12 DNA - Structure and Function
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
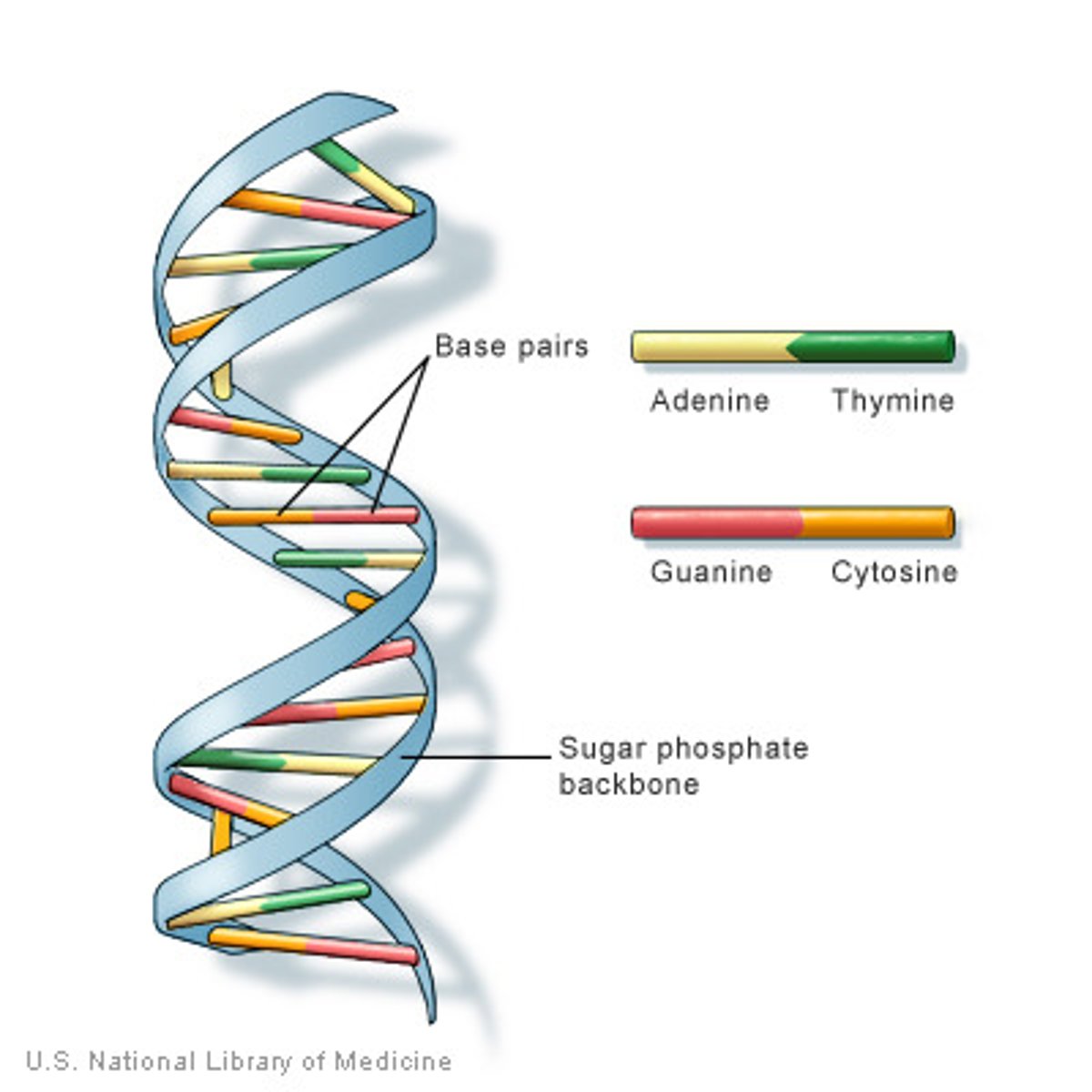
Double helix
Shape of DNA

Nucleotide
monomer (subunit) of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
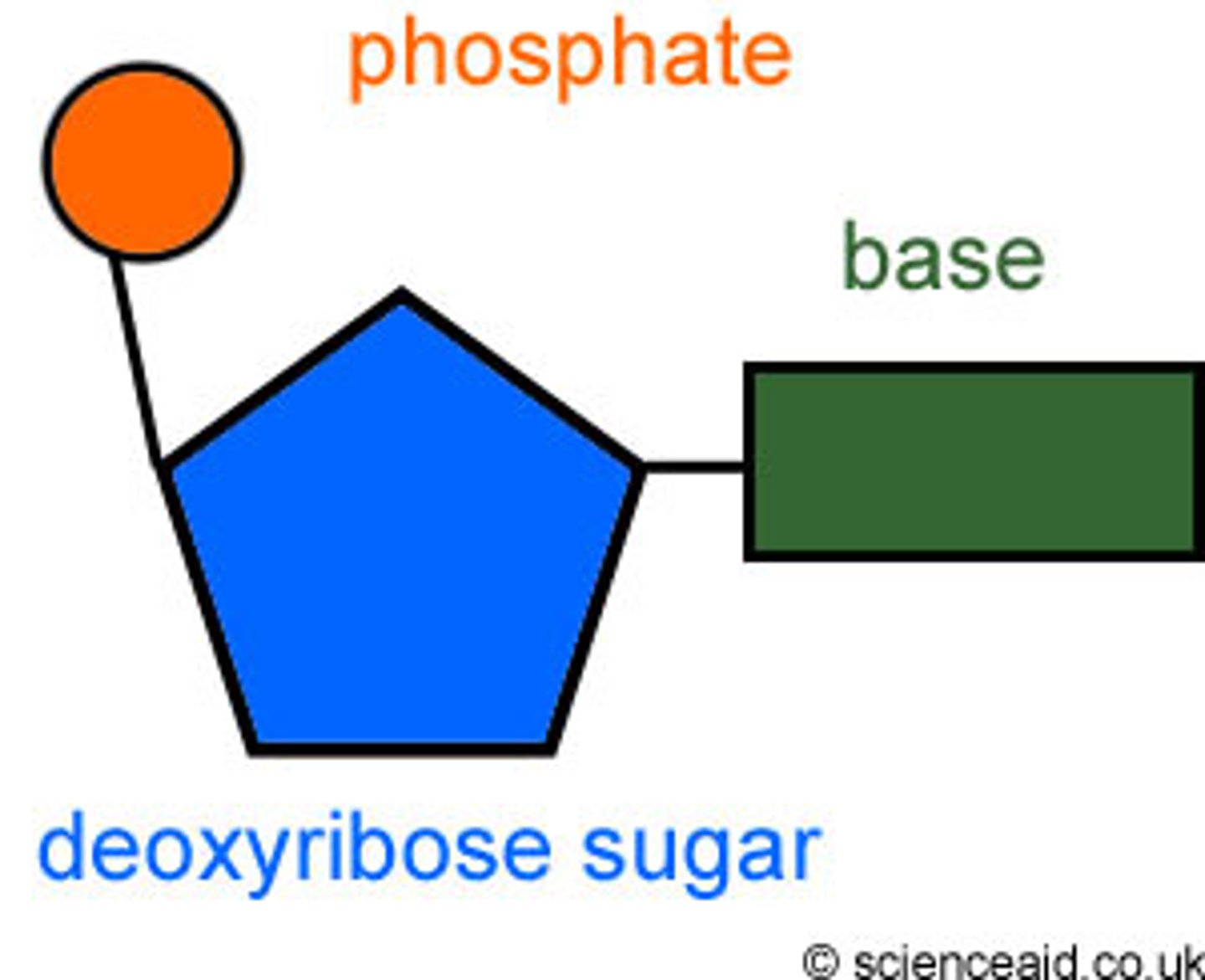
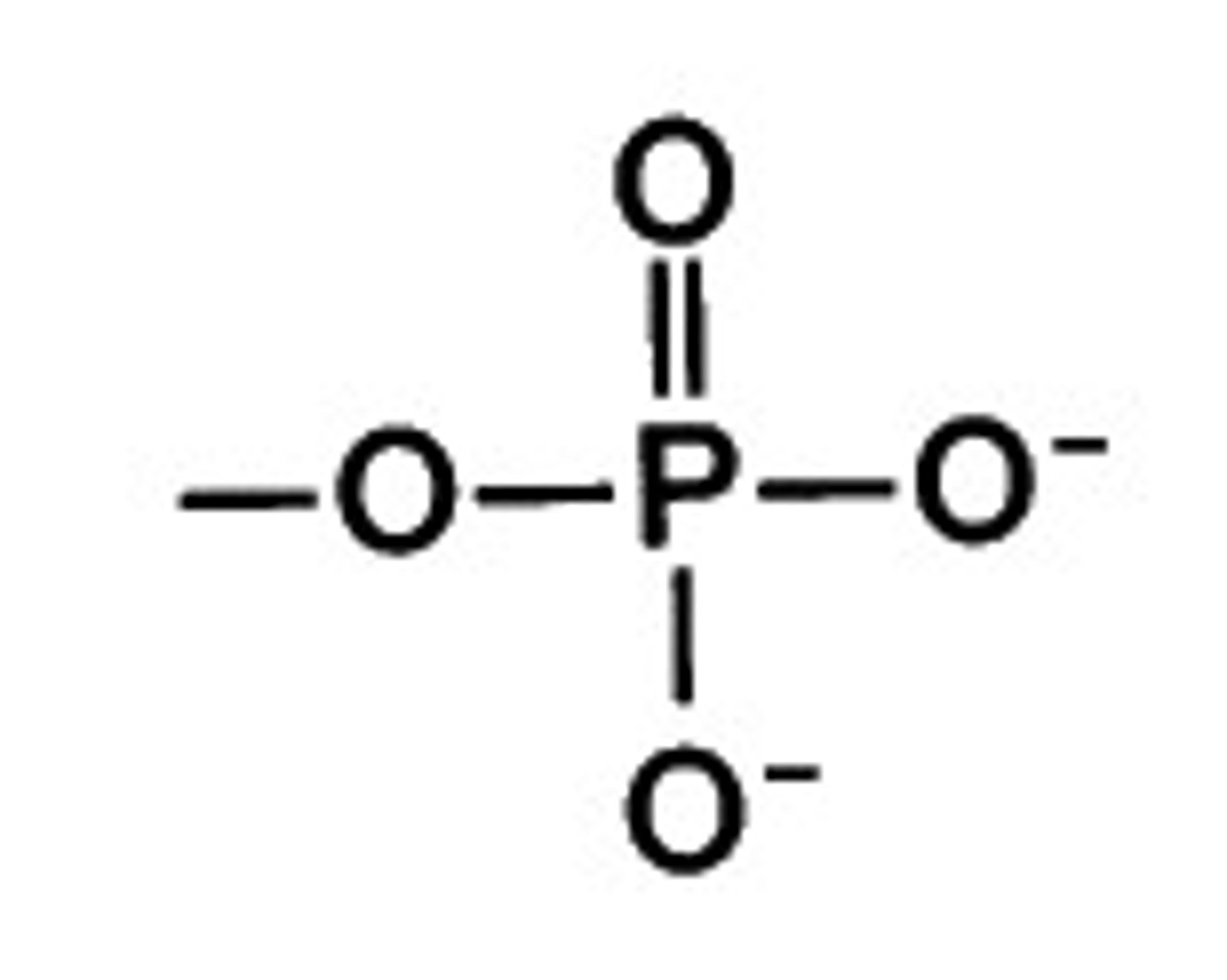
Phosphate group
group that covalently bonds to the deoxyribose sugar along the sides of DNA
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
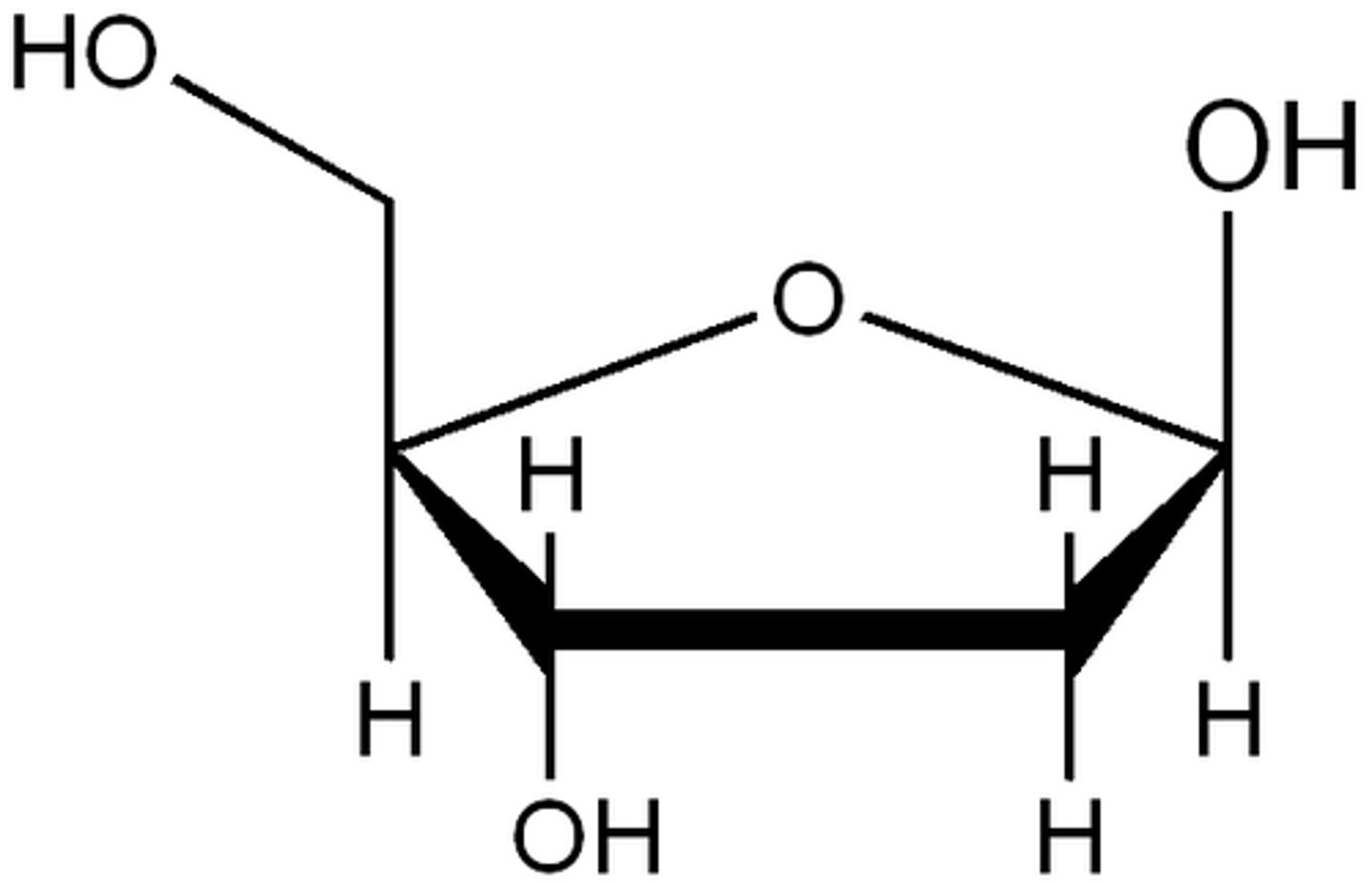
Nitrogenous base
A, T, C, G in the middle of DNA; the order determines traits, or characteristics
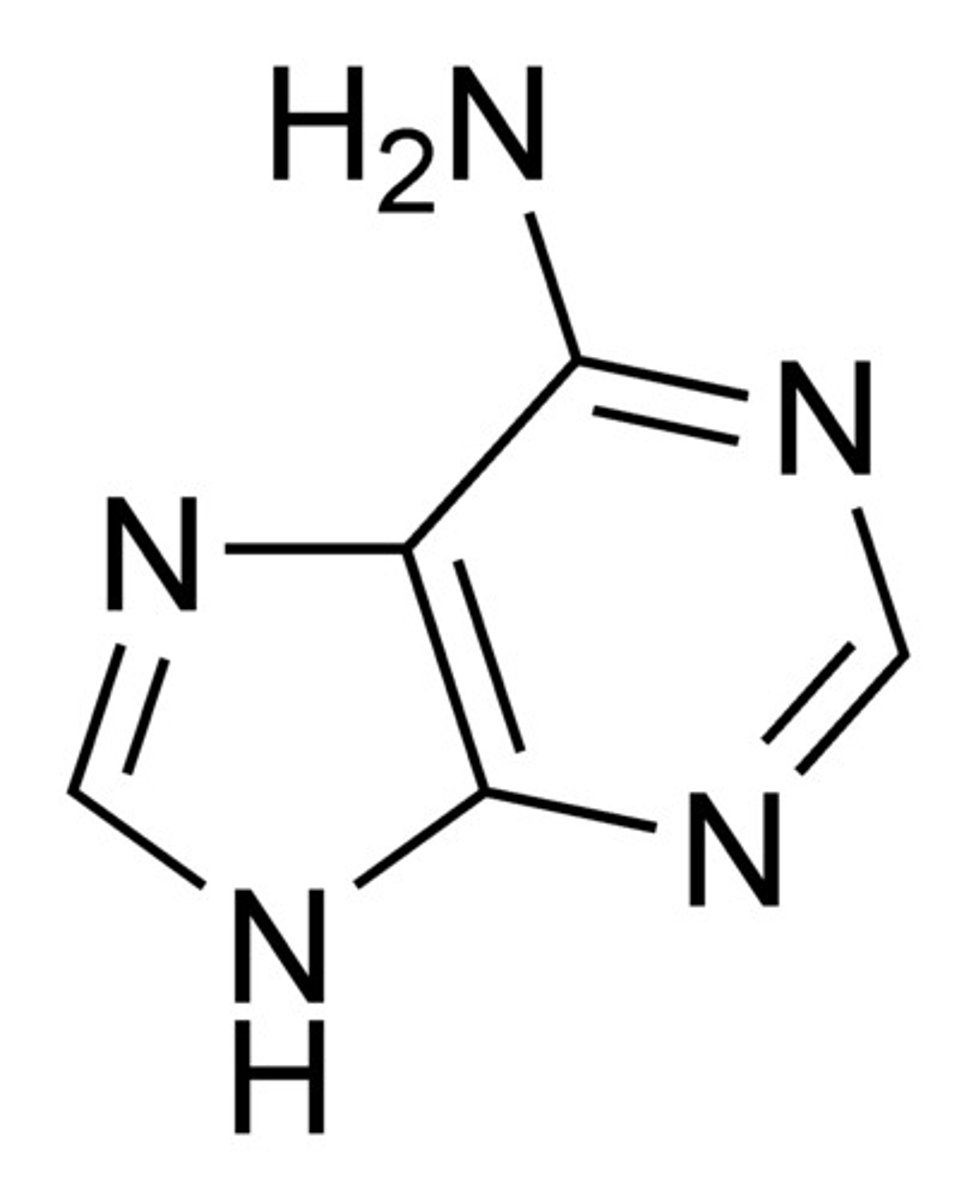
Adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA, purine structure
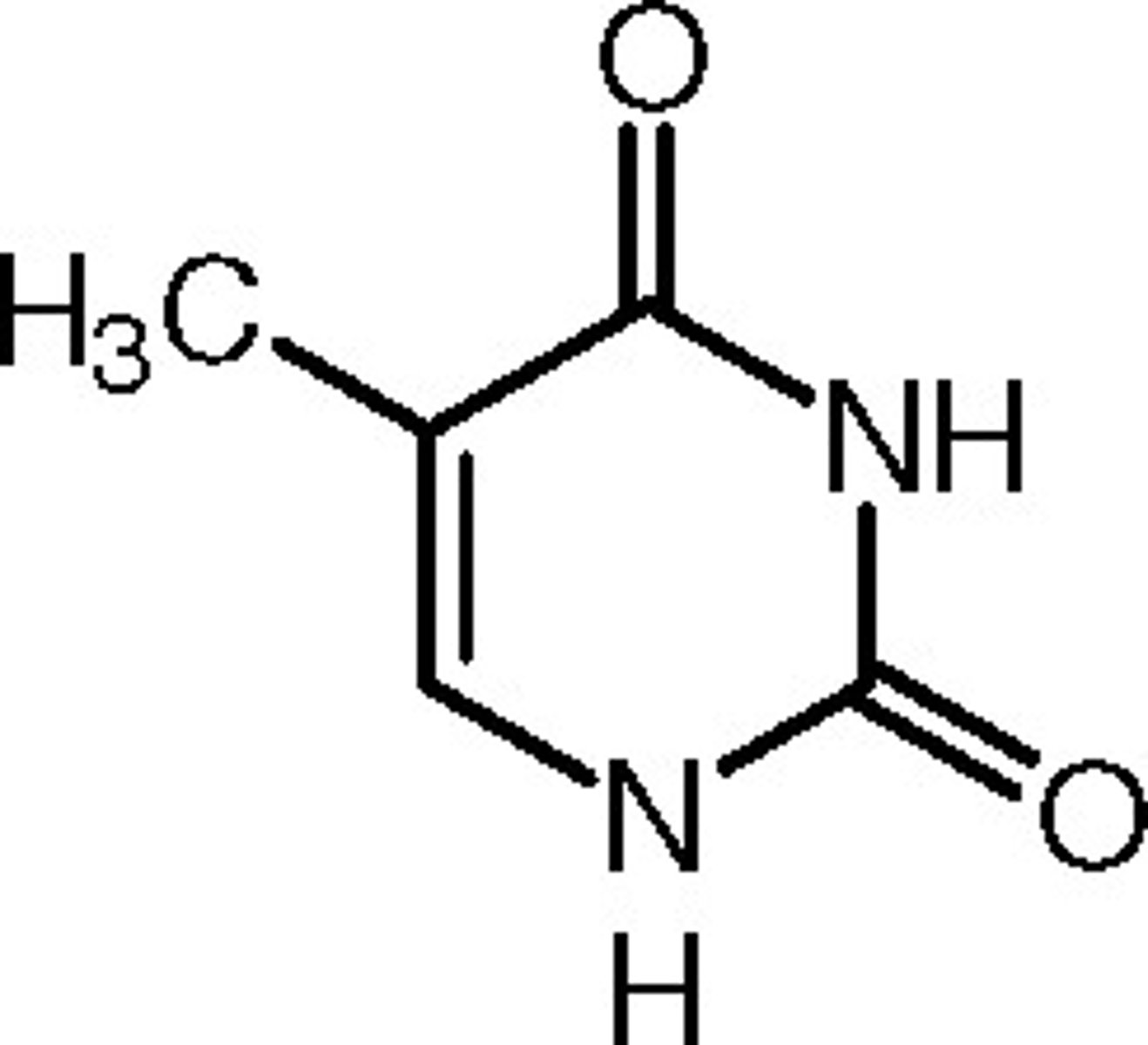
Thymine
The base that pairs Adenine in DNA, pyrimidine structure
Guanine
The base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA, purine structure
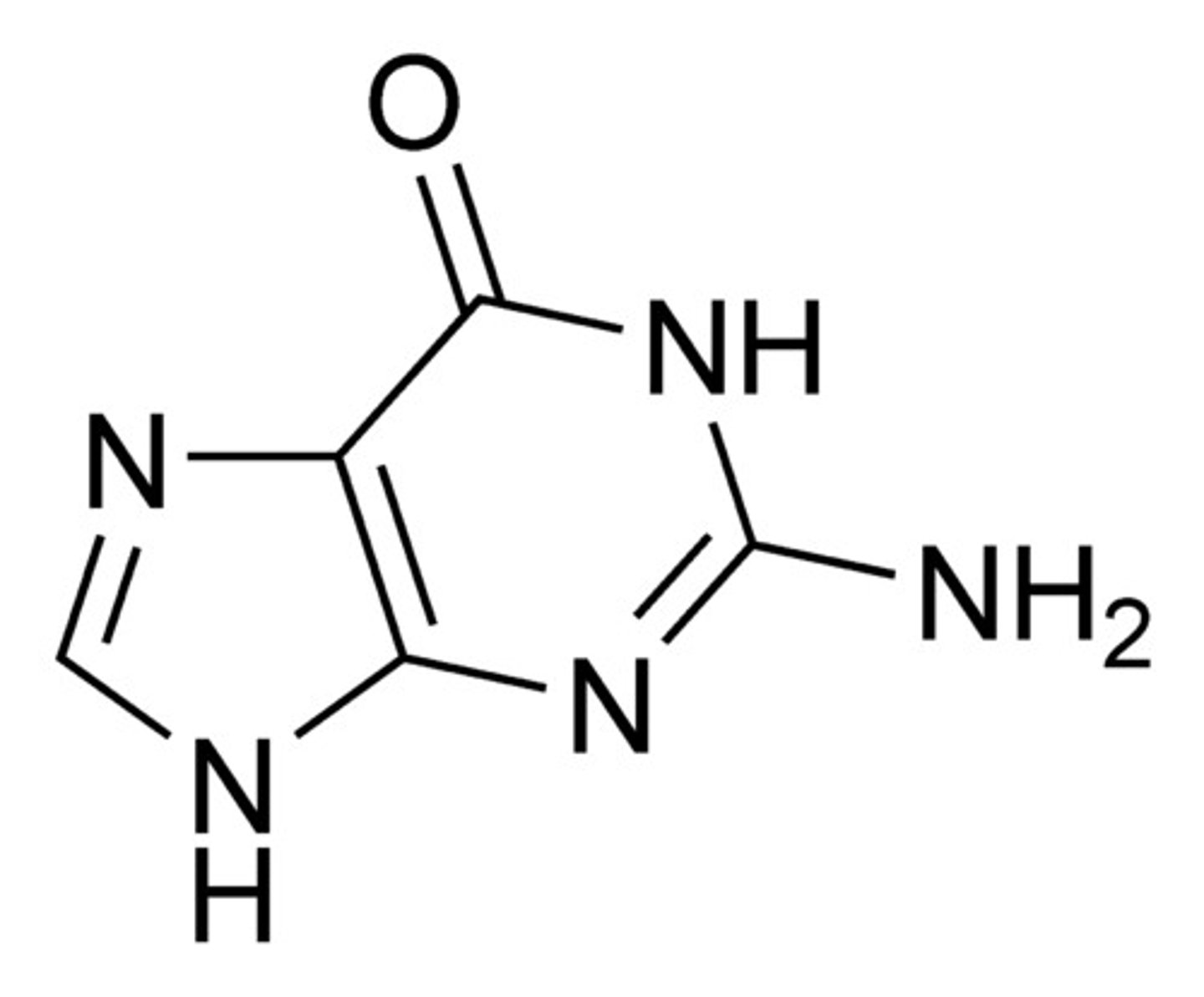
Cytosine
The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA, pyrimidine structure
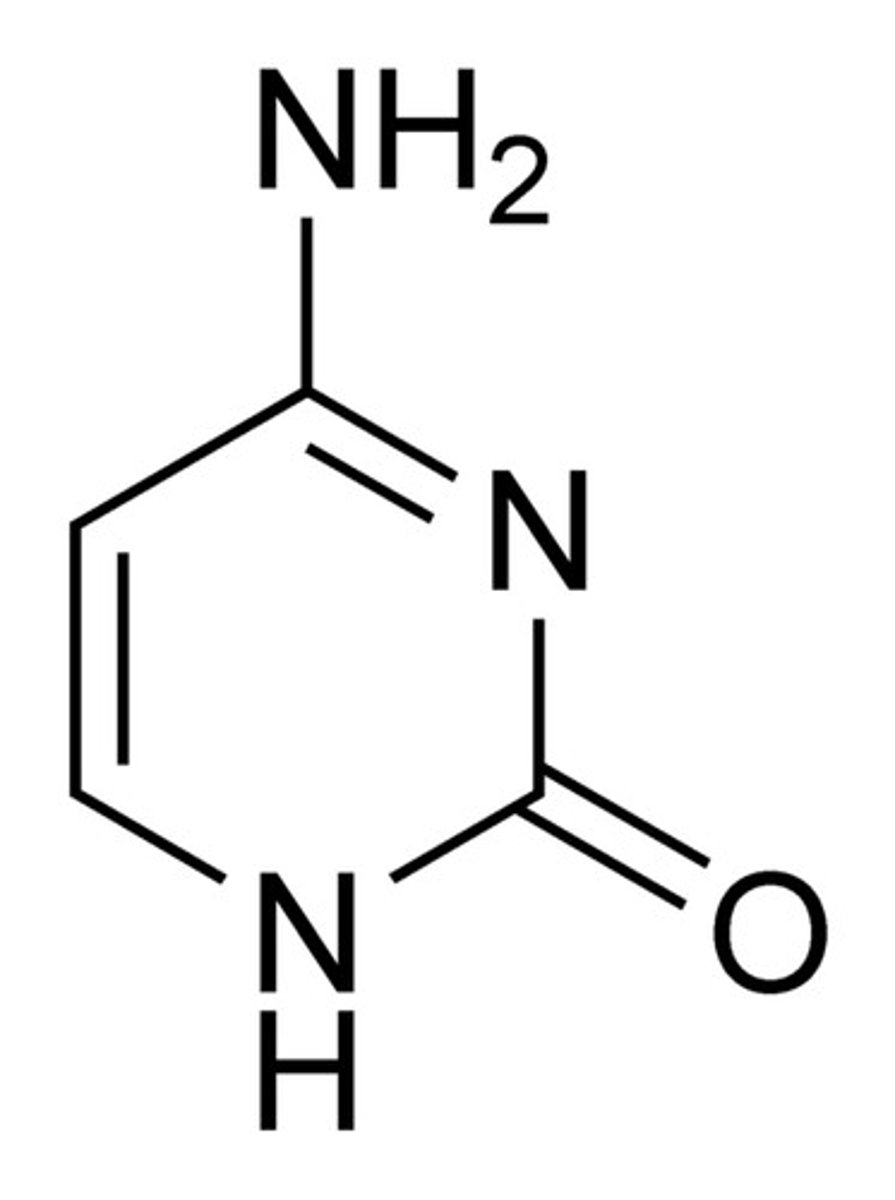
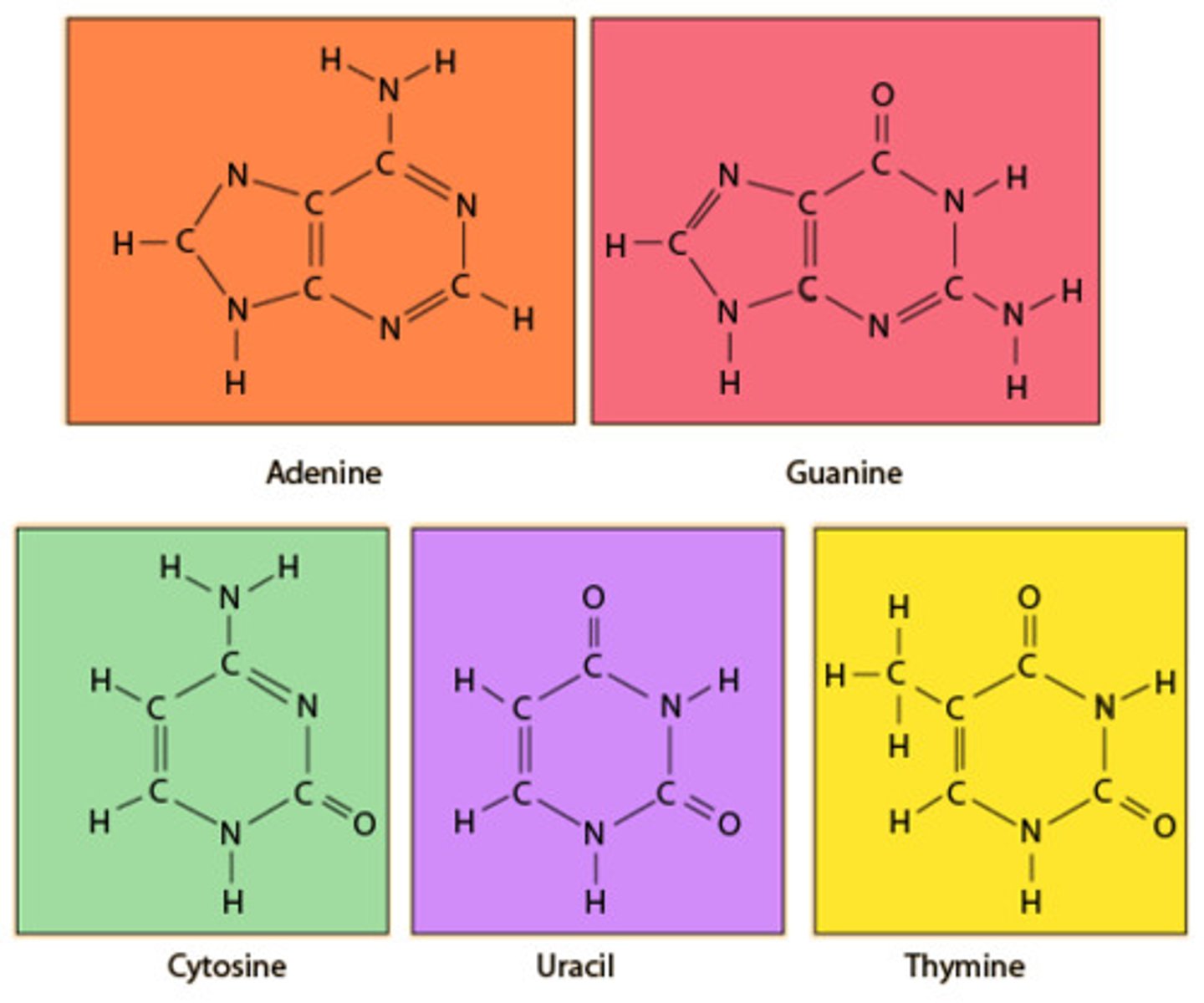
Purine
double ring nitrogenous bases (A and G)
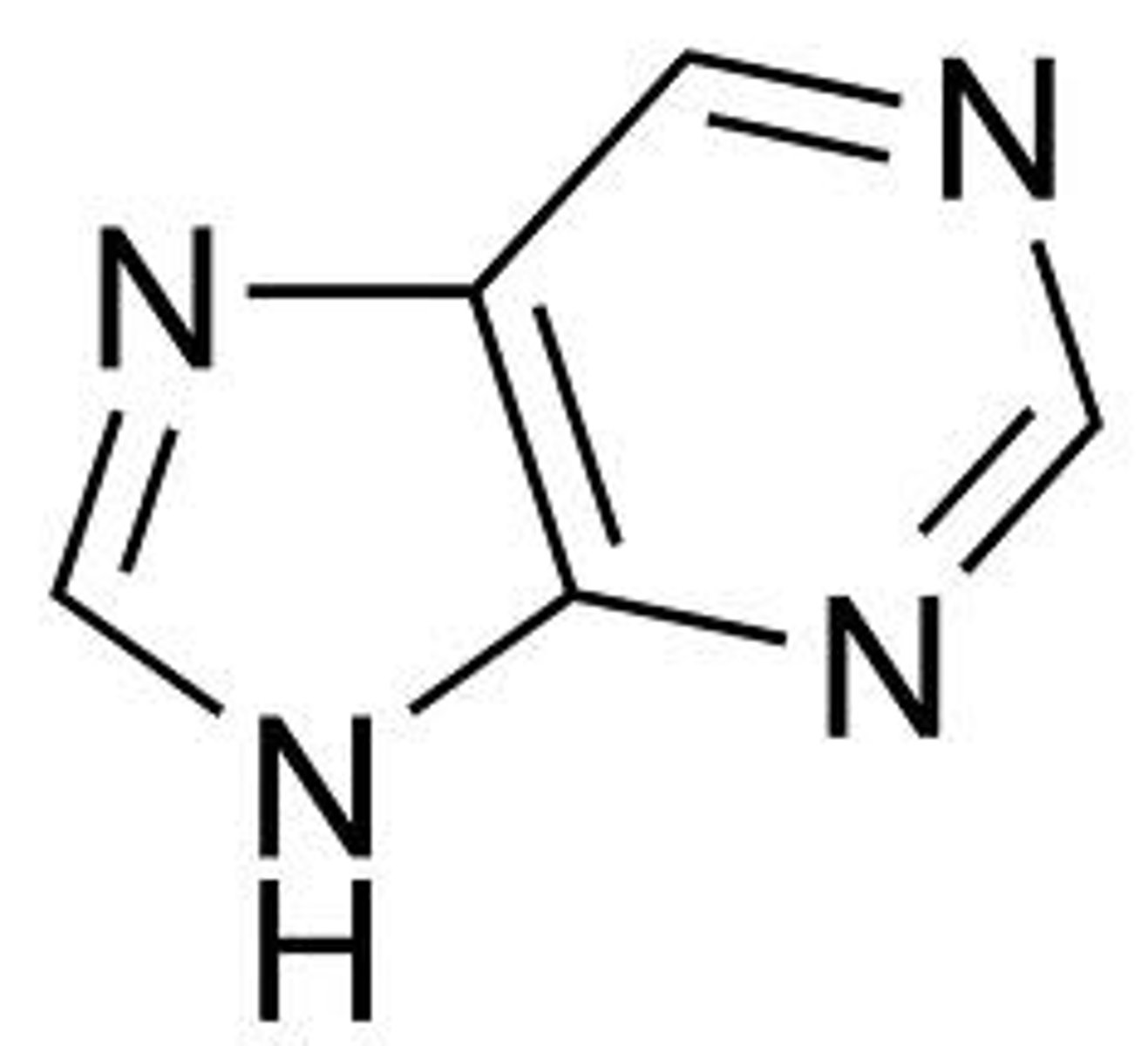
Pyrimidine
single-ring nitrogenous bases (C and T)
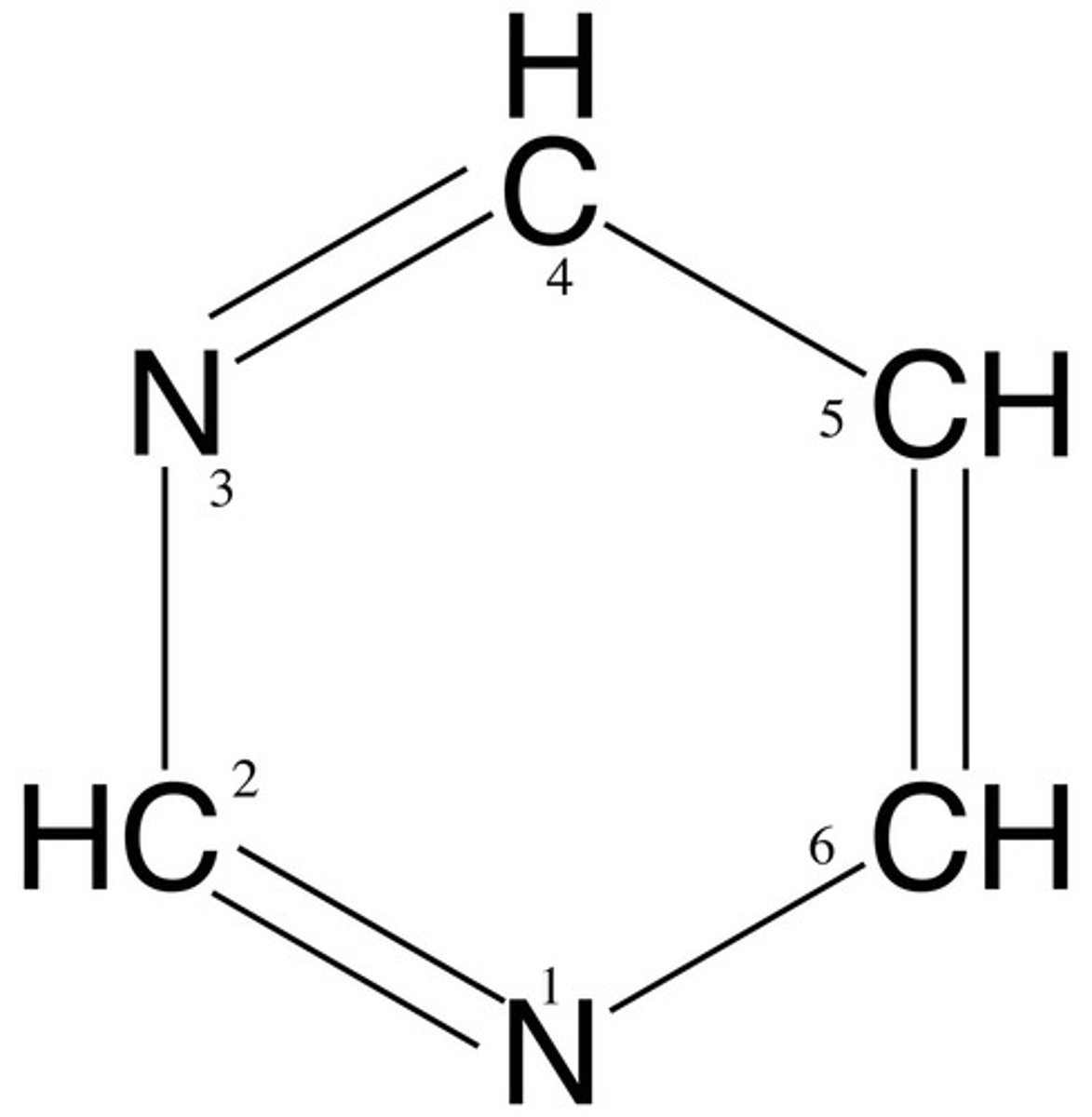
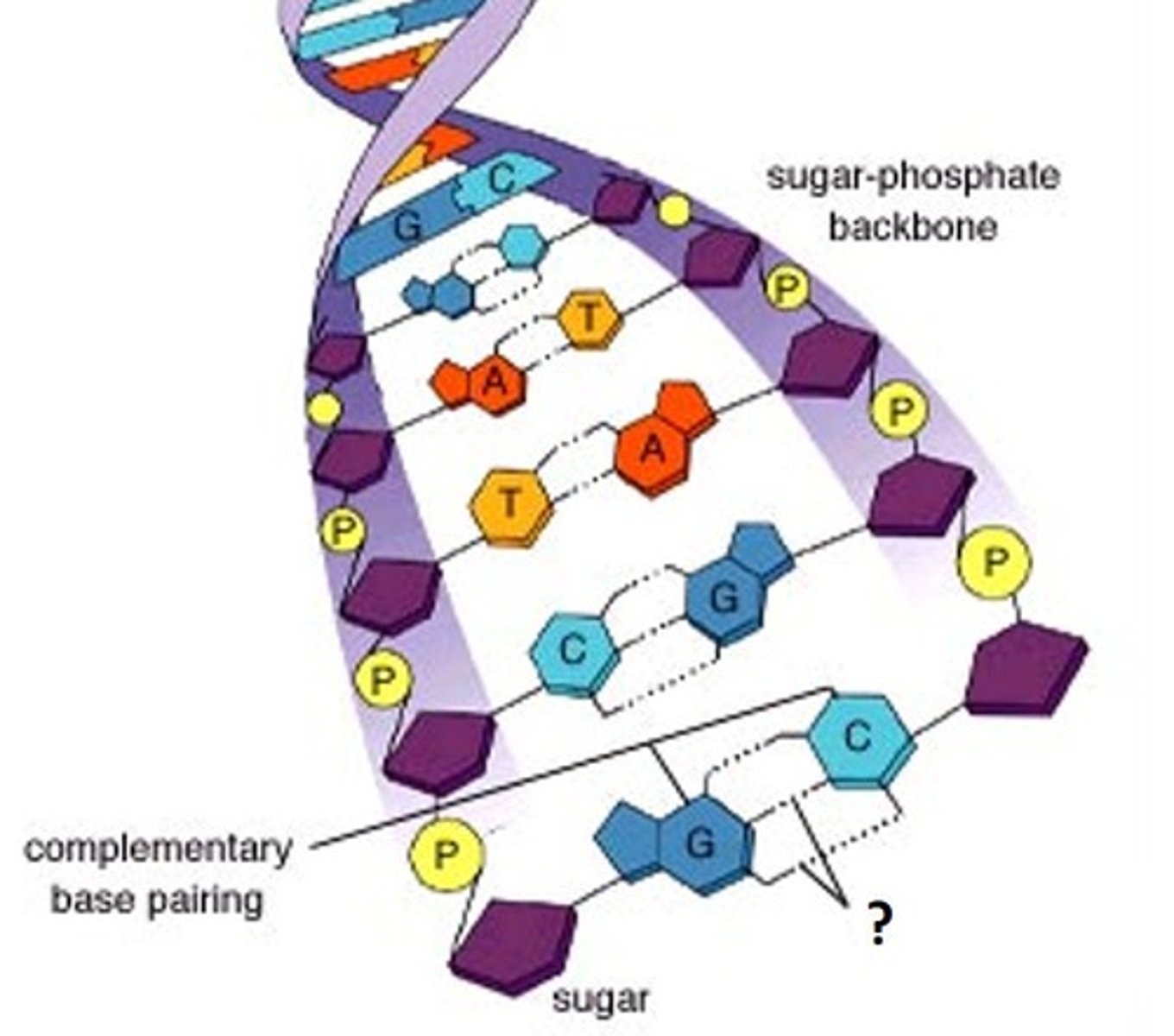
Complementary base pairing
Hydrogen bonding between particular pyrimidines and purines. A&T. C&G.
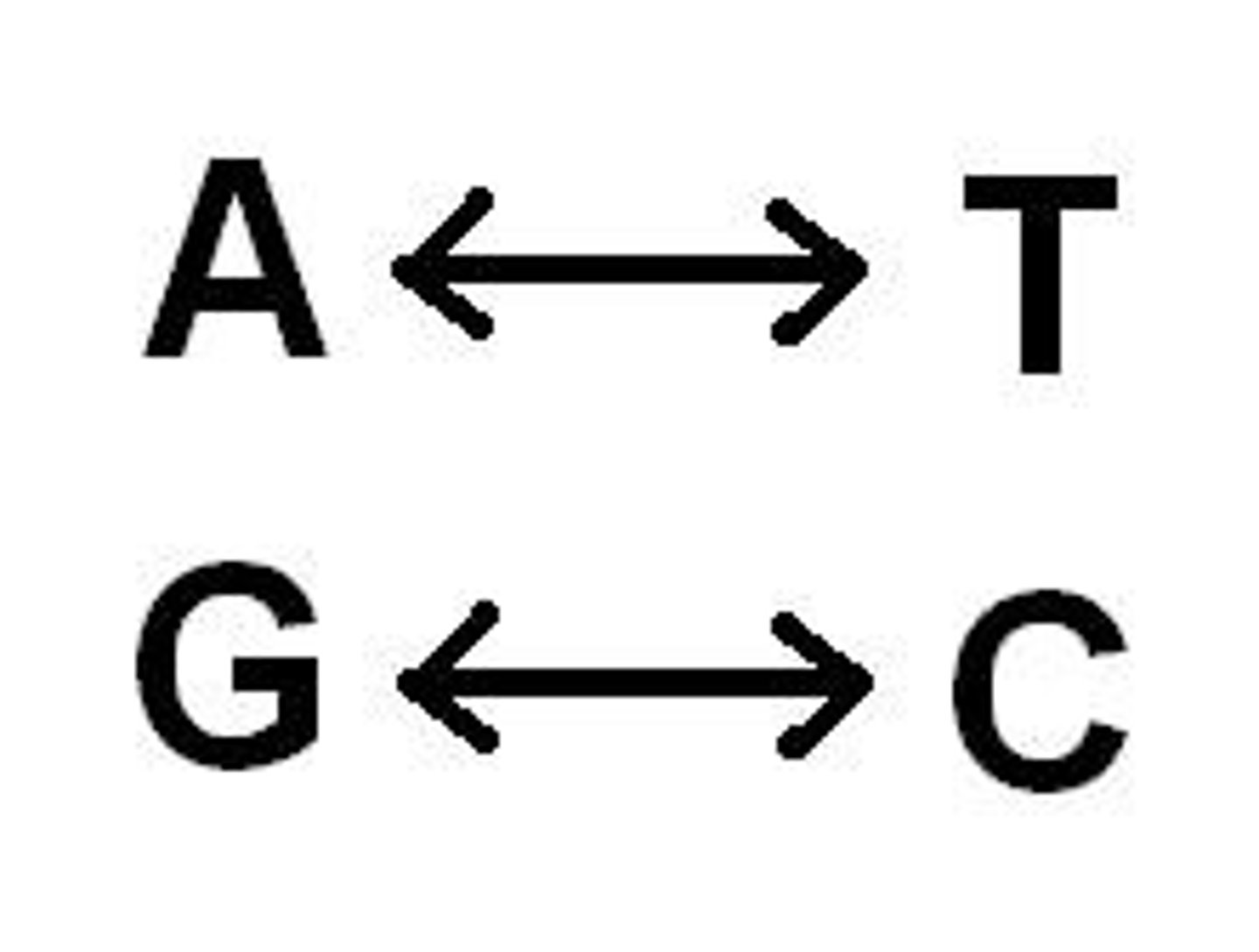
Hydrogen bonds
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom, holds bases together in the center of the double helical DNA molecule
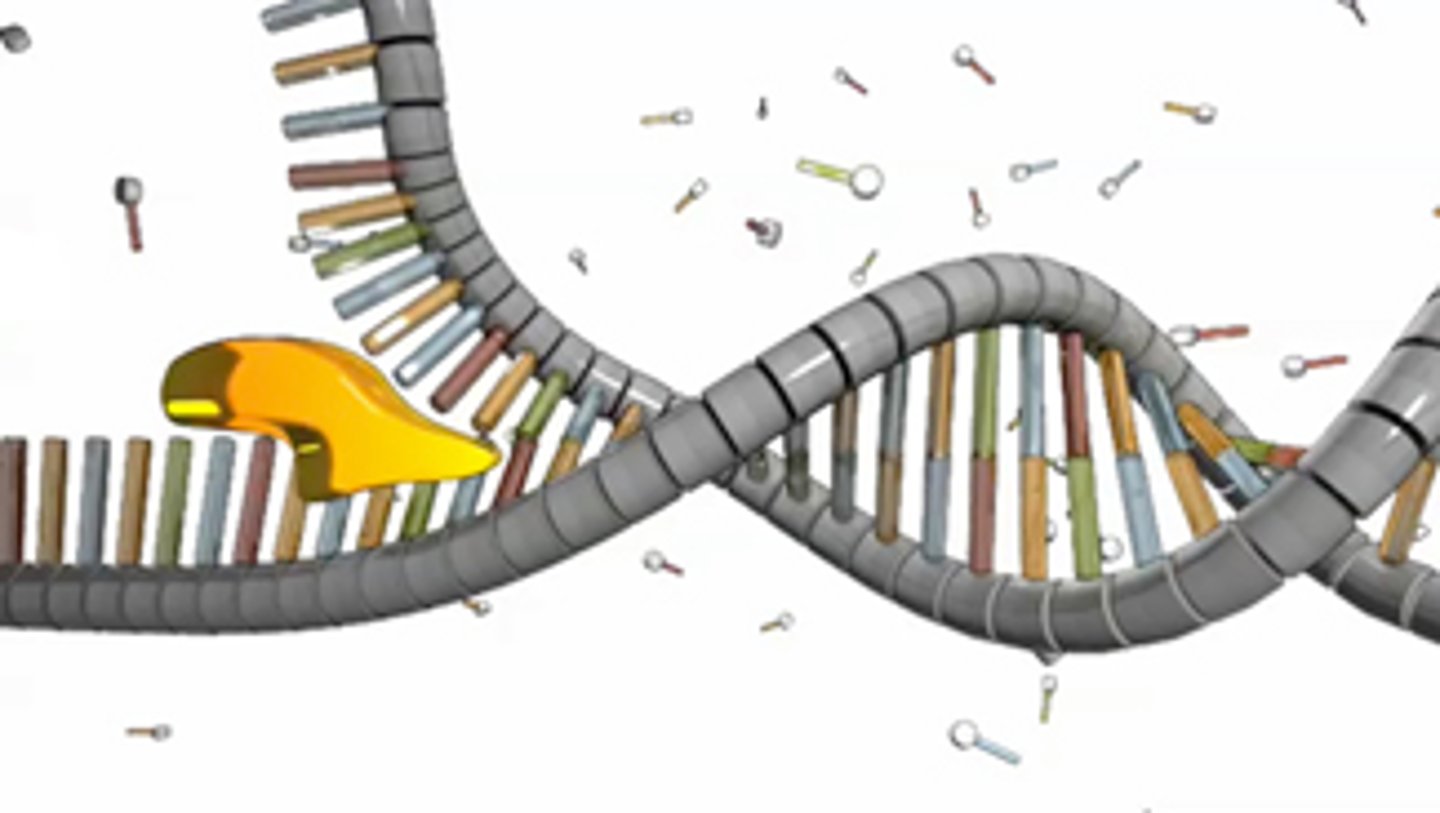
DNA Replication (semi-conservative)
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.

DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that adds complementary base pairs and proofreads to check for errors.
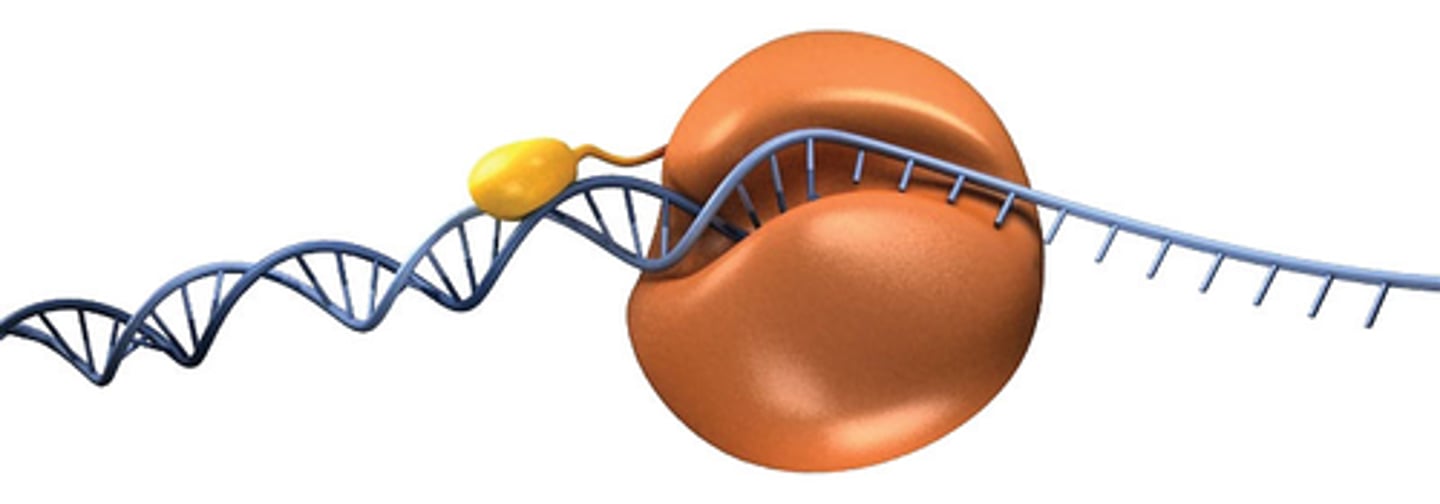
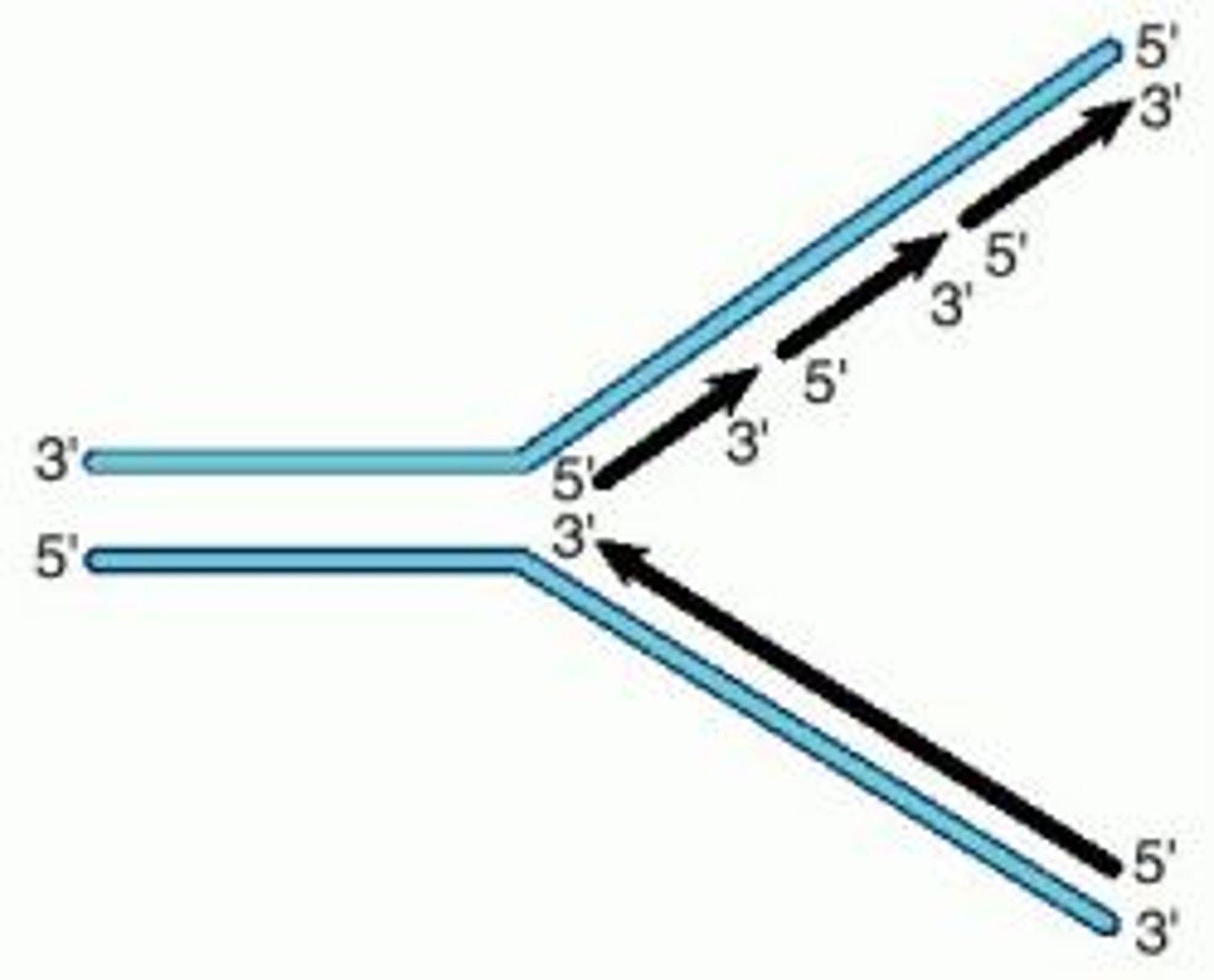
Replication fork
The point at which the two strands of DNA are separated to allow replication of each strand. (Area where replication of DNA occurs)