Metabolism in conformers and regulators (add graphs)
1/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What affects an organisms ability to maintain its metabolic rate?
External abiotic factors
What are three abiotic factors that are found in an environment?
pH
Salinity (how salty water is)
Temperature
Conformers (amphibians/fish/reptiles)
Their internal environment is directly dependent on the abiotic factors in the external environment
What is an advantage and a disadvantage of being a conformer?
Advantage - lower metabolic costs because no energy is used
Disadvantage - narrower range of ecological niches
What is a behavioural response in conformers?
Amphibians and reptiles will bask in the sun to keep warm, allowing them to tolerate variation in their environment to maintain their optimum metabolic rate
Regulators (birds/mammals)
Their internal environment is independent of the external environment
What is an advantage and a disadvantage of being a regulator?
Advantage - wider range of ecological niches
Disadvantage - higher metabolic costs because energy is used for homeostasis
What is a behavioural response in regulators?
Birds and mammals use metabolism to control their internal environment using physiological mechanisms (homeostasis)
Physiological homeostasis
A state of balance among all the body systems needed for the body to survive and function correctly
Thermoregulation
The regulation of internal body temperature
What part of the brain monitors temperature?
The hypothalamus
Negative feedback control
Information that is communicated by electrical impulses through nerves to the effectors, which bring about corrective responses to return the temperature to normal
What are the four stages of negative feedback control?
The ‘normal’ level of the body’s internal environment is known as the set point
Receptors detect any change from this point
Hormonal or nervous messages (electrical) are then sent to effectors
The effectors respond and rectify the change, returning to the set point (corrective response)
What two things makes regulating temperature important?
Allows optimal enzyme activity and ensures high diffusion rates
What are three examples of corrective responses in skin?
Blood vessels/colour of skin (vasodilation and vasoconstriction)
Hairs (the relaxation of hair erector muscles and the contraction of hair erector muscles)
Sweating
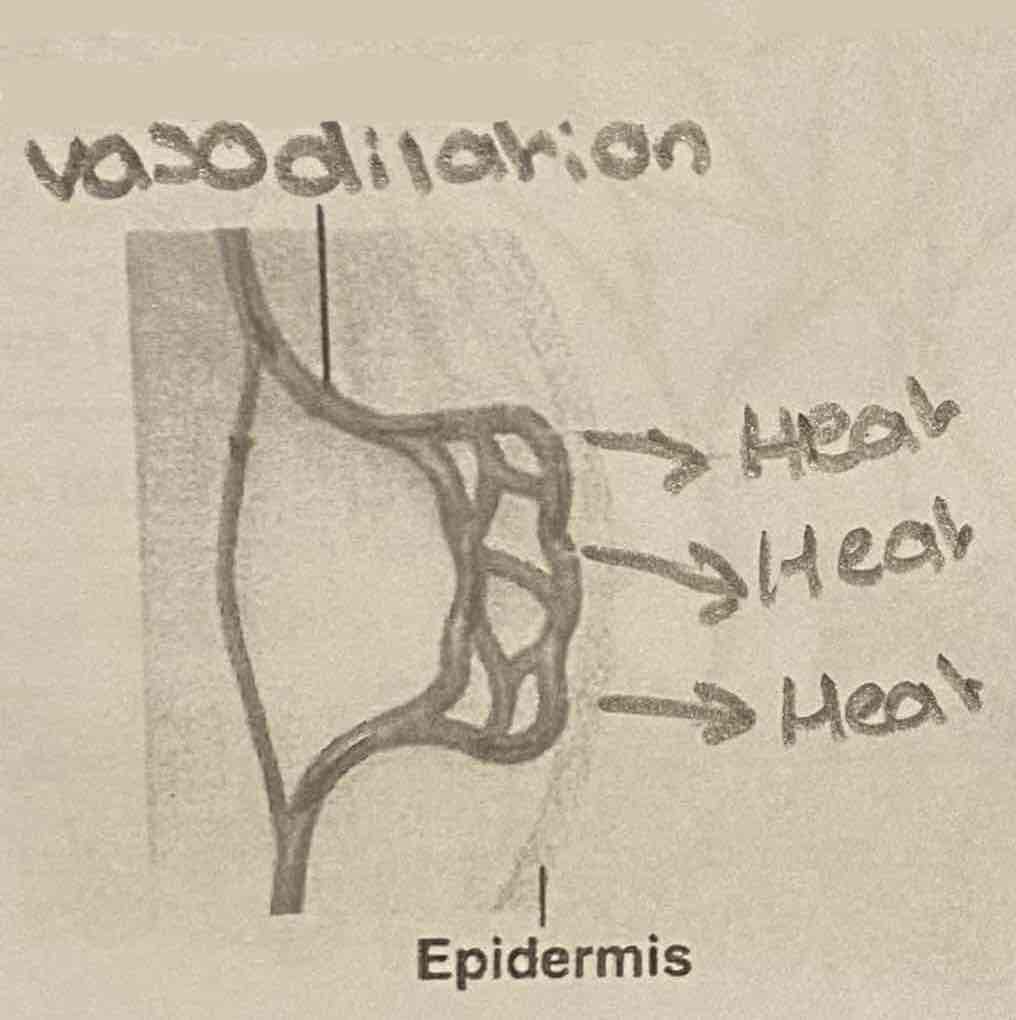
Vasodilation
Nerve impulses direct blood vessels to dilate, causing more blood to flow closer to the surface of the skin, allowing heat to radiate out
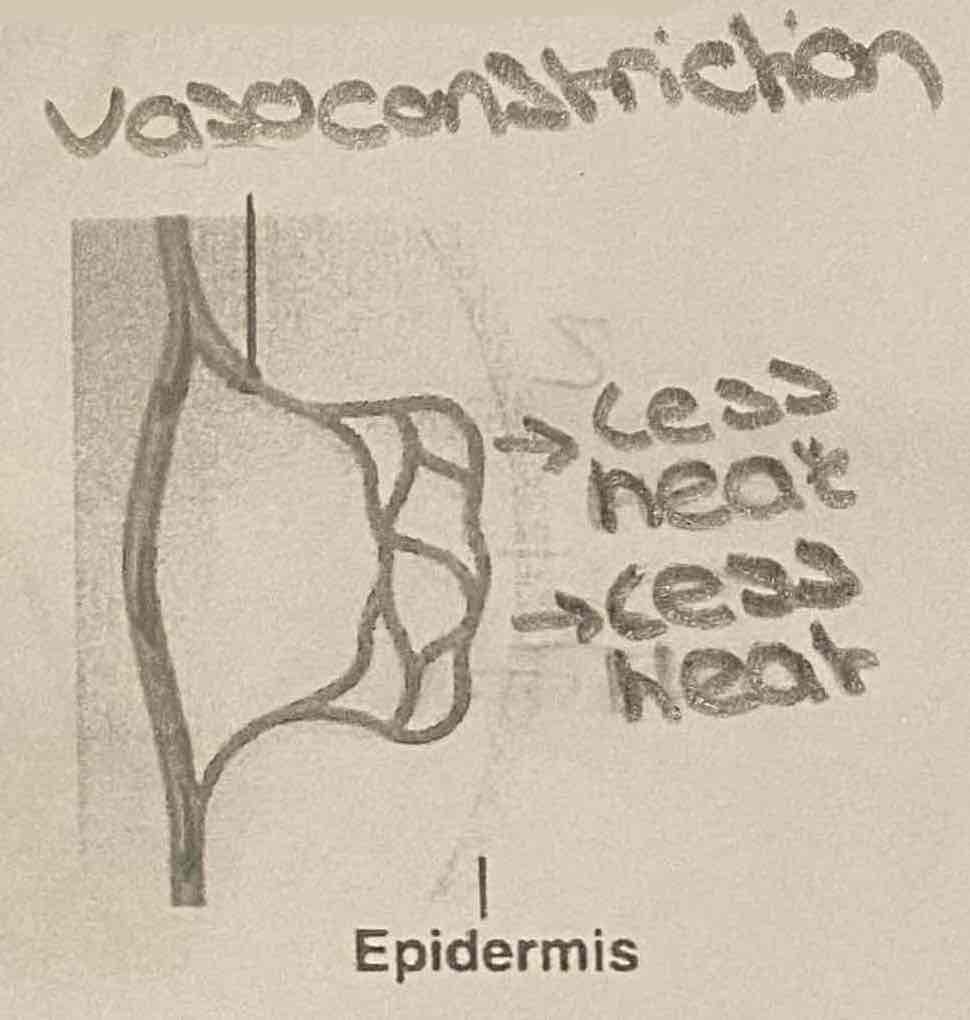
Vasoconstriction
Nerve impulses direct blood vessels to constrict, causing the blood vessels to become more narrow, limiting the volume of blood which reduces heat loss
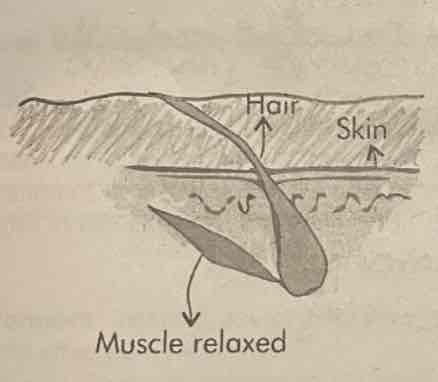
Relaxation of hair erector muscles
Hair on the body will lay flat on the skin, reducing insulation and allowing heat to escape
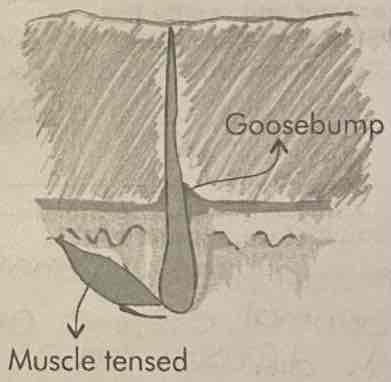
Contraction of hair erector muscles
Hair will stand up away from the skin, allowing a layer of air to be trapped which acts as an insulator
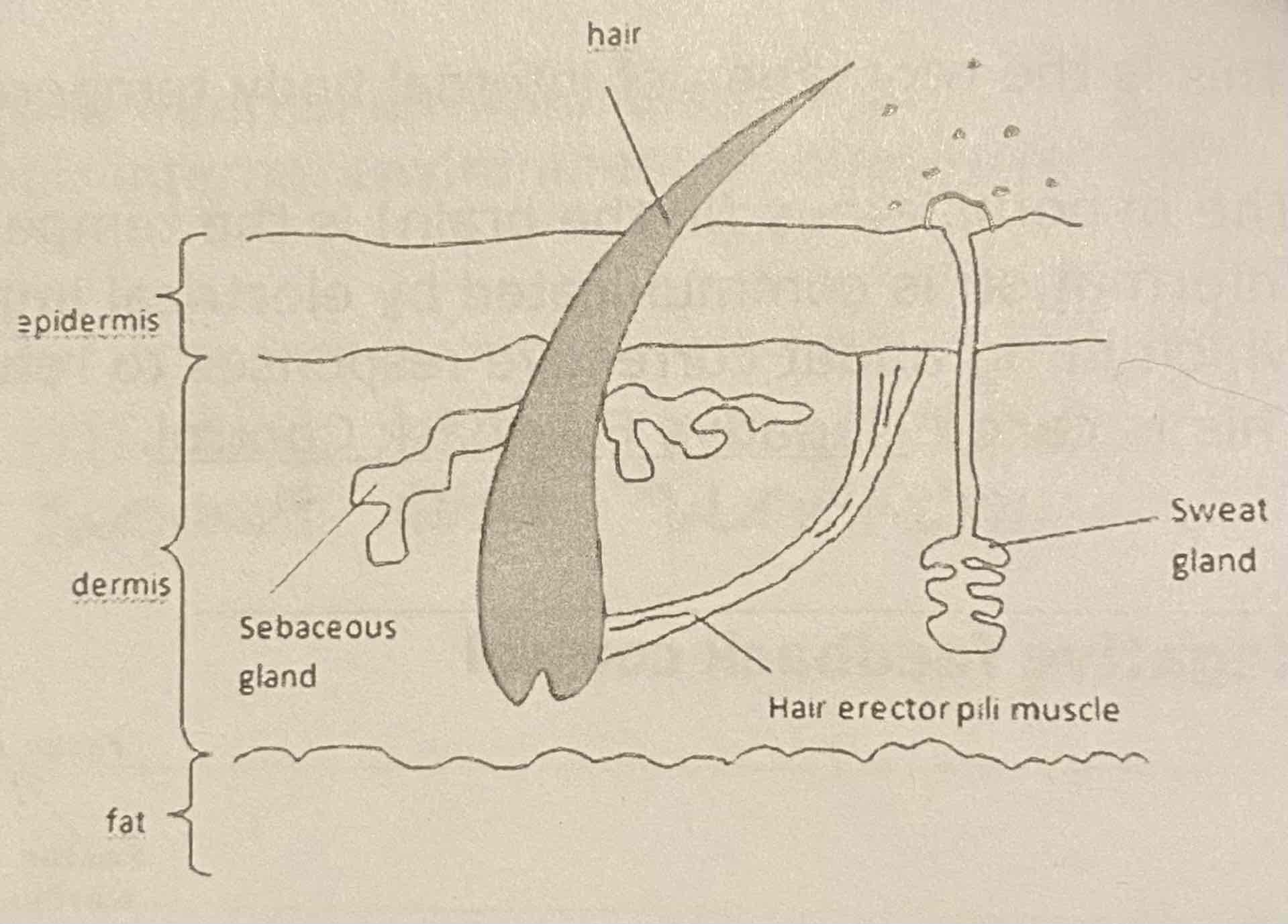
Sweating
Sweat rises from sweat glands and creates a thin layer of moisture on the surface of the skin which then evaporates using the heat off the body
What is an example of a corrective response in muscles?
Shivering
Shivering
Muscle constriction generates heat
What are two example of a corrective response in metabolism?
A decrease in metabolic rate and an increase in metabolic rate
Decrease in metabolic rate
Less heat is produced through metabolic activity
Increase in metabolic rate
More heat is produced through metabolic activity
What are the four corrective responses used to decrease body temperature?
Vasodilation
Relaxation of hair erector muscles
Sweating
Decrease in metabolic rate
What are the four corrective responses used to increase body temperature?
Vasoconstriction
Contraction of hair erector muscles
Shivering
Increase in metabolic rate