AP Chemistry-Chemical Reactions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
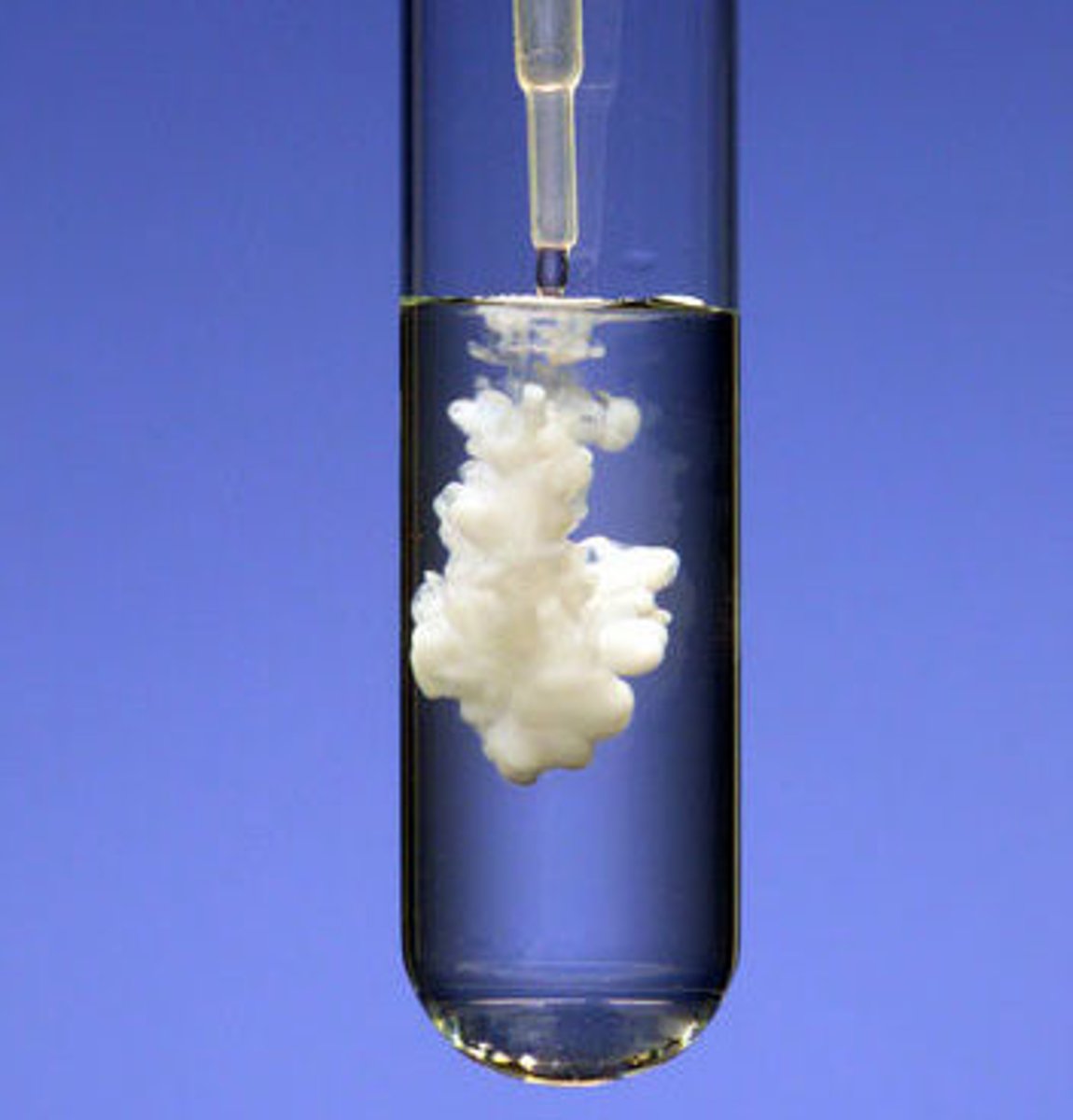
precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.

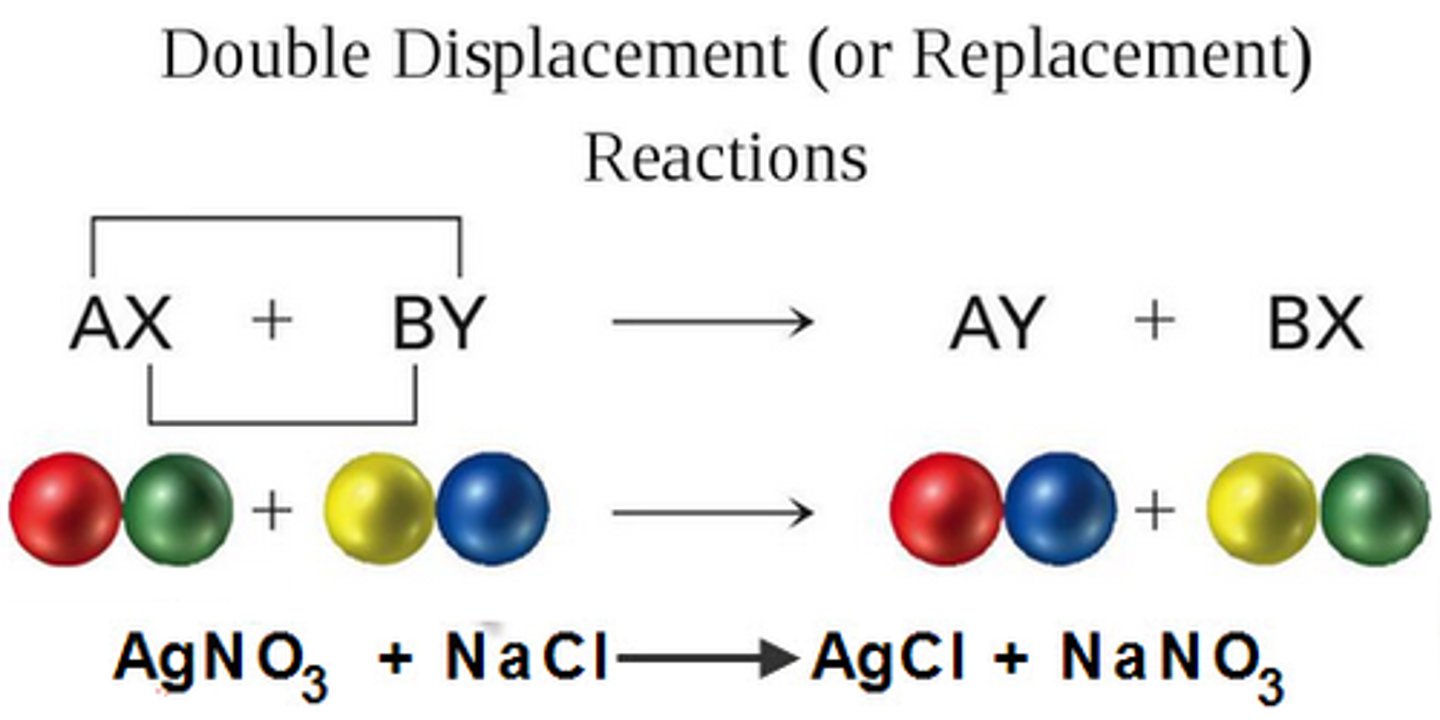
double replacement reaction
a chemical change that involves an exchange of positive ions between two compounds
metathesis reaction
double displacement reaction
combustion reaction
a chemical reaction that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light
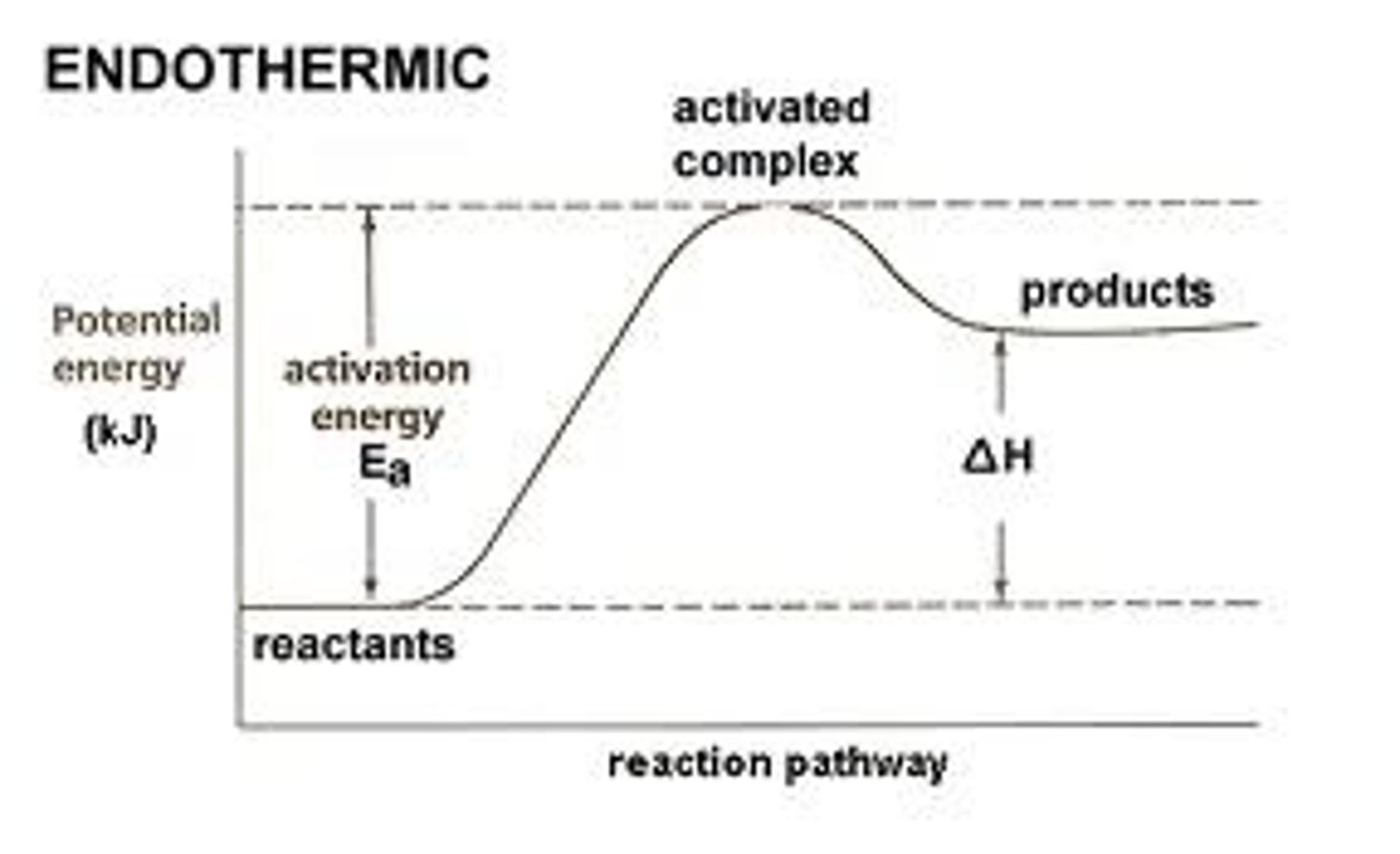
endothermic change
the system absorbs energy from its surroundings
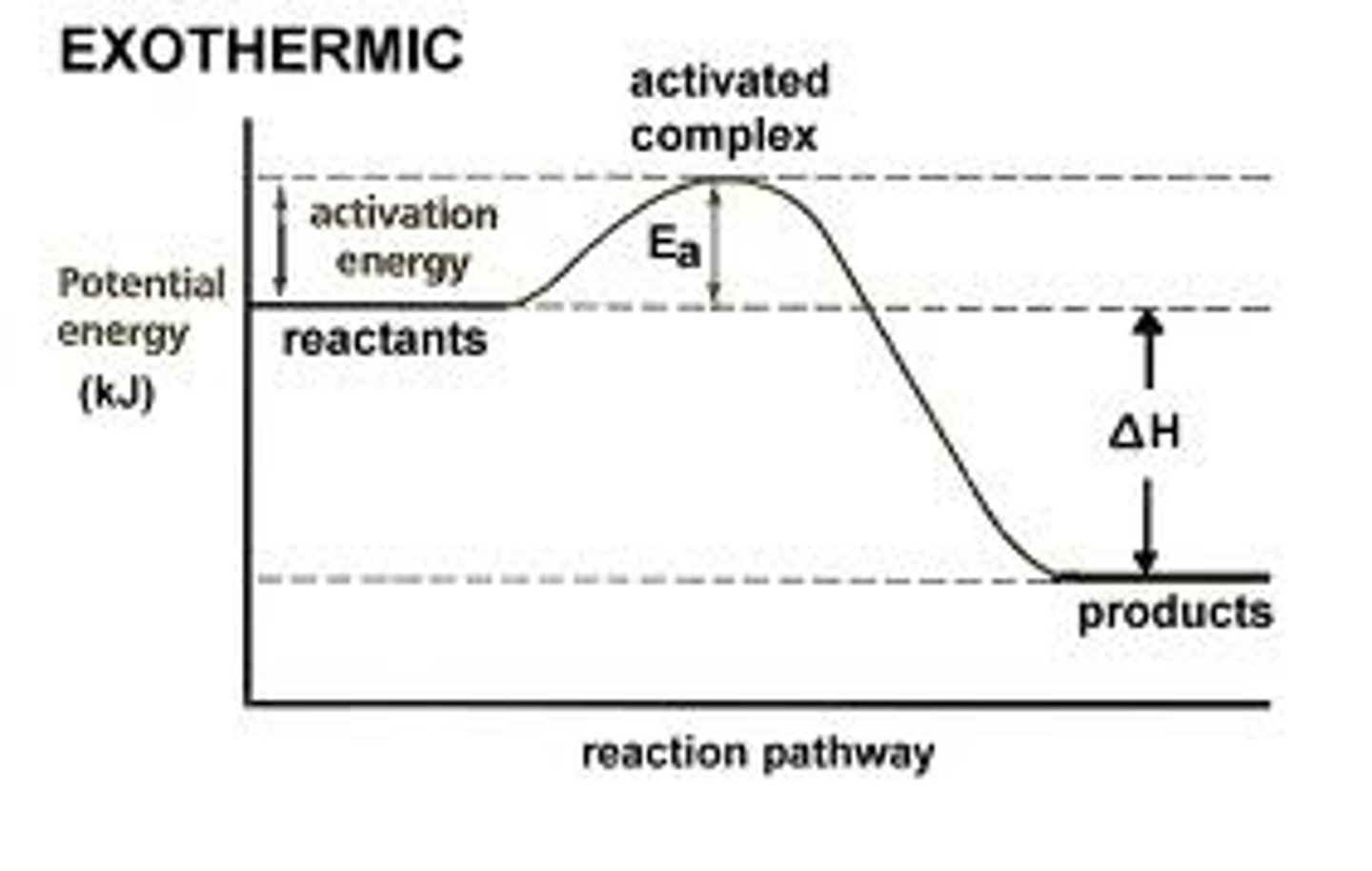
exothermic change
a change in which energy is released
synthesis reaction
a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new compound
decomposition reaction
a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances
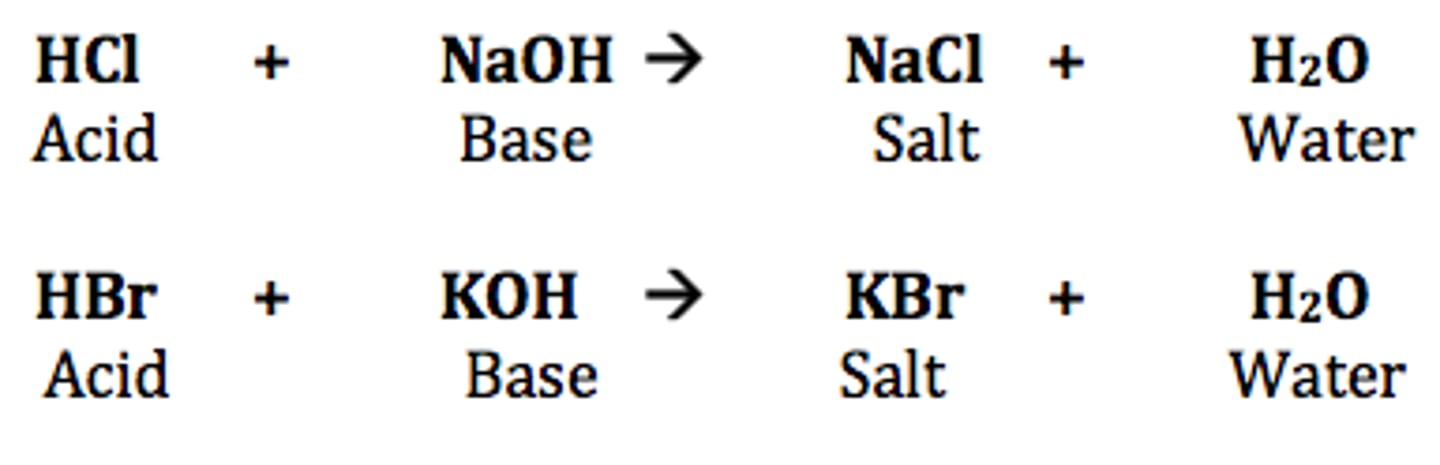
acid-base reaction
a reaction where an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt
oxidation number
Positive or negative number that indicates how many electrons an atom has gained, lost, or shared to become stable
oxidation-reduction reaction
a reaction that involves the transfer of electrons between reactants

Oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
single replacement reaction
a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound
oxidation half reaction
That half of a redox reaction where loss of electrons takes place. In this half, the oxidation number of the reactant atoms increases.
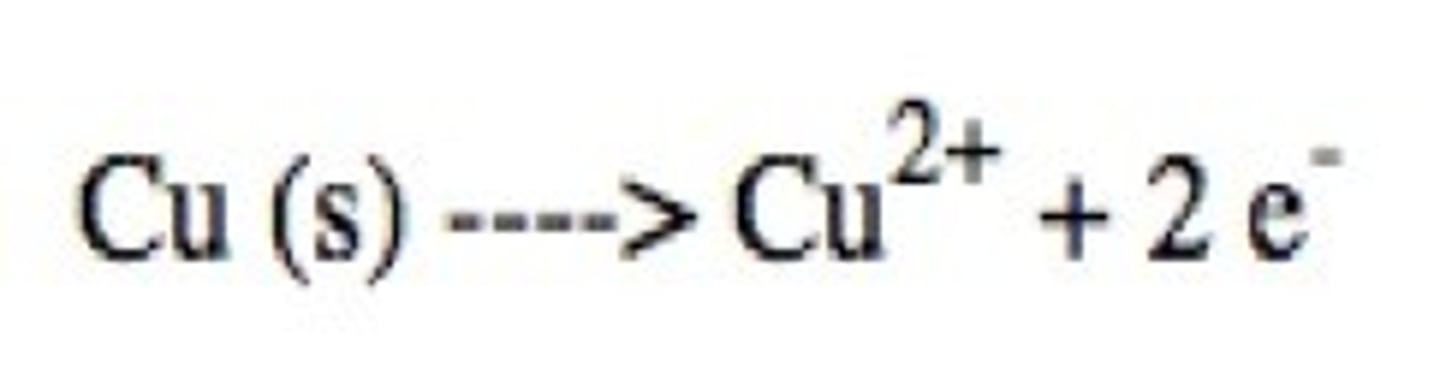
reduction half reaction
the "half" of an oxidation-reduction reaction involving reduction; the half-reaction in which electrons appear as reactants; balanced when each atom type, as well as the charge, is balanced
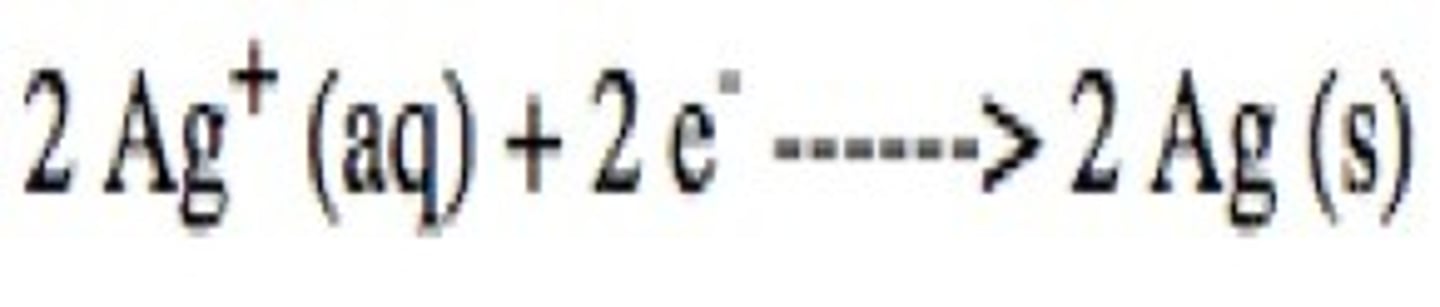
half-reaction
an equation showing either the oxidation or the reduction that takes place in a redox reaction
neutralization reaction
a reaction in which an acid and a base react in an aqueous solution to produce a salt and water
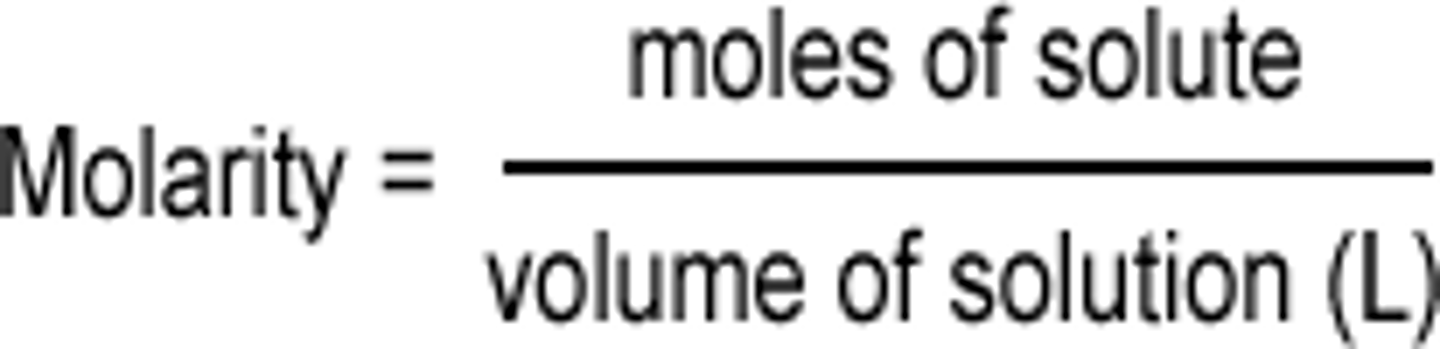
Molarity
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
Solution Stoichiometry
A method of calculating the concentration of substances in a chemical reaction by measuring the volumes of solutions that react completely; sometimes called volumetric stoichiometry.
Solute
the substance that is dissolved
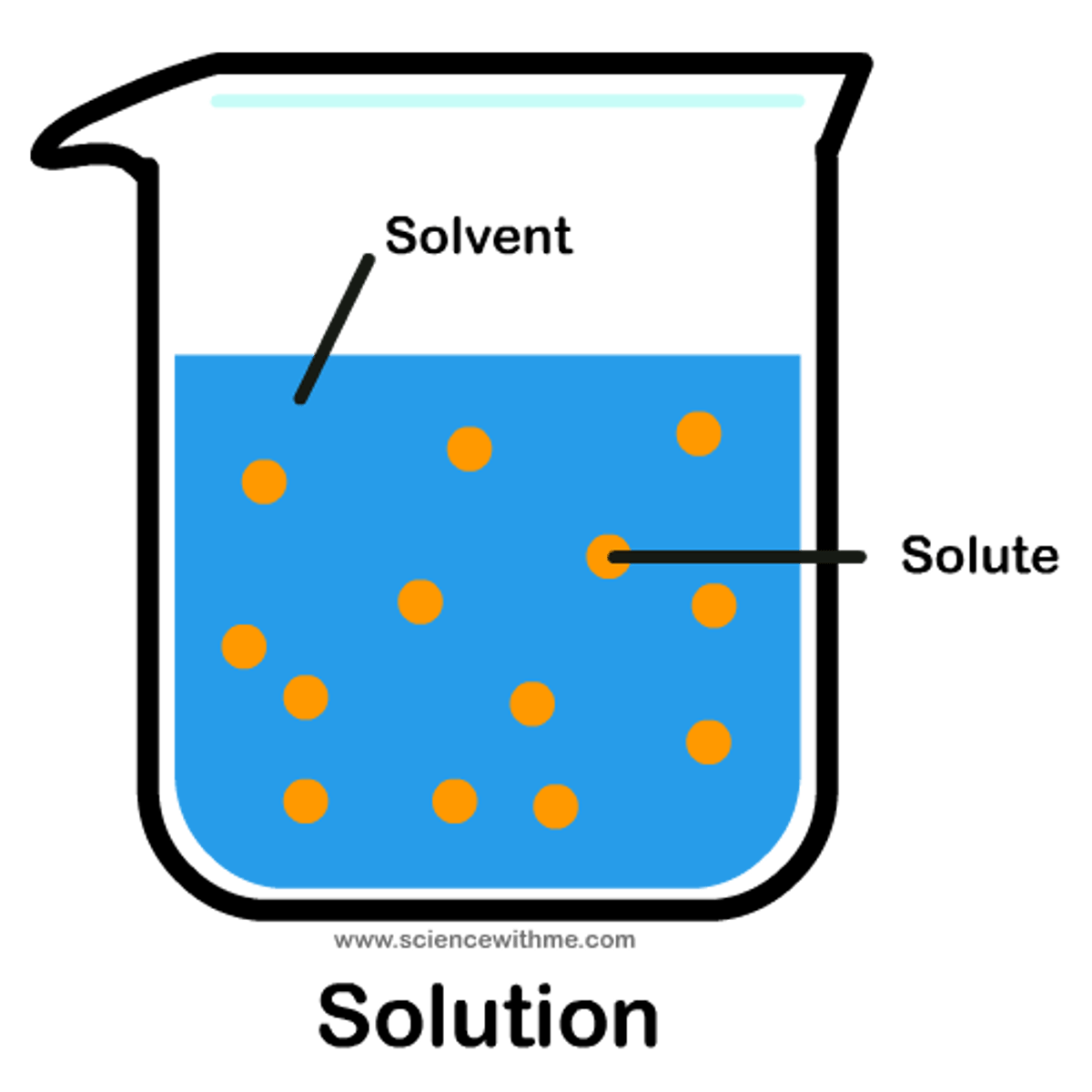
Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
Titration
process in which a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution
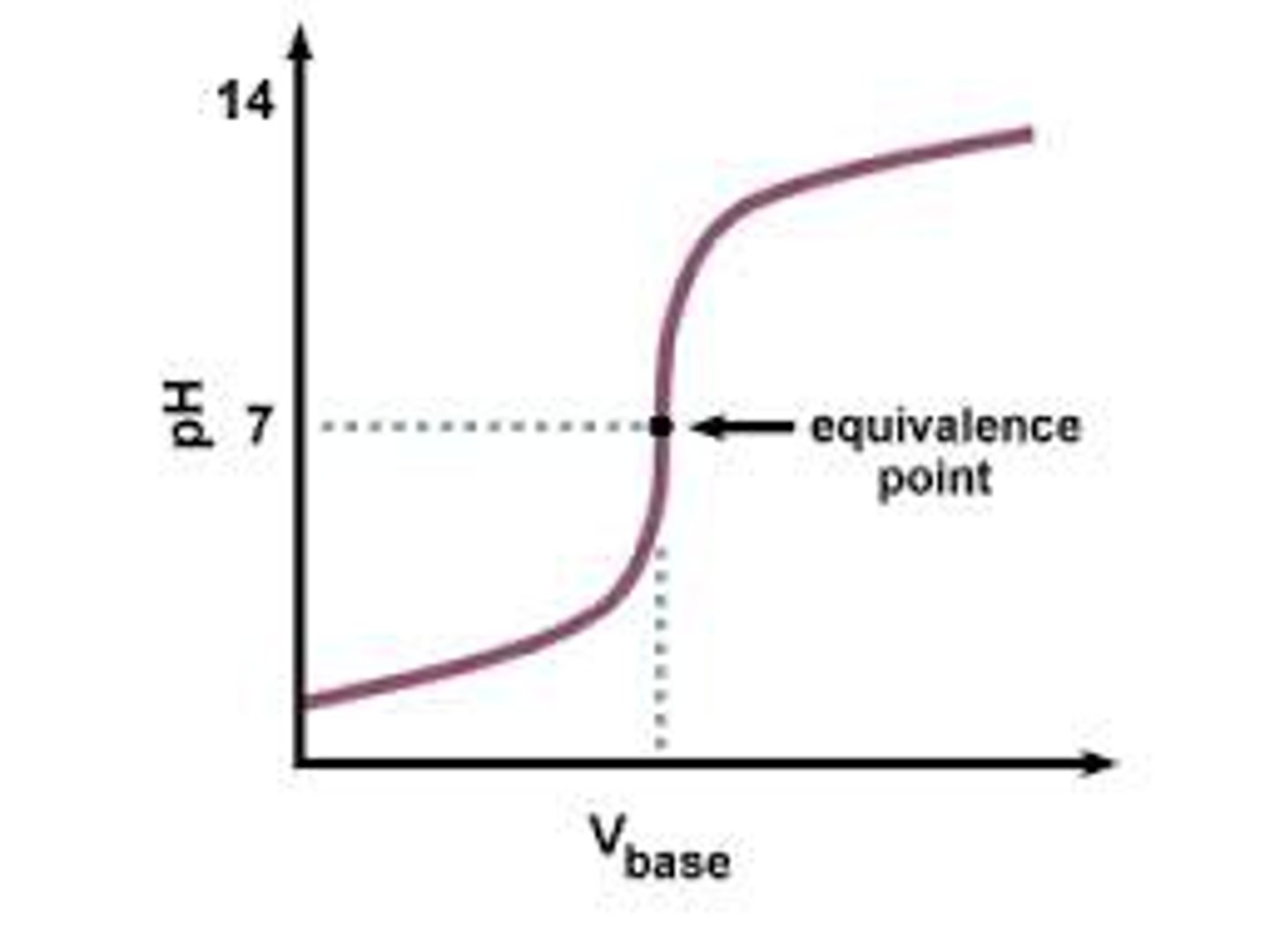
titration curve
graph showing how the pH of a solution changes as acidic and basic solutions are added together
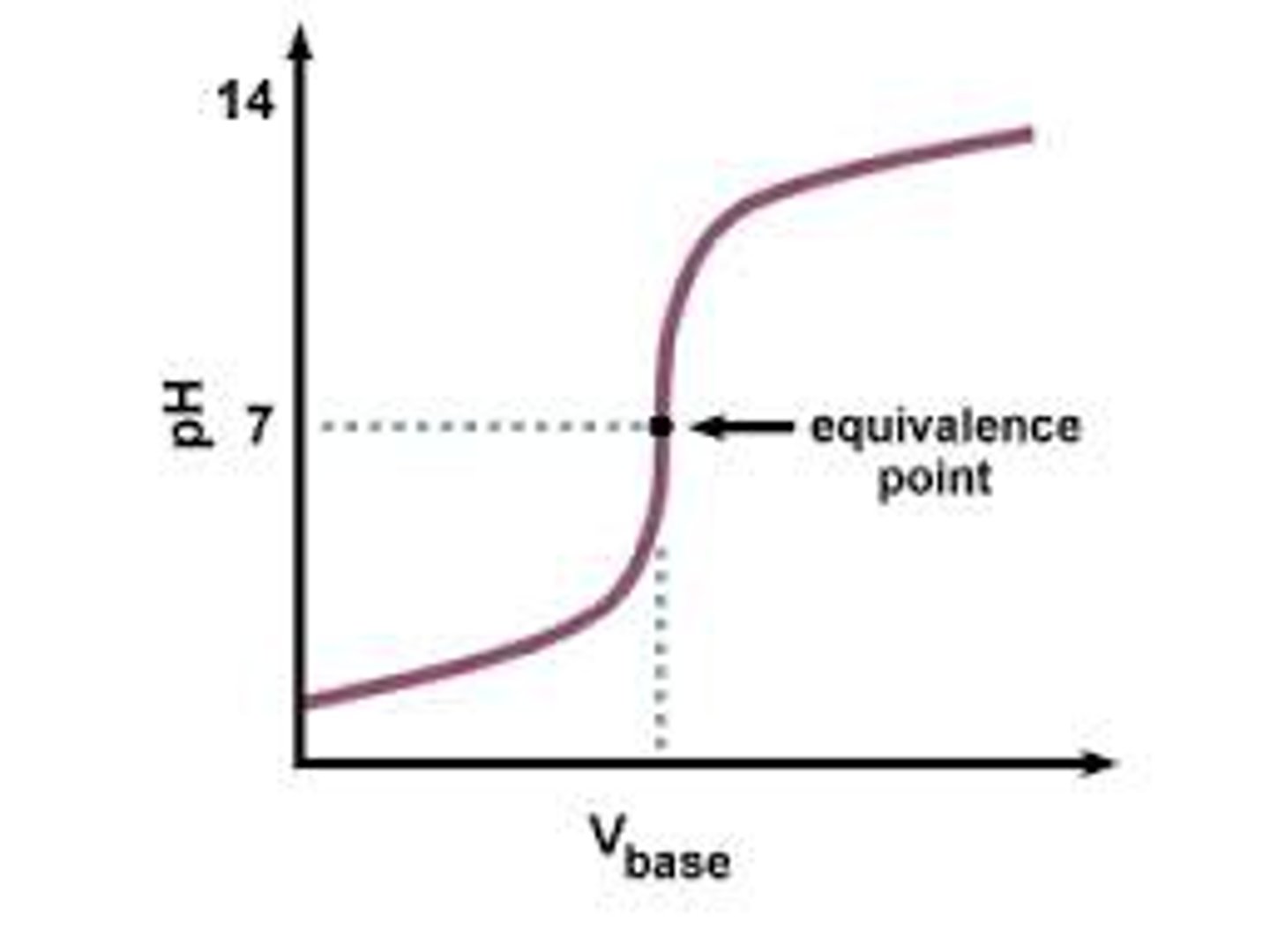
equivalence point
occurs when the moles of acid equal the moles of base in a solution
hydrogen ion (H+)
a positively charged ion (H+) formed of a hydrogen atom that has lost its electron
hydronium ion
hydrogen ion combines with a water molecule to form a hydronium ion, H3O(+)