[MEDORG-MID-02] ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS
1/318
Earn XP
Description and Tags
THIS FLASH CARDS IS ABOUT MEDORG; ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
319 Terms
John Lister
In 1867, he introduced phenol for antiseptic principles.
(Lister’s principle caused dramatic decrease in postsurgical infections).
Phenol (Carboxylic Acid)
John Lister used this as wash for the hand.
Paul Erlich
Who is the Father of Chemotherapy?
Paul Erlich
Disciple of Robert Koch, began to work with set of antibacterial dyes and anti-parasitic organic arsenicals.
Anti-microbial activity
Paul Erlich’s goal is to develop compounds that retain _________ activity at the expense of toxicity to human host.
Magic bullets
These are antimicrobial agents that selectively attack pathogens without significant toxicity to the host.
Paul Erlich
Who discovered that the anti-microbial properties of dyes are parallel to staining activity (first demonstration of selective toxicity)?
Salvarsan
This is the first anti-syphilitic drug.
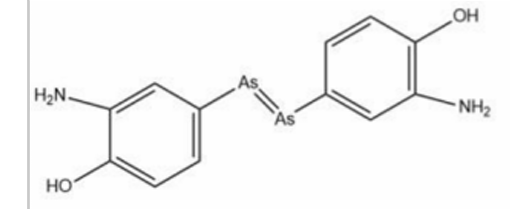
Compound 606
Salvarsan is also known as?
Selective Toxicity
Main tenet of modern antimicrobial therapy.
The property of certain chemicals to kill one type of organism while not harming other.
1920s
What year is the most successful anti-infective agents based on Group-IIB element mercury and the Group-VA elements arsenic and antimony?
Group-IIB element mercury and the Group-VA elements arsenic and antimony
These are the basis for anti-infective agent.
H.W. Thomas
In 1920, he discovered the most successful anti-infective agents based on the group-IIB element mercury and the group-VA element arsenic and antimony, Atoxyl.
Atoxyl
Sodium arsanilate and arsphenamine was used for sleeping sickness and these are drugs derived from synthetic dyes.
Gentian violet
Methylene blue
What are some examples of dyes where atoxyl was discovered?
Atoxyl
Somewhat effective were a few chemical conjurers of the quinine molecule.
Some of these agents represented significant achievements in anti-infective therapy but they also possess some important limitations.
Mercury
Arsenic
Antimony
Atoxyl contains elements used against parasites, exemplifying the use of heavy metals as therapeutic agents despite their potential toxicity.
Germicides
Anti-infective agents that are used locally.
Antisepsis
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
Application of an agent to living tissue for the purpose of preventing infection.
Disinfection
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
Chemical or physical treatment that destroys most vegetative microbe or viruses, but not spores, in or inanimate surface.
Decontamination
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
Destruction or marked reduction in the number of activity of microorganism.
Sanitation
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
Reduction of microbial load on an inanimate surface to a level considered acceptable for public health purposes.
Sterilization
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
A process intended to kill or remove all types of microorganism, including spores, and usually including viruses with an acceptable low probability of survival.
Pasteurization
Definition and Standard for Removing Microorganism:
A process that kill non-sporulating microorganism by hot water or steam at 65-100c.
65-100 degrees Celsius
What is the temperature needed in pasteurization?
Chemical type of the compound
Biological property
Therapeutic indication
What are the Classification of Anti-infectives?
Antiseptics
Local Anti-Infectives:
Applied to living tissue.
Must have low toxicity to be used directly on skin or wounds.
Bactericidal
Bacteriostatic
Cidal
Compound that kills bacteria.
Static
Prevents the growth of bacteria.
Disinfectant
Local Anti-Infectives:
Applied to inanimate objects.
Exerts a rapidly lethal action against all potentially pathogenic microorganism and spored.
Coagulation and denaturation of cell protein
What is the mechanism of action of local anti-infectives?
Antiseptics
Disinfectant
What are the two (2) local anti-infectives?
Formalin
Phenol > Alcohol
Local Anti-Infectives Mechanism of Action:
What are some examples of strong coagulators?
Iodine
Cresol
Phenol
Local Anti-Infectives Mechanism of Action:
What are some examples of denaturants?
Low-enough toxicity
Ideal Anti-Infective:
The ideal level of toxicity for it to be used directly on skin or wounds.
Lethal action
Ideal Anti-Infective:
Exert a rapid and sustained?
Low surface tension
Ideal Anti-Infective:
Ideal surface tension so that it will spread easily into the wound.
Body fluids (pus)
Ideal Anti-Infective:
Retain activity in the presence of?
Non-irritating
Non-allergenic
Ideal Anti-Infective:
Characteristics needed for tissues.
Systemic toxicity
Ideal Anti-Infective:
This should lack?
Healing
Ideal Anti-Infective:
This shouldn’t interfere with?
Alcohol and related compounds
Phenol and derivatives
Oxidizing agents
Halogen containing compounds
Cationic surfactants
What are the five (5) Classification of Anti-Infective Agents?
Alcohol
Classification of Anti-Infective Agents:
The activity of _______ against microorganisms is the result of their ability to denaturate important proteins and carbohydrates.
Denature
The activity of alcohols against microorganisms is the result of their ability to _______ important proteins and carbohydrates.
Ethyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol
What are the two (2) most commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants?
Protein and carbohydrate precipitation
What is the mechanism of action of alcohol?
8-carbon atom (octanol)
Structure-Activity Relationship: Alcohol
What is the molecular weight carbon atom of alcohol?
Antibacterial potency increases
Structure-Activity Relationship: Alcohol
MW up to 8-carbon atom (octanol).
Increase penetration to membrane
Structure-Activity Relationship: Alcohol
As the primary chain length increases.
Decreases antibacterial potency
Structure-Activity Relationship: Alcohol
Branching of the alcohol chain.
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
Structure-Activity Relationship: Alcohol
Isomeric alcohols’ potencies decreases in the order of?
Ethanol
Rectified spirit
Wine spirit
Grain alcohol
Spiritus vini rectificatus
What are the five (5) synonyms of ethyl acohol?
95%
What is the % of ethyl alcohol in commercial ethanol?
Azeotrope
Commercial Ethanol (95% EtOH):
This concentration forms an ______ with water that distills at 78.2c
78.2 degrees Celsius
Azeotrope forms with water that distills at temperature?
Grain Fermentation
Method of Preparation: Ethyl alcohol
Synthetically prepared by the sulfuric acid-catalyzed hydration of ethene.
Sulfuric acid-catalyzed hydration of ethene
Grain Fermentation is synthetically prepared by the?
Acetaldehyde
Alcohol is metabolized in the human body by a series of oxidations:
Nausea, vomiting, and vasodilatory flushing.
Disulfiram (Antabuse)
Alcohol is metabolized in the human body by a series of oxidations:
Block aldehyde dehydrogenase, allowing acetaldehyde to accumulate.
Antabuse
Disulfiram is also known as?
Ethanol
This is ineffective against spores.
Spores
Ethanol is ineffective against?
Solvent
Fuel
CNS depressant
Antipyretic
Germicidal
Disinfectant
What are the six (6) common uses of ethanol?
25%
What is the % of ethyl alcohol as antipyretic?
60-90%
What is the % of ethyl alcohol as germicidal?
70%
What is the % of ethyl alcohol as disinfectant?
Nerves
Ganglia
Medicinal Uses: Ethyl alcohol
Injected near (1)___ and (2)___ to alleviate pain.
Narcotic potency
Medicinal Uses: Ethyl alcohol
Ethyl alcohol has low?
Mild sedative
A weak vasodilator
Carminative
What are the internal uses of ethyl alcohol (diluted form)?
Spirits
Pharmaceutical Uses: Ethyl alcohol
Ethanol as the sole solvent.
Tinctures
Pharmaceutical Uses: Ethyl alcohol
Hydroalcoholic mixtures.
Fluid extracts
Pharmaceutical Uses: Ethyl alcohol
Alcohol as cosolvent.
Denatured Alcohol
This kind of alcohol is:
Intoxicating beverages
Unfit for human use
In alc lamps
Wood alcohol
Acetone
Benzene
What are the three (3) denaturants?
Denatured Alcohol
This alcohol is completely denatured with wood alcohol and benzene.
Wood alcohol and Benzene
Denatured Alcohol is completely denatured with?
Methanol
Wood alcohol is also known as?
Rubbing Alcohol
(CH3CHOHCH3) — 2 propanol
What alcohol is this?
Astringent
Rubefacient
Mild local anesthetic
What are the uses of Rubbing Alcohol?
68-72%
Rubbing alcohol contains how many % of isopropyl alcohol?
Sulfuric Acid
Preparation of Rubbing Alcohol:
This acid is catalyzed by hydration of propylene.
Isopropyl Alcohol
This alcohol is a disinfectant for the skin and surgical instruments.
Skin and surgical instruments
Isopropyl Alcohol is a disinfectant for the?
50-95%
What is the % of bactericidal property of Isopropyl Alcohol?
60% Ethyl Alcohol
40% Isopropyl Alcohol equals to?
Azeotropic Isopropyl Alcohol
This alcohol is used on gauze pads for sterilization of the skin prior to hypodermic injections.
Dehydrated Alcohol
This is an absolute alcohol.
99% ethanol
Dehydrated alcohol must contain no less than how much (%) ethanol?
Diluted Alcohol
Mixture of alcohol and water containing 41-42% by weight.
41-42%
Diluted alcohol is a mixture of alcohol and water containing % by weight.
Ethyl alcohol
Denatured alcohol
Rubbing alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol
Azeotropic Isopropyl alcohol
Dehydrated alcohol
Diluted alcohol
What are the seven (7) Types of Alcohol?
Mnemonics: Every Drunk Racoon in Antarctica Dies Daily
Glycerin (Glycerol)
The first polyhydric alcohol which can yield both an aldose and a ketose.
1,2,3-propanetriol
Aldose and Ketose
Glycerin (Glycerol) is the first polyhydric alcohol which can yield both?
1,2,3-propanetriol
What is the chemical name of Glycerin (Glycerol)?
Solvent and Humectant
What are the uses of Glycerin (Glycerol)?
Ethylene Oxide (C2H40)
A gas sterilant and used for temperature sensitive medical equipment.
3-80%
Ethylene Oxide (C2H40) forms an explosive mixtures in air conditions ranging from (%)?
Carboxide
This contains 10% ethylene oxide and 90% carbon dioxide by volume; without danger of explosion.
10% ethylene oxide
90% carbon dioxide
Carboxide contains these two (2) sterilant gas mixture?
Germicidal
What is the mechanism of action of Carboxide?