cram packet - 1450-1750
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Overall Changes
1) The world became truly global - the western hemisphere came into continued contact with the eastern hemisphere. Technological innovations, strengthened political organization, and economic prosperity all contributed to this change that completely altered world trade patterns.
2) Maritime trade dominated the world - Technological advancements and willingness of political leaders to invest in it meant that sea-based trade became much more important. As a result, old land-based empires lost relative power to the new sea-based powers.
3) European kingdoms gained world power - The relative power and prosperity of Europe increased dramatically during this time in comparison to empires in the longer-established civilization areas.
4) Nomads began to become a thing of the past - Nomads continued to play an important role in trade and cultural diffusion, and they continued to threaten the borders of the large land-based empires. However, their power dwindled as travel and trade by water became more important.
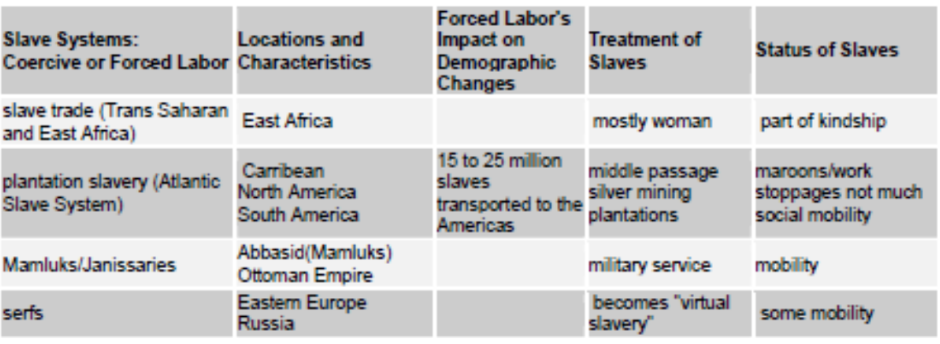
5) Labor systems were transformed - The acquisition of colonies in North and South America led to major changes in labor systems. After many Amerindians died from disease transmitted by contact with Europeans, a vigorous slave trade from Africa began and continued throughout most of the era. Slave labor became very important all over the Americas. Other labor systems, such as the mita and encomienda in South America, were adapted from previous native traditions by the Spanish and Portuguese.
6) "Gunpowder Empires" emerged in the Middle East and Asia - Empires in older civilization areas gained new strength from new technologies in weaponry. Basing their new power on "gunpowder," they still suffered from the old issues that had plagued land-based empires for centuries: defense of borders, communication within the empire, and maintenance of an army adequate to defend the large territory. By the end of the era, many were less powerful than the new sea-based kingdoms of Europe.
ottoman
o Founded by Osman, the Ottoman Empire included a collection of Turkish tribes from Asia Minor. In 1453 they conquered Constantinople and ended the Byzantine Empire. From Constantinople (soon to be called Istanbul) they launched raids into the Balkans of Europe.
o Under Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottomans controlled land on three continents. They took land from Baghdad to Belgrade and laid siege to Vienna. The Siege of Vienna (1530) was a turning point in Ottoman expansion and European unity to fight Muslim invaders.
o They used an extensive civil service and bureaucracy (like what other groups?) they maintained a large, multiethnic empire for 600 years. The Sultan was an absolute ruler; however, he allowed for petition from the people. Their wealth came from the control of the Dardanelles and Black Sea.
o Great army of mounted and foot soldiers; made use of Janissaries, Balkan Christians captured as boys who became skilled soldiers. Slaves were used for labor.
o Most Turks were Sunni; however, Orthodox Christians and Jews also made up sizable portions of the empire. The empire was culturally diverse largely due to trade connections and diversity of lands governed. The merchant class was important.
o Women had more equality than other areas, including the right to own property.
mughal
o Continuation of the Delhi Sultanate – descendents of the Mongol invaders (hence Mughal)
o Land included modern day India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan
o Strong military required high taxes
o Military service was rewarded with land grants – upset regional rulers
o Muslim authority over Hindus; Akbar married a Hindu woman and tried to reconcile with the majority Hindi population
o Sikhism emerges in some areas – a combination of Islam and Hinduism
o Limited trade
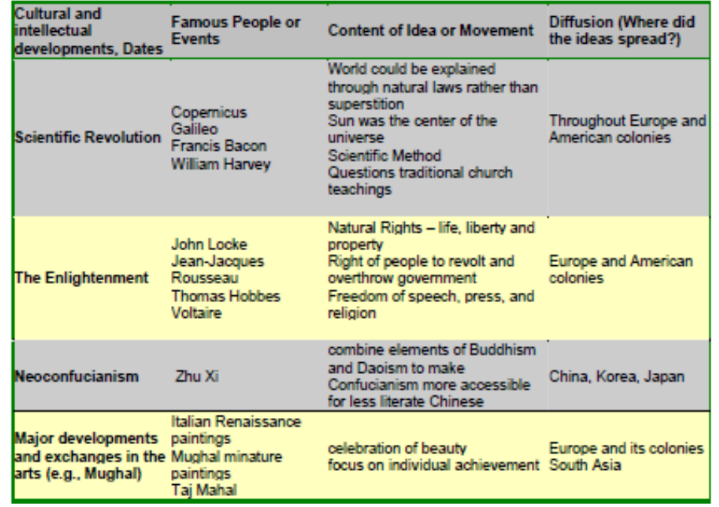
o The Taj Mahal was built during this time. It is an “Islamic” building
tokugawa japan
A "gunpowder empire" emerged in Japan, unusual in the sense that Japan was not an expansive land-based empire.
The Japanese daimyos, or regional lords, had operated fairly independently from the
shoguns before the early 17th century, when these military, feudalistic leaders were unified under one powerful family, the Tokugawa.
worried that Europeans might conspire
with the daimyos to destroy Tokugawa control. In the 1630s the shogunate literally "closed Japan," by forbidding all Japanese from going abroad and expelling all Europeans from Japan.
ming + early qing
China had some of the same problems that the Muslim empires had: borders difficult to guard, armies expensive to maintain, and transportation and communication issues.
declining
Some particular factors that weakened Ming China included:
1) Climatic change - A broad change of climate swept from Europe to China during the 1600s, with the weather turning much colder. This change seriously affected agriculture and health, and also contributed to serious famine across China. These conditions led frustrated peasants to frequent rebellion.
2) Nomadic invasions - The 1500s saw the reemergence of the Mongols as a regional power, this time with the help and support of Tibet. In gratitude, the Mongols bestowed the Tibetan leader with the title of Dalai Lama, or "universal teacher" of Tibetan Buddhism. The Japanese also attacked Korea, a Chinese tributary state, requiring Ming armies to defend the area.
3) Pirates - As sea-based trade became more and more important, the number of pirates also increased in the Chinese seas, just as they did in the Americas. Pirates were both Chinese and Japanese, and they lay in wait for ships going in and out of Chinese ports.
4) Decline of the Silk Road - After so many centuries, the famed Silk Road trade finally fell into decline during this era. New technologies and European control meant that more and more trade was conducted by water, and land-based trade decreased.
5) Inept rulers - The last emperors lived in luxury in the Forbidden City, and had little to do with governing the empire. For example, the last emperor was so disengaged that he did not know that he was under attack until the enemy literally was climbing over the palace walls.
The Early Qing Dynasty
The Manchus (from Manchuria) finally overthrew the Ming Dynasty in 1644. The Manchus had been asked by the Mings to help fight off the Mongols and the Japanese. After fighting the Mongols and Japanese off, they decided to take China as their own.
called themselves the Qing ("pure") Empire because they saw themselves as restoring China to glory.
The Qing Dynasty was to rule China until 1911, and in the years before 1750, the empire was very strong. The emperors ruled under many of the same precepts that China had always had, such as the Mandate of Heaven, which they saw as justification for their takeover. The Manchu did keep their ethnic identity, forbidding intermarriage between Manchus and Chinese.
outlawed the Chinese from learning the Manchurian language, and they required Chinese men to shave their heads and grow long queues at the back of their heads as a sign of submission.
China was so prosperous in these early Qing days that Qianlong cancelled taxes
Chinese Contact with Europeans
East-west contacts between China and Europe intensified during the early Qing Dynasty.
The Jesuit priests were an
order of the Catholic Church that specialized in international missionary work. One of the early Jesuits, Matteo Ricci, very much impressed the Chinese, who admired his education, brilliance, and respect for Chinese customs and accomplishments. The Jesuits dazzled their hosts with European science and
technology.
emperors saw to it that Jesuits had a special place in their courts. However, they had limited success in converting people to Christianity.
Chinese products - tea, porcelain, silk, wallpaper, and decorative items - became quite
fashionable among the European elite,
CULTURAL AND INTELLECTUAL LIFE IN CHINA
Based upon Chinese traditions
Neo-Confucianism
Civil Service Exams
Printing press increased the number of books, including novels which Confucian scholar condemned
o Journey to the West was an account of the journey of the Buddhism monk Xuan Zang to India where he learned the Buddhism that would be brought to China
EUROPEAN EMPIRES
Key European Empires emerged during this time. They included:
1) Portugal – power came from exploration and colonization; important in the early slave trade; first to set up trading centers along Africa’s coast and to trade directly with India and China through maritime trade
2) Spain – unified by the marriage of Isabella and Ferdinand; wealth came from exploration and colonization; expelled Muslims and Jews; Inquisition; Spanish control of Latin America; decimation of the Native Americans; beginning of American slave trade
3) England – power from trade and colonization; mercantilism – economic system where the “mother country” has colonies and restricts them to trade only with the mother; long history of Constitutionalism – power to Parliament and limited monarchy; King Henry VIII and Queen Elizabeth bring England to its height in power and prestige
4) France – power from trade and colonization; Louis XIV highlighted the system of absolutism – total power to the monarchy; controlled nobles by having them live at Versailles
Patterns of Social and Gender Change
o Major cities included Paris, London, and Amsterdam
o Rise of the bourgeoisie – middle class emerges
o Rising gap between poor and everyone else
o Marriages take place later in life; less likely to be arranged than before; more freedom for women ‘
o More women become educated
o Renaissance brings a new age of art and literature to Europe
o Reformation brings an end to unified European Catholicism
RUSSIA
For the AP World History Exam, Russia is considered “nonwestern.” During this time period, Russia converted to Orthodox Christianity and began to have more contacts with the West. Peter the Great made it his goal to “westernize” Russia. He mandated western style clothing, education, and military structures. Russia becomes a major power in world affairs.
EXPLORATION AND COLONIZATION OF THE AMERICAS
Upon the arrival of Europeans, the Americas had millions of inhabitants. Some were advanced and some were primitive. The Aztecs and Incas had unified large segments of land and people under their control. The Europeans, primarily the Spanish began the systems that would decimate the populations of the Americans and set in motion the eventual Atlantic Slave Trade.
Major changes and results from the interaction between Europeans and Native Americans (Columbian Exchange) included:
1) Diseases – small pox, tuberculosis, measles, and influenza attacked the Native Americans who did not have the immune systems to fight exposure; Europeans contracted a more deadly form of syphilis
2) Animals – pigs, cows, and horses were taken to the Americas leading to an increase in transportation and food stuff
3) Crops – Native American crops of corn, squash, beans, tomatoes, potatoes, and chilies led to a population increase in Europe
population shifts
rise in europe, decrease in america, increase in asia (middle east included)
Major environmental changes occurred in the New World in two major ways:
1) Soil exhaustion - Plantations in the Americas tended to rely on single crops, a process that depletes the soil of nutrients, and since land was plentiful, often the planters just moved on to clear more land. For example, in the Caribbean, instead of rotating sugar with other crops, planters found it more profitable to clearly new lands when yields began to decline. Eventually, they moved on to other islands.
2) Deforestation - The Spanish first cut down forests in the Caribbean to make pastures for the cattle they brought, and deforestation accelerated when more areas were cleared for plantations. In North America, shipbuilding in the northern English colonies took its toll of forests. In all of the Americas, the forests near the coasts were the first to go, so that deforestation was significant in many areas by 1750.
3) Deforestation was also taking place in Europe during this period. Timber was needed for ships, buildings, wagons, barrels, and many other items. The Little Ice Age that began in Europe during the 1590s made wood shortages worse. People burned wood to keep warm, and by the mid- 17th century, forests were growing scarce and wood prices skyrocketed. This wood shortage encouraged the use of coal for fuel, and since England had coal in great supply, deforestation almost certainly helped their economy grow. However, deforestation had many negative effects, especially on the poor.
4) The Little Ice Age spread as far as China, where it caused hardship that led people to rebellion and discontent, a condition that contributed to the mid-17th century demise of Ming China.
Diverse interpretations What are the debates about the timing and extent of European predominance in the world economy?
o The first argument is that Europe was visionary in thinking and that a few greats, such as Prince Henry the Navigator and Sir Isaac Newton spurred others on. The idea was that a “great man” such as one just mentioned caused Europe to be great.
o The second argument is that European culture caused Europe to ultimately dominate the world. From the Renaissance, Europeans developed the idea that life on earth was to be enjoyed and dominated.
o A third theory is economic. Europe needed markets and resources, so they went and got them.
o A final theory is that political theory was the driving force for Europe dominating the world. Monarchs needed monarchs to finance wars and increase their power.