ChETE 3 - Shaping Plastic (Extruders)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Thermoplastic materials
are fuily reacted or polymerized products that, when subjected to sufficient heat, will soften.
Thermoset plastics
are polymers that have not fully completed their polymerization reaction, but do so when activated, usually by heat.
tooling cost
One of most important considerations when thinking of producing a plastic dimensional part is
tooling cost
the cost of molds and other devices that will be needed to shape the plastic into the desired form. The cost of tooling is directly related to the forces that will be required to create the form.
Profile extrusion
to make continuous solid profiles or tube simply requires a shaped aperture through which to push the plastic. Tooling cost is low
Thermoforming
is done with open molds using vacuum and compressed air at moderate levels.
Extrusion blow molding
__________________ of bottle forms requires a water-cooled mold consisting of two matched halves.
Injection blow molding
Which has higher cost, Injection or extrusion blow molding?
Resin type
Geometry of the finished part
Number of units required
Dimensional tolerance requirements
Container wall thickness
Other factors that need to be considered in molding are:
Melt flow rate
is a method of quantifies the behavior of plastics at elevated temperatures
(reference method ASTMD 1238)
Melt flow rate reference test method
thermoforming
The finished product of the extruder is also used for
heat, shear, and pressure
The purpose of an extruder is to use this to transform the solid plastic into a uniform melt
Regrind
Scrap from plastic processes converted into granular form
barrel
Most extruders contain a single screw inside a hollow tube called a
Hopper and feed port
Barrel
Screw
Motor
Screen packs/breaker plates
Instrumentation devices
Die
Machine elements of extruder:
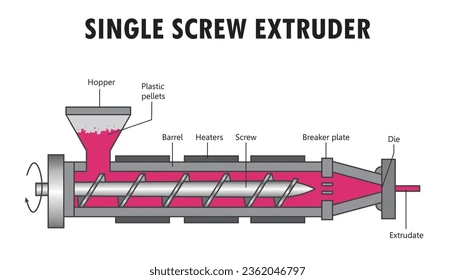
Identify parts of extruder

Hopper and feed throat
This is where the pellets are placed
Barrel
Hollow tube which contains the screw and is equipped, on its exterior, with elements for heating and cooling
Screw
Has helical channels and acts to heat and melt the pellet to a liquid state and convey them to the die.
Motor
Also called the gear reduction system is used to turn the screw
Screen packs/ Breaker plates
Used to filter the melt and create back pressure
Die
Determines the shape of the extrusion
Instrumentation
Includes the thermocouples, pressure gauge valves, and other devices used to indicate and control machine variables like T, P, and screw rotation speed
Conveying/Feeding
Melting/Transition
Pumping/Metering
Mixing (optional)
The melting phase is broken down into three distinct steps:
Hopper
Are usually circular in cross section and the diameter gradually decreases as it nears the feed port
Bridging
A too rapid decrease in diameter can cause this where a compressed plug of material cuts off the flow to the extruder
Gravity
This is usually the driving force for the flow of the plastic into the extruder
Augers
Some hoppers have this to help force plastic material into the feed throat
Stirrer
Some hoppers have this to help wipe the material from the hopper walls
Hoppers
Extruders can have more than one _______
Starved
If the rate is too low, the screw is ____________. There will be less molten plastic in the other sections and output will be low
Melting will not be complete, and output may contain unmelted particles
What happens if rate is too high?
Melting of the plastic
What is the main function of the melting section?
Metering section
This is responsible for delivering the molten polymer at a desired and uniform rate to the die.
Single screw extruder
These are used to melt and convey the polymer but are not used to mix the polymer resin and other additives.
5-20 cm (2-8 in)
A typical extruder would have a barrel diameter of
20:1 - 30:1
Extruder sizes are described as the screw length to barrel diameter ratio. Most extruders fall in this range
Channel depth ratio
This is the ratio of the depth of the channels in the feed section to the depth of the channels in the metering section.
2-4, 3 (most common)
Typical channel depth ratio
Die
Where the melted plastic leaves in a desired shape
50C above melting point
Extrusion temperature for crystalline polymers
100C above Tg
Extrusion temperature for amorphous polymers
lower temperatures
Extrusion temperature for heat sensitive polymers
higher temperatures
Extrusion temperature for highly viscous polymers
Vented extruder
A vacuum is applied on the melt through a vent port on the side of the barrel
Vented extruder
Used for plastics with residual volatiles like PS
Twin-screw extruder
Contains two screws and can facilitate mixing
Twin-screw extruder
Can be rotating or counter-rotating