation of small arteries and arterioles allow for?
control of heart rate via the vagus nerve
The Parasympathetic nervous system is mainly important in control of?
Distribution is greater in kidneys, gut, spleen, and skin
Less potent in coronary circulation and the brain
Where is sympathetic vasoconstrictor fibers distribution greater and less potent in?
all segments of the circulation
Where are Vasoconstrictor fibers distributed throughout
Cardiac Output x Total Peripheral Resistance
What does arterial pressure = ?
1. Constricting almost all arterioles of the body which increases total peripheral resistance
2. Constricting large vessels of the circulation thereby increasing venous return and cardiac output
3. Directly increasing cardiac output by increasing heart rate and contractility.
How can arterial pressure be increased? (3)
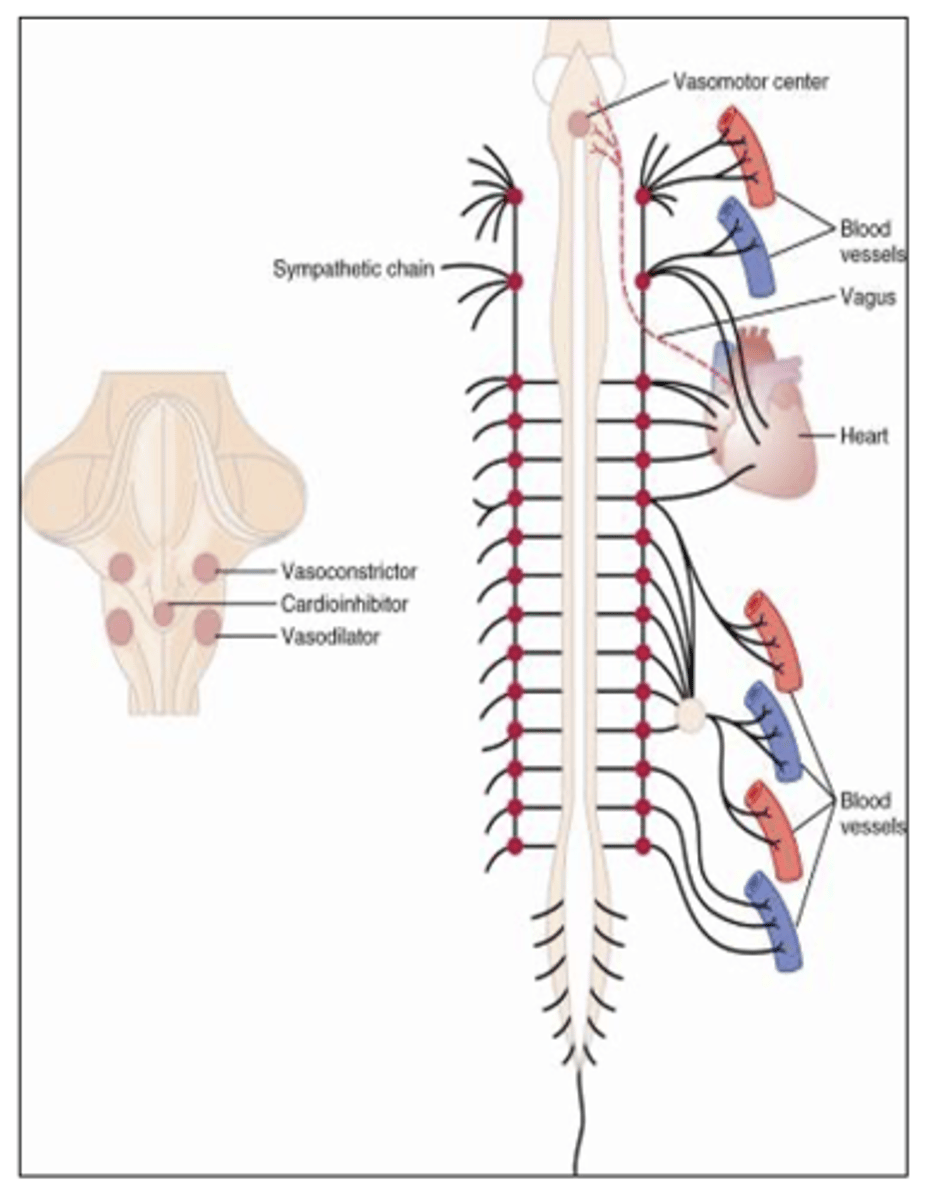
The VMC transmits impulses downward through the cord to almost all blood vessels
Where does the Vasomotor center (VMC) transmit impulses?
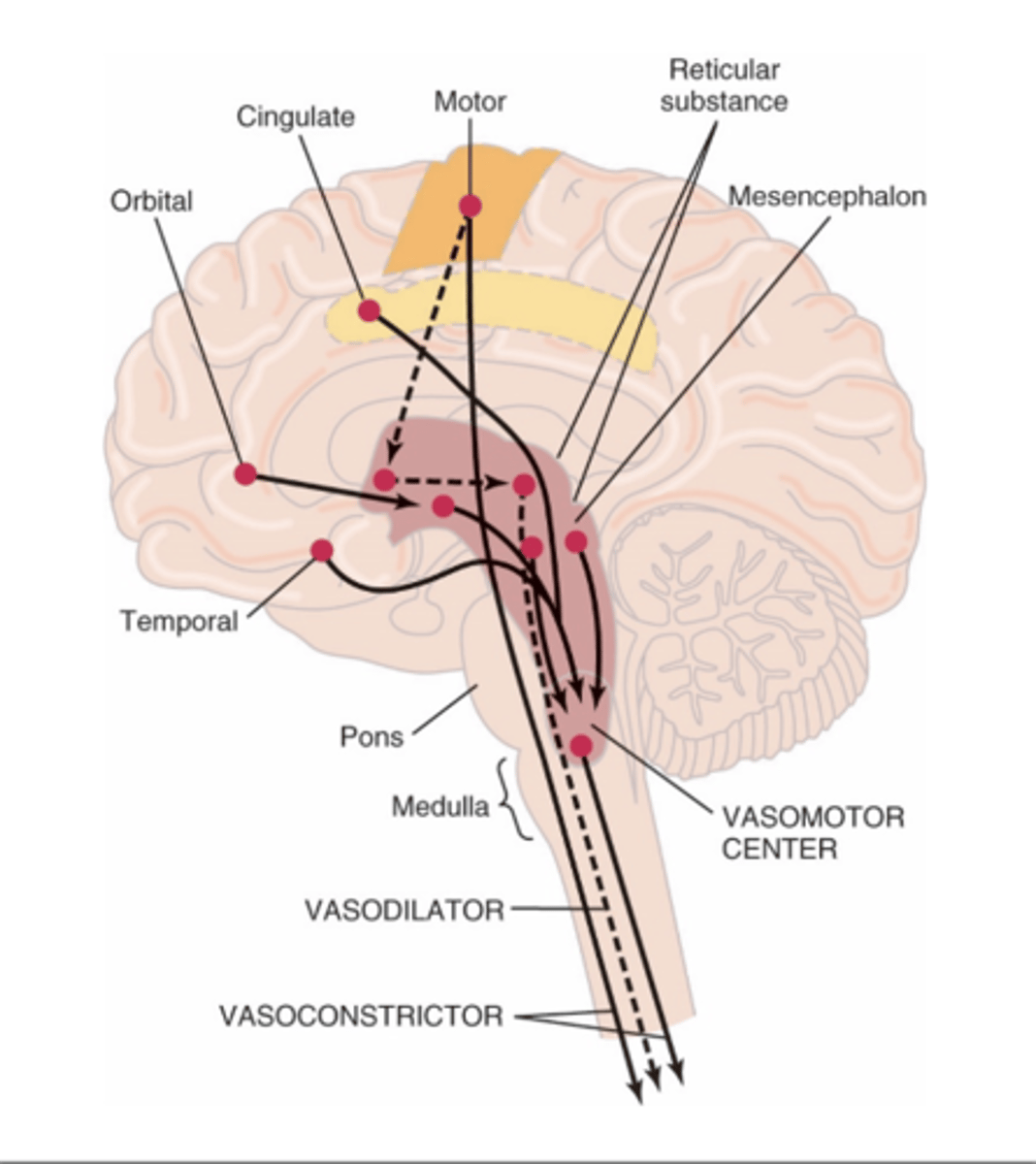
VMC is located bilaterally in the reticular substance of the medulla and the lower third of the pons
Where is the vasomotor center (VMC) located?
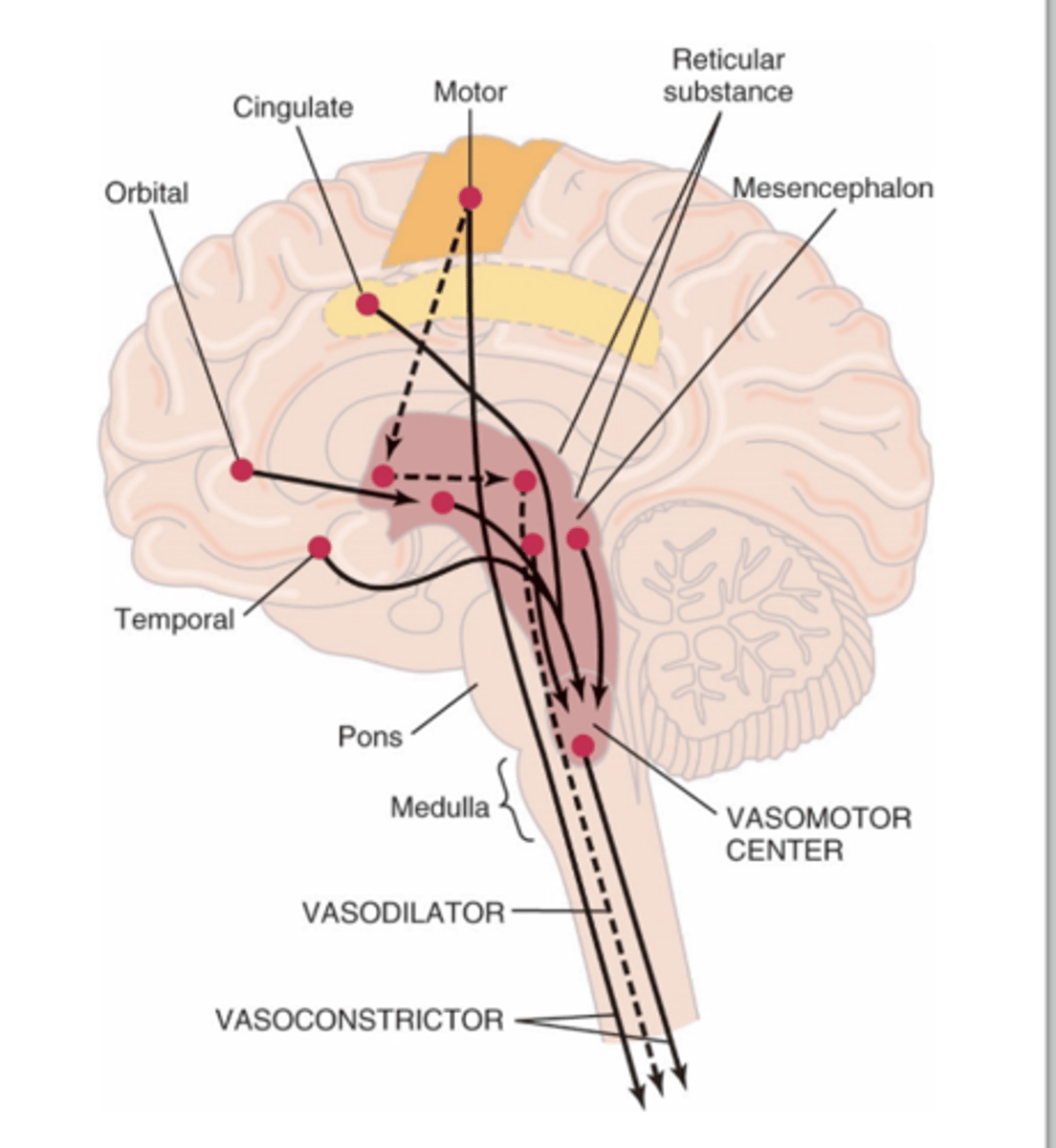
1. Vasoconstrictor area
2. Vasodilator area
3. Sensory area
The vasomotor center (VMC) is composed of what three areas?
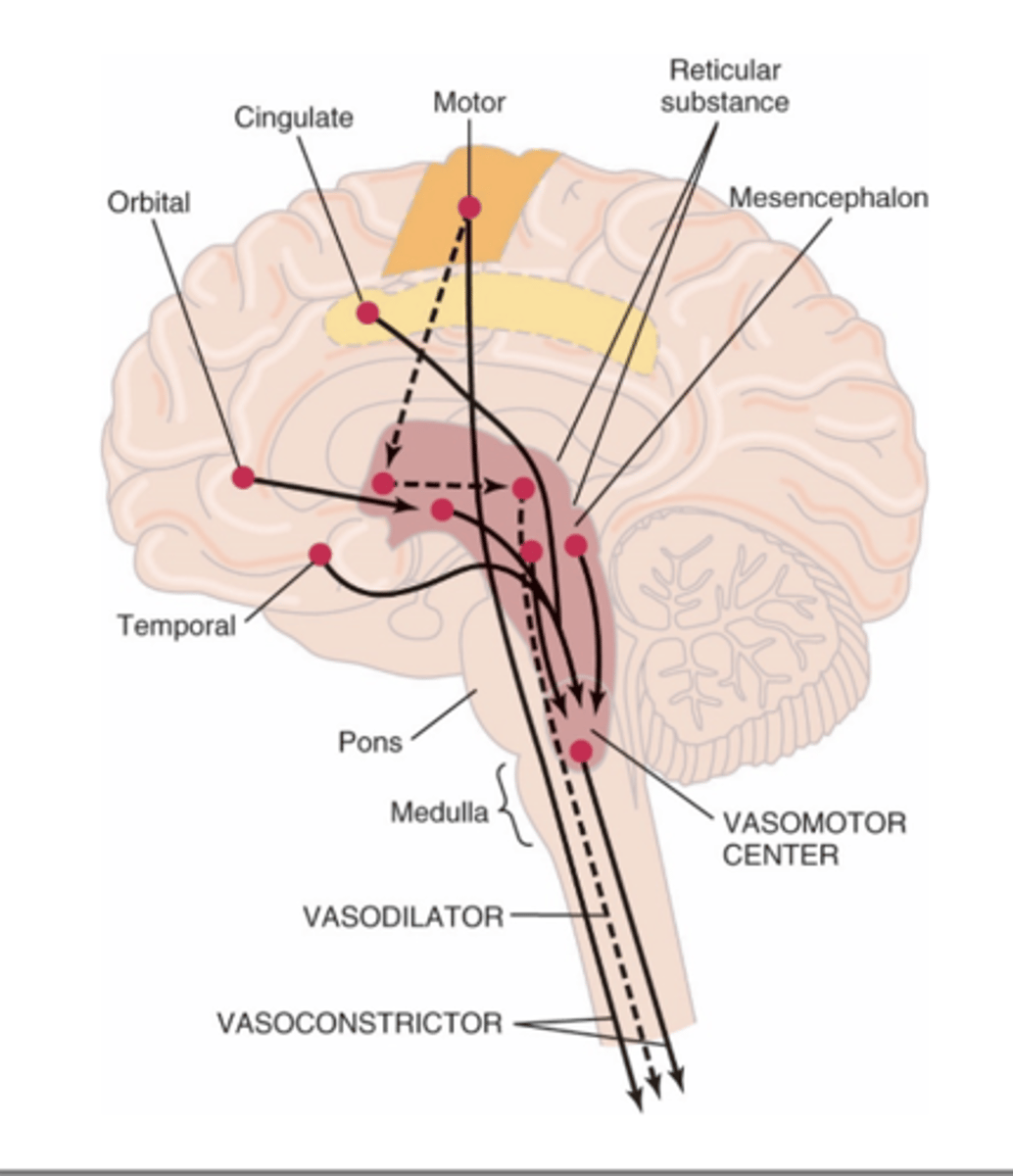
Vasoconstrictor area of VMC transmits signals continuously to sympathetic nerve fibers called sympathetic vasoconstrictor tone. These impulses maintain partial state of contraction in blood vessels called vasomotor tone.
What does the vasoconstrictor area do in the (VMC)?
Lateral portions of VMC controls heart activity by increasing heart rate and contractility
What does the lateral portions of the vasomotor center control?
Medial portion of VMC transmits signals via vagus nerve to heart to decrease heart rate
What does the medial portion of the vasomotor center control?
Norepinephrine (NE)
What is the neurotransmitter for the vasoconstrictor nerves?
constricts blood vessels via alpha adrenergic receptors
The Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine which does what to blood vessels?
Beta2 receptor
Epinephrine can also dilate vessels through a potent
Intense emotional disturbances cause fainting due to
vasodilator reaction.
What is vasovagal syncope?
1. Constricting almost all arterioles of the body which increases total peripheral resistance (TPR)
2. Constricting large vessels of the circulation thereby increasing venous return and cardiac output
3. Directly increases cardiac output by increasing heart rate and contractility
The nervous system via the vasomotor center (VMC) can increase arterial pressure (AP) within seconds by (3).

during exercise or with fear
When can rapid increases in arterial pressure occur?
important in short term regulation of arterial pressure
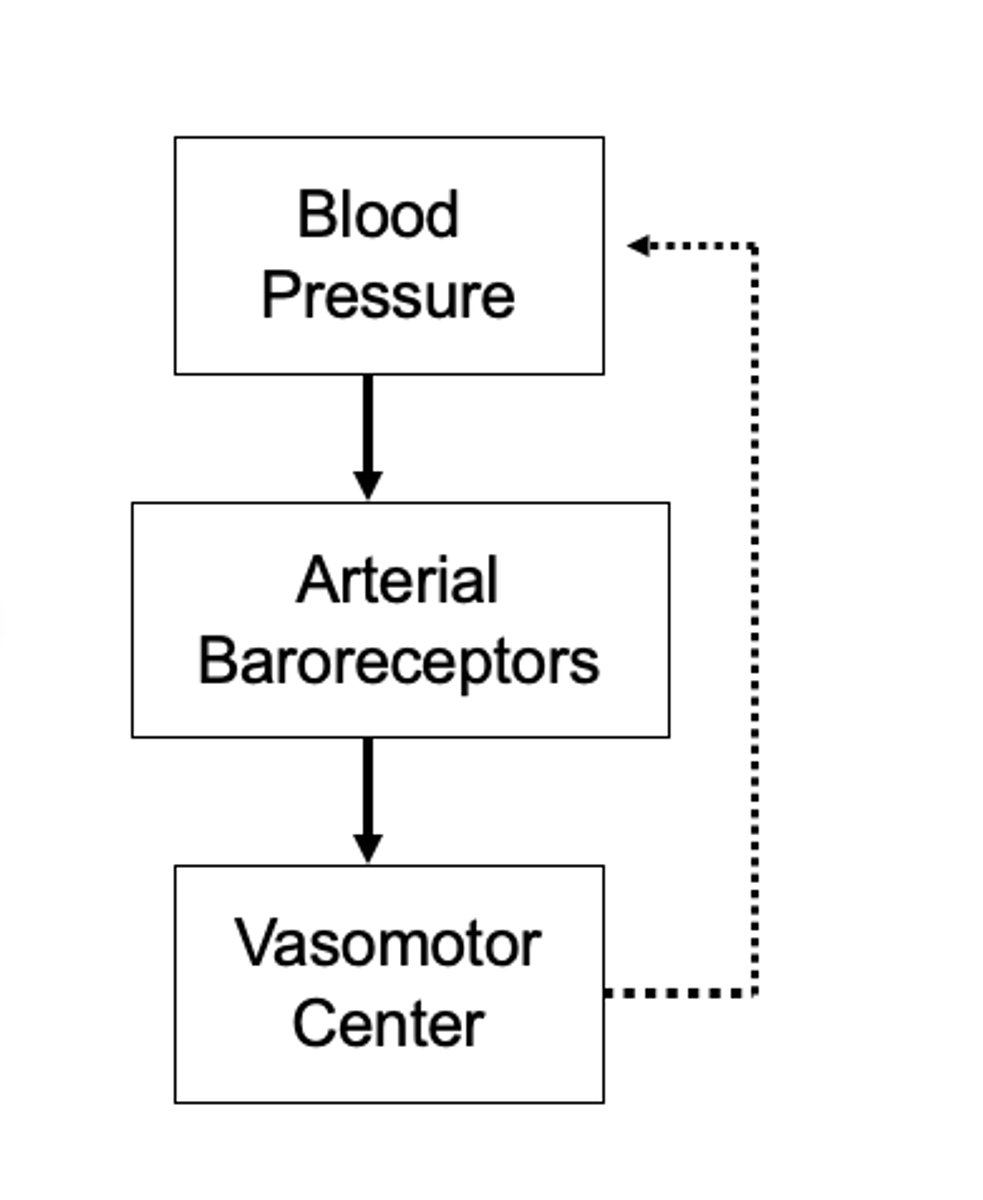
What is the arterial baroreceptor reflex important for?
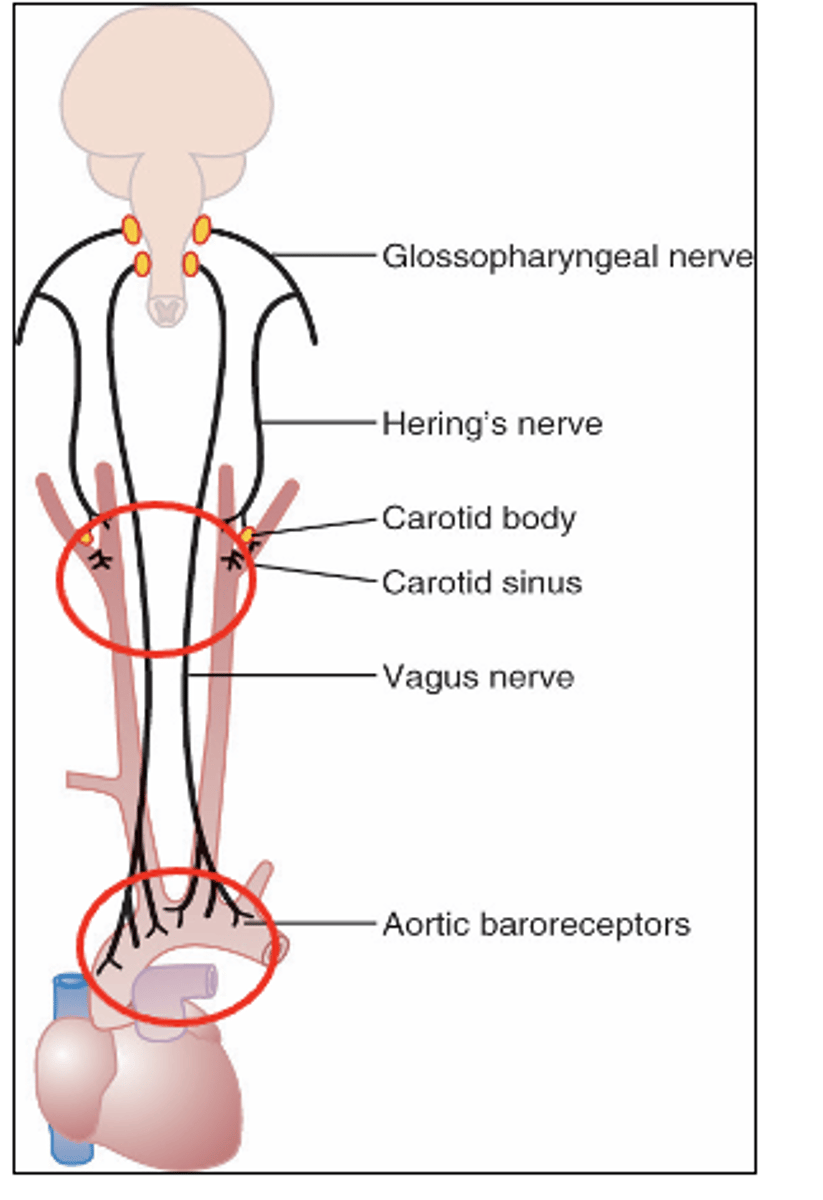
Reflex is initiated by stretch receptors called baroreceptors or pressoreceptors located in the walls of the large systemic arteries
What is the reflex initiated by in arterial baroreceptors?
transmit signals to the VMC and feedback signals are sent via the automonic nervous system to the circulation to reduce BP back to normal
A increase in BP stretches baroreceptors and causes them to
walls of the carotid bifurcation called the carotid sinus and in the walls of the aortic arch
Baroreceptors are nerve endings located in the (2)
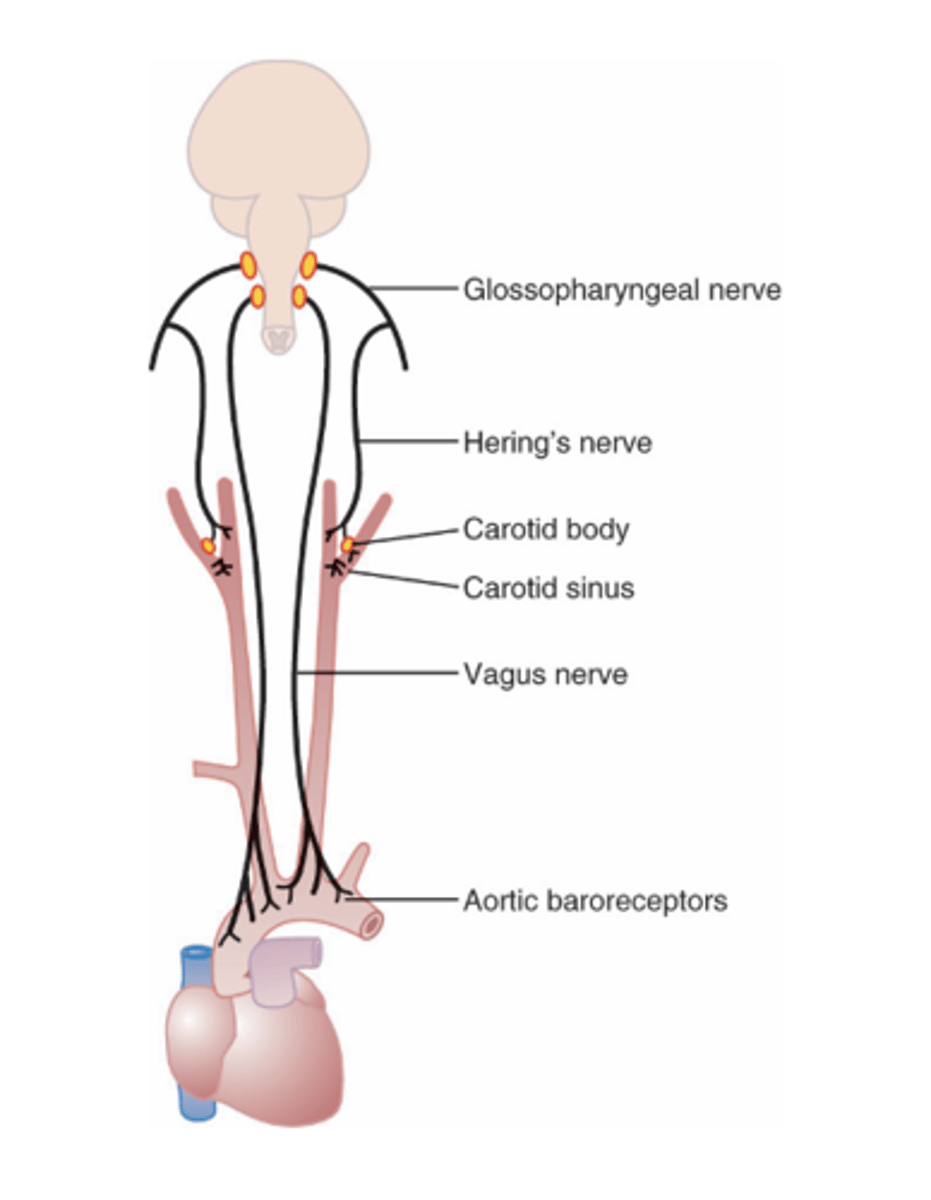
are transmitted by the Hering’s nerve to the glossopharyngeal nerves and then to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the medulla
Where are signals from the carotid sinus in baroreceptors transmitted by and to?
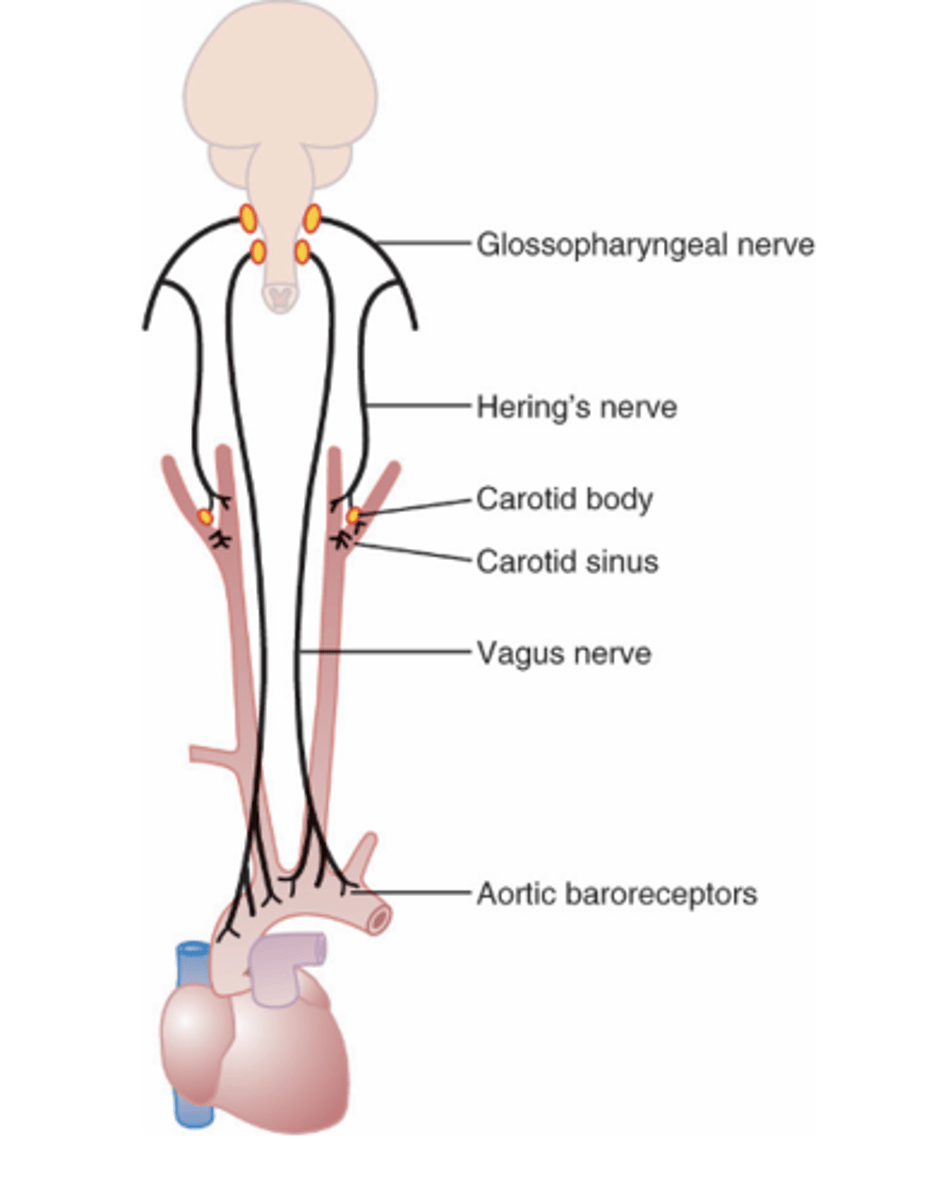
transmitted through the vagus into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS)
Where are signals from the aortic arch in the baroreceptors transmitted through?
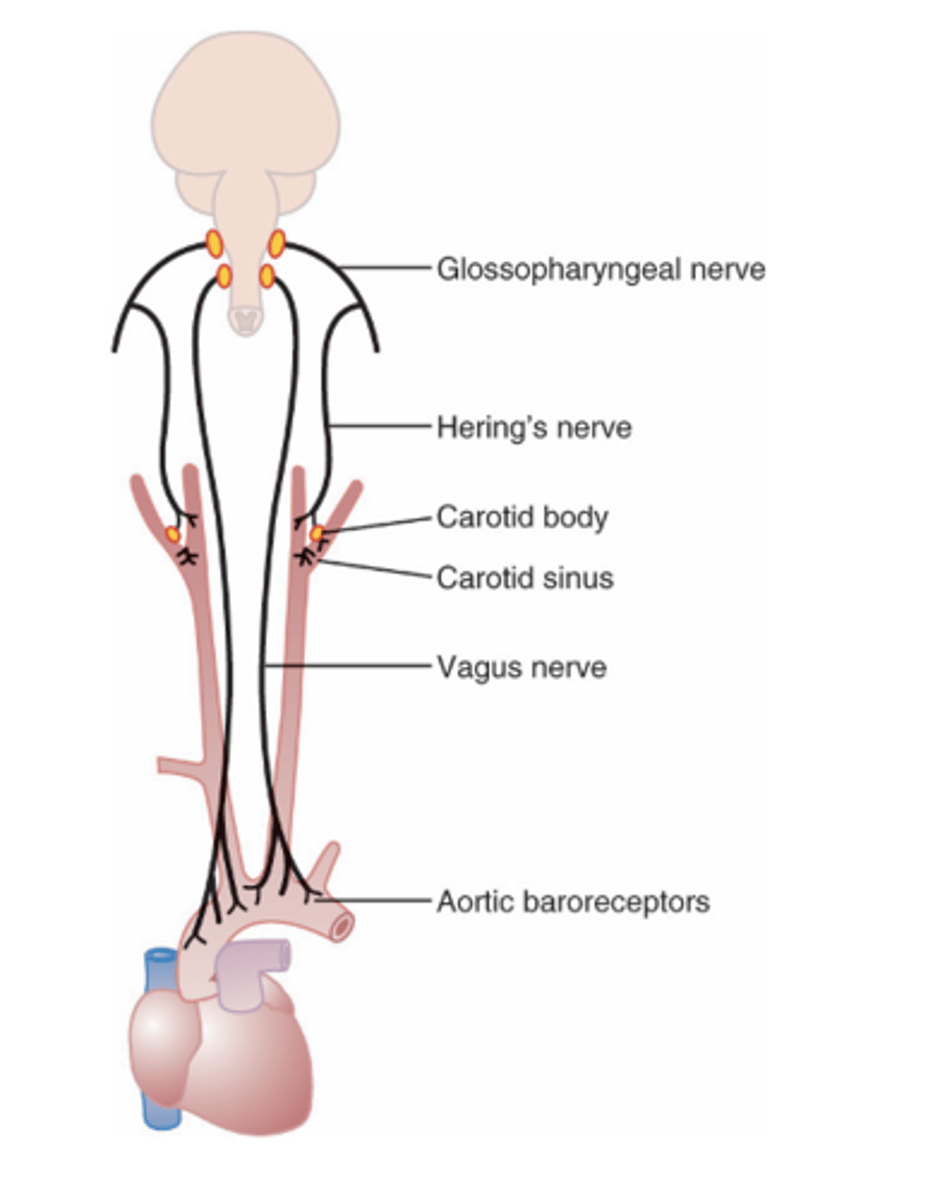
Between 60 and 180 mmHg
What do carotid sinus baroreceptors respond to pressures between?
arterial pressure
Baroreceptors respond to changes in
100mmHg
Baroreceptors reflex is most sensitive at a pressure of
1) Inhibition of the vasoconstrictor
2) Activation of the vagal center
As pressure increases the number of impulses from carotid sinus increases which results in (2)
1. increase in heart rate
2. an increase in total peripheral resistance
3. constriction of veins
MOVING FROM THE SUPINE TO A STANDING POSITION RESULTS IN AN (3)
body posture
Baroreceptors maintains relatively constant pressure despite changes in
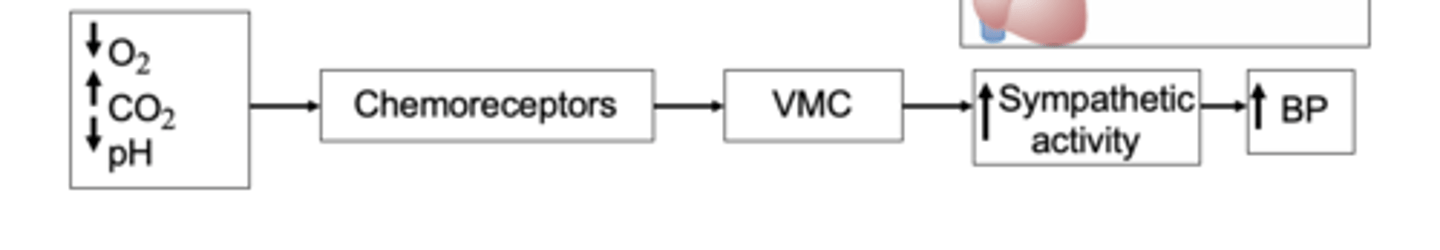
1. Lack of O2
2. Excess of CO2
3. H ion excess
Chemoreceptors are chemosensitive cells sensitive to what? (3)
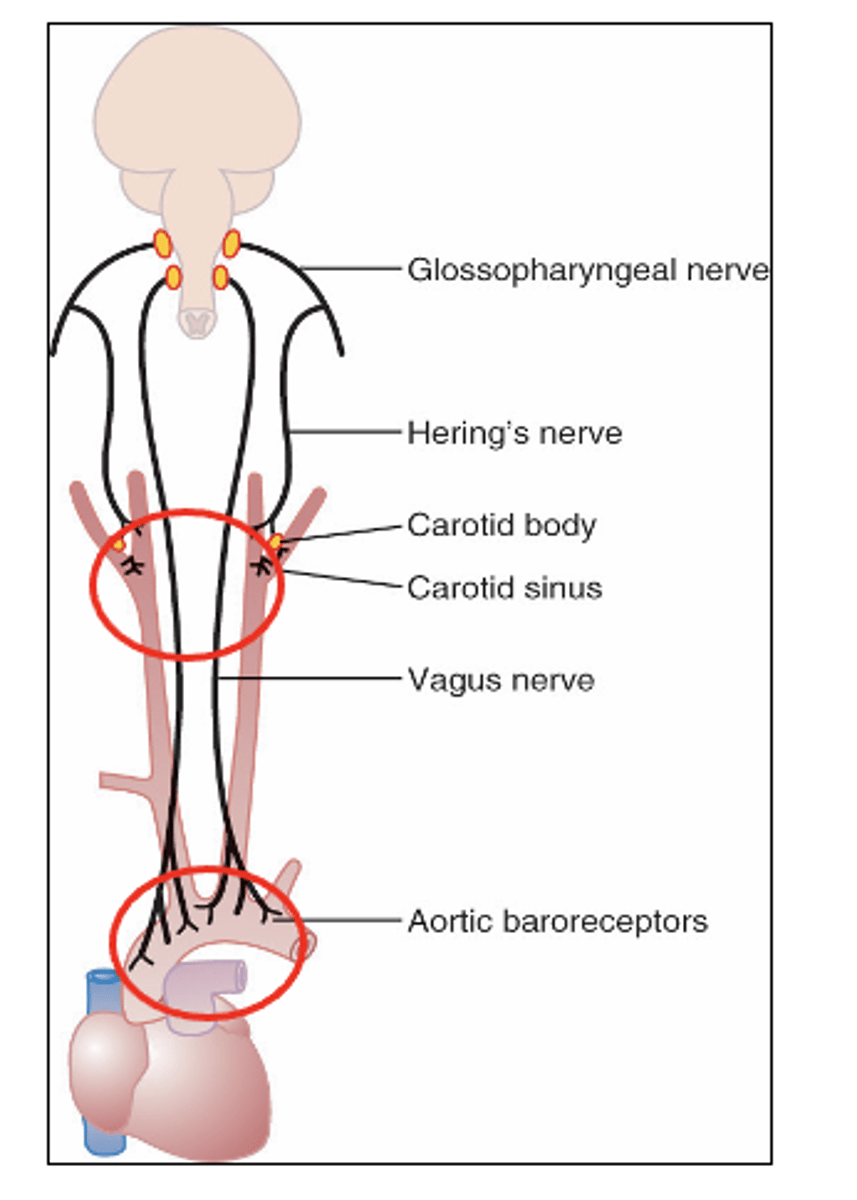
Chemoreceptors are located in carotid bodies near the carotid bifurcation and on the arch of the aorta.
Where are chemoreceptors located?
excitation of the vasomotor center
What does the activation of chemosensitive receptors results in
Chemoreceptors are not stimulated until pressure falls below 80 mmHg
When are chemosensors stimulated?
cerebral ischemia
What is the CNS ischemic response activated in response to?
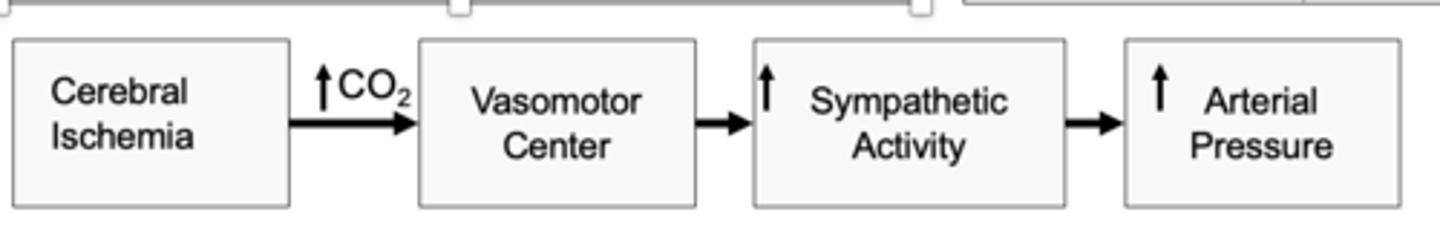
vasomotor center (VMC) thereby increasing arterial pressure
in CNS ischemic response reduced cerebral blood flow causes CO2 buildup which stimulates
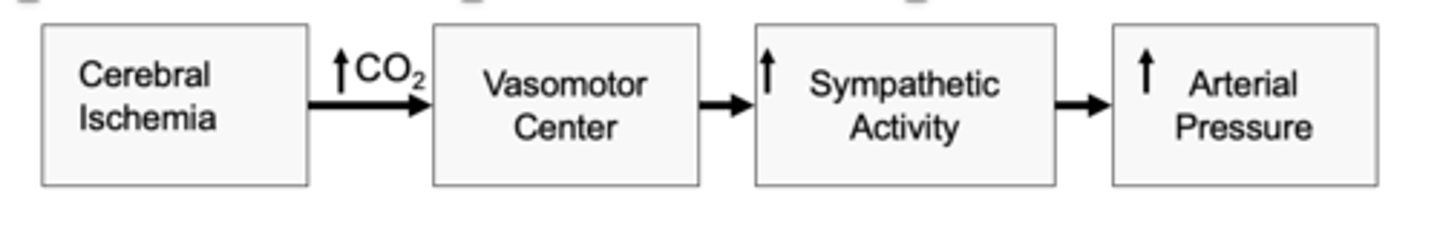
CNS Ischemic response
What is one of the most powerful activators of the sympathetic vasoconstrictor system?
until pressure falls below 60 mmHg; greatest activation occurs at pressures of 15-20 mmHg
when is CNS Ischemic response is activated?
vasomotor center
Prolonged CNS ischemia has a depressant effect on the
blood volume
Low pressure receptors in atria and pulmonary arteries minimize arterial pressure changes in response to changes in
low pressure receptors which in turn lower arterial pressure
Increases in blood volume in atrial and pulmonary artery reflexes activates
1. Decreasing rate of ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
2. Increasing glomerular filtration rate
3. Decreasing Na+ reabsorption
Activation of low-pressure receptors in atrial and pulmonary artery reflexes enhances Na+ and water by: (3)?
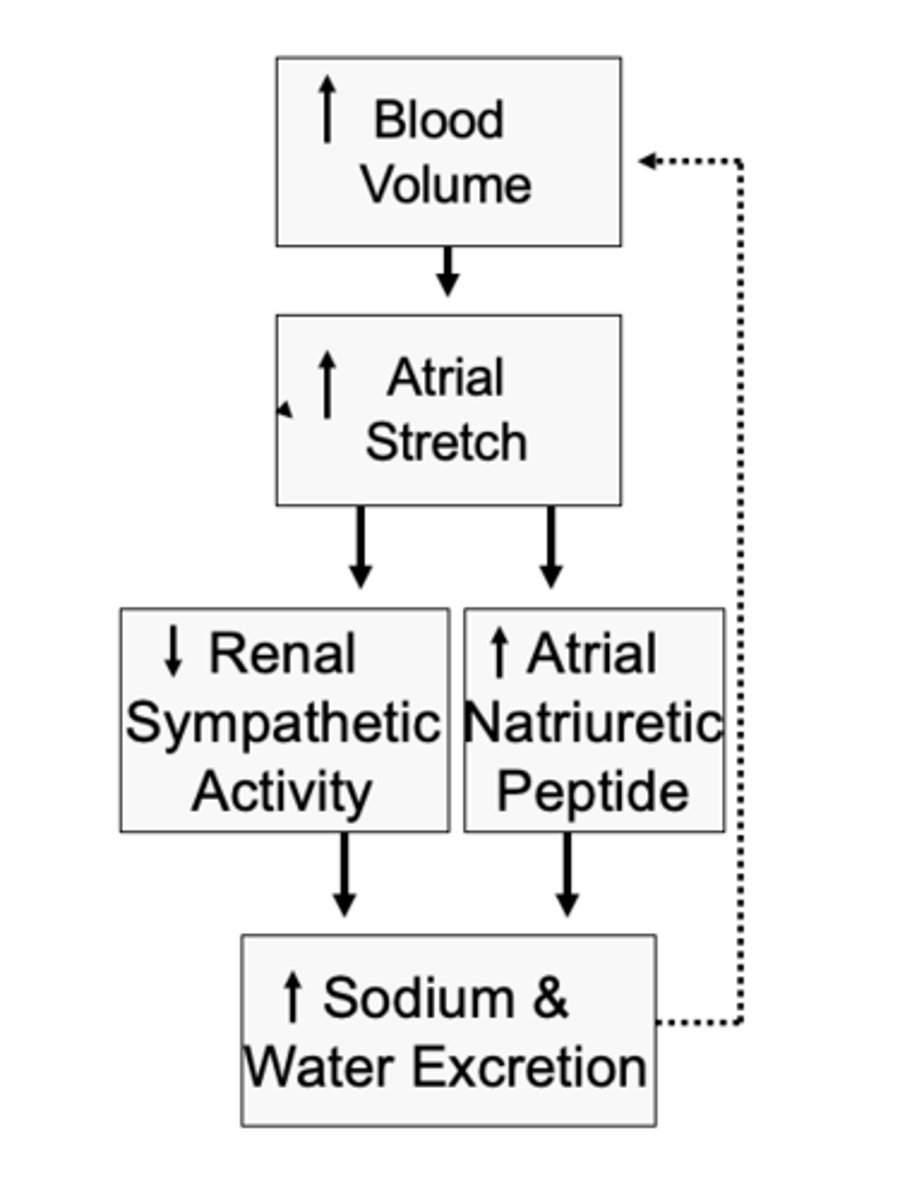
Prevents the accumulation of blood in the veins, atria and pulmonary circulation.
What does the bainbridge reflex (atrial reflex) prevent?
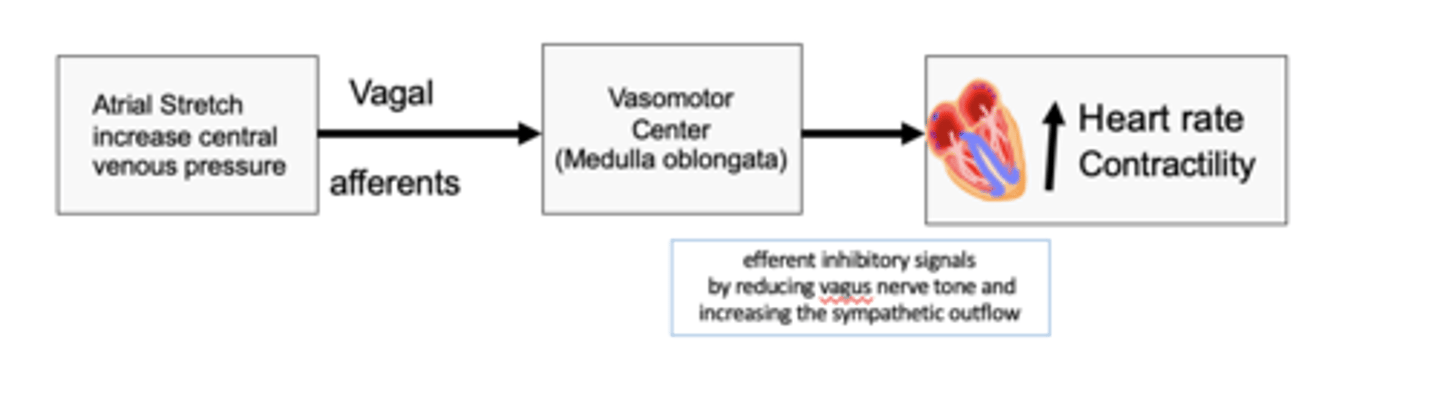
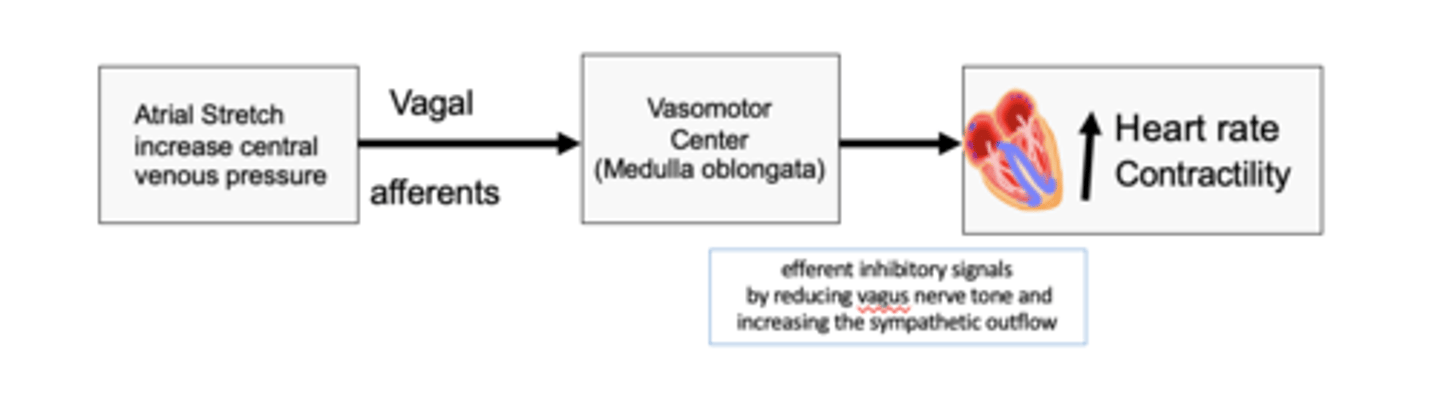
occurs when the heart rate increases in response to a rise in atrial pressure
The brainbridge reflex (artial pressure) occurs when?
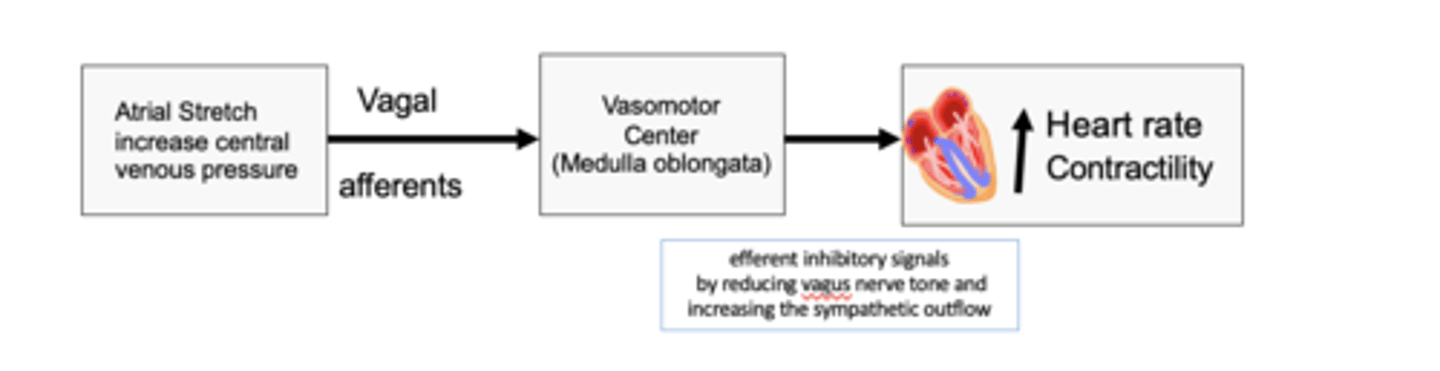
to increase heart rate and contractility
The bainbridge reflex (atrial reflex) stretch of the atria sends signals to VMC via vagal afferent to do what?
Increase in blood volume stretch of the atria leading to:
- (+) ANP release causing vasodilation of renal vessels, diuresis, natriuresis.
b.Hypothalamus:
1. (-) ADH (vasopressin) water diuresis.
2. (-) sympathetic discharge vasodilation of renal vessels
c. stretch SA node and increase HR (the tachycardia is not as a result of sympathetic rather than the stretch receptors )
Anti-diuretic hormone = ADH (released by the hypothalamus) It is secreted by the posterior pituitary in response to ↑blood osmolarity (often due to dehydration). - Action: Promote water reabsorption by the kidney tubules: H2O moves back into the blood and less urine formed
What does atrial reflex do when blood volume increases?
Decrease in blood volume causes
a. (-) ANP release causing vasoconstriction of renal vessels, diuresis,
natriuresis.
b. Hypothalamus:
1. (+) ADH water retention.
2. (+) sympathetic discharge vasoconstriction of renal vessels
What does atrial reflex do when blood volume Decreases?
renin-angiotensin system (RAS).
What is constant long-term control of blood pressure determined by what system?

CO or TPR
Increased Fluid Volume Can Elevate Arterial Pressure by Increasing (2)?
Increases
As the arterial pressure rises, the urine volume output
As the arterial pressure rises, the urine volume output increases. This increased urinary output.
What is pressure diuresis?
approximately equal increase in Na+ output
what is pressure natriuresis?
Renin
What is the protein enzyme released by the kidneys when the arterial pressure falls too low
1. When there is excess salt in the ECF, the osmolality of the fluid increases, and this in turn stimulates the thirst center in the brain, making the person drink extra amounts of water to return the extracellular salt concentration to normal. This increases the ECF volume.
2. The increase in osmolality caused by the excess salt in the ECF also stimulates the hypothalamic-posterior pituitary gland secretory mechanism to secrete increased quantities of ADH hormone that causes the kidneys to reabsorb greatly increased quantities of water from the renal tubular fluid, thereby diminishing the excreted volume of urine but increasing the ECF volume.
As salt accumulates in the body, it also indirectly increases the extracellular fluid volume for what two basic reasons?