The Marketing Mix
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2Y2 | Midterms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Marketing Objectives and Strategies
Technopreneurs should set goals specific to how much money the business makes. The goal of marketing should be to bring in more money from sales.
On the other hand, the brand should be the focus of the marketing efforts (Kotler et al., 2018).
Primary Goals of Marketing
- Focusing on customer wants and needs to distinguish products from the competition;
- Integrating all the organization’s activities to satisfy customer wants and needs; and
- Achieving the organization’s long-term goals by satisfying customer wants and needs
The Marketing Mix
According to The Economic Times (2023), a company’s strategy to promote brands or products in the market is referred to as the marketing mix. A typical marketing mix includes price, product, promotion, and place.
However, in today’s marketing mix, additional Ps like packaging, positioning, people, and process are becoming increasingly essential.
The marketing mix’s various components interact with one another. They can make a company’s business plan successful if done correctly. However, the business’s recovery could take years if mismanaged.
Understanding the marketing mix, conducting market research, and consulting with various stakeholders are all necessary.
Figure 1: The 8Ps of Marketing
The Eight Ps of Marketing (Hill, 2022):
- Product
refers to the item the business offers customers, whether tangible (like physical goods) or intangible (like digital goods or services).
- Price
refers to the amount customers are willing to pay for a product or service.
- Place
the location of the product or service’s purchase, sale, and experience. It varies from business to business, depending on retail and direct online sales.
- Promotion
refers to the activities used to promote a product, brand, or service. The goal is to
make people aware of the product, entice them to buy it, and get them to do so over other
options.
- People
is all about those involved in the launch or campaign, including the company’s key executives, endorsers, and the marketing team. These people will be accountable for delivering marketing promises, so they must possess the skills necessary to implement the marketing strategy.
- Physical Evidence
refers to anything that helps the target audience trust the business. It could be the item itself, its packaging, the setting where it is sold (like a physical store), or how it is delivered (like by courier). In the digital business, this could be in the form of testimonials, reviews, or even digital products like e-books and online courses.
- Process
a set of steps that help businesses figure out customer problems, look at market opportunities, and make marketing materials to reach the people they want to see.
- Positioning
refers to the capacity to alter how consumers perceive a brand or product compared to competitors. Establishing a brand’s image or identity so that consumers perceive it in a certain way is the goal of market positioning.
Types of Promotion
The promotion strategies utilized to generate demand for a product or service are called the promotions mix. In contrast to the marketing mix, it focuses on specific product or service promotion methods. Each of these promotion methods contributes to a company’s revenue generation in its unique way (Indeed, 2021).
Figure 2: The Promotional Mix
- Advertising
is a mass communication method used to get people to do something, usually regarding a commercial product or service.
Four (4) types of advertising (Shopify, 2022):
• Print Advertising – newspaper, magazines, catalog mail
• Broadcast Advertising – television, radio, podcast
• Public/Outdoor Advertising – billboards, transit advertising, street walk ads
• Digital Advertising – online display ads, search engine marketing, social media ad placement
- Selling
personal selling is a face-to-face selling technique by which a salesperson uses interpersonal skills to persuade a customer to purchase a particular product by highlighting various features.
Examples: Salespersons at retail stores, Real Estate Agents, Insurance Agents, Medical
Representatives
- Direct Marketing
any marketing that communicates or distributes directly to individual customers rather than through a third party like the mass media.
Examples: E-mail, direct mail, telemarketing, text blast, leaflet distribution, social media marketing
- Sales Promotion
a sales promotion is a marketing strategy in which a company uses short term campaigns to get people interested in a product, service, or other offer and make people want it (Kelwig, 2022).
Examples: Product bundles, flash sales, free trials, free shipping, Buy-1-Take-1, Coupons, Vouchers
- Public Relations
the set of techniques and strategies for managing how information about an individual or company is disseminated to the public, especially the media.
Public Relations
tries to portray a person or brand naturally, like getting positive press from outside sources and recommending business decisions that will get support from the public (Hayes, 2022).
Examples: Product placement, sponsorship, consumer education, brand ambassadors, corporate social responsibilities, social media advocacy and campaigns
Digital Marketing
Digital channels
for direct customer communication and sales are the newest and fastest-growing marketing medium.
Internet
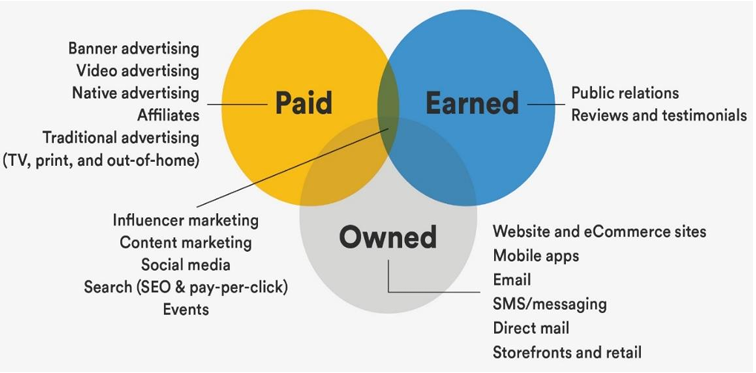
The gives marketers and customers more opportunities for individualization and interaction. Marketers separate earned (or free) media from paid and owned media.
• Paid media
is an outbound strategy comprising public relations, marketing, and other promotional activities produced for and paid for by th company.
• Earned media
includes news articles, blogs, and social network discussions that mention a brand and provide word-of-mouth and PR benefits to a business without paying for them directly.
• Owned media
is any online property owned and controlled by the company, such as a blog, website, or social media channels.
Figure 3. The Media Framework
The variety of online communication options means companies can offer or send tailored information or messages that engage consumers by reflecting their unique interests and behavior.
The four (4) main categories of online marketing communications are:
A. Web sites
Nowadays, companies design websites that embody or represent their purpose, history, products, and vision. They aim to make it attractive and interesting on the first view encouraging repeat visits.
A website also measures the number of unique visitors, length of visit, number of page views, etc.
However, companies must be sensitive to online security and privacy-protection issues. It should also pay special attention to context, content, and constant change.
There are seven (7) key design elements of an effective website:
• Context
layout and design
• Content
text, pictures, sound, and video the site contains
• Community
how the site enables user-to-user communication
• Customization
the site’s ability to tailor itself to allow users to personalize the site
• Communication
how the site enables site-to user, user-to-site, or two-way communication
• Connection
the degree that the site is linked to other sites
• Commerce
the site’s capabilities to facilitate commercial transactions
B. Pay-per-click ads (PPC)
Pay-per-click ads, also known as paid search or search ads, are now considered an integral component of online marketing. Pay-per-click ads have significantly increased the competition on product or service terms that serve as a proxy for consumer interest.
The following are suggested guidelines when using pay-per-click ads (PPC) on search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing) for online marketing communications:
• Broader search terms
(“MP3 player” or “iPod”) are helpful for general brand building.
• Specific terms
identifying a particular product model or service (“Apple iPod classic 160GB”) are useful for generating and converting sales leads.
• Search terms
must be spotlighted on the appropriate pages of the marketer’s website so search engines, such as Yahoo, Google, and Bing, can quickly identify them.
• Any product can usually be identified using multiple keywords, but marketers must bid on each keyword according to its likely return on revenue. It also helps to have popular sites link to the marketer’s website.
• Data
can be collected to track the effects of paid searches.
C. Display ads
Display or banner ads are small, rectangular boxes typically containing text and a picture that businesses pay for to be posted on relevant websites.
C. Display ads
The more people see it, the more it costs; Internet users only actively look for things online 5% of the time.
C. Display ads
Compared to common search advertisements, display ads still have a lot of potential for the information. However, advertising must be persuasive, attract attention, and be targeted and monitored.
Interstitials
are adverts that appear in-between pages, frequently with video or animation. Unfortunately, some consumers find such pop-up ads intrusive and distracting.
D. E-mail Marketing.
E-mail enables marketers to reach out and inform customers at a fraction of the cost of a direct mail campaign. E-mails are a highly effective tool for sales. The frequency with which they ask for purchases has been projected to be at least three (3) times that of social media ads, and the typical order value is higher.
Companies like Nissan and Kellogg focus on combining search engine marketing and e-mail. Although consumers are inundated with e-mails, many use spam filters to stop the flow. Privacy concerns are also rising. Customers of some businesses are being asked whether and when they want e-mails sent to them. E-mails need to be relevant, timely, and targeted.
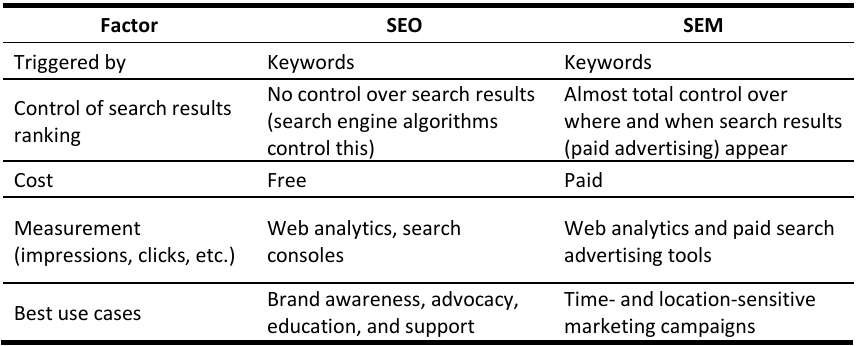
E. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
is optimizing a website to receive the most visitors through a search engine.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
By contrast, focuses on paid search business solutions.
SEM
involves buying traffic through paid search listing paired with specific keywords being searched for on the search engine. SEO and SEM have advantages, and marketers should combine both since most organizations have several initiatives to benefit from both types of searches.
Factor SEO SEM
Search engines
are Internet services or software designed to search information on the Web that corresponds to a request (e.g., keywords) specified by the user. Considering that there are billions of websites on the Internet, search engines play a crucial role in helping us find the correct information in a limited amount of time.
Digital marketers use search engines for the following reasons:
• Brand awareness
A brand is seen and recognized by consumers in a top search result once a branded search term or the brand’s name is searched for.
• Online sales
Search engines drive traffic to the webpage to purchase a product or service.
• Lead generation
Organic search can acquire potential consumers through the content or targeted keywords used. Paid search aids in search and web analytics employed in Return on Investment (ROI) calculations.
Marketing Development Plan
Market development plan
also known as a market development strategy, focuses on expanding existing product lines into new markets. Businesses often use it to find and develop new opportunities to sell their products in markets that have not been explored before. It can also be used to develop a new product line for selling to new and existing customers (Coleman, 2022).
Figure 4: Marketing Development Plan
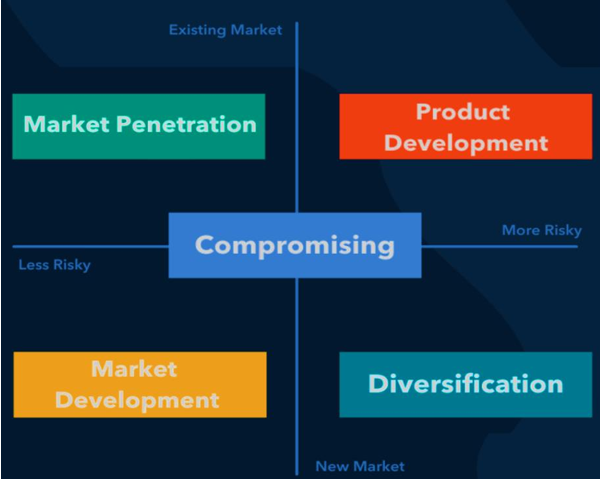
- Market Penetration
A market penetration strategy may be attempted by businesses when they want to expand with low risk within their existing markets.
• Product Launches
A business may introduce new versions of a product that it already sells well. Launching a new product boosts sales by creating excitement and buzz about the brand.
- Product Development
Product development is a more risky way to expand into an existing market, but this market development strategy can be profitable. The process of creating new products is delicate. Because product development is driven by market interest, businesses should know their market. This strategy can be challenging if the audience is not receptive due to inadequate product education, a poor marketing campaign, or even the wrong time to launch the product.
• Rebranding
Companies can rebrand themselves to reconnect with their existing market and
position themselves as a viable alternative to the competition. A company can rebrand a product to better position it within its current market by altering its packaging, offering a new size, flavor, or color, or even changing its name or brand.
• Price Update: An additional strategy for expanding into an existing market is to change the
price of a product to make it more affordable or more appealing to that market.
Repositioning the brand in the market to emphasize luxury or value, thereby justifying
higher prices to attract those customers.
- Market Development. Businesses can use a market development growth strategy to direct their
efforts in a manner that encourages market development and business expansion. It is accomplished