8.2: Enzymes and Energy - Reaction Rates
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
how are reaction rates measured
decreasing substrate concentration and increasing product concentration = both measure rate of change
Michaelis-Menten Model
describes the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions based on substrate concentration and enzyme affinity.
v = velocity of reaction
Vmax =maximum rate achieved by system
S = concentration of substrate
Km = Michaelis constant
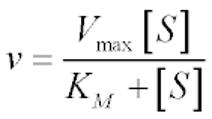
Michaelis constant
a value that represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of Vmax, indicating enzyme affinity for the substrate.
factors which effects enzymes
enzymes have optimal temp and pH - rate of reactions decrease when outside range
inhibitor
Substance that makes an enzyme inactive by interfering with its ability to react with a substrate.
competitive inhibitor
structure similar to substrate and binds to active site - reversed by increasing substrate concentration
noncompetitive inhibitor
doesn’t resemble substrate and binds to enzyme not at active site and alters enzyme’s shape preventing substrate binding - not reversed by increasing substrate concentration but still reversible
irreversible inhibitor
molecule that causes enzyme to lose all activity such as pesticides, antibodies, toxins or poisons. Usually forms covalent bonds with amino acid side chain that prevents catalytic activity