Sociocultural Approach
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Social identity theory
Tajfel et al.
|
Abrams et al.
|
Social cognitive theory
Bandura, Ross, and Ross
|
Charlton et al.
|
Stereotyping
Steele and Aronson
|
Allport and Postman
|
Cultural dimensions and cognition
Berry
|
Kulkofsky et al.
|
Enculturation
Odden and Rochat
|
Fagot
|
Acculturation
Lueck and Wilson
|
Wang et al.
|
Social identity theory
Argues that a person has not just one ‘personal self’, but rather several social selves that correspond to group membership. |
Social cognitive learning theory
Assumes that humans learn behavior through observational learning (by watching models and imitating their behavior). |
Stereotype
A social perception of an individual in terms of group membership or physical attributes; a generalization that is made about a group and then attributed to members of that group. |
Spotlight anxiety
Results from stereotype threat, causing emotional distress and pressure that can undermine performance. |
Cultural dimensions
How the values of a society affect behavior. |
Individualism
Uniqueness is valued, speaking one’s mind is important, self is defined by individual achievement, freedom is valued. |
Collectivism
Social harmony is valued, modesty is important, self is defined by group membership, common fate is valued. |
Enculturation
The learning and maintenance of the behaviors and norms of our own culture. |
Acculturation
When people move into another culture and begin to adopt the norms and behaviors of the majority culture. |
Berry’s acculturation model
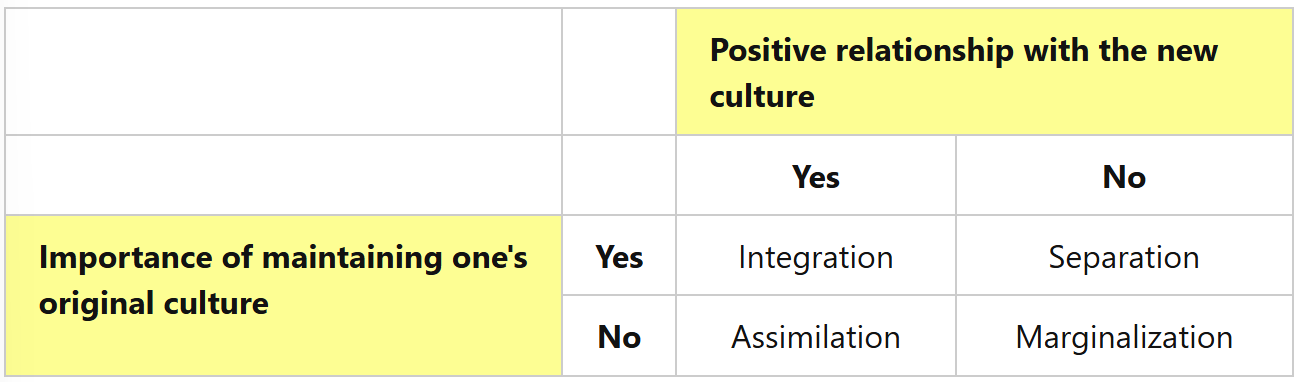
Acculturative stress
The psychological, somatic, and social difficulties that accompany acculturation, often resulting in anxiety or depression. |
Immigrant paradox
Greater degrees of acculturation are associated with problematic health outcomes. |
Power-distance index
The extent to which a culture respects authority and status. |