Nematode Parasites of the Respiratory System - Lecture 15
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
The following general morphology and biology represents nematode parasites of which system:
small worms with superfifical resembalnce to hookworms
dioecious and sexually dimorphic
males with rudimentary copulatory bursa
generally feed on host cellular tissue
companion and production animals
most develop to infective stage in obligate intermediate host (there are some exceptions)
occupy lungs, pulmonary vasculature
respiratory system
Metastrongyloidea has what common name?
dog lungworms
Which species of dog lungworms is described by the following:
adult worms are parasitic in lung parenchyma
prepatent period approximately 35 days (5 weeks)
Filaroides hirthi
Which species of dog lungworms is described by the following:
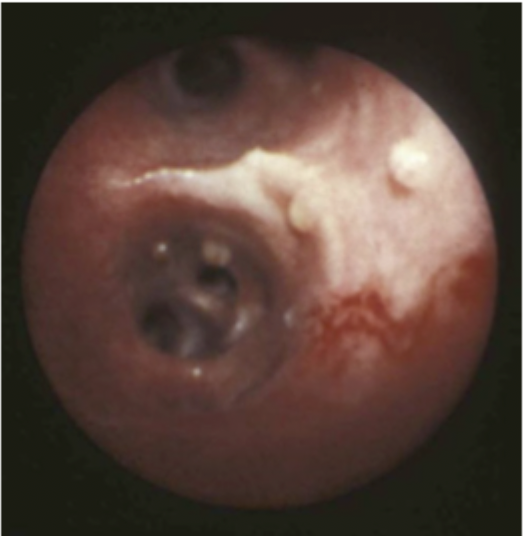
adult worms are parasitic in nodules in the trachea and bronchi
nodules detected by bronchioscope at 2 months
prepatent period approximately 6-7 months
Filaroides osleri
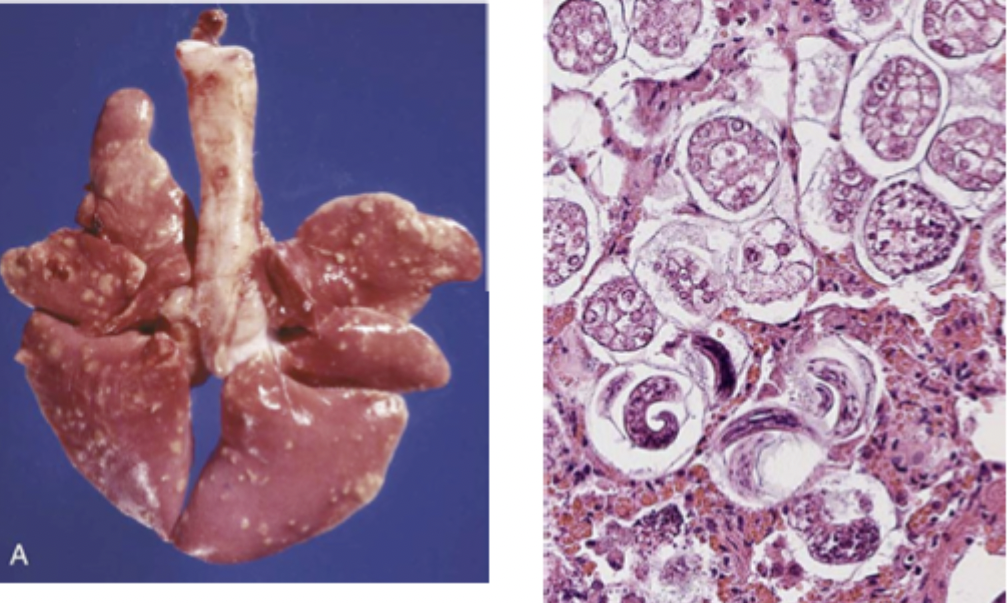
This image matches which species?
Filaroides hirthi
This image matches which species?
Filaroides osleri
The following life cycle matches which species:
direct life cycle
1st stage larvae passed in feces of infected mother (ovoviviparous: eggs hatch within uterus of adult female worms)
puppies infected by ingestion of first stage larvae through coprophagy, ingestion of larvae in regurgitated stomach contents, tracheal migration by hepatic circulation
Filaroides spp
What is the prepatient period for F. hirthi?
aprrox 32 days post infection
What is the prepatent period for F. osleri?
approximately 6-7 months post infection
What is the only nematode where the 1st larval stage is infective to the final host?
Filaroides spp
How do we diagnose Filaroides spp (dog lungworm) or Aleurostrongylus abstrusus (cat lungworm)?
fecal examination via Baermann exam or zinc sulfate flotation
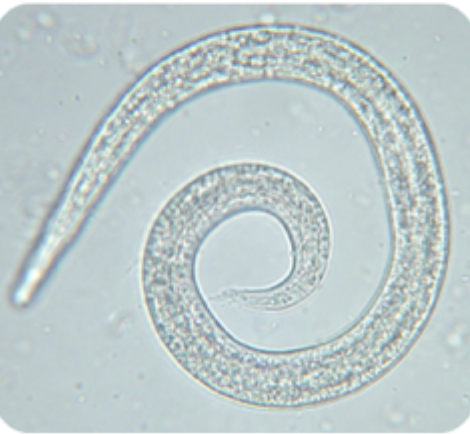
The image matches which species?
Filaroides spp
The larvae description matches which species:
larvae approximately 350 micrometers
kinked tail with dorsal spine
Filaroides spp (dog lungworm) or Aleurostrongylus abstrusus (cat lungworm)
Which exam techinque is described:
developed in 1917 by Dutch physician working in Java for recovery of hookworm larvae in soil samples
preferential for recovery of live larvae in fecal samples and cultures
active migration of larvae out of fecal sample suspended in water
larvae concentrate in stem by gravity
microscopic wet mount by pipetting larvae from bottom of stem
Baermann exam techinque
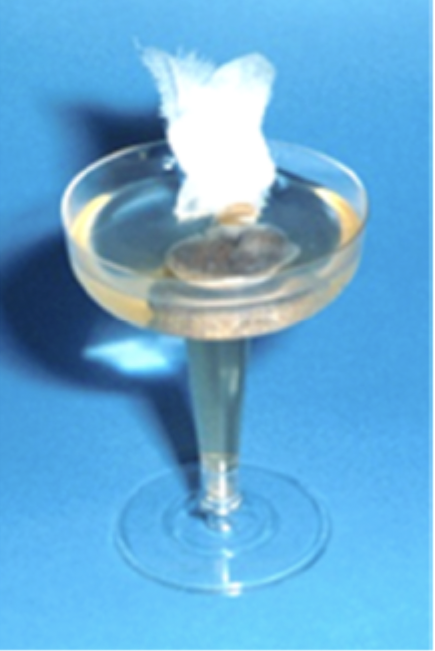

Which exam technique is shown in this image?
Baermann exam technique
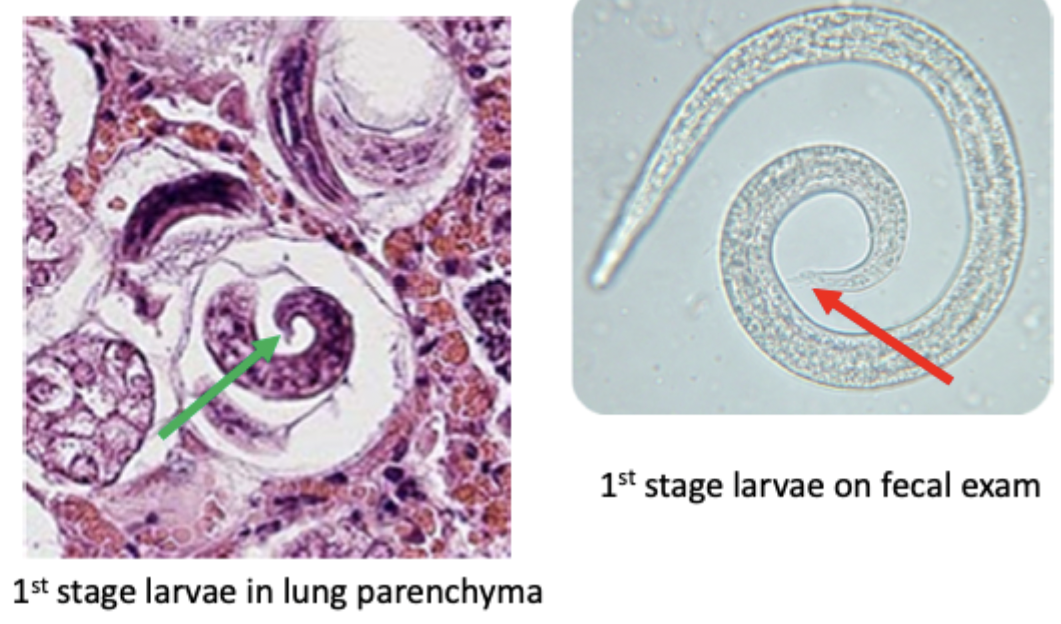
Which first stage larvae is shown in the image? How do you know?
Filaroides spp (dog lungworm) or Aleurostrongylus abstrusus (cat lungworm), kinked tail
What are the clinical signs of Filaroides spp?
generally asymptomatic
hard, dry coughing stimulated by cold air or exercise
The pathology of Filaroides spp is seens as focal areas of inflammation and necrosis where?
in the parenchyma of the lung lobes
Severe disease of Filaroides spp can be seen in which animals?
those that are hyper-infected and immunocompromised
What can occur with nodular fomation in hyper-infections of Filaroides spp?
obstruction of trachea
What is the treatment and prevention protocol for Filaroides spp?
prevention by avoiding contact with infective larvae (easier said than done)
treatment with FBZ at 50mg/kg SID x7 days resolved symptoms
IVM at 1000 micrograms/kg for one dose 44% effective, for two dises 74% effective
criteria for efficacious chemotherapy includes clinical imrpvoement, cessation of symptoms, resultion of nodular lesions, and cessation of larval shedding
What is the common name for Angiostrongylus vasorum?
French heartworm
Is Angiostrongylus vasorum zoonotic?
No
The following description matches which species:
small worms living in the right heart or pulmonary artery
widepsread in Europe
associated with pulmonary thrombosis, clotting disorders, hemorhhage from deposited eggs and larvae
Angiostrongylus vasorum
How do we treat Angiostrongylus vasorum?
0.5mg/kg Milbemcyin weekly x4 weeks
Which Angiostrongylids have zoonotic significance?
Angiostrongylus costaricensis
Angiostrongylus cantonensis
Which Angiostrongylid is described:
associated with abdominal pain, fever, vomiting from worms living in emsenteric artiers
endemic to central and south america and caribbean
spread in FL associated with deaths in primate colonies
sperad to africa with cuban mercenaries in angola in 1980s
Angiostrongylus costaricensis
Which Angiostrongylid is described:
associated with neurologic disease from larvae in the meninges and inflammatory response
naturally occurring in rats in southeast asia
spread to north america 1986-87 in wharf rats from asia
Angiostrongylus cantonensis
What is the common name for Aleurostrongylus abstrusus?
cat lungworm
The lifecycle described matches which species:
indirect
1st stage larva passed in feces ingested by snail/slug intermediate host
3rd stage larvae are infective stage
mice/birds are opportunistic paratenic hosts
prepatent period 5-6 weeks
Aleurostrongylus abstrusus
Tiny adult worms of Aleurostrongylus abstrusus are parasitic where?
in the terminal bronchioles and alveolar ducts
Where are eggs of Aleurostrongylus abstrusus laid in the host?
lung parenchyma
How do “nests” of Aleuostrongylus abstruse appear?
small nodules with associated inflammatory response and focal necrosis
What is the most common lungworm parasite in companion animals?
Aleurostrongylus abstrusus
What clinical signs are associated with Aleurostrongylus abstrusus?
often clinically inapparent and unremarkable
coughing and dysorexia may be associated with moderate infection
cough, dyspnea and polypnea in severe cases
What is the treatment and prevention protocol for Aleurostrongylus abstrusus?
prevention by reducing predation of paratenic hosts and infective larvae (easier said than done)
FBZ at 50mg/kg SID x3-15 days has been standard treatment with moderate success
criteria for efficacious chemotherapy includes clinical improvement, cessation of symptoms, and cessation of larval shedding
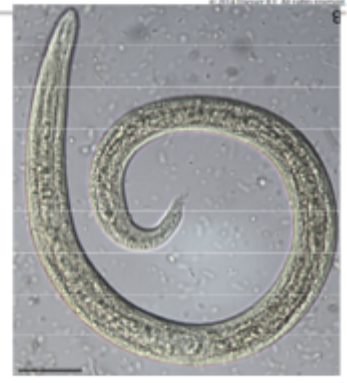
The image depicts what species?
Troglostrongylus sp
What is the lifecycle of Troglostrongylus sp?
indirect lifecycle with infective 3rd stage larvae in snail intermediate host
Which parasite has been increasingly recognized as an agent of feline respiratory disease in Europe and Mediterranean?
Troglostrongylus sp
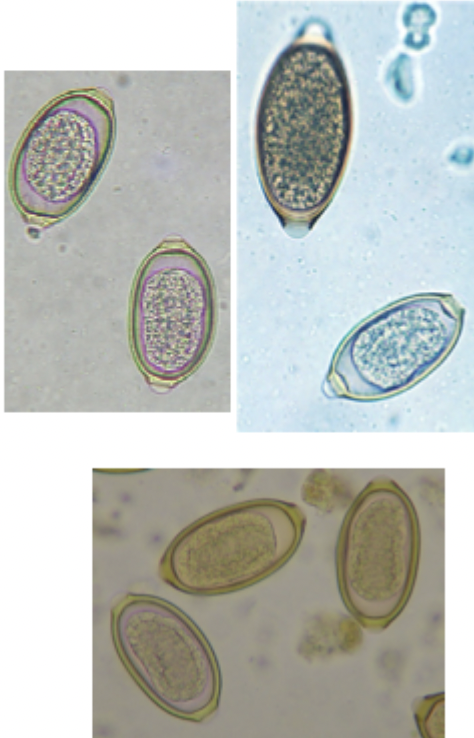
The image depicts what species?
Capillaria spp
Which parasite species are small worms with whip like anterior ends and are parasites of all class of vertebrates?
Capillaria spp
What is the lifecycle of Capillaria spp?
highly variable: some are simple direct, some facultative indirect with paratenic host, and others obligate indirect with intermediate hosts
What is the common name for Capillaria sp?
cat AND dog lungworms
Which Capillaria spp has adults that are parasitic in bronchi?
Capillaria (Eucoleus) aerophila
Which Capillaria spp has adults that are parasitic in nasal sinuses?
Capilaria (Eucoleus) bohemi
What are the clinical signs of Capillaria spp in dogs and cats?
silent cough, sneezing
bronchopneumonia, rattling wheezy respiration, coughing, not doing right
How do you diagnose infection with Capillaria spp?
fecal flotation
How do we control infection of Capillaria spp?
environmental hygiene
How do we treat Capillaria spp?
macrocyclic lactone drugs
Capillaria aerophila and Capillaria bohemi can have direct or facultative indirect lifecycles. What is the paratenic host for facultative indirect?
earthworms
What are the lungworm parasites of domestic livestock (cattle, sheep, goats)?
Muellerius capillaris
Dictyocaulus spp.
The following life cycle matches which species:
obligate indirect
tiny parasites embed into respiratory tissue of goats and sheep
larvae are then coughed up, swallowed, and passed in feces (1st stage larvae are diagnostic via recovery by Baermann method)
1st stage larve ingested by snail/slugs with development to infective stage
ingested 3rd stage larvae migrate to lungs, adults reproduce, and begin apssing larvae approximately 4 weeks post infection
Muellerius capillaris
How do we treat Muelerius capillaris?
macrocyclic lactone drugs at 200 to 500 micrograms/kg
What are the clinical signs of Muellerius capillaris?
most infections are asymptomatic in healthy adult animals
clinical signs resulting from heavy infections in immunocompromised animals may include coughing and rapid breathing, weight loss, etc
What class do Muellerius capillaris belong to?
Metastrongyloides
What classification do Dictyocaulus spp belong to?
Trichostrongyloidea
The following lifecycle mataches which species:
direct
larvated eggs hatch before passage in feces
1st stage larvae are diagnostic stage via recovery by Baermann technique
development to infective stage in 5 days
ingested larvae migrate to lungs via mesenteric lymph nodes and thoracic dict, arrive in lungs approximately 5 days post infection
adults reproduce and begin passing eggs approximately 4 weeks post infection
Dictocaulus spp
Which Dictyocaulus spp is found in the respiratory passages of horses and donkeys?
D. arnfeldi
Which Dictyocaulus spp is found in the respiratory passages of cattle?
D. viviparus
Which Dictyocaulus spp is found in the respiratory passages of sheep and goats?
D. filaria
Light infections of Dictyocaulus spp have what symptoms?
often asymptomatic
Heavy infections of Dictyocaulus spp have what symptoms?
occlude airway and obstruct airflow
clinical signs include increased respiration, harsh breathing, occasional crepitation
decreased eating/weight gain resulting from increased stress to breathe
How do we treat infections of Dictyocaulus spp?
macrocyclic lactones
Host resistance is a function of what for Dictyocaulus spp?
age, vigor, genetics, established infection, and acquired immunity
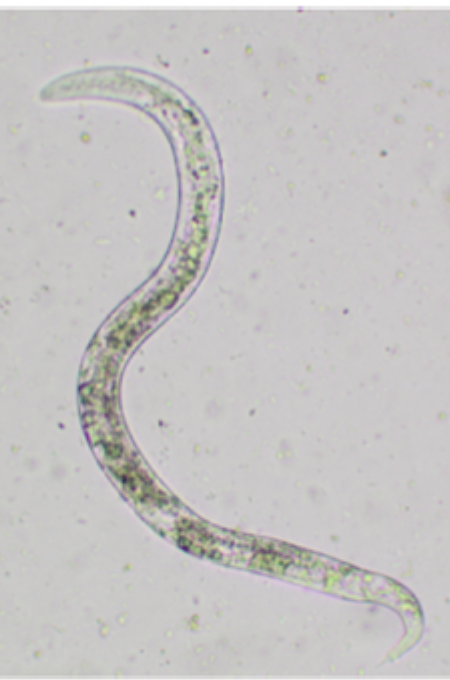
The image depicts what species?
Dictyocaulus
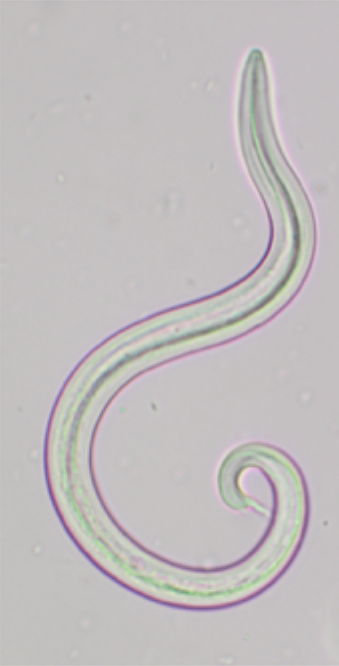
The image depicts what species?
Mullerius
What is the common name for Metastrongylus sp?
Swine lungworm
The image depicts what species?
Metastrongylus elongatus
The following life cycle matches which species:
direct/facultative indirect
hatch, larvae ingested by earthworm, and develop to infective stage
migrate to lung, reproduce
prepatent period with eggs in feces approx 25 days post infection
Metastrongylus sp
The following description matches which species:
adult worms live in respiratory tract, most often in bronchioles and trachea
thread-like, superficial resemblance to hookworms
3 species
Metastrongylus sp
How do we diagnose infection of Metastrongylus elongatus?
fecal flotation
The following egg description matches what species:
superficial resemblance to Ascaris suum
40×50 micrometers
thinner shell
embryonateed with larvae in feces or sputum
Metastrongylus elongatus
What is the clinical significance/clinical signs of Metastrongylus elongatus?
presence in lungs results in alveolitis/bronchitis
chronic and paroxysmal coughing
unthriftiness/fail to meet ADG production goals
secondary pneumonia with dyspnea and abdominal respiration
What is the control and prevention protocol for Metastrongylus elongatus?
prevention by treatment to remove patent infections (FBZ effective for removal of adults and immature stages, Ivermectin and Doramectin for 21-24 days)
clean farrowing environemnt for sows
raise in confinement when possible
Parasitic infections of Filaroides olseri and Filaroides hirthi are associated with respiratory complaints in which species?
Dogs
Parasitic infections of Aleurostrongylus abstrusus are associated with respiratory complaints in which species?
cats
Parasitic infections of capillaria aerophila and Capillaria bohemi are associated with respiratory complaints in which species?
dogs and cats
Which species is an important emerging zoonosis and One Health issue in the FL gulf coast region of the U.S?
Angiostrongylus cantonensis
What species can act as an asymptomatic reservoir for Dictyocaulus infection in horse sharing pastures?
donkey
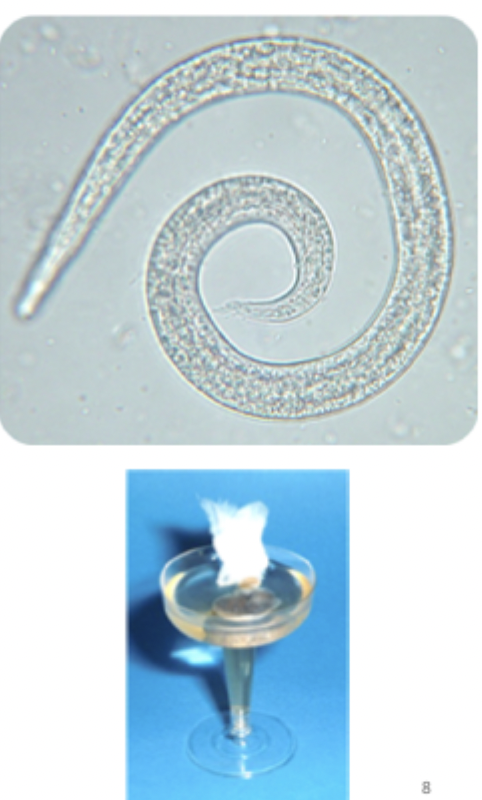
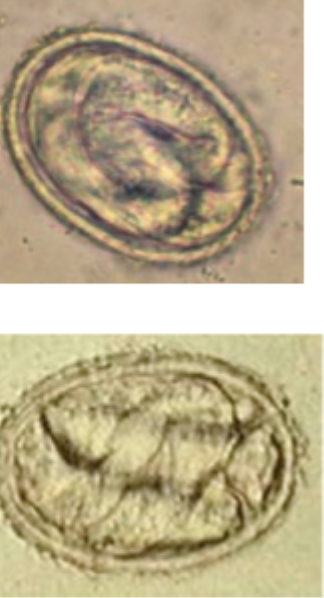
Larvae that look like this were found on a Baermann exam of a fecal sample from a yorkie presenting with a chronic cough aggravated by cold air. What are they?
first stage larva from Filaroides sp
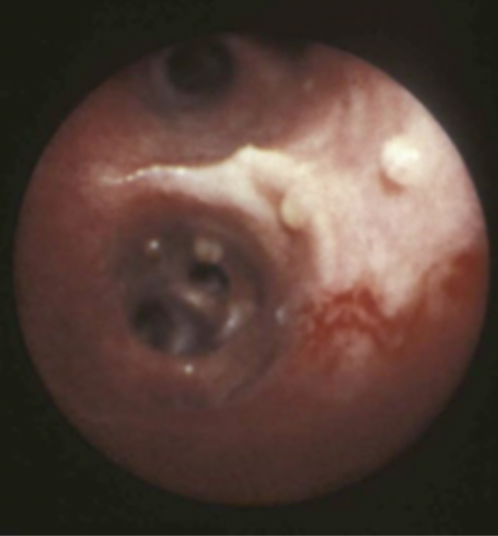
A 2 year old poodle mix presented with a chronic dry cough. The owner believes it is worse on mornings when the air is cooler. Bronchoscopy reveals nodules in the trachea and bronchi that look like this. What parasite is implicated?
Filaroides osleri
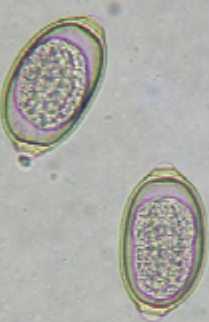
The eggs in the accompanying image were seen on the fecal flotation of a beagle with occasional sneezing. The eggs measure approximately 65 micrometers. What is the diagnosis?
Capillaria Eucoleus) bohemi