8- Clinical Intro to Neurological PT
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Initial conditions, Preparation, Initiation, Execution, Termination
The motor control framework includes:
Initial conditions
which step in motor control framework?
Posture, ability to interact with environment, environmental context
Preparation
which step in motor control framework?
Stimulus identification, response selection, response programming (Is the pt processing the information and able to pick a response and perform it?)
Timing, direction, smoothness
what’s in this step of motor control framework?
Initiation: start of movement
Execution- continuation of movement
which step in motor control framework?
Amplitude, direction, speed, smoothness
Termination- stop
which step in motor control framework?
Timing, stability, accuracy
general system screen done on all patients
What is a Health Screening/Wellness Screen?
Comprehensive Examination Process
identify red flags from examination, Identify comorbid conditions, Understand/interpret data
Generate a PT or Movement Systems diagnosis
diagnosis that relates to the movement system, not to a patho-anatomical element
Screening Process
- identify possible problems that require consultation with, or referral to, another provider
- TREAT, TREAT AND REFER, OR REFER
Red flag warranting a med screen
Warning sign of a serious condition, Any biomedical factor that requires investigation or referral, includes medical conditions
Yellow flag warranting a med screen
• Psychosocial features/aspects (pt is seen in same clothing = elderly neglect)
• Catastrophizing, anxiety, finding painful experiences unbearable, etc.
• Becoming preoccupied with health
• Expectation of passive treatment (e.g., pills, modalities, etc.)
• Kinesiophobia: Fear of movement and of re-injury
red
A patients has slurred speech and heart rate is jumping is an example of a ____ flag?
Yellow
An elderly patient is seen wearing the same clothing everyday. This is a _____ flag.
Frontal pole, temporal pole, occipital lobe
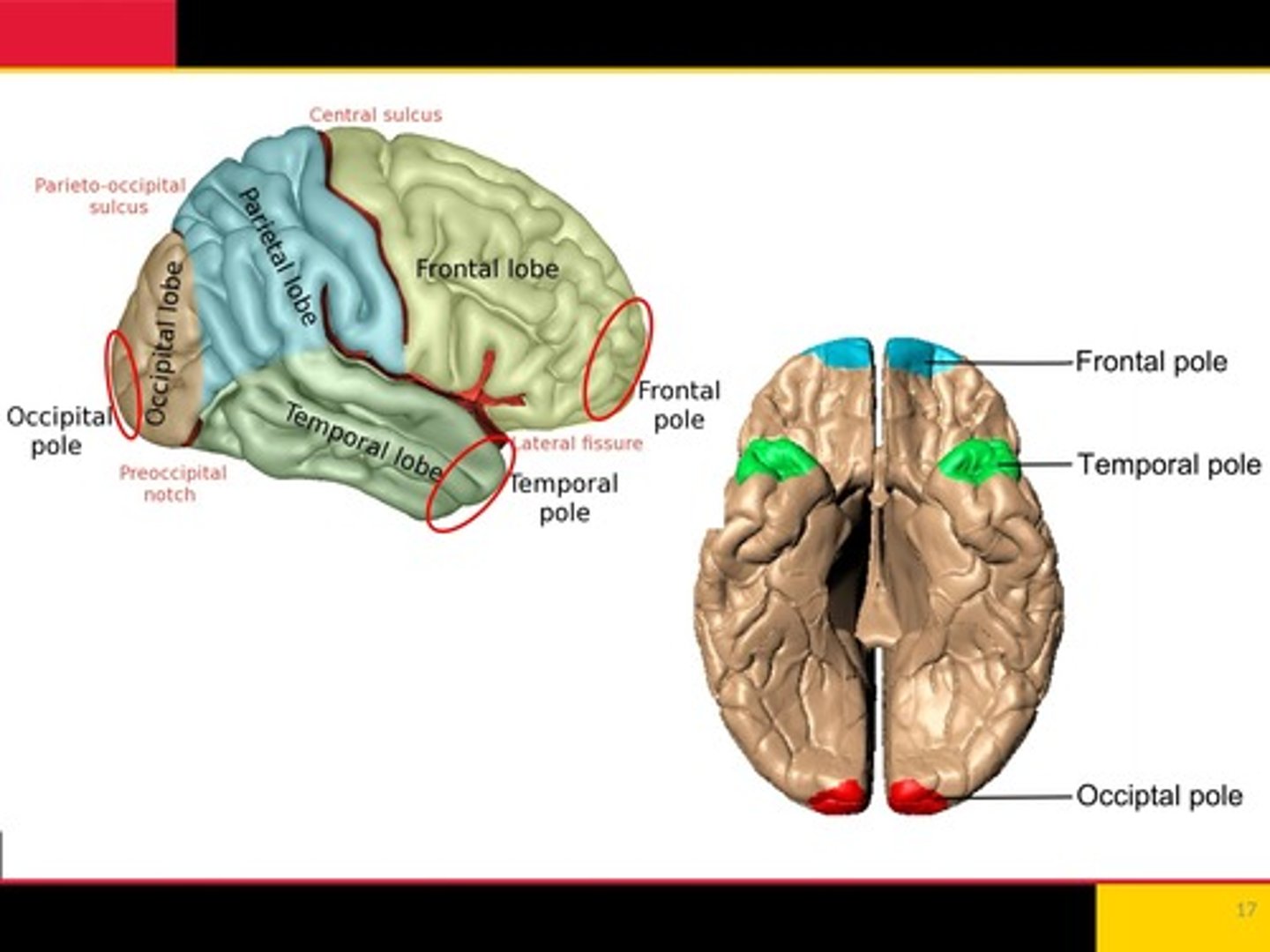
Decision making, planning and organizing, problem solving, movement
what does the frontal lobe control?
Sensation, perception, integrating environment
Parietal lobe controls what?
Balance and coordination
what does the cerebellum control?
Broadmans area 17
Trouble with vision
Sensory and motor, body representation of the cortex in M1 And S1
What is the homunculus?
Midbrain, pons, medulla
What are the components of the brainstem?
putamen, substantia nigra, globus pallidus, caudate, subthalamic nucleus
components of the Basal Ganglia
circle of willis
Connects posterior and anterior circulation
helps with redundancy and circulation
Neurophysiology
Study of the nervous system and the mechanisms by which it functions - uses EEG, EMG, MEPs, behavioral presentation
Why neurophysiology is important for PT
- Hypothesis formation for predicting patient status: Body structure and function; Activities
- Initial and re-evaluation testing
- Intervention selection
- Referral need or patient status change
- Understanding how neural injury can impact
movement/function
- Understanding how we impact healing/movement
Weakness in R leg of pt, recover? Compensatory?
Recover: add weight bearing - forceful use for strengthening
Compensatory: tumor of pt was removed=give walker
multipolar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, unipolar
Types of neurons
Multipolar neuron
Have one axon and multiple dendrites
most common neuron in brain and spinal cord
ex: alpha motor neuron
Bipolar neuron
Have two processes, one axon and one dendrite
usually has a sensory function
ex: neurons in eye that receive light then transmit signals to the brain
Pseudo-unipolar neurons
neuron where the single process branches into two, one extending to the periphery and the other to the spinal cord
primary neurons responsible for coordinating the movement of the arms and legs using input from the brain
usually has a sensory function
Unipolar neurons
Have one process that branches into an axon and a dendrite
rare in vertebrates
Oligodendrocytes (drops myelin on axon)
in CNS, what cells produce myelin?
Schwann cells
in PNS, what cells produce myelin?
Neuroglia
• Supporting cells of CNS
• Outnumber neurons 5-10-fold
• Do not have axons or dendrites
• Do not participate directly in synaptic interactions and signaling
• Help maintain an appropriate environment for neural
function
• Participate in the Blood Brain Barrier
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia
Types of neuroglia
Astrocytes
- Cell only in CNS
- Modulate rate of nerve signal propagation
- Help with neurovascular coupling
- Provide a scaffold for some aspects of neural development
- Aid or prevent recovery from neuronal injury
Oligodendrocytes
- Cell only in CNS
- Responsible for axonal myelination
Microglia
- Primarily scavenger cells, remove debris from injury or normal cellular turnover
- in CNS
Synaptic communication
1:1 nerve connection is rare in the CNS (usually multipolar)
Spatial and temporal summation
What are the 2 ways post-synaptic neuron can be excited?
Spatial summation
• Multiple signals arrive simultaneously
• The signals are superimposed
• The result: the post-synaptic neuron is triggered
Single pre-synaptic neuron fires, multiple pre-synaptic firing brings the post-synaptic neuron to threshold, action potential is generated
What happens during temporal summation?
Reflex (sensory stimulus directly triggers an immediate motor response)
What is the simplest neural connection?
Behavior (CNS processing, integrated neural networks)
What is a complex neural connection?
Upper: CNS (brain and spinal cord)
Lower: CNS, muscle
Upper vs Lower motor neurons originate and terminate where?
Central: brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nerves
Central vs Peripheral
Pyramidal: Neurons originating from cortical pyramidal cells forming the corticospinal tract
Extrapyramidal: motor neurons that form other descending (motor) tracts
pyramidal vs extrapyramidal
Sensory: Ascending
Motor: Descending
is sensory ascending or descending? is motor ascending or descending?
Traumatic brain injury, stroke, cerebral palsy
CNS injuries
falls, carpal tunnel syndrome, sports injuries
PNS injuries
trauma, ischemia
Mechanisms of spinal cord injury
Neurological level: lowest level where motor and sensory function is normal on both sides
Spinal cord injury: level of injury
traumatic brain injury
A blow or jolt to the head or penetrating head injury that disrupts brain function
- Closed head injuries, coup contra-coup injuries (assoc. with contusions)
- Severe acceleration and deceleration (shaken baby syndrome)
- Blast injuries
- Penetrating object
falls
What is the leading cause of traumatic brain injury?
traumatic brain injury
II, III, VI, VII, VIII
_____________ can result in:
- Cranial nerve injury (______________ most often injured)
- Abnormal muscle tone and reflexes
- Hypersensitivity to light, dizziness/vertigo, apraxia
Those at greater risk of dying or experiencing long-term health problems
- Racial and ethnic minorities
- Service members and Veterans
- People experiencing homelessness
- People in correctional and detention facilities
- Survivors of intimate partner violence
- People living in rural areas
Falls, Firearm-related suicide, Motor vehicle crashes, Assaults
Most common modes of traumatic brain injury:
Contusions, Lacerations, Diffuse axonal injuries/shearing, Hematomas
primary damage of traumatic brain injury
TMI - secondary damage
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) - skull
- Cerebral hypoxia - caused by ICP
- Seizures (from pressure or swelling)
TMI - release of blood and hemoglobin breakdown
Toxic vs. neuroprotective properties
• Heme, red blood cells: toxic to neurons & glia
Stroke
The sudden loss of neurological function causes by an interruption of blood flow to the brain
Ischemic and Hemorrhagic
What are the 2 types of strokes?
Ischemic stroke
Most common accounting for approx. 80% of stroke (ex. Like drinking a milkshake and something blocks the straw so nothing somes up
Hemorrhagic stroke
Rupture of a blood vessel (Vessels have exploded/ pushes out into surrounding tissue: more fatal of the 2 strokes)
Hemiplegic
Paralysis on one side of the body
Weakness on one side of the body
Hemiparesis
True
Stroke: cell death primarily via apoptosis or necrosis. T/F?
Apoptosis
Cutting off dead area of a leave to prevent further degeneration is an example of what?
Stroke injury
• Concurrent vascular & neuronal loss of homeostasis: Temporary or leading to cell death
• Vessel ischemia: Vessel obstruction, Vessel permeability changes occur, Endothelial release of leukocytes
• Ischemia contributes to inflammatory response of neurons & glia: Macrophages (microglia), Cytokines
True, with assistance from Schwann cells; very limited in CNS
The PNS does a better job at neural recovery/ repair/ regeneration and has a much greater capacity. T/F?
Why is repair/regeneration very limited in the CNS?
Lack of ability for mature CNS neurons to regenerate is
"unusual" (Occurs quite naturally during development)
• Possibly due to the brain's ability to remodel its basic wiring
• Once changes have occurred it's beneficial to stabilize them
54
CNS inflammatory response
• Up-regulation of perivascular macrophages
• Microglia activation (cytokine, interleukin release)
• Cumulative effect is blood brain barrier modification (fluid level changes)
• Impairs neurogenesis
Thus, one emphasis is on prevention/treatment of inflammatory response: anti-inflammatory corticosteroids
redundancy, compensation, and regeneration
What factors influence nervous system recovery?
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
A neurotrophic that helps to stimulate and control neurogenesis, support survival of existing neurons
true
Physical exercise is shown to increase BDNF. T/F?
neuronal survival, sprouting of new connections, increases dendritic spine formation
BDNF promotes:
Behavior and environmental changes & emotions, thinking, bodily injury
Neuroplasticity can be driven by:
True
Neuroplasticity is often used in context of stroke rehab/recovery. T/F?
Experience, Injury, environment, Learning/behavior
Axonal sprouting/pruning, Synaptogenesis, Excitation/inhibition
How does plasticity occur?
axons and dendrites
What is modified with plasticity?
For a spinal cord injury, what is a neurological level?
The lowest level of the spinal cord where there is normal spinal;........... watch video
Increase inflammation, hematoma
How can a TBI lead to intracranial pressure increases?
Compression or blockage from a clot
What is an ischemic stroke?
vessel ruptured
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
Programmed cell death
What is apoptosis?
BDNF supports and facilitated neurons in how they are grown and communicating
What is BDNF's role in neurogenesis?
65 66
neuromuscular
what system is this?
Assessment of tone, quality of movement, coordination, sensation, proprioception, kinetics awareness
musculoskeletal system
which system is this?
Assessment of gross symmetry, ROM, strength, posture, height and weight
Integumentary system
Assessment of skin integrity, perfusion
Cardiovascular/pulmonary system
what system?
Assessment of HR, RR, BP, pulses, and edema
Hemorrhagic brain injury, stroke, brain bleed
Refer bc of confusion and slurred speech
JD presents with confusion, R sided weakness, and slurred speech following a fall from a height at work. What are some differential diagnosis?
What tasks can’t be delegated to others
• Interpretation of physician referrals
• Initial examination, evaluation, dx, and prognosis
• Development/modification of plan-of-care
• Re-examination and discharge exam/planning
• Any time the PT determines that expertise of a PT is required
• Supervision of all documentation
Summary
-Foundational knowledge is required for later clinical
decisions
-Systems background will help you to identify red flags
as well as complete your PT differential diagnosis for PT
specific interventions
-With doctoral level training, knowledge of systems that
contribute to the "Movement system" is essential
Motor and Sensory Homunculi
The homunculi's can change for an amputated pt. Sensation will span out to others and fill in for other parts
health condition, participation, activities, body functions and structures, personal factors, environmental factors
what are the 6 components of the ICF model?