Bio 30 - Cell Division
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions (G1, S, G2)
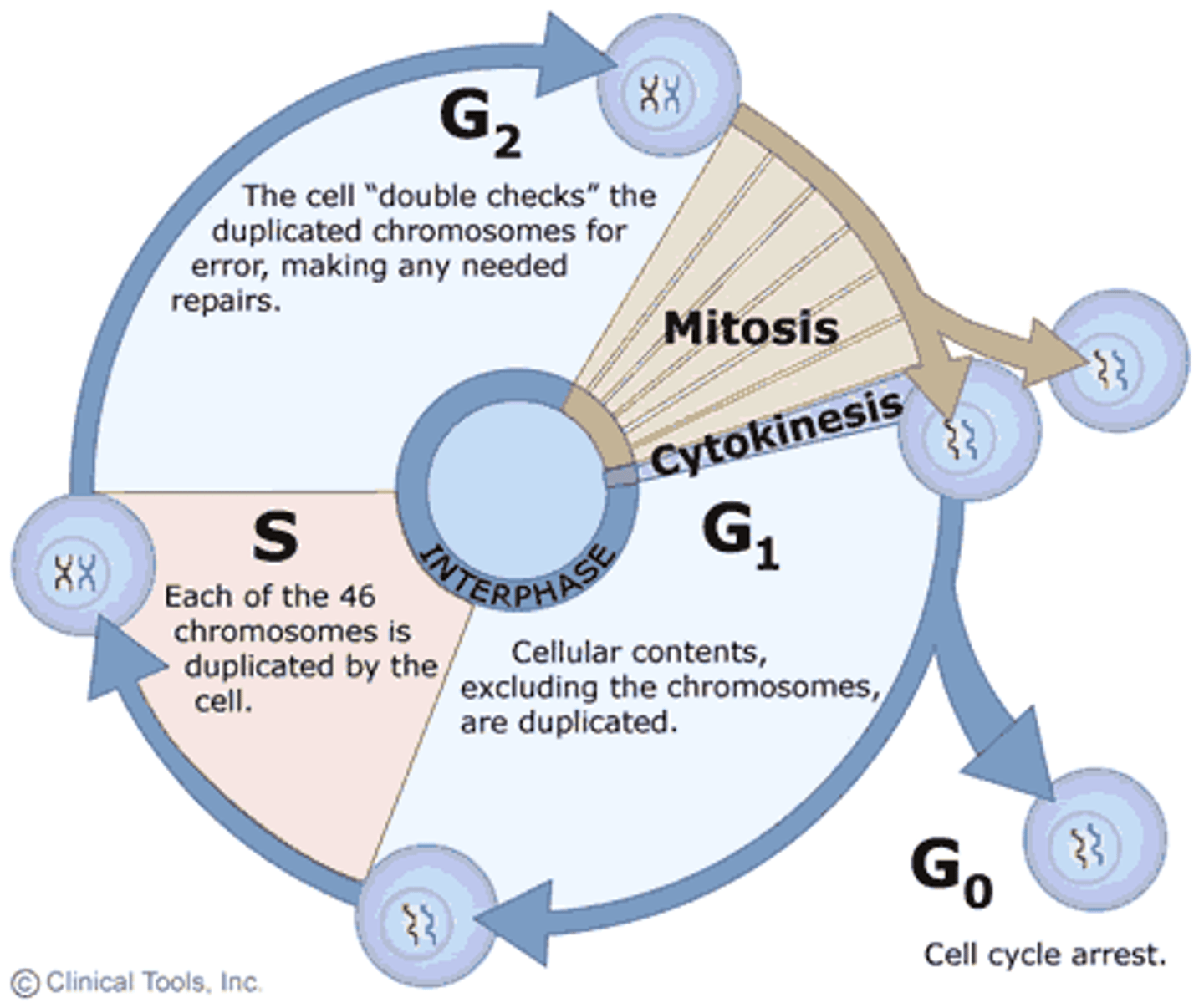
G1 phase
stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions
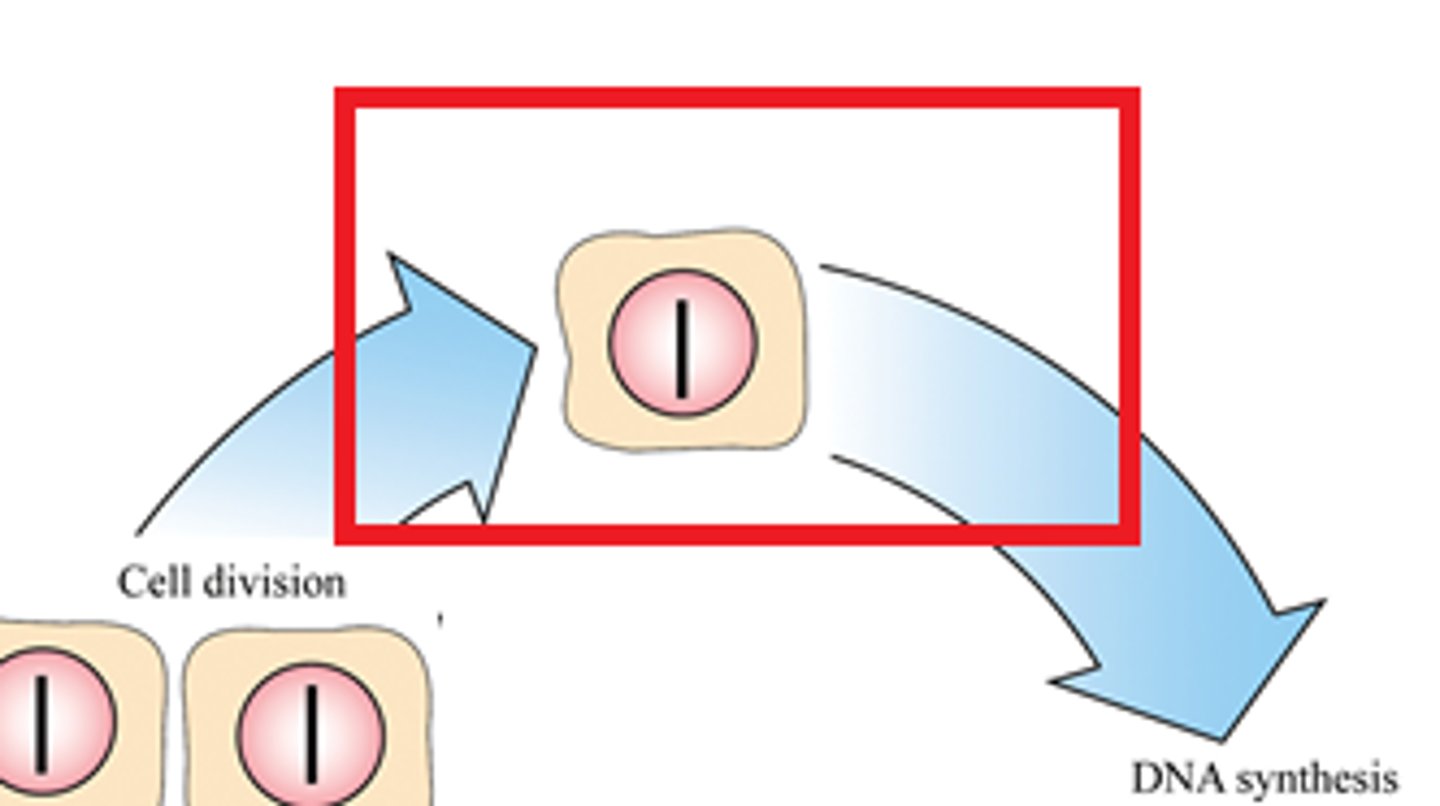
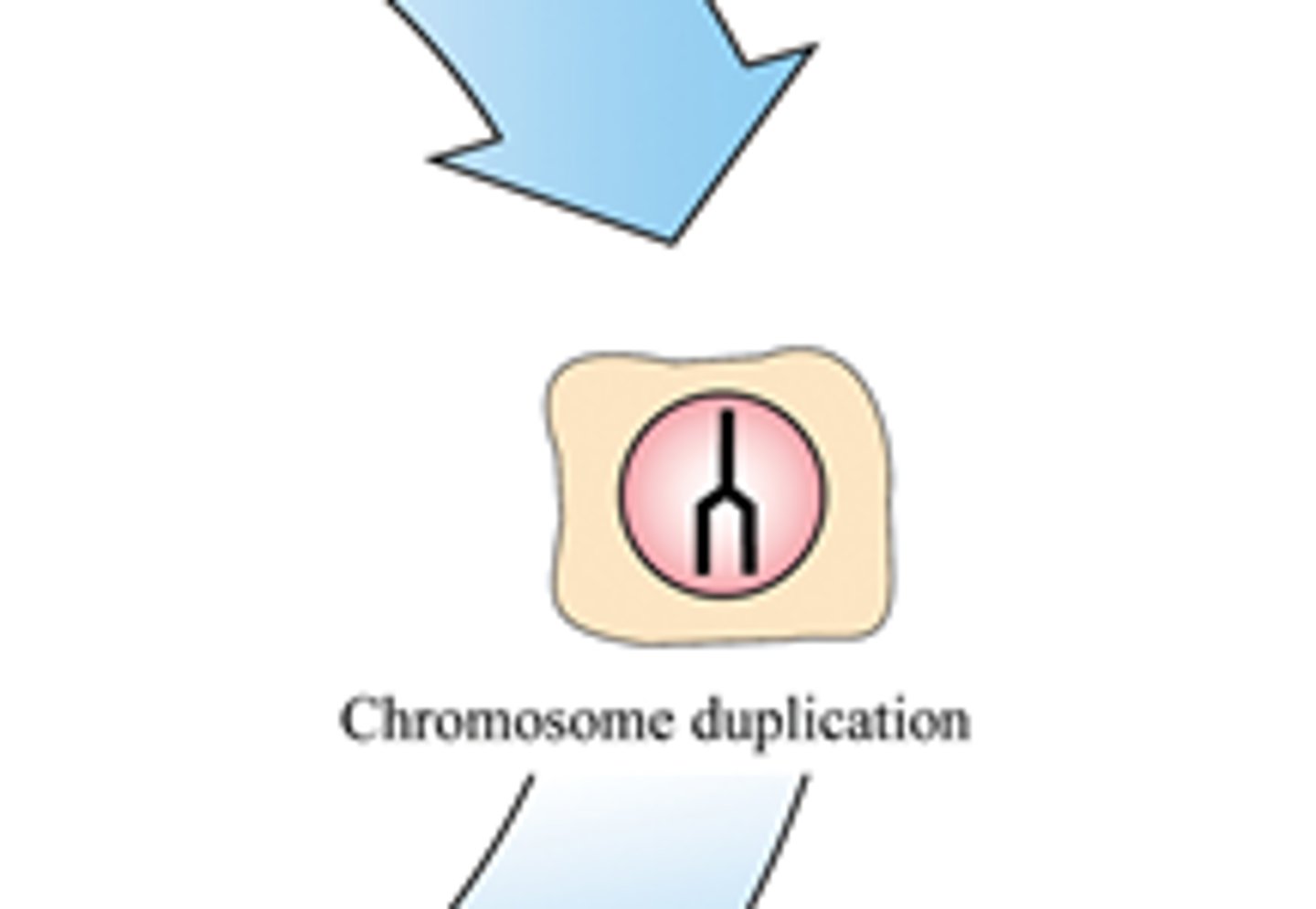
S phase
chromosome replicate and DNA synthesizes
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
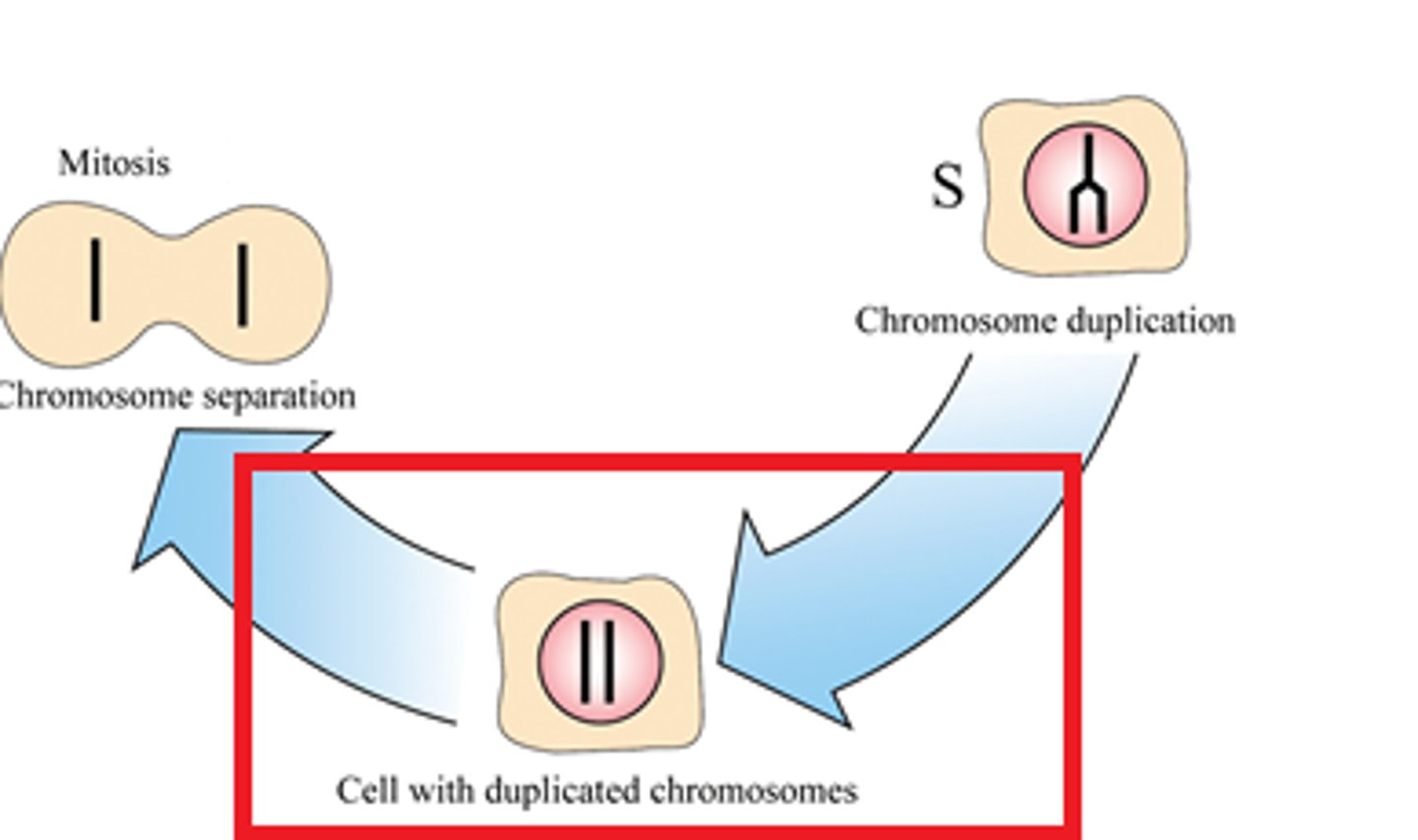
Prophase
Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
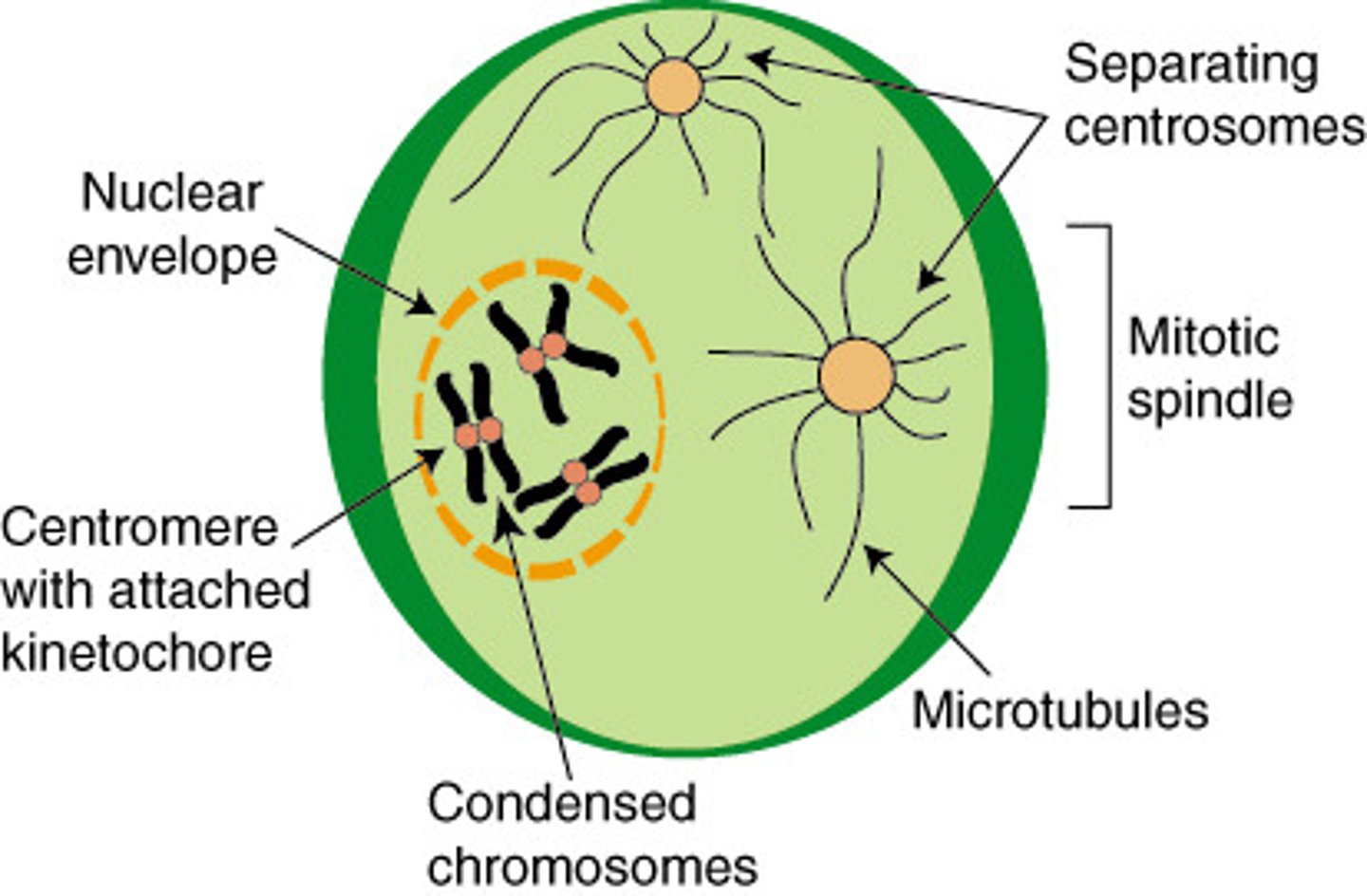
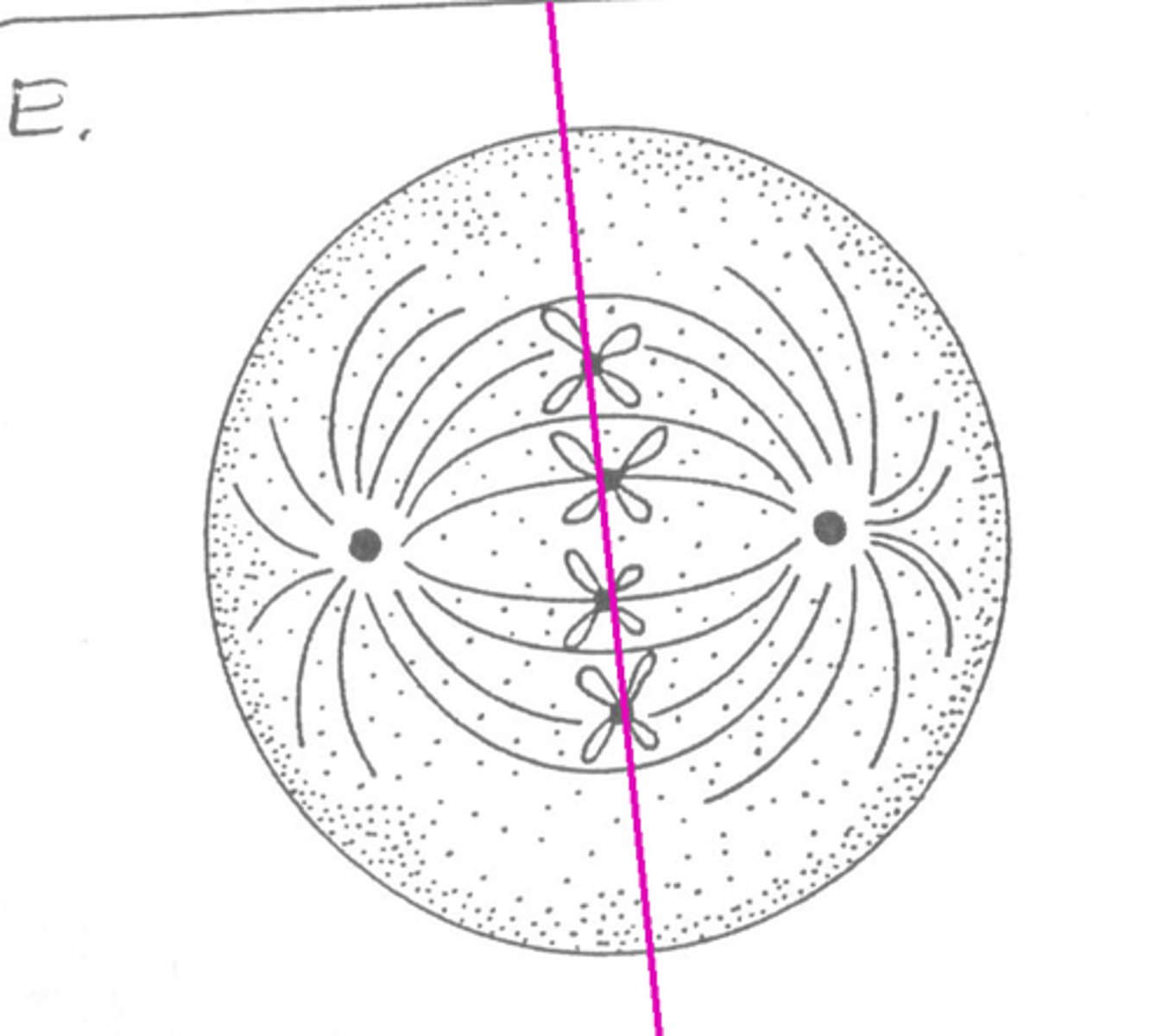
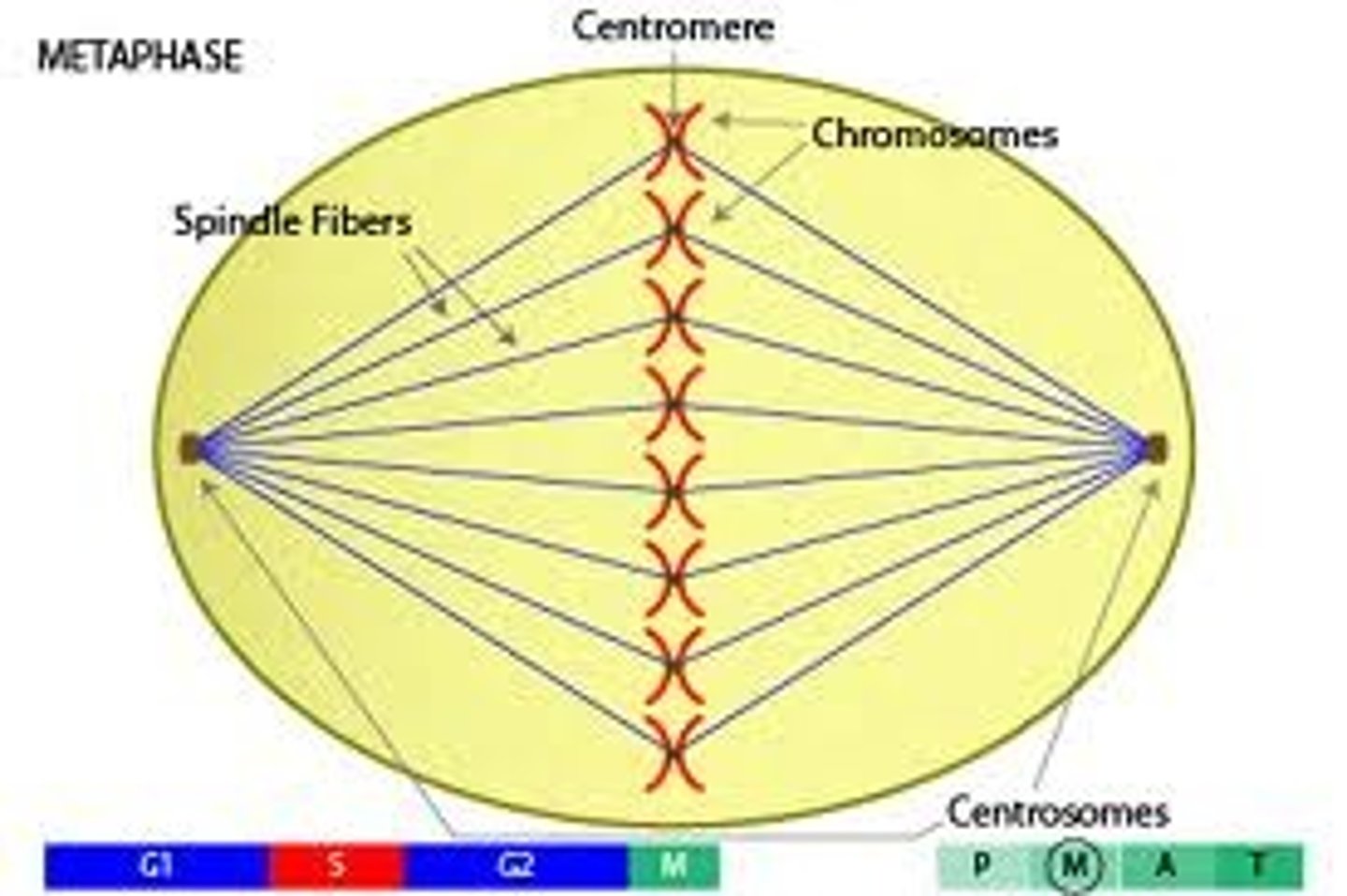
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
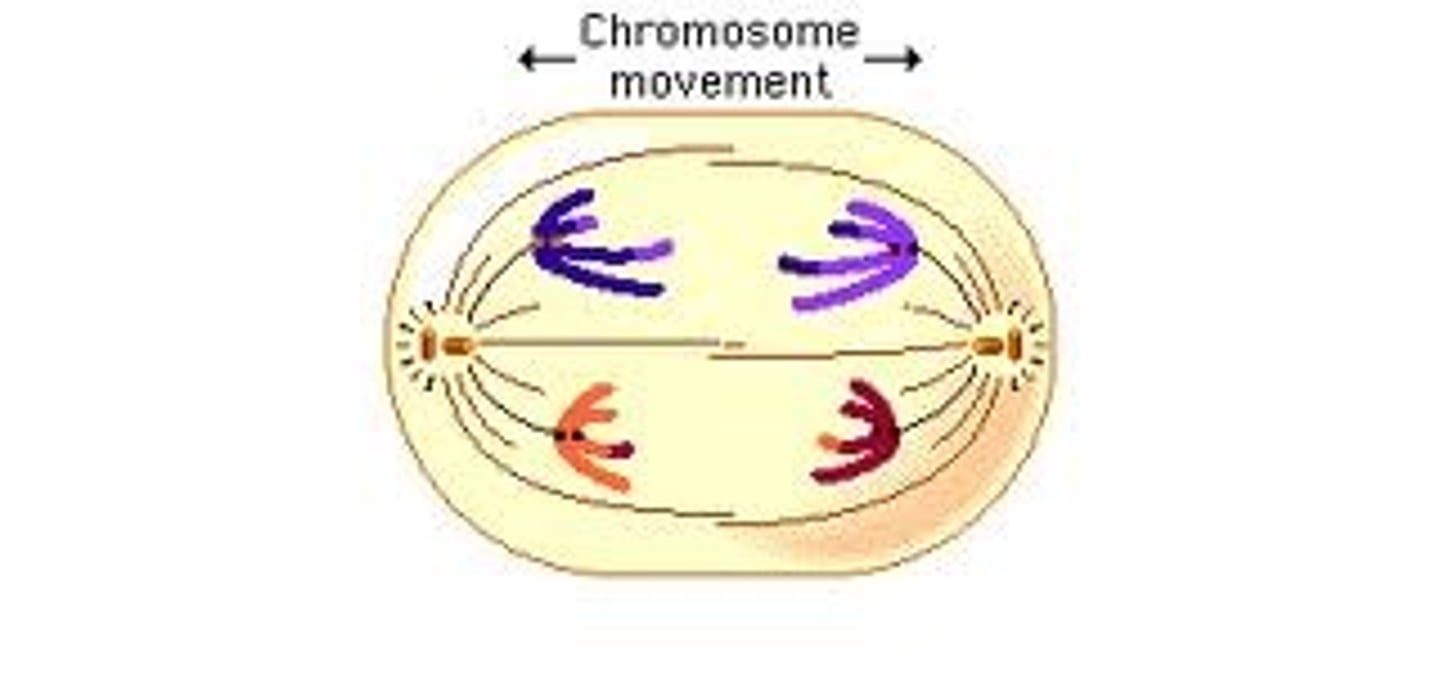
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
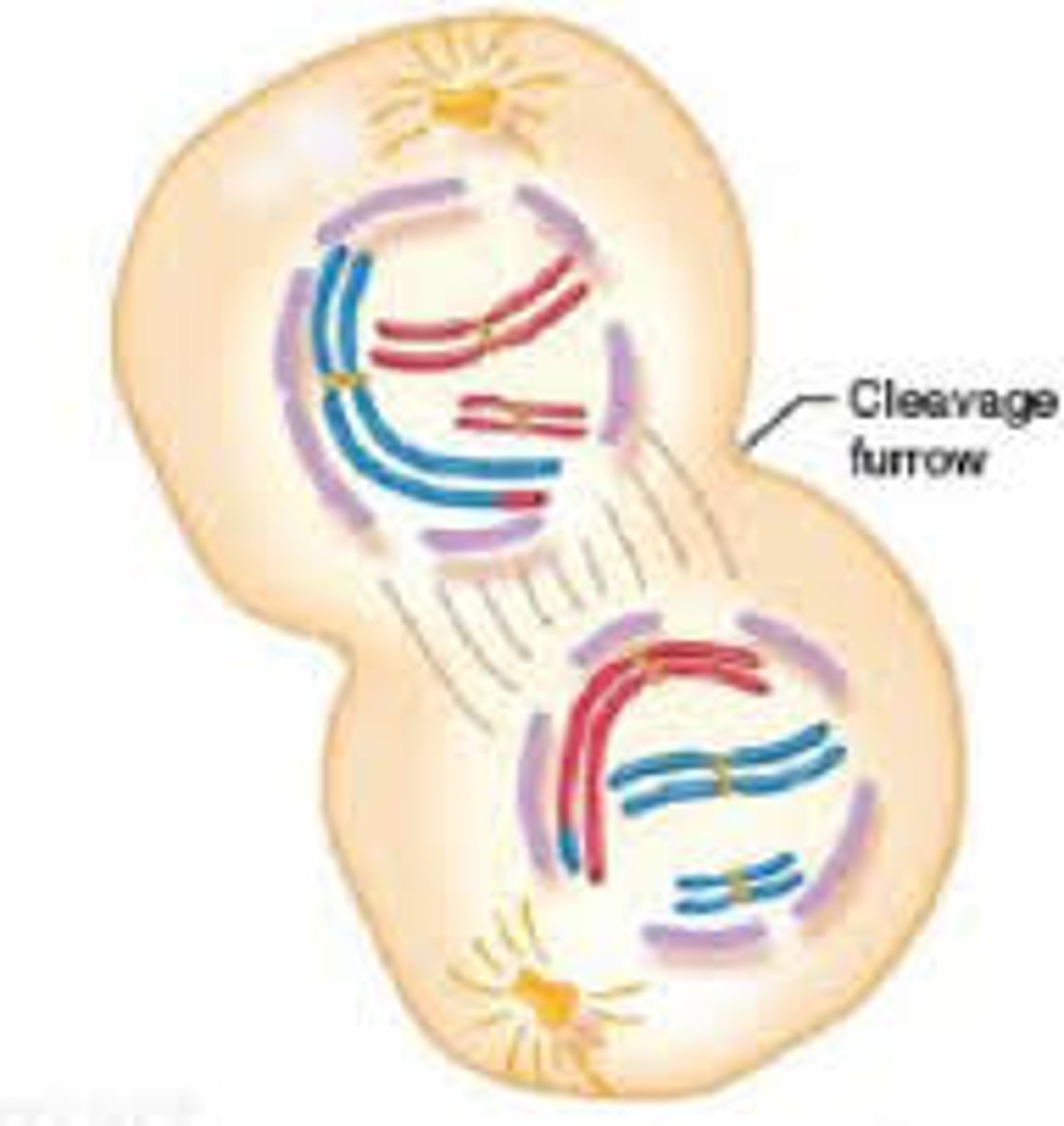
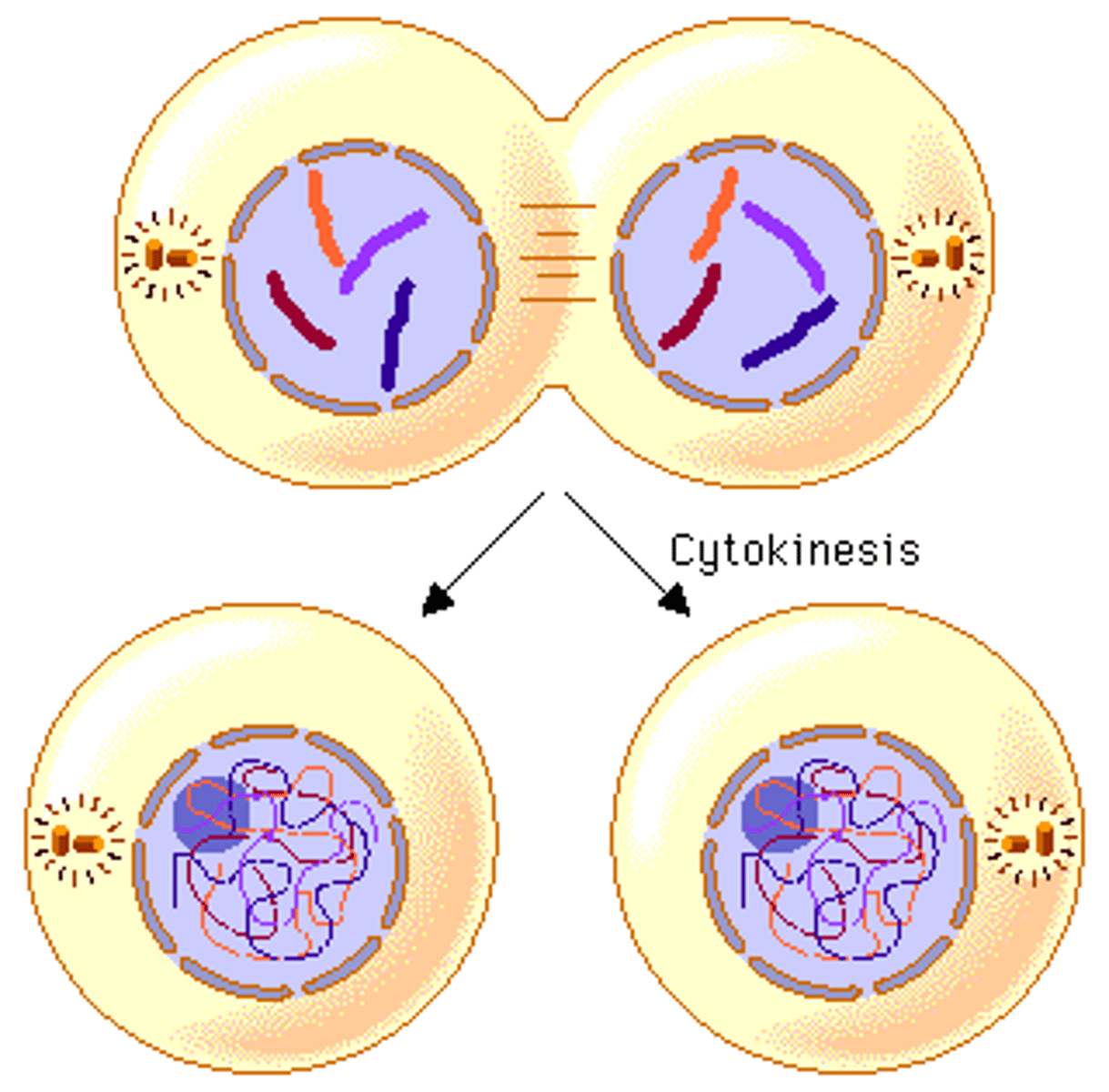
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
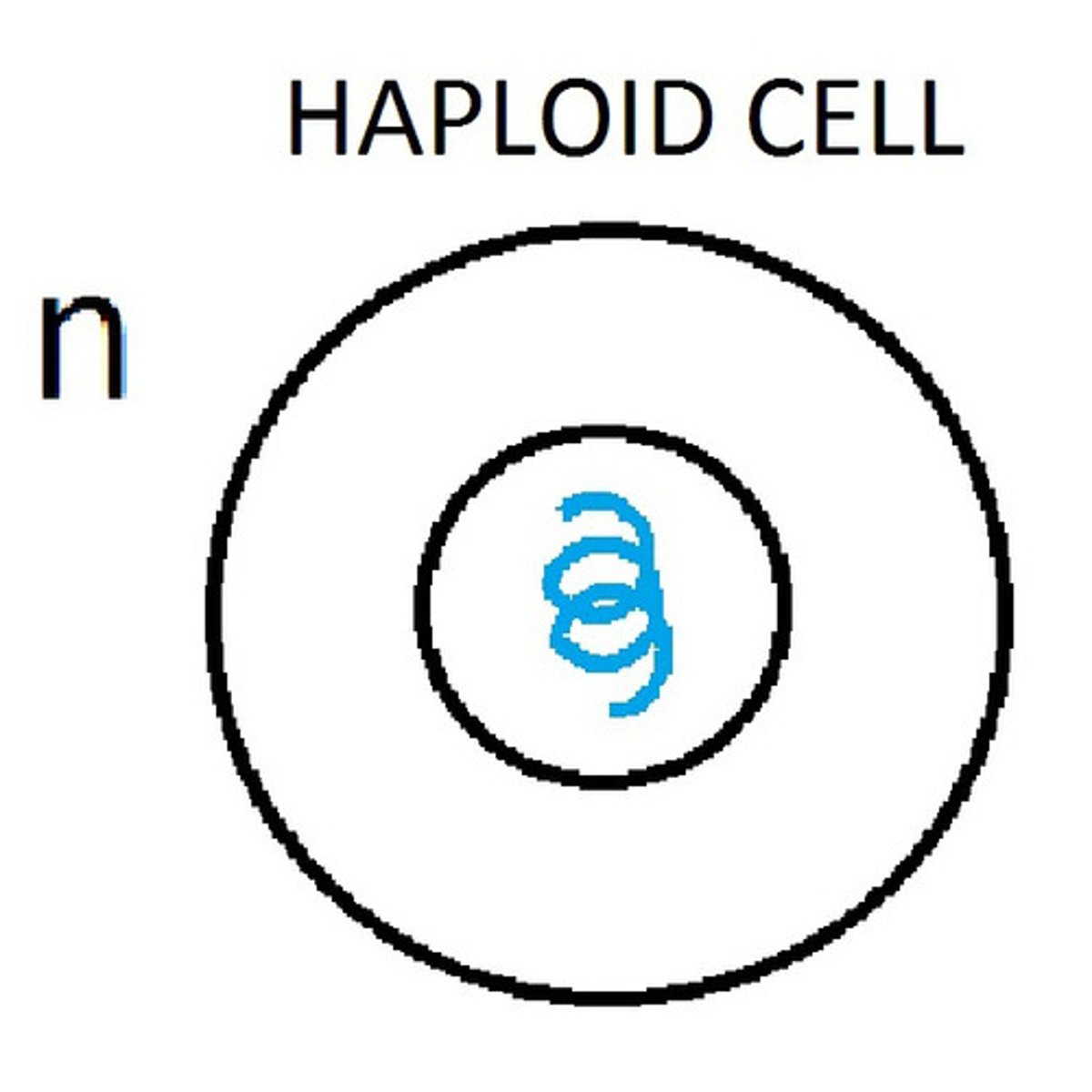
Haploid
cell having only one complete set of chromosomes
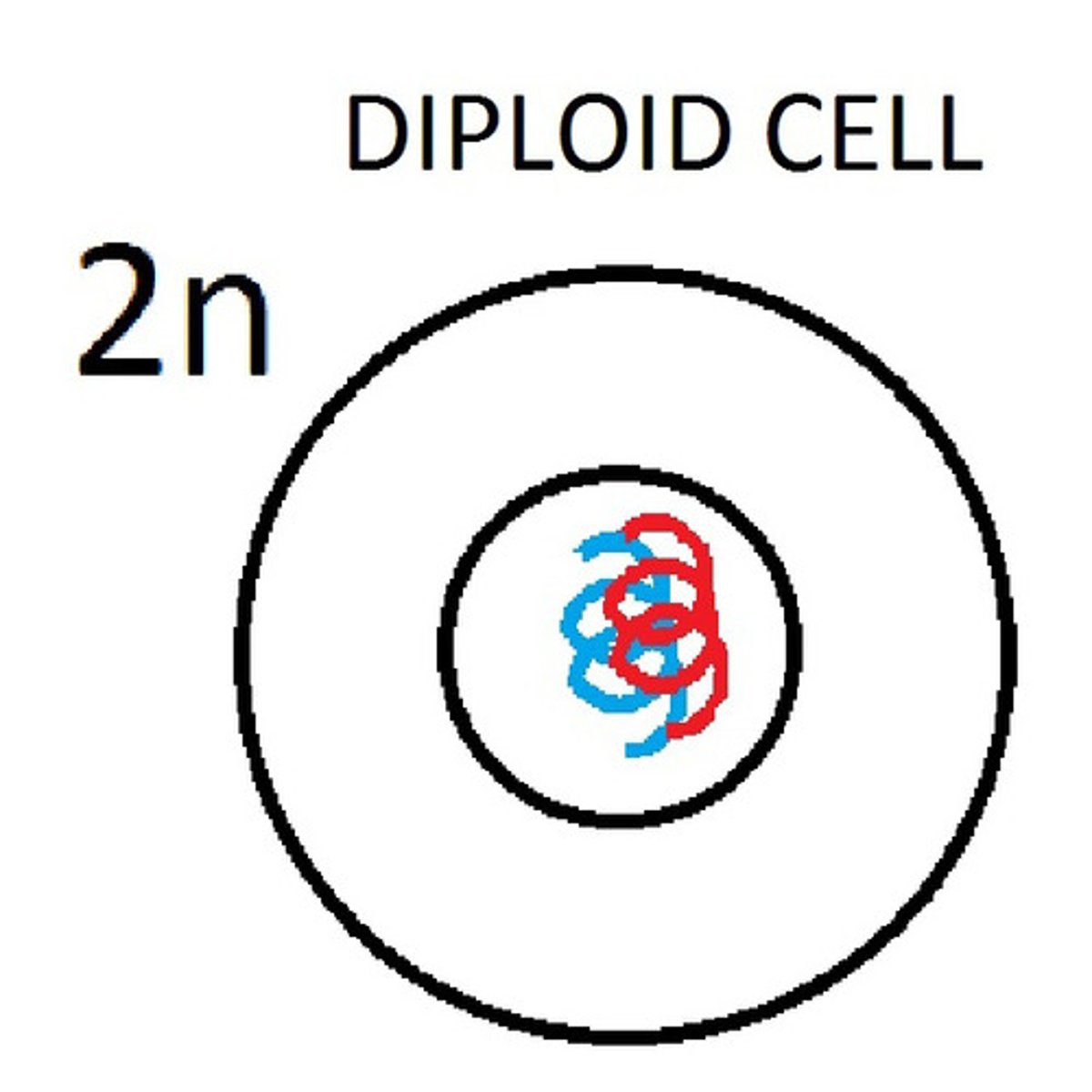
Diploid
cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number
functions of mitosis
embryonic development, tissue growth, replacement of dead cells, repair of injured tissues
function of meiosis
sexual reproduction
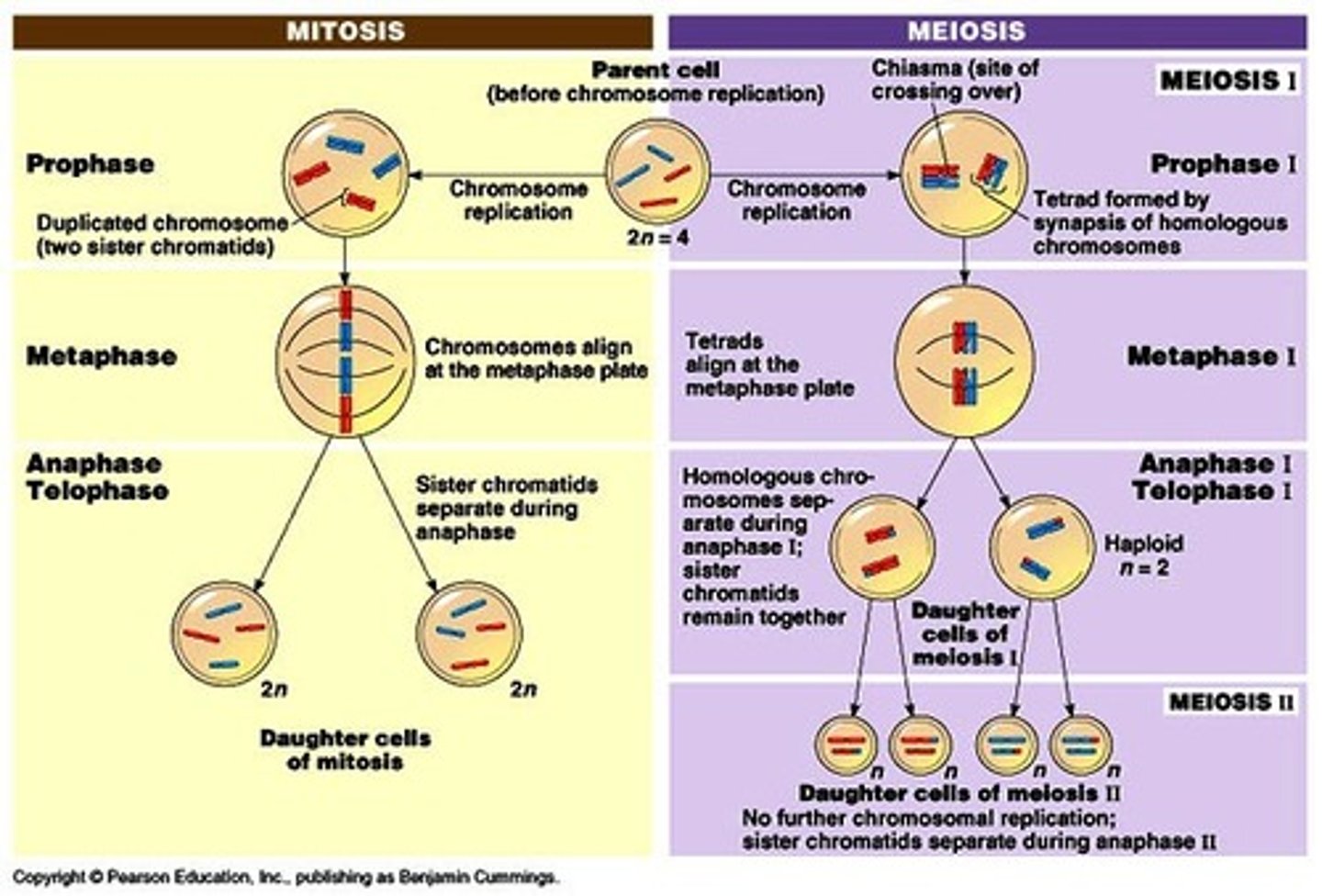
Stages of Mitosis
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Stages of meiosis
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
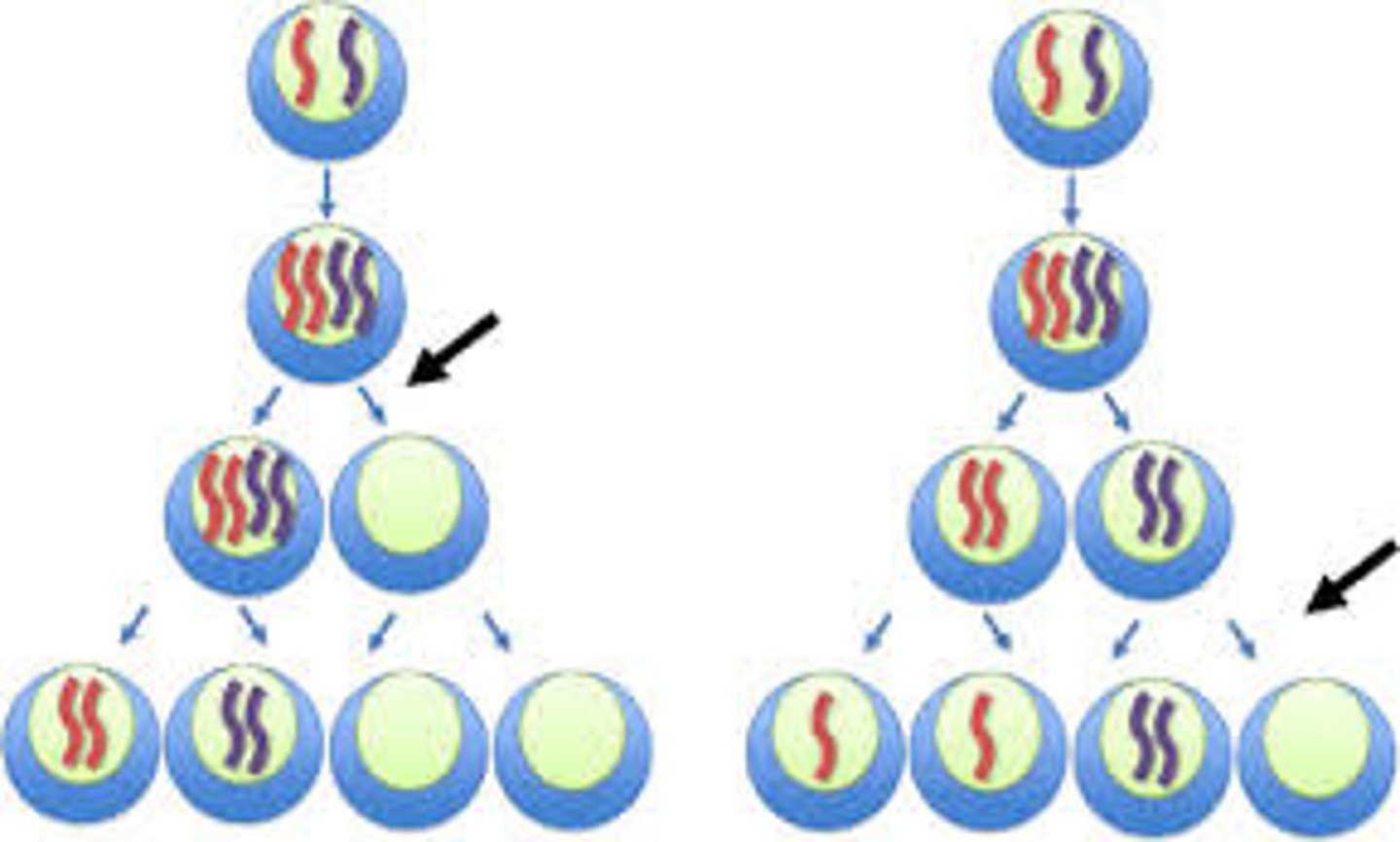
Difference between Meiosis I and Meiosis II
In Meiosis I, DNA is replicated and cross over occurs; in Meiosis II, chromosome replication does NOT occur. I results in 2 haploid cells, II results in 4 haploid cells. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes while meiosis II separates sister chromatids.
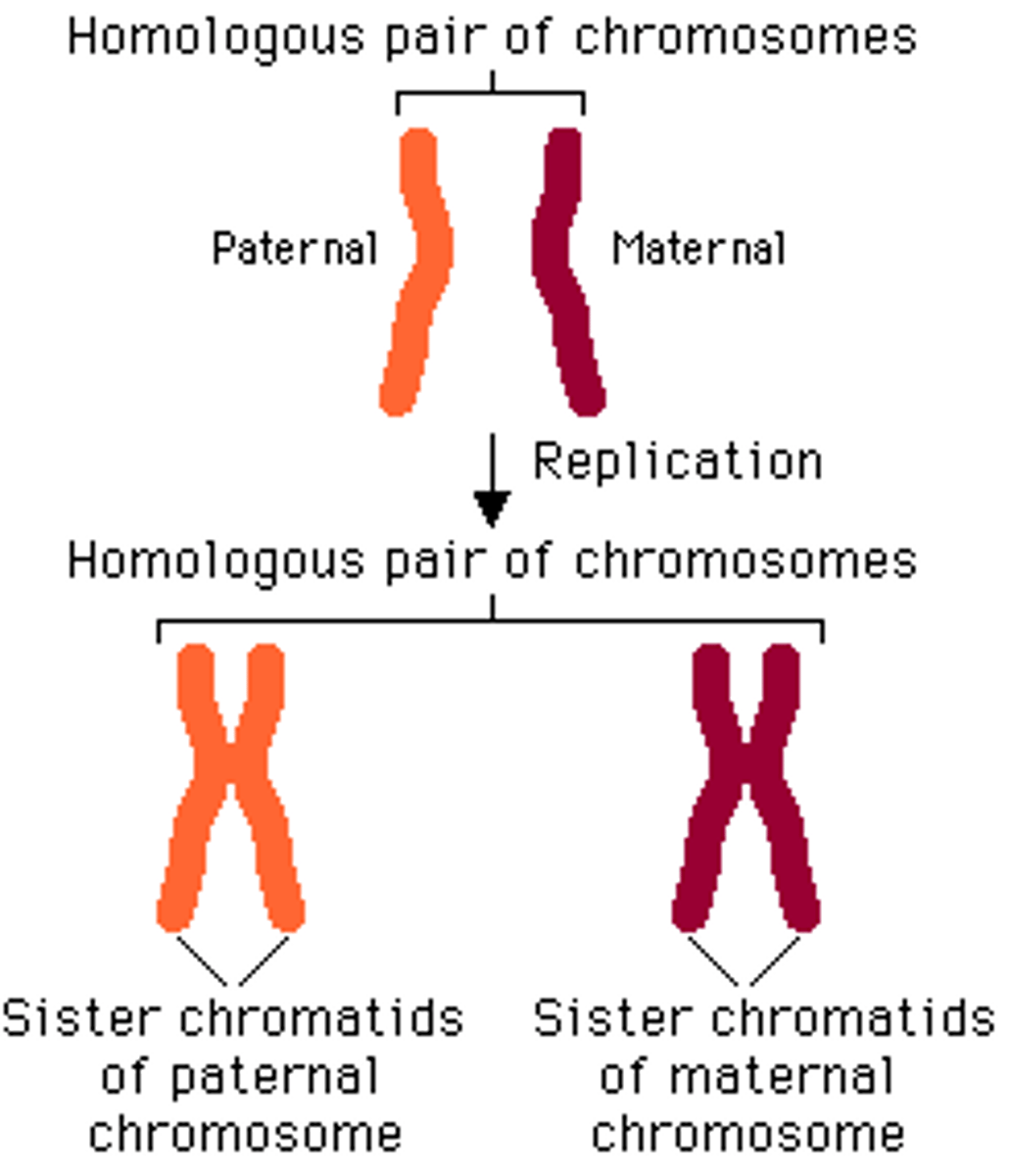
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
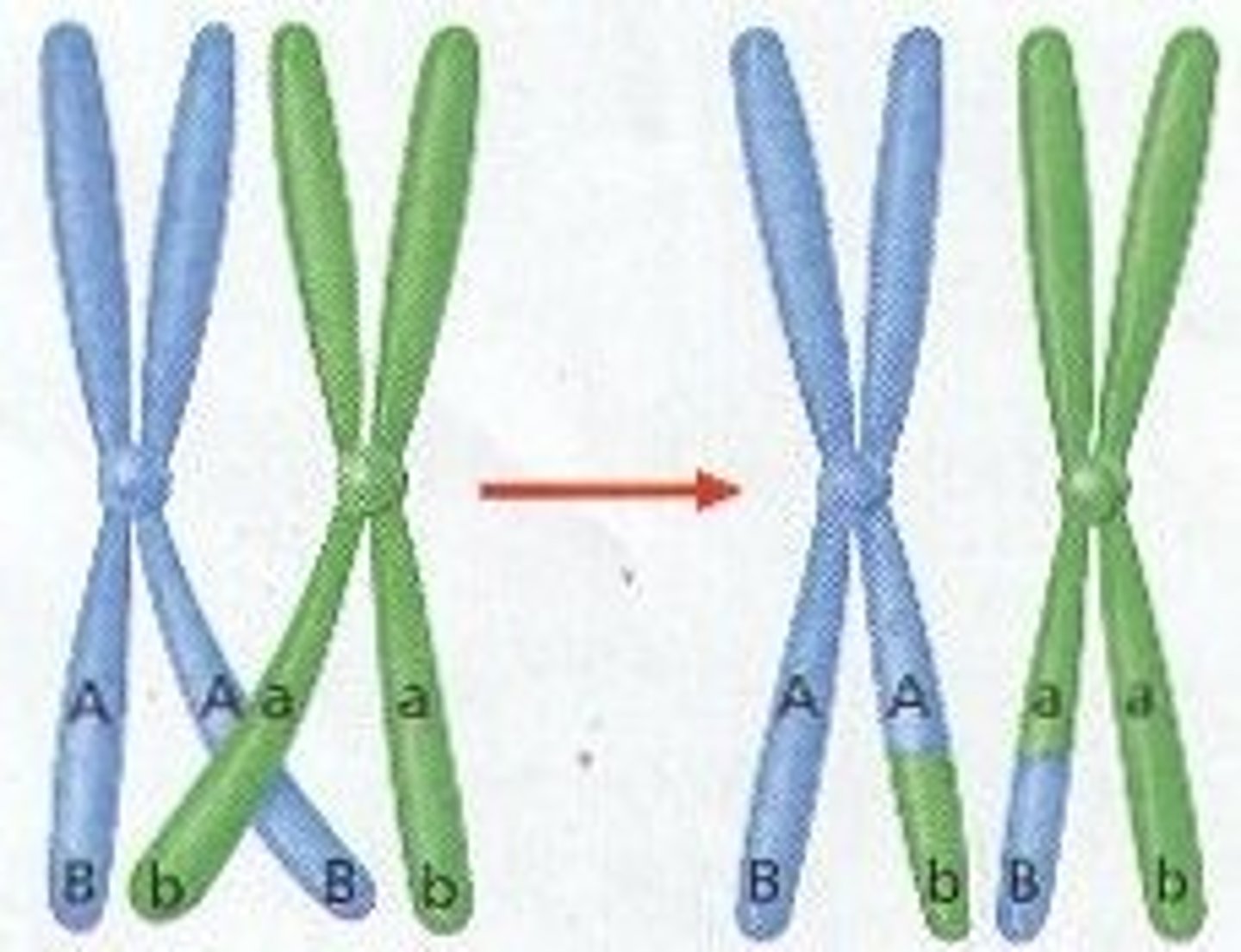
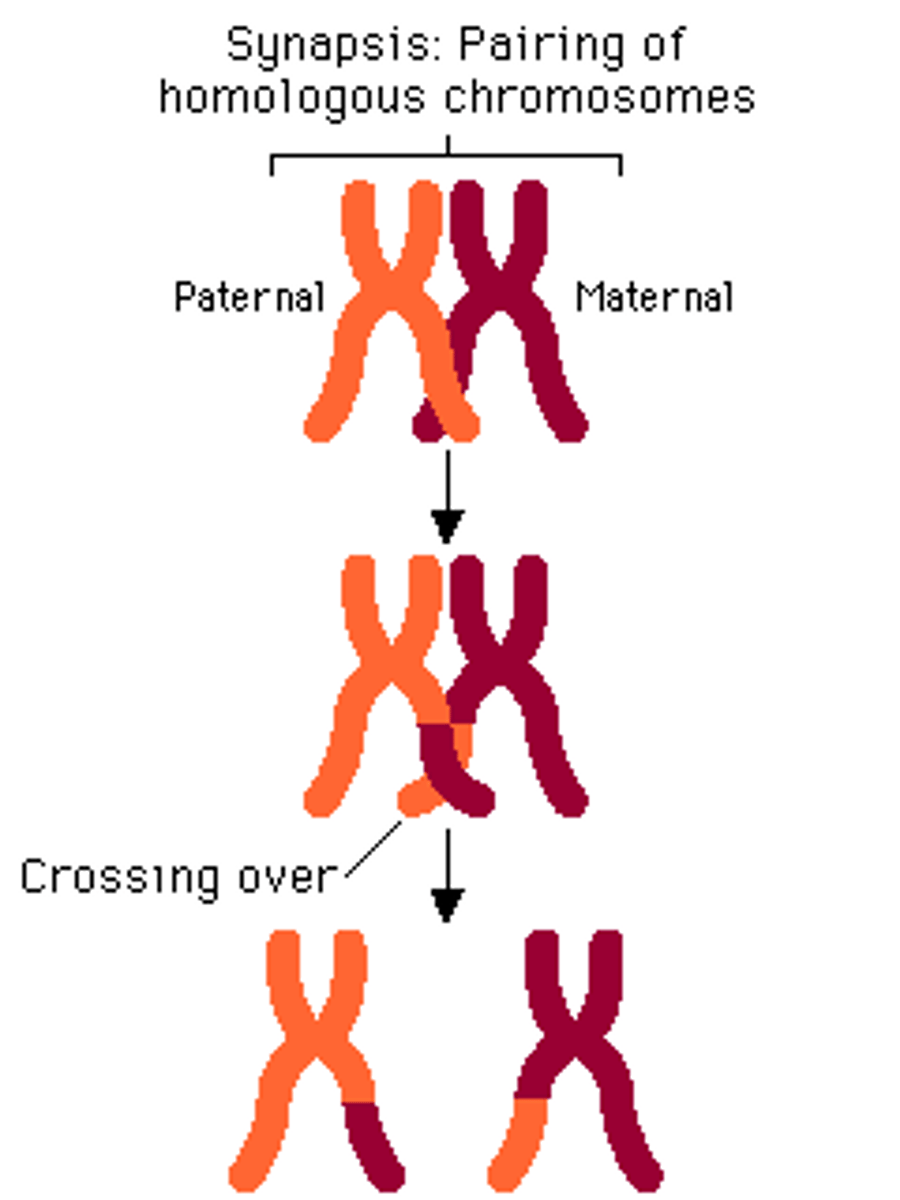
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis. Occurs during the Prophase of Meiosis I.
spindle fibers
help pull apart the cell during replication and are made up of microtubules
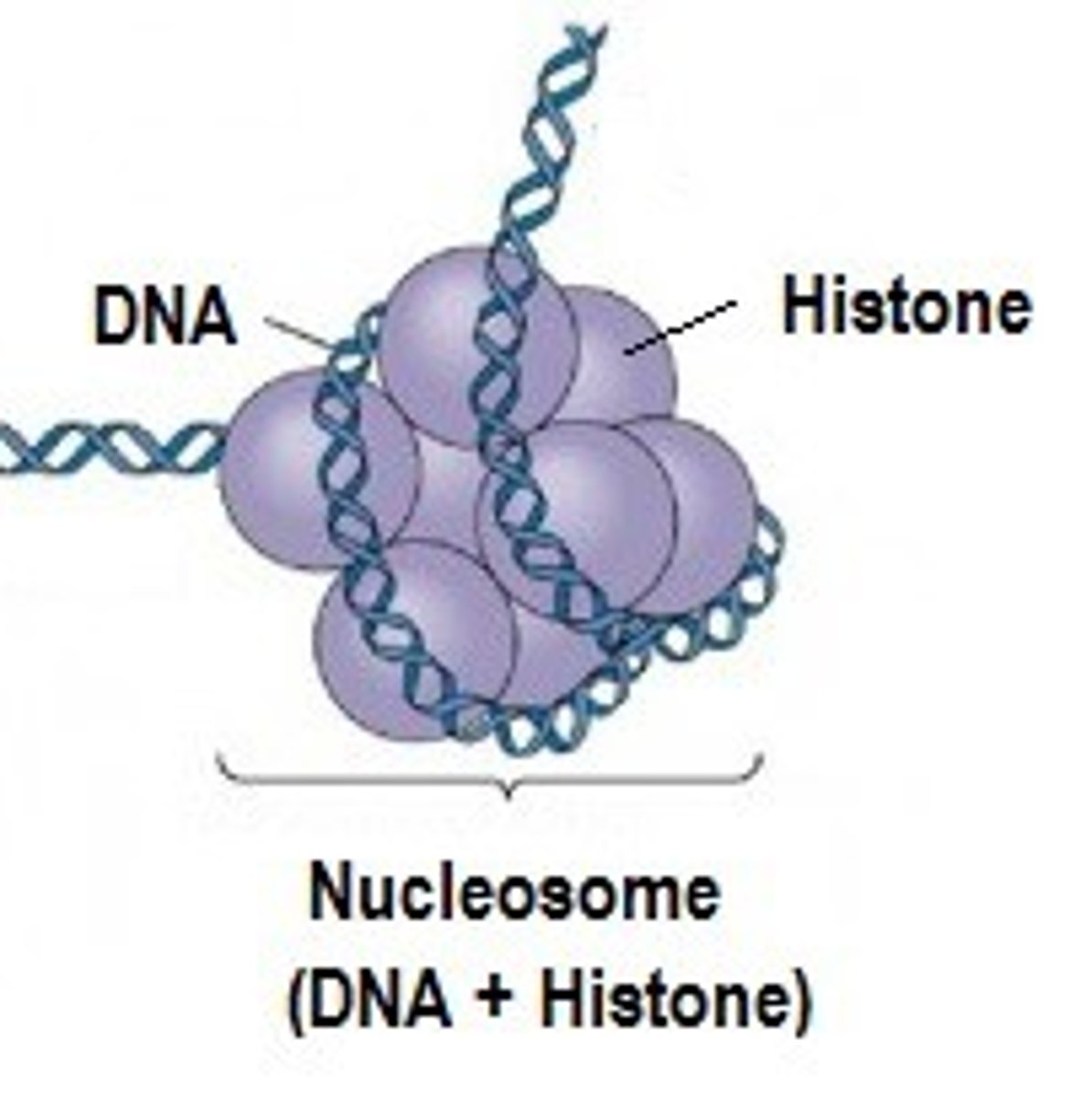
histomes
the protein that the DNA strands winds up around
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
sister chromatids
joined copies of the original chromosome
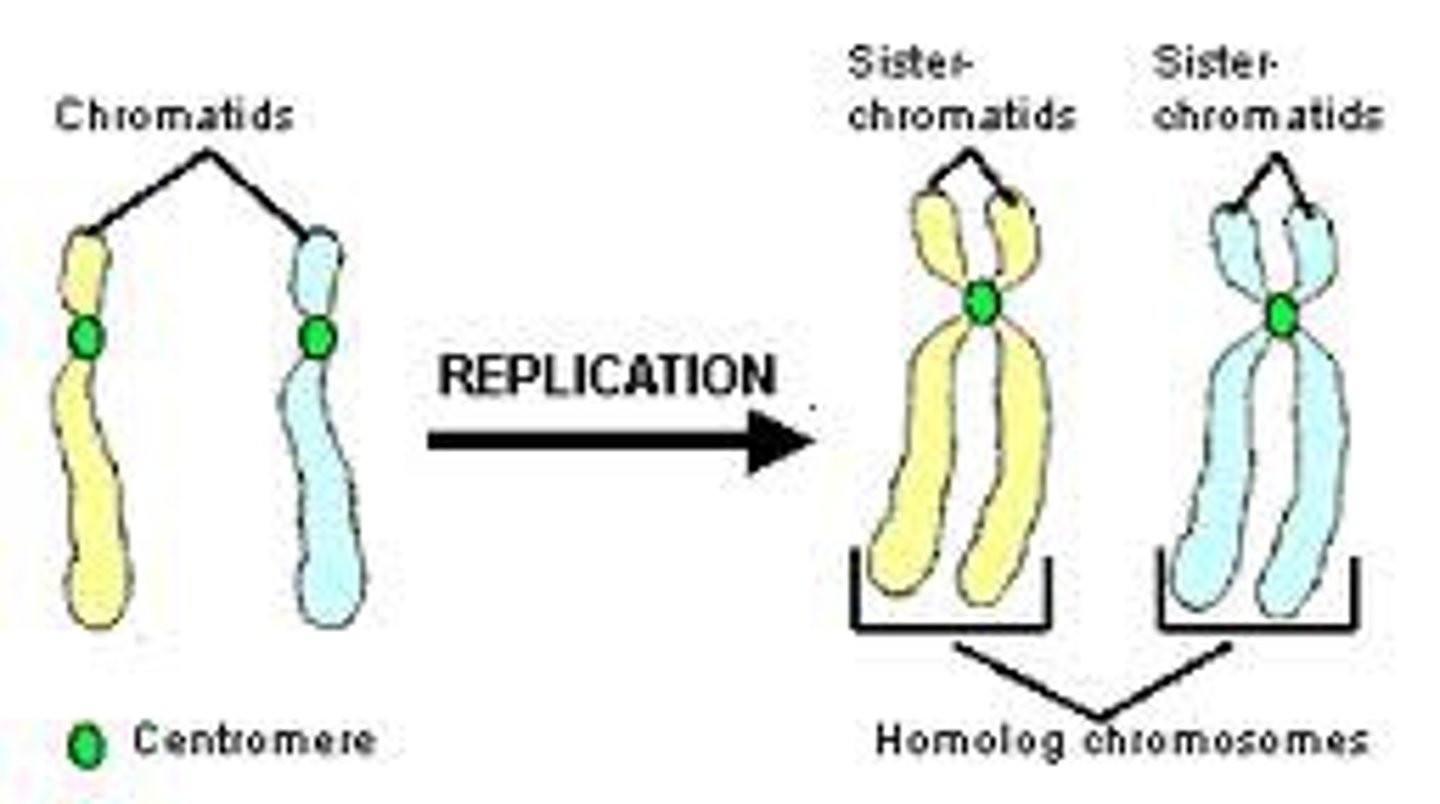
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
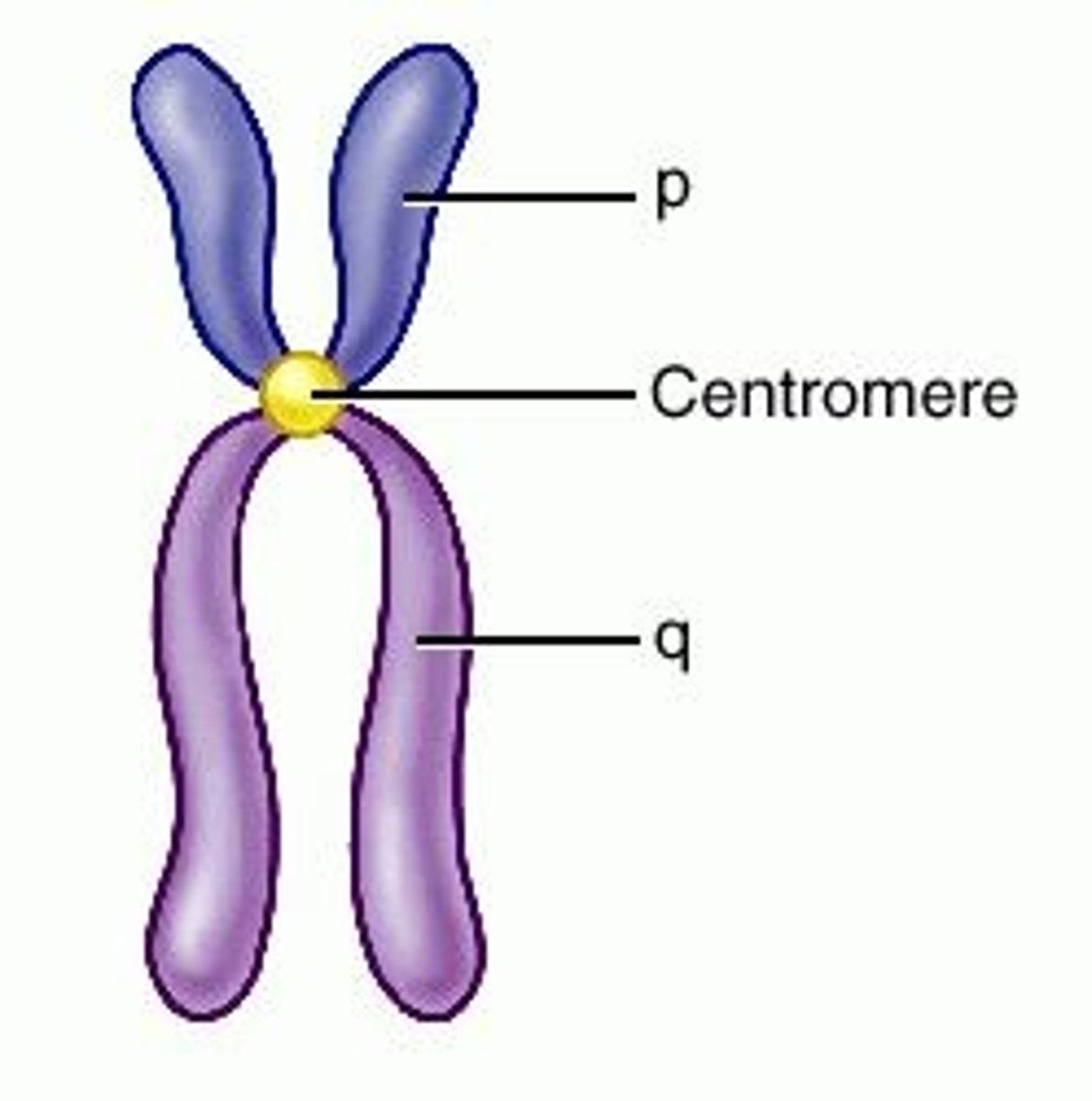
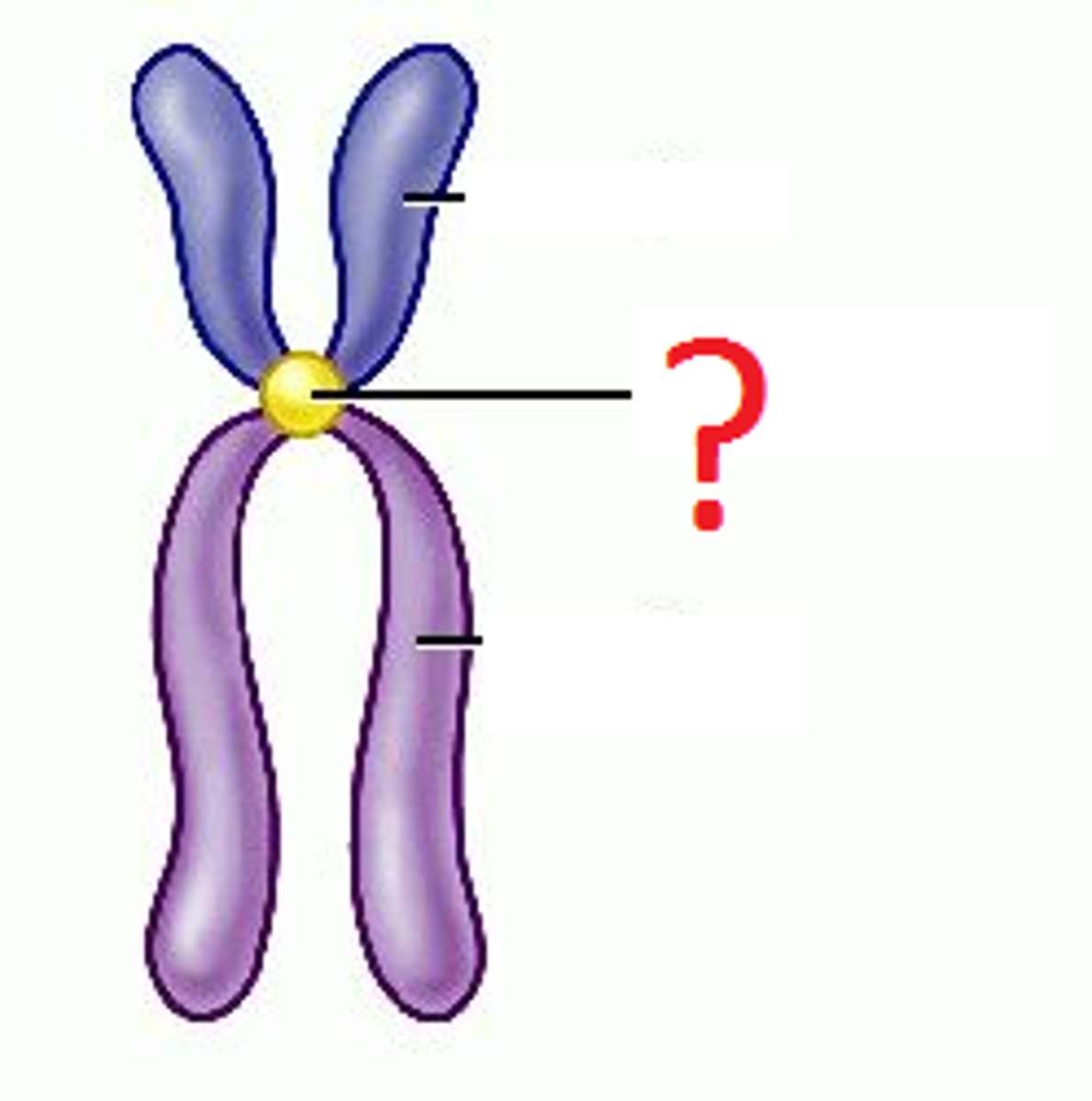
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
what undergoes crossing over?
Homologous Chromosomes
From one spermatogonia how many sperm cells do you get?
4 Sperm Cells
somatic cells
Any cells in the body other than reproductive cells. Contain double the count of chromosomes as Gametes.
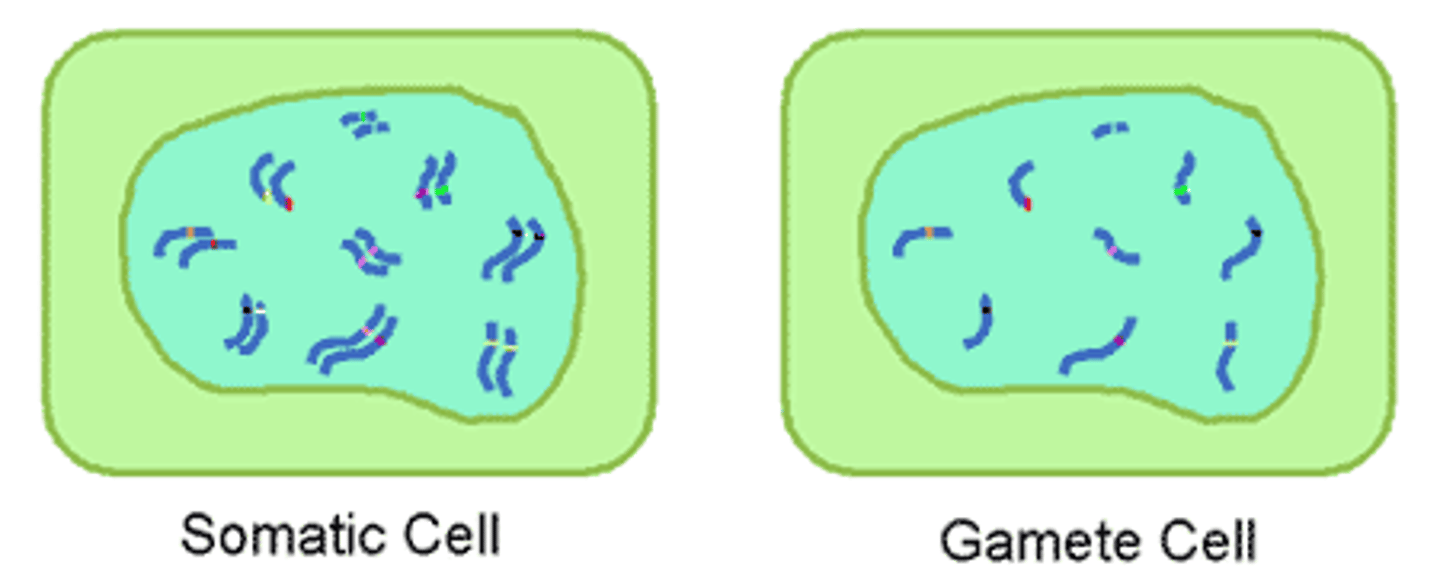
Gametes
Sex cells. Contain half as many chromosomes as somatic cells
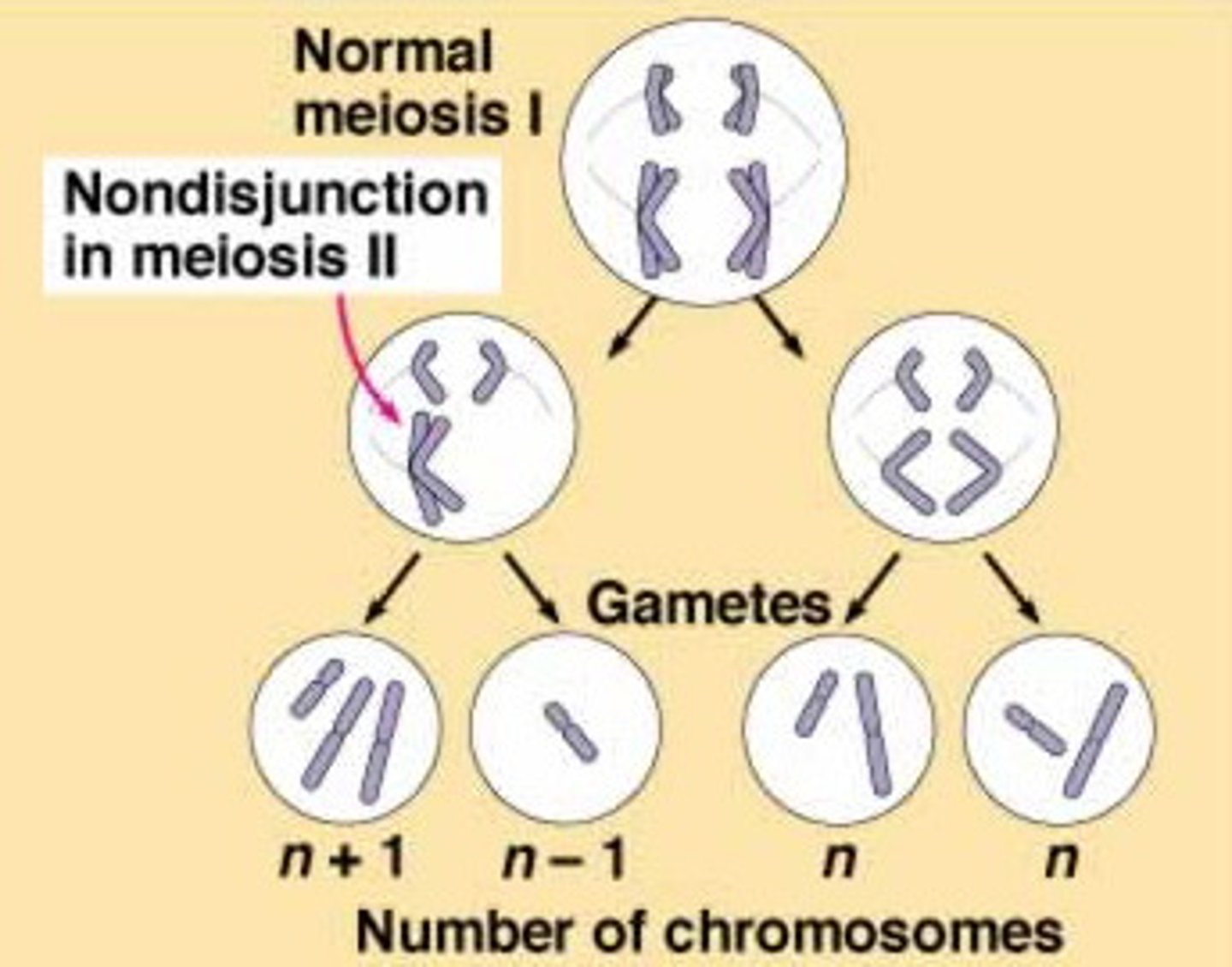
Nondisjunction
An error in meiosis or mitosis in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate properly from each other.
Meiosis I nondisjunction
Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate
Gamete w/ 24 chromosomes has both paternal and maternal pairs. Results two gametes that lack one chromosome and two gametes with two copies of one chromosome
Meiosis II nondisjunction
tumor suppressor genes
A gene whose protein product inhibits cell division, thereby preventing the uncontrolled cell growth that contributes to cancer.
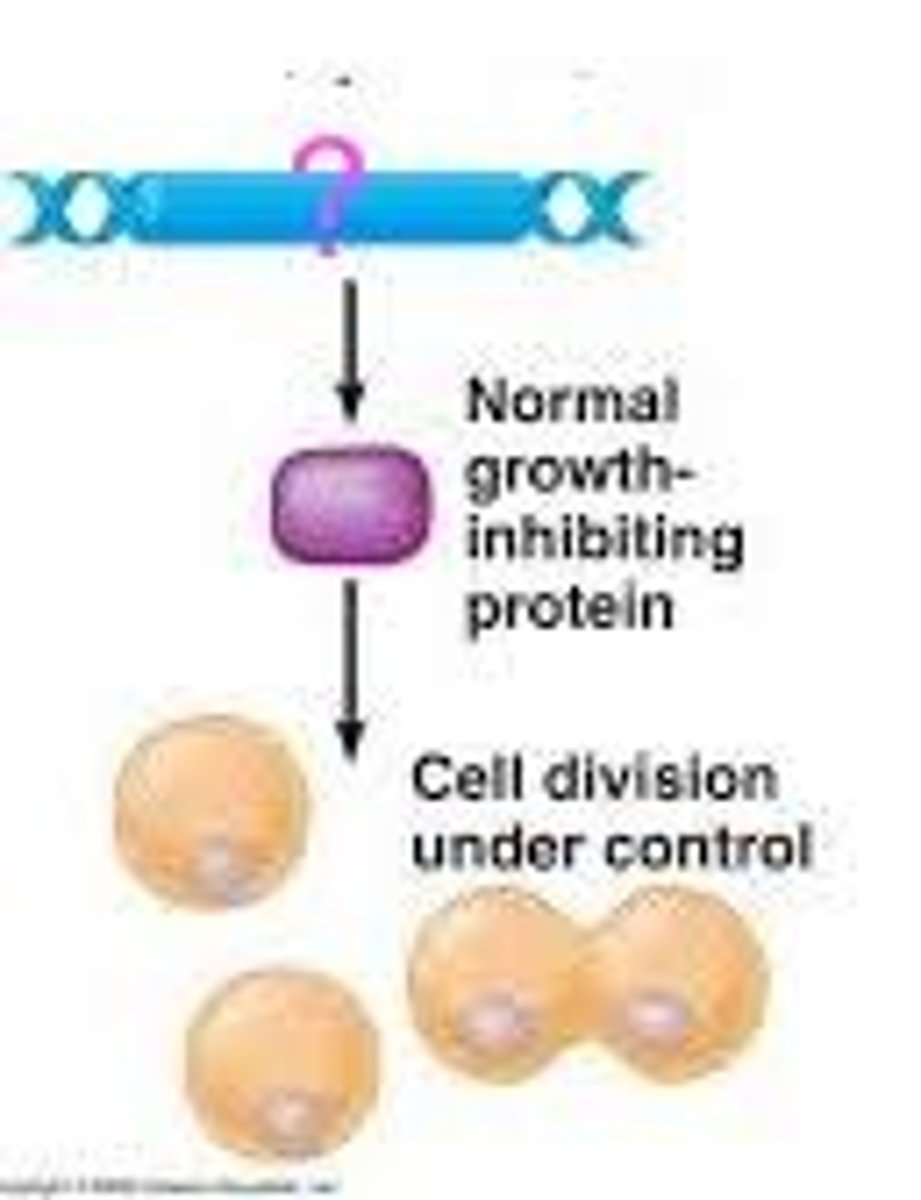
Cell that has its tumor suppressor cell deactivated and has become immortal
Cancer cell
recombinant chromatids
chromatids with a combination of DNA from both homologous chromosomes, formed by crossing over and chiasmata in meiosis.
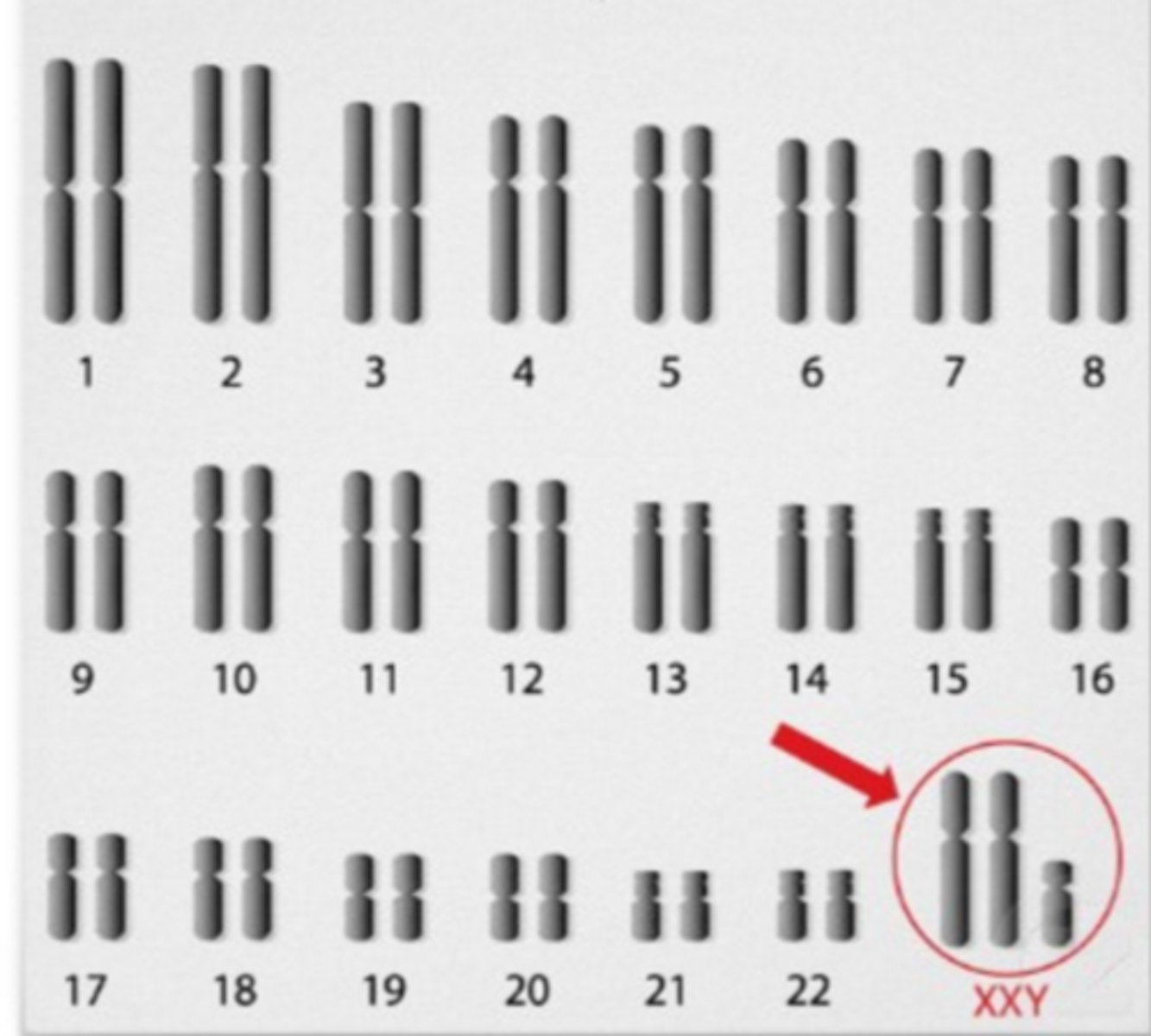
trisomy 23 (XXY)
Klinefelter syndrome

Trisomy
a condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nuclei, causing developmental abnormalities.
Trimsomy 18
Edward's Syndrome
Trisomy 21
condition in which an individual has three number 21 chromosomes, resulting in Down syndrome
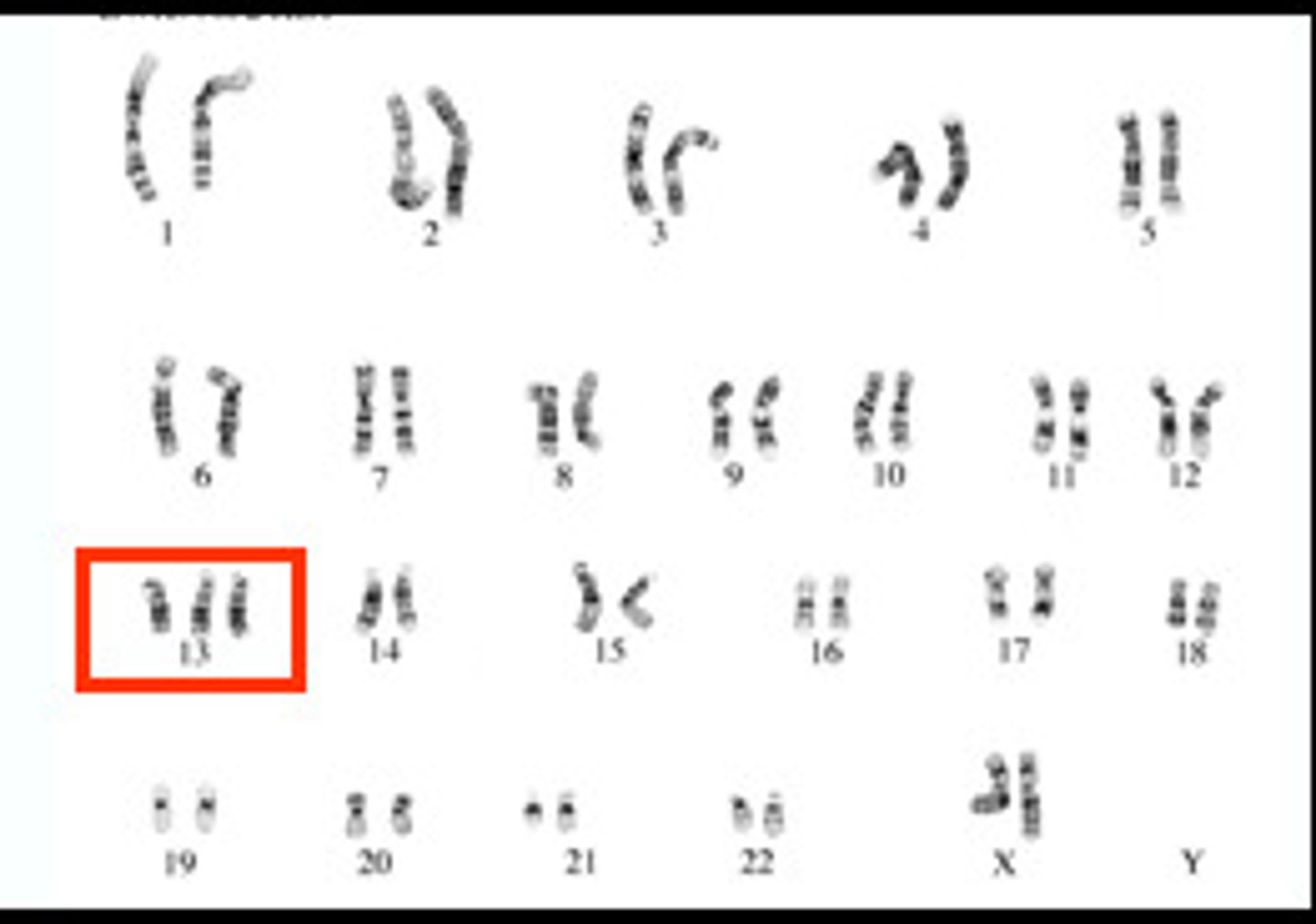
Trisomy 13
Patau syndrome
alteration of generations
The alteration of two or more different forms in the life cycle of a plant or animal.
identical twins
twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
fraternal twins
twins who come from two different eggs fertilized by two different sperm.
Monosomy
Chromosomal abnormality consisting of the absence of one chromosome from the normal diploid number
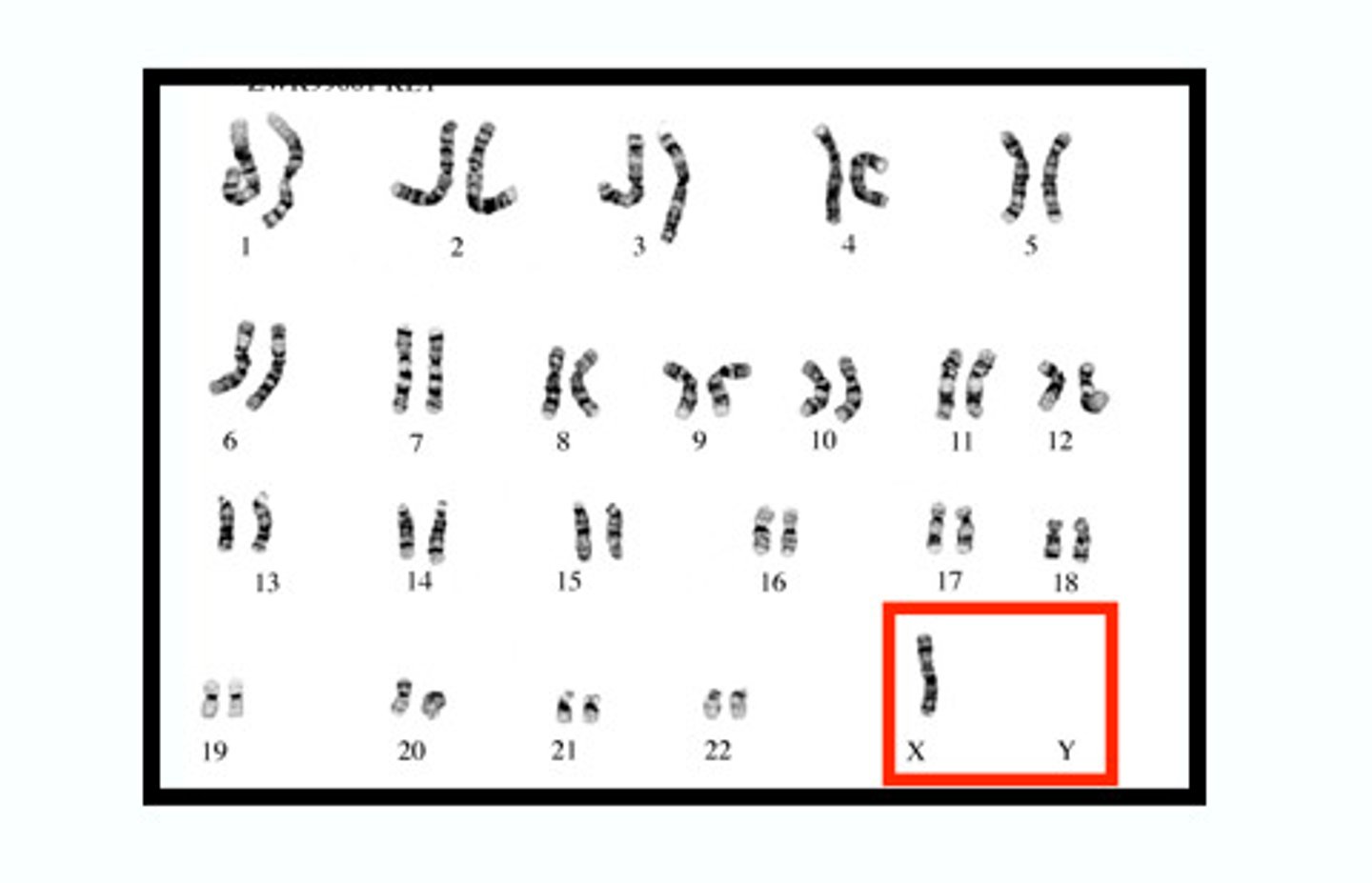
Carcinogen
A cancer-causing substance, An agent that effects the genetic make-up of the cell.

Telemeres
DNA at the tips of chromosomes
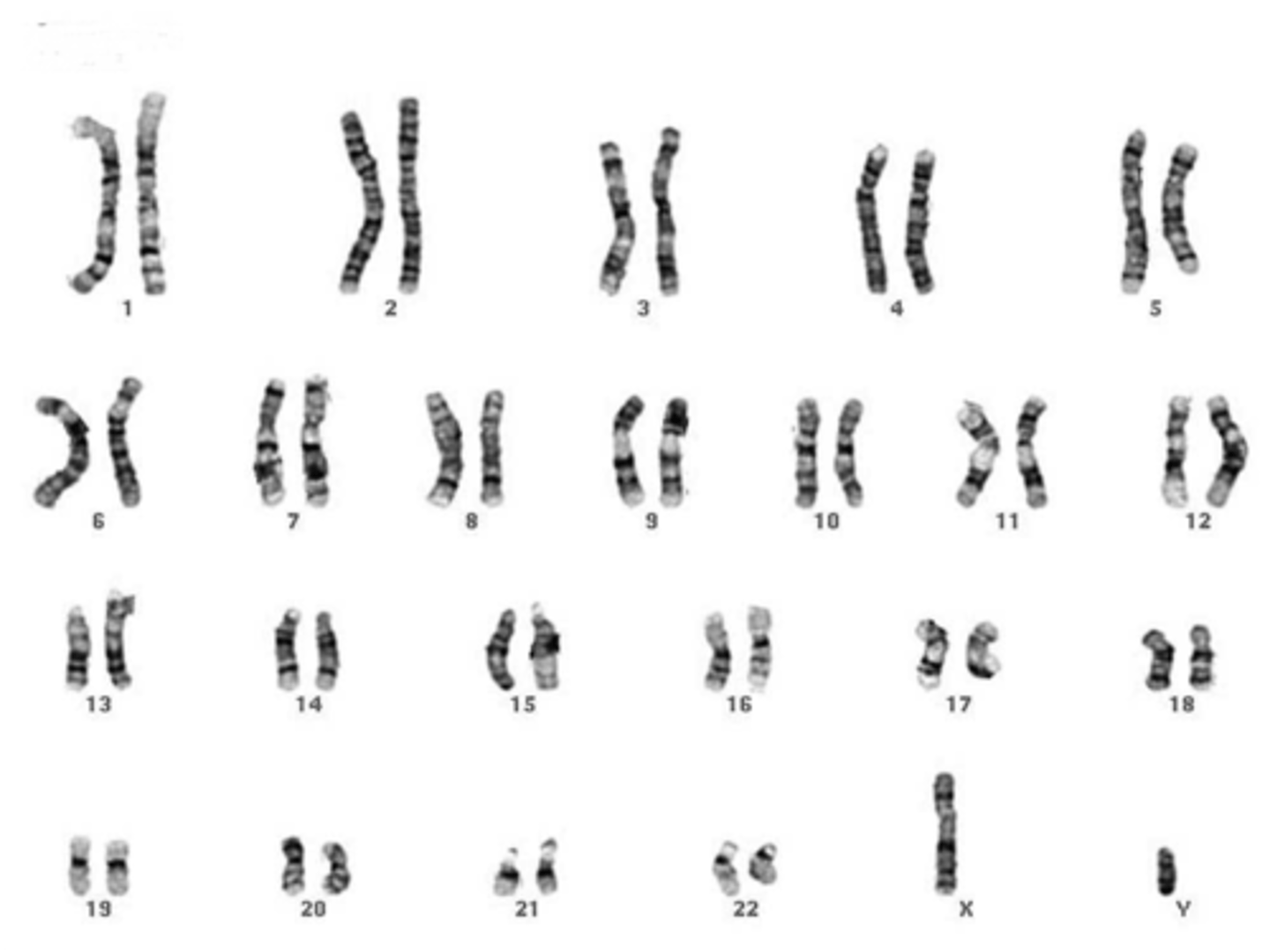
Karotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
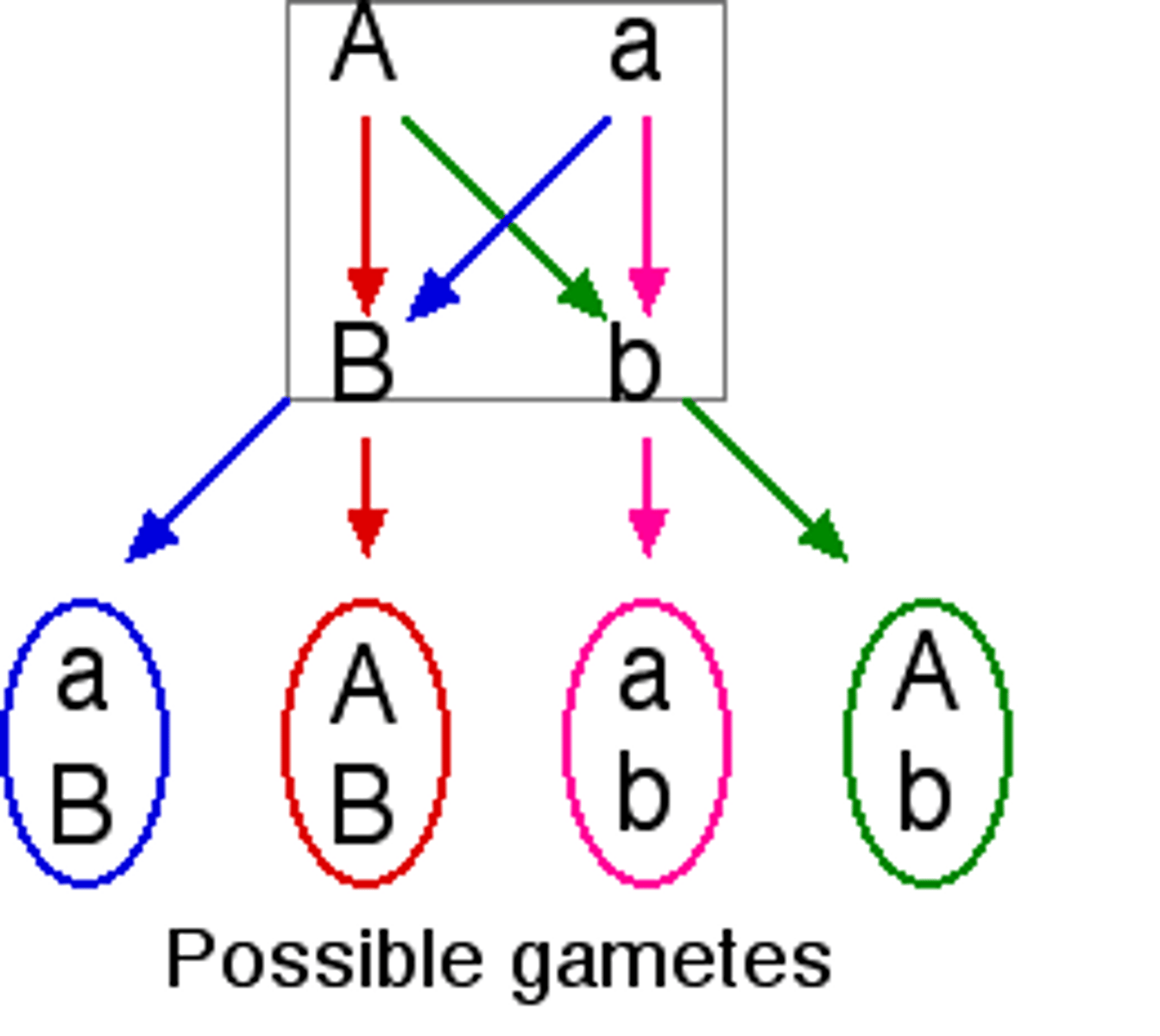
independent assortment of chromosomes
The random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes into gametes during meiosis.
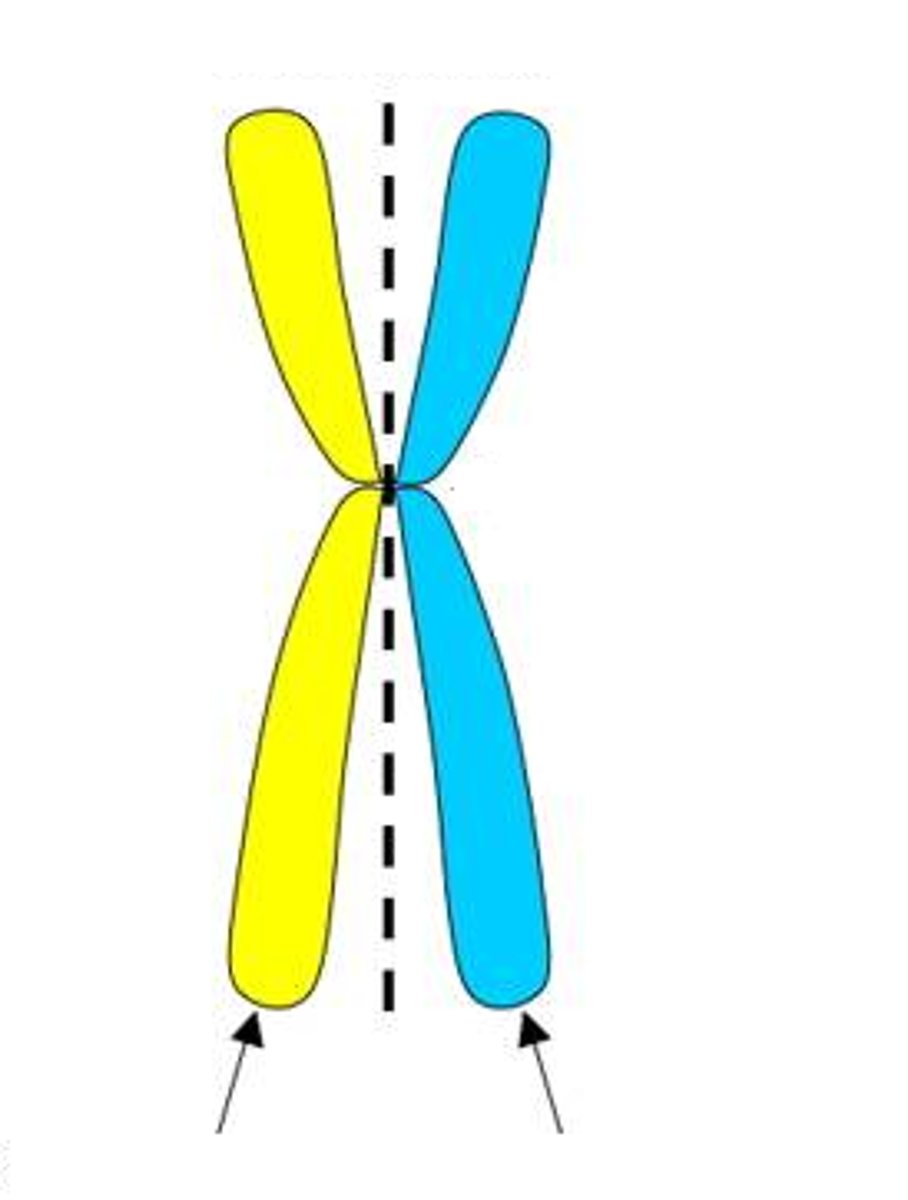
synapsis
the pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
reduction division of meiosis
Reduces chromosome number from 2n to n