Respiration - Chp 12
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
External respiration
process by which organisms exchange gases with their environment
Internal respiration
controlled release of energy (ATP) from food, which is controlled by enzymes
Aerobic respiration
controlled release of energy (ATP) from food using oxygen
What is the role of aerobic respiration?
make energy in the form of ATP + maintain a body temperature of 37 degrees celcius
Where does aerobic respiration occur?
in the mitochondria
Equation for aerobic respiration
6O₂+C₆H₁₂O₆ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
What are the two stages of aerobic respiration?
stage one - glycolysis
stage two - krebs cycle + electron transport chain
Stage 1 overview:
- oxygen independent
- takes place in the cytosol
- only produces a small amount of energy as ATP
- inefficient energy releasing system
- only partially breaks down the glucose
- end products are pyruvic acid and a small amount of energy
Stage 1 process:
glucose is split
two molecules of pyruvic acid/pyruvate are formed (C₃)
small amount of energy released
2 ATP made
2 NADH formed (NAD⁺ + 2e⁻ + H⁺) and carry electrons to ETC
most energy remains in the bonds of the pyruvic acid
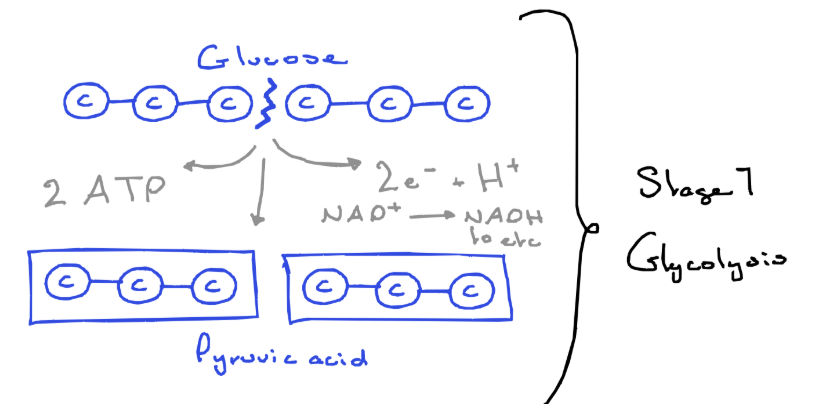
Stage 1 reaction:
Glucose (C₆) → 2 3Carbon molecules (C₃) + Small amount of energy
Stage 2 overview
- oxygen dependent
- takes place in the mitochondria
- end products are carbon dioxide and water
Stage 2 process A
Pyruvic acid enters the mitochondria if oxygen is present
Pryuvic acid converted to an acetyl group
Pyruvic acid loses a carbon in the form of carbon dioxide
Pyruvic acid loses 2H (2e⁻ + 2H⁺), used to make NADH + H⁺
Co-enzyme A links to acetyl group to form Acetyl CoA
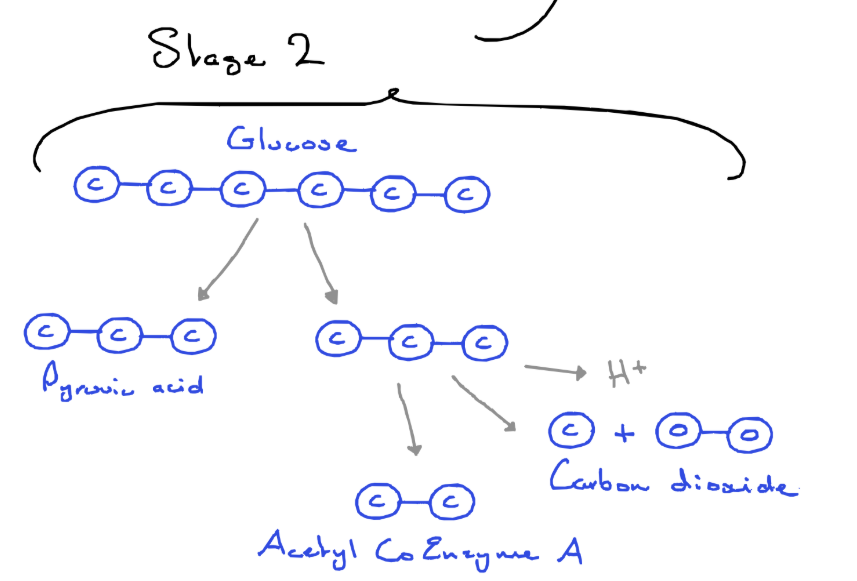
Stage 2 process B - The krebs cycle
- Acetyl CoA combines with a 4C molecule to form 6C molecule
- A carbon is removed as carbon dioxide, and 2H are removed and used to form NADH + H⁺
- Now there is a 5C molecule
- A carbon is removed as carbon dioxide, and 2H are removed and used to form NADH + H⁺
- Energy released used to make ATP molecule (and a H₂O molecule)
- Now there is a 4C molecule again
- 2H are removed and used to form NADH + H⁺
Products: 2CO₂, 3NADH & ATP (H₂O)
Stage 2 process C - The electron transport chain
NADH releases the 2e⁻ +H⁺
The high energy 2e⁻ are passed along a series of electron acceptors (mostly proteins)
The 2e⁻ release energy which is used to join ADP + phosphate to form ATP
Some energy is lost as heat
The now low energy electron joins with O₂ + H⁺ to form water
The NAD+ was regenerated
Products ATP, Water, NAD⁺
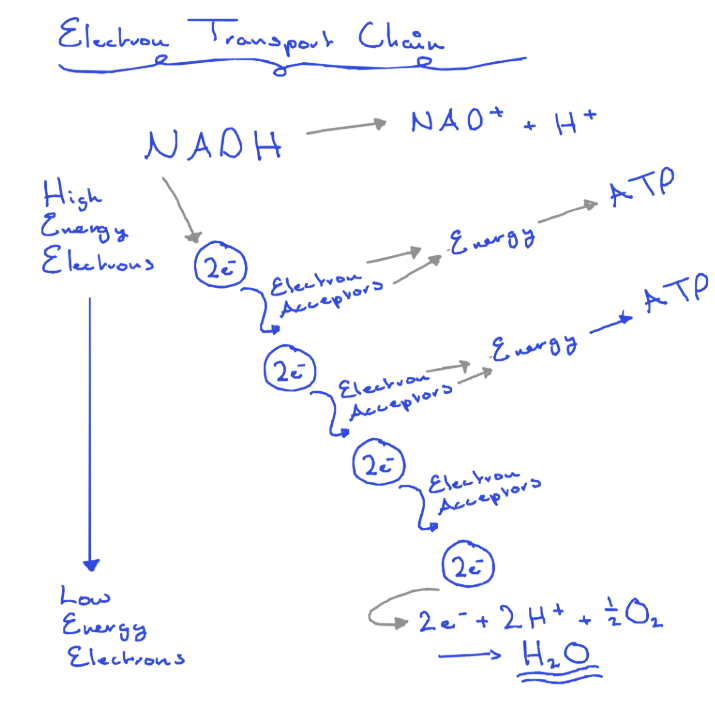
What is significant about the electron transport chain?
- it produces energy rich ATP
- if oxygen is absent aerobic organisms may die as there is no oxygen to accept the low energy electrons and ATP is not formed
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
the production of ATP by the electron transport system as it requires both oxygen and a phosphate
Why is cyanide fatal?
it prevents some of the proteins from receiving and passing on electrons meaning ATP cannot be produced
Anaerobic respiration/Fermentation
controlled release of energy (ATP) from food without the use of oxygen
Where does anaerobic respiration occur?
cytosol
Anaerobic respiration overview
- can occur in the presence of oxygen but does not need it
- a small amount of energy is released in this way, and is less efficient
- 2 ATP and 2 NADH are produced in this process
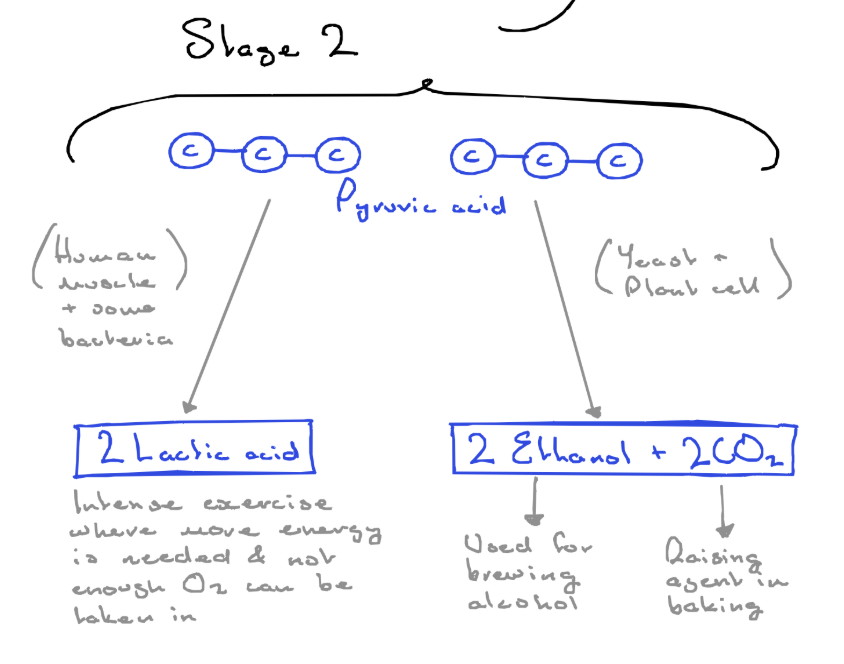
- pyruvic acid is converted to either lactic acid or ethanol & carbon dioxide
- in either case the 2 NADH break down into 2e⁻ and 2H⁺ which combine with the pyruvic acid to form either products
- only one stage involved
What are the two types of fermentation?
type one - lactic acid fermentation
type two - alcohol fermentation
Type 1 - lactic fermentation
occurs in some anaerobic bacteria and fungus, and in animal muscles when there is not enough oxygen
if we get out of breath while exercising not enough oxygen can reach out muscles and anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscles which forms lactic acid, contributing to cramps
when you rest the lactic acid is broken down by the liver
Uses for lactic fermentation
forms when milk goes sour
when bacteria respire on cabbage to form sauerkraut, in silage and yogurt production
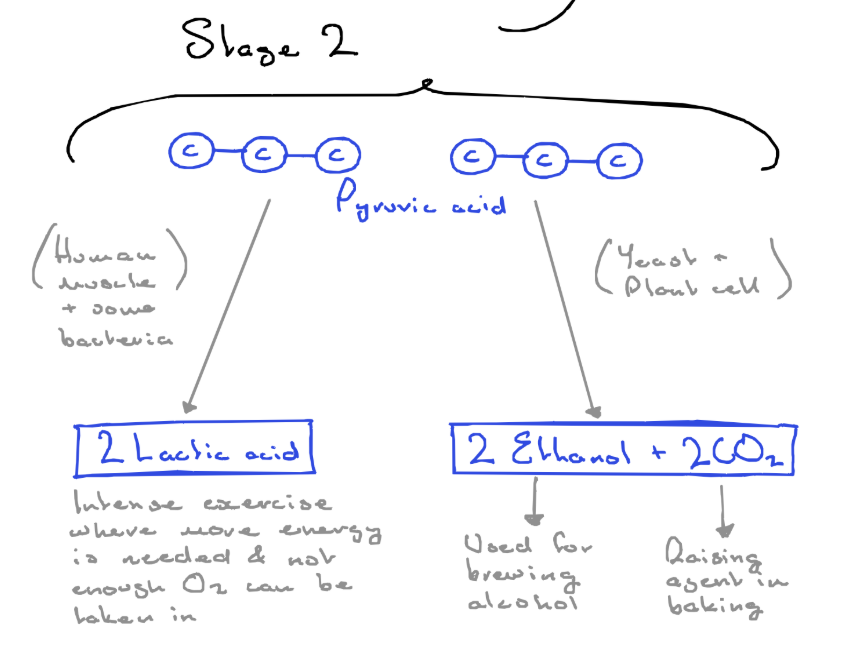
Lactic fermentation word equation
glucose →2lactic acid + small amount of energy
Type 2 - alcohol fermentation
- takes place in bacteria, fungi, and plants when they are deprived of oxygen
- involved the partial breakdown of glucose
Use of alcohol fermentation
- in baking yeast is used, the alcohol evaporates but the carbon dioxide causes the dough to rise (baking powder is used instead in very hot ovens
Alcohol fermentation word equation
glucose→ 2ethanol + 2carbon dioxide + small amount of energy
Advantages & disadvantages of fermentation
A - Used by some organisms to survive in oxygen deficient environments
A - Extra energy supply when energy demand exceeds oxygen supply to the cell
D - inefficient as much less ATP is produced per glucose (2:38)
D - the organic end products are toxic
Biotechnology/Bioprocessing
use of living things or their components to manufacture useful products of to carry out useful reactions
What is fermentation in bioprocessing?
the growth of micro-organisms in liquid under any condition
Industrial fermentation process
- micro-organisms are placed in a container (bioreactor) with a suitable substrate on which they can react
- when micro-organisms are mixed with the substrate foam may be formed, so a foam breaker is used
- oxygen is pumped through a sparger
What impacts the quality and quantity of the industrial fermentation product?
- the quality and the micro-organism and substrate
- the design of the bioreactor
- a correct rate of mixing
- a correct temperature
- pH
- elimination of contaminating microorganisms
What microorganisms are used? What do they produce?
- new microorganisms are being produced by genetic engineers
- bacteria can be used to make yogurt, antibiotics, hormones
- fungus can be used to make antibiotics, citric acid
- yeast can be used to make beer, wine, single cell proteins (eg quorn)
Use of immobolised cells in bioprocessing
- to ensure the microorganisms used in the bioreactor are not lost
- used in the treatment of sewage, bacteria and fungi may be attached to sand and gravel to decompose the waste
- in the production of alcohol, yeast cells are immobilised with sodium alginate, which created beads that are then soaked in calcium chloride, causing the alginate to enclose and immobilise the yeast cells
Advantages of immobilised cells
- does not damage cells
- can easily recover the microorganism
- reduces need for filtration
- redusing costs by reusing
- saves time instead of immobilising enzymes
- ensures a pure product
What organism is used in this experiment?
yeast
What does yeast respire with? How is this prepared?
glucose, which is boiled to eliminate gases from the solution
Why is the solution covered with oil?
to prevent O₂ from re-entering the solution
Why is limewater in the fermentation lock?
to detect the presence of CO₂
Why is the apparatus placed in a water bath?
to keep the temperature constant
How can you tell when the organism has finished respiring?
no more bubbles seen in the limewater
What is used as a control?
water instead of boiled glucose
What colour change is observed in the iodoform test?
brown/orange → colourless
What indiciates a positive result in the iodoform test?
the formation of pale yellow crystals